4 Upgrading Oracle Service Bus (without Oracle SOA Suite) from 11g
Note:
If Oracle Service Bus is part of your SOA 11g or a previous 12c domain, and you will be upgrading Oracle Service Bus as part of your Oracle SOA Suite upgrade to 12c (12.2.1.2), follow the standard upgrade process described in Upgrading SOA Suite and Business Process Management from 11g or Upgrading Oracle SOA Suite and Business Process Management from a Previous 12c Release.- Understanding the Oracle Service Bus Standalone Upgrade to 12c
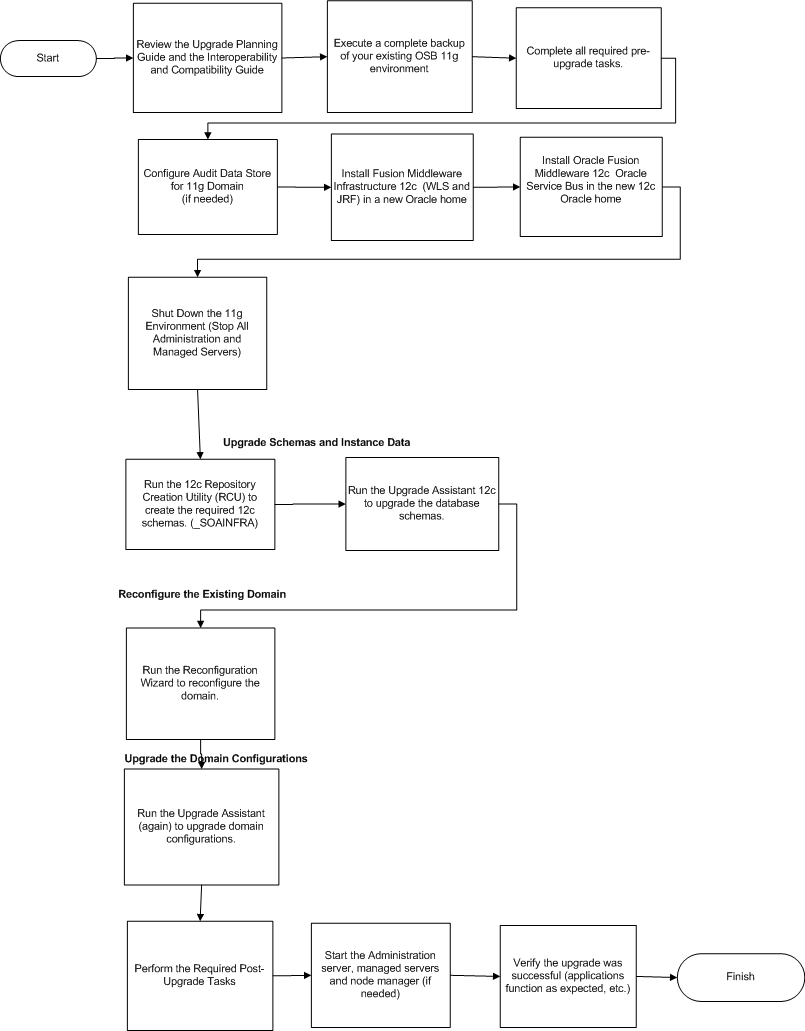
Follow this process flow to upgrade an Oracle Service Bus 11g deployment that does not include Oracle SOA Suite. - Upgrade Limitations for Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2)
If your Oracle Service Bus 11g topology is configured with more than one component within a single domain, then you will not be able to upgrade to 12c (12.2.1.2) - Performing Pre-Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Service Bus (OSB)
- Installing Oracle Service Bus
Before beginning your upgrade, use the Oracle Universal Installer to install the required product distribution on the target system. You can install and upgrade Oracle Service Bus without Oracle SOA Suite and Business Process Management, but you must still install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12c (12.2.1.2) before upgrading Oracle Service Bus. - Creating the Required 12c Schemas with the RCU
When upgrading from 11g, you must use the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create the required 12c schemas before you begin the upgrade. - Stopping Servers and Processes
Before running the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade your schemas and configurations, you must shut down all processes and servers, including the Administration server and any managed servers. - Upgrading an Oracle Service Bus Domain (without SOA)
- Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.2). - Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration. - Performing Post Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Service Bus
- Troubleshooting Oracle Service Bus Upgrade
4.1 Understanding the Oracle Service Bus Standalone Upgrade to 12c
Follow this process flow to upgrade an Oracle Service Bus 11g deployment that does not include Oracle SOA Suite.
