19 Finding Documents
Check with your system administrator to see which search solution or database is used and to see if full-text indexing is enabled.
This chapter covers the following topics:
19.1 Search Pages
You can search for content using one of the following ways:
19.1.1 Quick Search Field
With the Quick Search field, you can perform a search regardless of the page in the content area. The Quick Search field performs a substring search of the title and content ID metadata, and the indexed full-text if it is supported on your system.
A substring search is equivalent to including a wildcard at the beginning and end of the search term. For example, if you enter form in the Quick Search field, the search returns items with words such as forms, performance, and reform in the title or content ID metadata, or in the indexed full-text if it is supported on your system.
You or your system administrator can also build custom searches targeted to search one or more metadata fields you specify, and make them available through the Quick Search field. You can create targeted searches with either the Query Builder Form or Expanded Form.
The Quick Search field supports Internet-style search syntax, complex construction, and alternate query formats. For more information, see Using Additional Search Capabilities.
19.1.2 Home Page Search Fields
With the search fields on the Home page, you can perform a metadata search, a full-text search, or a combination of both. Only the most commonly used search fields are available from the home page.
Note:
Your home page may have a different appearance than the default "out-of-the-box" content server home page, which includes search fields. If search functionality is not available from your home page or to search on additional metadata fields, use the Search Tray or Advanced Search Page.
19.1.3 Search Tray
With the Search tray, you can perform a metadata, full-text, or combination search. Only the most commonly used search fields are available from the Search tray.
The Criteria tab on the Search tray displays a form where you can enter your criteria. The Results tab displays the search results.
19.1.4 Advanced Search Page
With the Advanced Search page, you can perform a metadata search, full-text search, or a combination of both on all available fields.
To access this page, click the Advanced link in the Search Tray or use the Search menu on the Toolbar.
The expanded form on the Advanced Search Page displays all search fields available to you on a single page. You can alternate between the expanded form and the query builder form using the Search Forms menu at the top of the search page.
You can also select a different search profile from the Switch Profile menu, if your system administrator has defined them for you. You can specify the default search form to use the Advanced Search page.
Note:
Queries built using the Expanded Form separate the metadata fields with the <AND> operator. Each search criterion entered into each field must be met for a result to be returned. For example, if you enter January into the Title field and presentation into the Type field, then a search finds content only if it has a presentation type and has January in the title.
Note:
When using Oracle Text Search with your Content Server instance, you cannot enter complex search queries into the Full-Text Search field on the Expanded Form of the Advanced Search page. Instead, you must use the Query Builder form.
19.1.5 Query Builder Form
The Query Builder form creates and saves complex queries by selecting options from a series of lists. After a query is built, you can edit the query directly, perform the search, or save the query for easy access from My Saved Queries.
With the Query Builder form, you can separate the metadata fields with either the <AND> operator or the <OR> operator. If you use the <AND> operator, then each search criteria entered into each field must be met to return a result.
If you use the <OR> operator, then only one of each field's criteria must be met. For example, if you enter January into the Title field and presentation into the Type field separated by <OR>, then results include content that has either presentation as the type or has January in the title.
Note:
When using Oracle Text Search with your Content Server instance, you cannot enter complex search queries into the Full-Text Search field on the Expanded Form of the Advanced Search page. Instead, you must use the Query Builder form.
19.2 Working with Search Results
You can specify how to display the results of your search based on the number of content items returned per page and the order of the content items. For example, to find the most recent files that match your criteria, sort the results by release date. If you are searching for specific text such as changed address, sort your search results by score.
Use the Results Options area of the Advanced Search Page to control the display of the Search Results page:
19.2.1 Displaying Search Results
To specify how to display the search results:
- Display the home page search fields or the Advanced Search page.
- Scroll down to the Results Options.
- Set Results Per Page to the maximum number of content items to display on each Search Results page.
- Specify the Sort By method and order.
- Click Search.
- From the Content Actions menu on a Search Results page, choose the view option to specify the search results view.
Note:
-
The Clear button clears the search fields, but does not clear the Results Options settings.
-
The system administrator can use the Content Server Configuration Manager to add or remove sortable fields. To change the fields available for sorting, see your system administrator.