Oracle Service Bus (OSB) can be upgraded to 12c (12.2.1.2) with or without Oracle SOA Suite and Business Process Management. The upgrade steps in this topic describe how to upgrade Oracle Service Bus without SOA.
If Oracle Service Bus is part of your SOA 11g or a previous 12c domain, and you will be upgrading Oracle Service Bus as part of your Oracle SOA Suite upgrade to 12c (12.2.1.2), follow the standard upgrade process described in Upgrading SOA Suite and Business Process Management from 11g.
Note:
Even though your domain does not include SOA, you will still have to upgrade the_SOAINFRA schema to upgrade Oracle Service Bus metadata. Oracle Service Bus does not have a separate schema.| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Required if Oracle Web Services Manager is not already deployed.
Deploy Oracle Web Services Manager Policy Manager in your existing 11g environment. |
If Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) Policy Manager is not already deployed in your Oracle Service Bus 11g environment, then you must manually deploy it before you upgrade to 12c. |
|
Required Export services, projects and resources when upgrading Oracle Service Bus |
You must export services, projects and resources into a configuration JAR file before you can upgrade to Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2). After the upgrade, you will import the JAR file to the new 12c environment. |
|
Required Delete all services, projects and resources from the existing environment. |
After the export, you must delete all user-created services, projects and resources before the upgrade. |
|
Required Install the 12c Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure distribution into a new Oracle home. |
You must install the 12c Infrastructure (which includes Oracle WebLogic Server and JRF components). |
|
Required Install Oracle Service Bus into a new Oracle home. |
Obtain the Oracle Service Bus distribution and install the content to a new Oracle home. |
| Required
Run the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create the new required schema. |
The Service Table schema (_STB) is a new required schema for all domains. If you are upgrading from 11g, you will have to create this schema before you can upgrade to 12c.
Oracle Service Bus also requires the SOA schema ( If you are upgrading from a previous 12c release, do not create another Service Table schema. |
| Required
Stop all servers and processes. |
You must stop all servers and processes before starting the upgrade. |
|
Required Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the required schemas. |
If you are upgrading from a previous 12c release, the |
| Required
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure the existing domain. |
You will continue to use the existing domain after the upgrade, so it must be reconfigured to work with the new components. |
| Required
Run the Upgrade Assistant to configure the component configurations. |
You will run the Upgrade Assistant a second time to update the component configuration to work in the new domain. |
|
Required Perform all post-upgrade tasks. |
Perform the standard 12c post-upgrade tasks, as well as any post-upgrade OSB-specific tasks, that apply to your deployment. |
4.2 Upgrade Limitations for Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2)
If your Oracle Service Bus 11g topology is configured with more than one component within a single domain, then you will not be able to upgrade to 12c (12.2.1.2)
Upgrading Multiple Components that use UMS in a Single OSB Domain (Not Supported)
Certain Fusion Middleware components such as Oracle SOA, Oracle Service Bus (OSB) and Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) have a dependency on User Messaging Service (UMS) in 12c. If you configure more than one of these components within a single 12c (12.2.1.2) domain, then each of these components must run within its own cluster — even if there is only one server that runs that component.
In order to upgrade these components, you must create a separate cluster for each component during the domain reconfiguration as described in Clusters.
The supported upgrade topology for these components is described in Upgrading a Clustered Topology.
4.3 Performing Pre-Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Service Bus (OSB)
If you are upgrading Oracle Service Bus, you must perform the following tasks before you begin the upgrade. Review your own use case scenarios and existing deployment to determine if the following tasks apply to your environment.
4.3.1 Deploying Oracle Web Services Manager Policy Manager in Your 11g Environment
If Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) Policy Manager is not already deployed in your Oracle Service Bus 11g environment, then you must manually deploy it before you upgrade to 12c.
In 11g, both WebLogic security policies and OWSM policies were supported on Oracle Service Bus. As of 11g (11.1.1.7), WebLogic Security policies were deprecated, and are not supported in 12c (12.2.1.2). Because WebLogic security policies were available in 11g, deployment of the OWSM Policy Manager and use of the OWSM policies was optional. Since only OWSM policies are supported in 12c, OWSM Policy Manager deployment is mandatory.
For information on manually deploying the OWSM Policy Manager in your 11g environment, see Installing OWSM with WebLogic Server in Securing Web Services and Managing Policies with Oracle Web Services Manager.
4.3.2 Exporting Services, Projects and Resources when Upgrading Oracle Service Bus
You must export services, projects and resources into a configuration JAR file before you can upgrade to Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2). After the upgrade, you will import the JAR file to the new 12c environment.
Note that you can manually export resources and services from older, supported releases. See Migrating Oracle Service Bus Resources from Previous Releases.
For more information, see Importing and Exporting Resources and Configurations in Developing Services with Oracle Service Bus.
4.3.3 Deleting All Services, Projects and Resources
After the export, you must delete all user-created services, projects and resources before the upgrade.
For information on using the Oracle Service Bus Console to delete resources, see How to Delete Projects, Folders, and Resources.
For information on using JDeveloper to delete resources, see How to Delete a Project or Resource.
4.3.4 Migrating Oracle Service Bus Resources from Previous Releases
You can manually export resources and services from the following releases and use them with Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2):
-
Oracle Service Bus 12c Release 12.1.3.0, 12.2.1.0, and 12.2.1.1
-
Oracle Service Bus 11g Release: 11.1.1.7.0
-
Oracle Service Bus 10.3 Releases: 10.3.1 and 10.3.0
-
AquaLogic® Service Bus Releases 3.0 and later
For more information, see Importing and Exporting Resources and Configurations in Developing Services with Oracle Service Bus.
4.4 Installing Oracle Service Bus
Before beginning your upgrade, use the Oracle Universal Installer to install the required product distribution on the target system. You can install and upgrade Oracle Service Bus without Oracle SOA Suite and Business Process Management, but you must still install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12c (12.2.1.2) before upgrading Oracle Service Bus.
Note:
You must install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure distribution first before installing other Fusion Middleware products, when Infrastructure is required for the upgrade.-
Oracle Service Bus requires the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure (Oracle WebLogic Server and JRF).
- If you want to use Oracle Web Services Manager policies with Oracle Service Bus, then you must select the Oracle Web Services Manager extension template after selecting one of the Oracle Service Bus domain templates when configuring the Oracle WebLogic domain.
4.5 Creating the Required 12c Schemas with the RCU
When upgrading from 11g, you must use the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create the required 12c schemas before you begin the upgrade.
Note:
If you are upgrading from a previous 12c release of Oracle Fusion Middleware, you do not need to re-create these schemas if they already exist. Refer to the steps below to identify the existing schemas in your domain.In Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g releases it was possible to run Oracle Service Bus (OSB) without a database, as the SOA schema was not required. In 12c, however, you must have a supported database configured with the required SOA schemas before you can run Oracle Service Bus 12c (12.2.1.2).
If you are upgrading from 11g, refer to the Pre-Upgrade Checklist to identify the existing schemas in your domain. The following schemas must exist before you upgrade to 12c:
-
Service Table schema (
prefix_STB). This schema is new in 12c and is required for domain-based upgrades. It stores basic schema configuration information (for example, schema prefixes and passwords) that can be accessed and used by other Oracle Fusion Middleware components during the domain creation. This schema is automatically created when you run the Repository Creation Utility (RCU), where you specify the existing schema owner prefix that you used for your other 11g schemas. Note: If the Service Table schema does not exist, you may encounter the error messageUPGAST-00328 : The schema version registry table does not exist on this database. If that happens it is necessary to create the service table schema in order to run Upgrade Assistant. - SOA Infrastructure schema (
prefix_SOAINFRA). - Oracle User Messaging Service schema (
prefix_UMS).
4.6 Stopping Servers and Processes
Before running the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade your schemas and configurations, you must shut down all processes and servers, including the Administration server and any managed servers.
An Oracle Fusion Middleware environment can consist of an Oracle WebLogic Server domain, an Administration Server, multiple managed servers, Java components, system components such as Identity Management components, and a database used as a repository for metadata. The components may be dependent on each other so they must be stopped in the correct order.