19.3 Search Result Templates
You can customize the metadata information you want to see on a search result. You can even specify different search results templates to be used for different saved queries. To personalize how search results are displayed, select an option from the list on the User Profile Page, or from the Search Results page. There are three templates available by default, and you have the option to create new views based on the three provided templates using the Search Results Templates for User page to identify the information and specify display options:
19.3.1 Classic View Template
The Classic template lists content items sequentially in single rows, based on the default sort field and order set on the User Profile page.
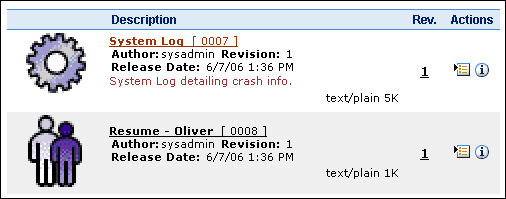
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
Content icon or Thumbnail image |
Displays an icon based on the content type. Optionally, if your system administrator has set up Content Server to create a thumbnail image of the content, then it displays the thumbnail image. |
|
Description |
Title and Content ID: The title and unique identifier of the content item, linked to display a Web-viewable version of the content, if it is available. If no Web-viewable version is available, it links to the native file. The title and content ID are displayed in all custom search result templates based on the Classic View, even if those fields are not specifically selected from the Classic View Template section of the Create/Edit Classic View Search Result Template page. Author: The person who checked in the content item. Revision: Identifies the revision number of the content item. Release Date: The date the content item was released. Comments: Comments entered when the item was checked in, if any. Content Format: The format of the native file. |
|
Rev. |
Displays the revision number of the content item. |
|
Actions |
Displays the Actions menu for an item and the Content Info icon. Actions icon: Click this icon to open a menu of actions for the selected content item. Content Info icon: Click this icon to display the Content Information page. |
19.3.2 Headline View Template
The Headline template by default lists items in a single line, with a minimum of information. The Headline template uses the sort field, sort order, and result count fields on the User Profile page to arrange the results.
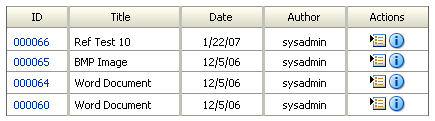
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
ID |
A unique identifier of the content item, linked to a Web-viewable version of the content item, if it is available. If no Web-viewable version is available, it links to the native file. |
|
Title |
Displays the title of the content item without any associated link. |
|
Date |
Displays the date the content item was released. |
|
Author |
Displays the user name of the person who last checked in the content item. |
|
Actions |
Displays the Actions menu for an item and the Content Info icon. Actions icon: Click this icon to open a menu of actions for the selected content item. Content Info icon: Click this icon to display the Content Information page of the selected content item. |
19.3.3 Thumbnail View Template
The Thumbnail template by default lists items in a grid from left-to-right and top-to-bottom and displays an icon based on the content type, or a thumbnail image of the content if your system administrator has set up Content Server to create one. This template is particularly suited for displaying images and other graphic content. The grid arranges results based on the sort field and order set on the User Profile page.
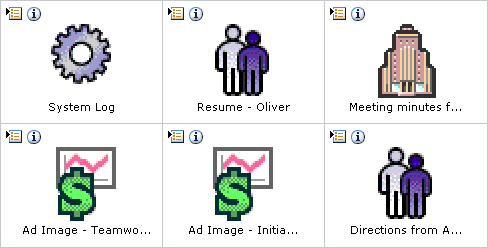
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
|
Icons |
Displays the Actions menu for an item and the Content Info icon. Actions icon: Click this icon to open a menu of actions for the selected content item. Content Info icon: Click this icon to display the Content Information page of the selected content item. |
|
Thumbnail Icon or Image |
Displays an icon based on the content type or a thumbnail image of the content if your system administrator has set up Content Server to create one, linked to a Web-viewable version of the content item, if it is available. If no Web-viewable version is available, it links to the native file. |
|
Title |
Displays the title of the content item without any associated link. To maintain the grid structure, long titles are truncated to a single line. Rolling the mouse over the title expands the text to display the full title. |
19.3.4 Creating a Custom Search Result Template
To create a custom search result template:
Note:
If you have Oracle WebCenter Content: Records installed with Department of Defense (DoD) functionality enabled, the Security Classification field must always be displayed in a search result. If you do not include the Security Classification field when you customize a search result template, the Security Classification field is included automatically.
19.4 Saving Queries
You can save and reuse search queries:
19.4.1 About Saved Queries
To quickly display results for a search that you perform often, you can save the search in the My Saved Queries folder in the My Content Server tray.
After you save a query link, you can modify or delete the link from your Saved Queries page.
You or your system administrator can also build custom searches targeted to search one or more metadata fields you specify, and make them available through the Quick Search field.
19.4.5 Creating Quick Search Queries
You can create targeted searches with either the Query Builder Form or Expanded Form. To customize the query string directly, you must use the Query Builder Form as shown in this procedure.
To build a targeted search available through the Quick Search field:
19.5 Searching with Oracle Text Search
If you have a license to use Oracle Text Search (in Oracle Database 11g) or Oracle Secure Enterprise Search 11g, the Oracle Text Search option enables the use of those technologies as the primary full-text search engine for Oracle WebCenter Content Server.
Oracle Text Search can filter and extract content from different document formats in different languages. It supports a large number of document formats, including Microsoft Office file formats, Adobe PDF, HTML, and XML. It can render search results in various formats, including unformatted text, HTML with term highlighting, and original document format.
If the system administrator configured Oracle Text Search, this option enables you to find a content item or items based on information about the file, actual text in the file, or both. The system administrator can also configure Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (Oracle SES) as the back-end search engine for Oracle Text Search.
If your system administrator has configured the Oracle Text Search option, you can specify full-text and metadata searches and select options to filter the results of a search by categories:
19.5.1 Searching with the Expanded Form
On the Expanded Form, you can specify a metadata search, a full-text search, or both to identify a content item or items to search for. Also, you can specify result options.
Figure 19-1 shows part of the Expanded Form for specifying Oracle Text Search queries.
Figure 19-1 Expanded Form for Oracle Text Search
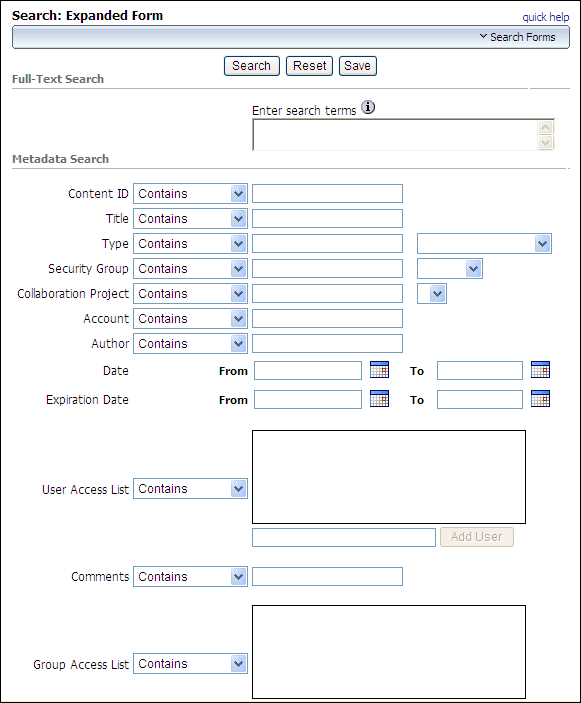
To specify a search on the Expanded Form:
The content item or items that match your search criteria are displayed on the Search Results page.
19.5.2 Filtering Search Results
The Search Results page displays a menu bar with metadata categories you can use to filter the search results. Each category lists values that are valid for the particular search results. The system administrator can add or remove categories. The default set of categories include Content Type, Security Group, and Account.
Figure 19-2 Search Results with Oracle Text Search Default Menu
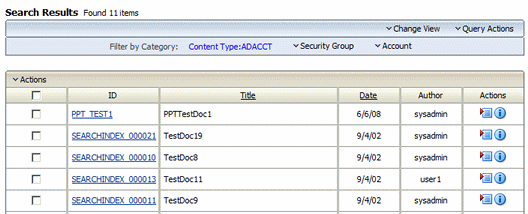
An arrow next to the category name indicates that the search results include multiple values for that category. When you move your cursor over the option name, a menu displays the list of the values found in the search results for that category and the number of content items for each value. Click a value to filter the Search Results page to list only the items that have the selected value in the selected category.