Note:
The procedures in this section describe how to stop servers and processes using the WLST command-line utility or a script. You can also use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Control and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. See Starting and Stopping Administration and Managed Servers and Node Manager in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.To stop your Fusion Middleware environment, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Stop System Components
To stop system components, such as Oracle HTTP Server, use the stopComponent script:
-
(UNIX)
DOMAIN_HOME/bin/stopComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
DOMAIN_HOME\bin\stopComponent.cmd component_name
You can stop system components in any order.
Step 2: Stop the Managed Servers
To stop a WebLogic Server Managed Server, use the stopManagedWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
DOMAIN_HOME/bin/stopManagedWebLogic.sh managed_server_name admin_url -
(Windows)
DOMAIN_HOME\bin\stopManagedWebLogic.cmd managed_server_name admin_url
When prompted, enter your user name and password.
Stop SOA servers and processes in this order:
-
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) Managed Server
-
Oracle Service Bus (OSB) Managed Server
-
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) Managed Server
-
Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) Managed Server
Step 3: Stop Oracle Identity Management Components
Stop any Oracle Identity Management components, such as Oracle Internet Directory, that form part of your environment:-
(UNIX)
DOMAIN_HOME/bin/stopComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
DOMAIN_HOME\bin\stopComponent.cmd component_name
Step 4: Stop the Administration Server
When you stop the Administration Server, you also stop the processes running in the Administration Server, including the WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control.
To stop the Administration Server, use the stopWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
DOMAIN_HOME/bin/stopWebLogic.sh -
(Windows)
DOMAIN_HOME\bin\stopWebLogic.cmd
When prompted, enter your user name, password, and the URL of the Administration Server.
Step 5: Stop Node Manager
To stop Node Manager, close the command shell in which it is running.
Alternatively, after having set the nodemanager.properties attribute QuitEnabled to true (the default is false), you can use WLST to connect to Node Manager and shut it down. For more information, see stopNodeManager in WLST Command Reference for WebLogic Server.
4.7 Upgrading an Oracle Service Bus Domain (without SOA)
Although there is no Oracle Service Bus schema, the database schema data for Oracle Service Bus is incorporated in the SOAINFRA schema. Therefore, to upgrade Oracle Service Bus, you must upgrade the SOAINFRA schema.
- Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.2). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
4.7.1 Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.2). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
4.7.1.1 Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-5 Upgrade Assistant Command Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
NOTE: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant will create log files and temporary files. The default locations are: UNIX:
Windows:
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command line options. |
4.8 Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.2).
When you reconfigure a WebLogic Server domain, the following items are automatically updated, depending on the applications in the domain:
-
WebLogic Server core infrastructure
-
Domain version
Note:
Before you begin the domain reconfiguration, note the following limitations:
-
The Reconfiguration Wizard does not update any of your own applications that are included in the domain.
-
Transforming a non-dynamic cluster domain to a dynamic cluster domain during the upgrade process is not supported.
The dynamic cluster feature is available when running the Reconfiguration Wizard, but Oracle only supports upgrading a non-dynamic cluster upgrade and then adding dynamic clusters. You cannot add dynamic cluster during the upgrade process.
-
The domain version number in the
config.xmlfile for the domain is updated to the Administration Server's installed WebLogic Server version. -
Reconfiguration templates for all installed Oracle products are automatically selected and applied to the domain. These templates define any reconfiguration tasks that are required to make the WebLogic domain compatible with the current WebLogic Server version.
-
Start scripts are updated.
If you want to preserve your modified start scripts, be sure to back them up before starting the Reconfiguration Wizard.
Note:
Once the domain reconfiguration process starts, it is irreversible. Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, ensure that you have backed up the domain as covered in the pre-upgrade checklist. If an error or other interruption occurs while running the Reconfiguration Wizard, you must restore the domain by copying the files and directories from the backup location to the original domain directory. This is the only way to ensure that the domain has been returned to its original state before reconfiguration.- Backing Up the Domain
- Starting the Reconfiguration Wizard
- Reconfiguring the SOA Domain with the Reconfiguration Wizard
You must first reconfigure your existing domain using the Reconfiguration Wizard before running the Upgrade Assistant.
4.8.1 Backing Up the Domain
Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, create a backup copy of the domain directory.
To create a backup of the domain directory:
4.8.3 Reconfiguring the SOA Domain with the Reconfiguration Wizard
You must first reconfigure your existing domain using the Reconfiguration Wizard before running the Upgrade Assistant.