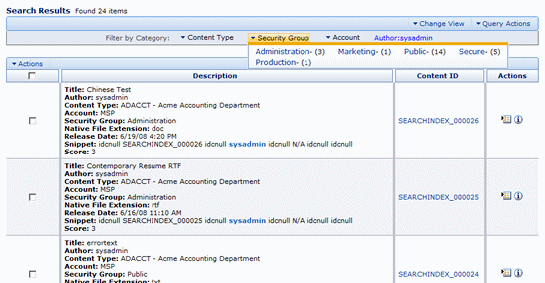
Figure 19-3 shows a list of categories under Security Group and the number of items found in each category.
Figure 19-3 Search Results with Expanded Oracle Text Search Menu
19.5.3 Searching with the Query Builder Form
On the Query Builder form, you can select search criteria from menus as required. You can build and save complex queries by selecting options from a series of lists. You can also manually edit the query text.
Note:
When using Oracle Text Search with your Content Server instance, you cannot enter free-form metadata queries into the Full-Text Search field on the Expanded Form. Instead, you must use the advanced options on the Query Builder Form. For more information, see Searching with the Query Builder Form.
Figure 19-4 shows the Query Builder Form for specifying Oracle Text Search queries.
Figure 19-4 Query Builder Form for Oracle Text Search
To specify a search on the Query Builder Form:
19.5.4 Metadata Search Operators for Oracle Text Search
On the Advanced Search Page, you can use search operators to refine the search criteria. These operators are listed as options in lists to the left of each field.
The following table describes the search terms used and provides examples for use.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Finds content items with the specified whole word or phrase in the metadata field. This operator is available only for Oracle Text Search, or for Oracle Database and Microsoft SQL Server database with the optional DBSearchContainsOpSupport component enabled. For more information, see your system administrator. |
If you enter |
|
|
Finds items with the exact specified value in the metadata field. |
When you enter A query that uses the MATCHES operator on a nonoptimized field behaves the same as a query that uses the CONTAINS operator. For example, if the |
|
|
Finds all content items with the specified prefix at the beginning of at least one word in the metadata field. |
If you enter |
19.6 Searching with Database Metadata Search
Database metadata search enables you to find a content item or items based on information about the file. The metadata search functionality is installed by default and is available even if other search engines are configured.
19.6.1 About Metadata Searching
Metadata searching is similar to finding a book in a library by searching for its author, title, or subject. When you search by metadata, you specify as much information as you know about a file or a group of files. For example, to find all files written by your supervisor for your department that were released on or after 1/1/2002, specify the following on the search page:
-
Author: supervisor's user name
-
Department: department name
-
Release Date From: 1/1/2002
Note:
When you search for metadata, case sensitivity varies depending on how your system administrator has configured Content Server. For your specific configuration, see your system administrator.
When you use full-text searching, a search is case sensitive for metadata and case insensitive for full text. For Content ID, however, lowercase letters are converted to uppercase letters, so you cannot search Content ID with lowercase letters.
19.7 Searching with Database Full-Text Search
Database full-text search enables you to find a content item or items based on the actual text in the file. The database full-text search is available if the system administrator configured it.
19.7.1 Performing a Full-Text Search
To perform a full-text search:
The files that match your search criteria are displayed on the Search Results page or in the Results tab in the Search Tray.
19.8 Searching for Expired or Expiring Content
By default, if you have write permission to any security group, you can access the Expired Content page and perform a search for expired content. The search results include only the content for which you have at least read permission.
To search for content that has expired or is set to expire:
19.9 Using Additional Search Capabilities
This section covers the following topics:
19.9.1 Metadata Wildcards
A wildcard substitutes for unknown or nonspecific characters in the search term. You can use wildcards in metadata searches, even when using the Quick Search field.
Available wildcard characters and behavior are dependent on the search engine being used and how Content Server is configured. Check with your system administrator for guidance on what wildcards are available and how they behave. Asterisks (*) and question marks (?) are often used as wildcard characters, but not always. When available as wildcard characters, asterisks and question marks typically behave as follows when entered into metadata search fields:
-
An asterisk (
*) indicates zero or more alphanumeric characters. For example:-
form*matchesformandformula -
*ormmatchesformandreform -
*form*matchesform,formula,reform, andperformance
-
-
A question mark (
?) indicates one alphanumeric character. For example:-
form?matchesformsandform1, but notformorformal -
??formmatchesreformbut notperform
-
Note:
Because asterisks and question marks are often used as wildcards, it is not recommended that they be used in metadata fields such as title or Content ID when checking in a document.
19.9.2 Internet-Style Search Syntax
Search techniques common to the popular Internet search engines are supported in Content Server. For example, new product entered in the Quick Search field searches for new <AND> product, while new, product searches for new <OR> product. The following table lists how Content Server interprets common characters.
| Character | Interpreted As |
|---|---|
|
Space ( ) |
AND |
|
Comma (,) |
OR |
|
Minus (-) |
NOT |
|
Phrases enclosed in double-quotes (" |
Exact match of entered phrase |
The following table lists examples of how Content Server interprets Internet-style syntax in a full-text search.
| Query | Interpreted As |
|---|---|
|
|
new <AND> product |
|
|
(new <OR> product) <AND> images |
|
|
(new <AND> product) <AND> <NOT> images |
|
|
"new product" <OR> "new images" |
The following table lists examples of how Content Server interprets Internet-style syntax when searching title metadata using the substring operator.
| Query | Interpreted As |
|---|---|
|
|
dDocTitle <substring> 'new' <AND> dDocTitle <substring> 'product' |
|
|
dDocTitle <substring> 'new' <OR> dDocTitle <substring> 'product' |
|
|
dDocTitle <substring> 'new' <AND> <NOT> 'product' |
|
|
dDocTitle <substring> 'new product' |
Note:
Internet-style search syntax is enabled by default, but your system administrator can disable it. Check with your system administrator if you have questions.
19.9.3 Complex Queries and Alternate Query Formats
Content Server allows for the use of parentheses for complex query construction and field:value and site:value formats when creating a query. By using these alternatives, you can more easily search the metadata field you want across multiple servers, if necessary, and refine your results. For example, to search only the title metadata for new product without having to go to the Advanced Search page, enter dDocTitle:"new product" into the Quick Search field. The search looks only in the field you specified before the colon. You must know the Content Server identifier for the metadata field you want to search.
Note:
When using Oracle Text Search with your Content Server instance, you cannot enter complex search queries into the Full-Text Search field on the Expanded Form of the Advanced Search page. Instead, you must use the advanced options on the Query Builder Form.
The following table lists some examples of complex and alternate query formats.
| Query | Interpreted As |
|---|---|
|
|
dDocTitle <contains> `New` |
|
|
(dDocTitle <contains> `New`) <AND> <ftx>`product`</ftx> |
|
|
dDocTitle <contains> `New` <AND> dDocTitle <contains> `product` |
|
|
dDocTitle <contains> `New` <AND> dDocTitle <contains> `product` |
|
|
dDocTitle <contains> `New` <AND> dDocType <contains> `Presentations` |
|
|
dDocTitle <contains> `New` <OR> dDocType <contains> `Test Plan` |
19.10 Searching Referenced Links (optional)
If your administrator installed the optional Link Manager component, it evaluates, filters, and parses the URL links of indexed documents and then extracts the links for storage in a database table, making them available for searching. After the Link Manager component populates the table with the extracted URL links, it references this table to generate link search results, lists of link references for the Content Information page, and the resource information for the Link Info page. The Link Manager component shows these items:
-
Lists of links using specific search criteria
-
Detailed information about a specific link
-
The links to other documents for a specific content item, and any documents that reference this item
The search results, link references lists, and Link Info pages are useful to determine what documents are affected by content additions, changes, or revision deletions. For example, before deleting a content item, you can verify that any URL references contained in it are insignificant. Another use might be to monitor how content items are used.
Note:
Because the Link Manager component extracts the URL links during the Content Server indexing cycle, only the URL links of released documents are extracted. For content items with multiple revisions, only the most current released revision is available for searching.
This section covers the following topics:
19.10.1 About Searching Links
Use the Search Links page to search for links, using criteria stored in the repository database. Use this page to validate links, to determine where a resource is used, to determine if deleting a content item affects other documents, and so on.