Note:
If the source is a clustered environment, run the Reconfiguration Wizard on the primary node only. Use the pack/unpack utility to apply the changes to other cluster members in the domain.4.9 Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration.
- Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.2). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time. - Upgrading Domain Components Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain.
4.9.1 Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.2). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
4.9.1.1 Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-6 Upgrade Assistant Command Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
NOTE: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant will create log files and temporary files. The default locations are: UNIX:
Windows:
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command line options. |
4.9.2 Upgrading Domain Components Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain.
After running the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure the WebLogic domain to 12c (12.2.1.2), you must run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations to match the updated domain configuration.
4.10 Performing Post Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Service Bus
After a successful upgrade, you may need to perform one or more of the following tasks. Review your own use case scenarios and existing deployment to determine if the following tasks apply to your environment.
Note:
If you experience any post-upgrade issues with Oracle Service Bus, refer to Troubleshooting Oracle Service Bus for a list of common solutions.
4.10.1 Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the WLS_OSB Managed Servers
To enable Oracle HTTP Server to route to Oracle Service Bus console and Oracle Service Bus service, set the WebLogicCluster parameter to the list of nodes in the cluster.
For more information, see Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the Oracle Service Bus in the Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite.
4.10.2 Importing Domain Configuration Data
After the upgrade you will need to import the domain configuration data that you exported in Exporting Services, Projects and Resources when Upgrading Oracle Service Bus.
For more information, see How to Import Resources from a Configuration JAR File in the Console and Executing a Configuration File.
4.10.3 Importing Security Configurations
Use the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console to import the security data that you exported pre-upgrade into the new Oracle Service Bus domain.
For more information, see the "Import data into a security provider" section of the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
Note:
You must import the security information for each security provider separately.
4.10.4 Upgrading Your XQuery Resources
Oracle Service Bus supports XQuery 1.0. The older XQuery 2004 is also supported. Any new XQuery resource created in Service Bus uses the XQuery 1.0 version, by default.
If you have upgraded from a pre-12c Service Bus project, all XQuery resources in the project are configured to use the XQuery 2004 version.
For more information on upgrading XQuery Resources, see How to Upgrade Your XQuery Resources to use XQuery 1.0.
4.10.5 Understanding 12c Split-Joins
The Fusion Middleware 11g split-join business service will no longer exist in 12c because in 12c there is a direct way to invoke a split-join component from a pipeline or a proxy service. The upgrade process will automatically change all statically configured invoke references to a split-join business service as follows:
-
The flow business service is removed. This means the
Timeoutproperty configured for the Flow business service is also removed. -
If the business service is located in the same project as the proxy service that invokes it, then the pipeline associated with that proxy service invokes the split-join directly.
-
If the business service is located in a different project from the proxy service that invokes it, then a local proxy service is created to invoke the split-join. The local proxy service is invoked by the original proxy service.
4.11 Troubleshooting Oracle Service Bus Upgrade
If you experience post-upgrade issues with Oracle Service Bus, review the following and apply any relevant solutions.
4.11.1 Resolving the HTTP 404 Error After OSB Upgrade with OHS as Cluster Frontend Host
If you configure Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) as a cluster domain frontend host, then you must add the following code to the OHS configuration file (ohs.confg):
<Location /sbconsole> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicCluster [ADMIN_SERVER_HOST]:[ADMIN.SERVER:PORT] </Location> <Location /servicebus> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicCluster [ADMIN_SERVER_HOST]:[ADMIN.SERVER:PORT] </Location>
Where ADMIN.SERVER:PORT is the machine name, server name and port number used for the OHS.
mymachine.us.mycompany.com:7001 as shown in this sample code example:
<Location /sbconsole> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicCluster mymachine.us.mycompany.com:7001 </Location> <Location /servicebus> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicCluster mymachine.us.mycompany.com:7001 </Location>
4.11.2 Resolving the HTTP 404 Error When Accessing OSB Console
Prior to 12c, the OSB console was accessed using the following URL: http://[HOST]:[PORT]/sbconsole
In 12c, the OSB Console URL has changed to: http://[HOST]:[PORT]/servicebus.
After the upgrade, if you enter http://[HOST]:[PORT]/sbconsole, it should redirect to http://[HOST]:[PORT]/servicebus.
If the redirect fails, and you receive a HTTP 404 error, try direclty entering the 12c URL: http://[HOST]:[PORT]/servicebus.