The Link Search Results page displays items matching your search criteria. Invalid or broken links are listed in bold font. Each item has an Link Item Actions Menu and an Info icon which displays a Link Info page.
19.10.2 Link References on the Content Information Page
Use the References options to see whether the content item references or is referenced by other content items. References provides two options:
-
Show: By default, the links are hidden when the Content Information page opens. Click Show to display all applicable links. If this content item contains one or more references to other documents, then these links are listed in the Links contained in this content item section. If other documents reference this content item, then those references are listed in the Links to this content item section.
Links that are invalid or broken are listed using bold font. Click the Info link in the Actions column to display the Link Info page for that particular link.
To access the available link information for content items, click any Content Information icon, which displays the Content Information page and the References options. Or, you can choose either Content Information or Target Content Info from the Link Item Actions Menu, which also displays the Content Information page and the References options.
Note:
You cannot delete a content item revision if other content items reference it unless the system administrator has set the AllowForceDelete configuration variable to true. When you delete a content item revision, the message indicates if another content item references the content item and asks if you are sure you want to delete it. In this case, deleting a content item that is referenced by another content item breaks those links and makes them invalid.
19.10.3 Notification of Expiration
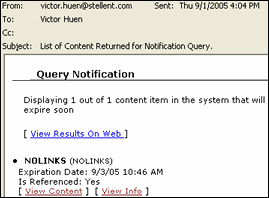
With Link Manager installed, the Notification of Expiration page includes additional information for each content item that is expiring soon. The e-mail notification specifies if the expiring content item is referenced by another content item:
-
Is Referenced: Yes
-
Is Referenced: No
The e-mail does not provide a list of the content items that reference the soon-to-expire document. This information is available in the References section on the Content Information page. For more information, see Checking Content Item Link References.
If the Content Server configuration variable (EnableExpirationNotifier) has been enabled, an e-mail notification is sent to each author when content expires. For more information about setting this configuration variable, see EnableExpirationNotifier in the Configuration Reference for Oracle WebCenter Content.
Note:
When a content item expires, it still exists in the Content Server. Expiration only removes the item from the index. Therefore, all links associated with an expired content item are functional if they involve a valid document.
Figure 19-5 Notification of Expiration E-mail for Author
19.10.4 Performing a Link Search
- Click the Managed Links Search link in the Content Management tray.
- On the Search Links page, enter the applicable values in the field(s).
- Click Search. The Link Manager component generates and displays the search results, as shown in the Link Search Results page.
19.10.5 Checking Content Item Link References
Use the Content Information page to display, check, and verify all the link references associated with a specific content item. You can access the Content Information page for a content item from either of two pages, as described in these topics:
19.10.6 Checking the Link Information About Specific Links
Use the Link Info page to view additional information about a specific link. You can access the Link Info page for any link from either of two pages, as described in these topics:
19.10.6.1 Checking Link Information from the Content Information Page
- Open the Content Information page for a specific content item and display the applicable links. For more information, see Checking Content Item Link References.
- Select a link from a list in the References sections (either Links contained in this content item or Links to this content item).
- Click the corresponding Content Info link in the Actions column.
19.10.6.2 Checking Link Information from the Search Links Page
- Open the Search Links page and search for links. For more information, see Performing a Link Search.
- Select a link from the Search Results section.
- Click the Actions icon in the Actions column.
- From the Link Item Actions Menu, choose Link Info.
19.11 Content Data Tracking
Content Tracker is an optional component that provides information about system usage:
19.11.1 About Content Tracker
Content Tracker monitors your system and records information about various activities. Content Tracker collects this information from various sources, then merges and writes the information to a set of tables in your Content Server database. You can customize Content Tracker to change or expand the types of information it collects. Content Tracker monitors activity based on:
-
Content item accesses:
Content Tracker gathers information about content item usage from Web filter log files, the Content Server database, and other external applications such as portals and websites. Content item access data includes dates, times, content IDs, current metadata, user names, and profile information about users.
-
Content Server services:
Content Tracker tracks all services that return content and services that handle search requests. And, with a simple configuration change, Content Tracker can monitor literally any Content Server service, even custom services.