7 Defining Polymorphic View Objects
This chapter includes the following sections:
7.1 About Polymorphic View Objects
ADF Business Components allows you to work with polymorphic view objects that are based on entity objects with inherited attributes from an inheritance hierarchy. A polymorphic view object has a heterogeneous row set.
The view object lets you create a table represented by its base entity object. Typically, when you create the entity-based view object, you create it to work with entity rows of a single type like Domestics, which perhaps include specific attributes that pertain to domestic customers. At other times you may want to query and update rows based on an entity object inheritance hierarchy in the same row set. For example, in the same row set, you might work with attributes that are common to the inheritance hierarchy of Customers, Domestics, and Internationals entity objects, where Domestics and Internationals are subtype entity objects of the parent Customers entity object. Such a view object is called a polymorphic view object. For a client to properly use the polymorphic view object, the view object must know which entity object to delegate to for each row in its heterogeneous row set. To identify the row type, the polymorphic view object relies on a discriminator attribute to identify each row's corresponding table.
ADF Business Component supports these types of polymorphism:
-
The entity object defines polymorphic subtypes, but the view object does not.
This is useful when the backend business logic needs to be aware of the different types but the presentation layer needs to treat view instances as a single type. In this case, the view instance will contain the common set of attributes defined by the entity subtypes.
-
Both the entity object and the view object usages define polymorphic subtypes.
In this case, both the backend business logic and the presentation layer need to distinguish between the various subtypes.
-
The entity object does not define polymorphic subtypes, but the view object usages do define polymorphic subtypes.
In this case, the presentation layer needs to distinguish between the view subtypes, but the backend business logic is not unique.
When you create polymorphic view object based on inheritance of entity subtypes, the various entity subtypes are not exposed to the client. As far as the client is concerned, every row in the view object's result set has the same set of attributes and the same row type. This is accomplished because ADF Business Components ensures that the correct entity object row subtype is created based on the value of the discriminator attribute. In other words, with a polymorphic entity usage, only the entity row parts of a view row can change type, while the view row type is constant.
Whereas, when you create polymorphic view object based on the inheritance defined by a view object hierarchy (not entity subtypes), you configure the application module to allow one or more view row subtypes in the result. Only polymorphic view rows produce different subtypes of client-visible view row types. And, unlike view objects derived from polymorphic entity usages, only polymorphic view rows allow you to expose view row subtypes to the client with additional attributes.
Note:
To experiment with the examples that demonstrate the concept in this chapter, use the SummitADF_Examples workspace, as described in Running the Standalone Samples from the SummitADF_Examples Workspace. For information about how to obtain and install the Summit ADF standalone sample applications, see Setting Up the Summit Sample Applications for Oracle ADF.
7.1.1 Polymorphic Entity Usages and Polymorphic View Rows Usages
You can work with either type of polymorphism, or you can combine the two.
While often even more useful when used together, the view row polymorphism and the polymorphic entity usage features are distinct and can be used separately. In particular, the view row polymorphism feature can be used for read-only view objects, as well as for entity-based view objects. When you combine both mechanisms, you can have both the entity row part being polymorphic, as well as the view row type.
Note to use view row polymorphism with either view objects or entity objects, you must configure the discriminator attribute property separately for each. This is necessary because read-only view objects contain no related entity usages from which to infer the discriminator information.
A limitation exists when defining polymorphic view objects that requires view objects with discriminator attributes to be defined no more than one level deep. Your project may define a polymorphic view object with discriminator attributes to specify the row subtypes, but using another view object to specify further subrows based on the first polymorphic view object will cause the display of subrows to fail. When creating polymorphic view objects, limit the discriminator attribute definition to one level.
In summary, to create a view object with a polymorphic entity usage:
-
Configure an attribute to be the discriminator at the entity object level in the root entity object in an inheritance hierarchy.
-
Define a hierarchy of inherited entity objects, each of which overrides and provides a distinct value for the Subtype Value property of that entity object level discriminator attribute.
-
List the subclassed entity objects in a view object's list of subtypes.
-
Update the application module to expose the entity-based subtype view objects in this hierarchy in the application module's list of subtypes.
Whereas, to work with view row polymorphism:
-
Configure an attribute to be the discriminator at the view object level in the base view object in an inheritance hierarchy.
-
Define a hierarchy of inherited view objects each of which provides a distinct value for the Subtype Value property of that discriminator attribute at the view object level (identified as
DefaultValuefor the attribute in the view object definition file). -
Update the application module to expose the subclassed view objects in this hierarchy in the application module's list of subtypes.
7.2 Working with Polymorphic Entity Usages
You can use an ADF view object with a polymorphic entity usage to create a heterogeneous row set based on a base entity object and its subtypes as well.
A polymorphic entity usage is one that references a base entity object in an inheritance hierarchy and is configured to handle subtypes of that entity as well. Figure 7-1 shows the results of using a view object with a polymorphic entity usage. The entity-based CustomerList view object has the Customers entity object as its primary entity usage. The view object partitions each row retrieved from the database into an entity row with attributes specific to the various subtypes of Customers. It creates the appropriate entity row subtype based on consulting the value of the discriminator attribute. For example, if the CustomerList query retrieves one row for domestic company ABC Company and one row for international company Simms Athletics, the underlying entity rows would be as shown in the figure.
Figure 7-1 View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage Handles Entity Subtypes
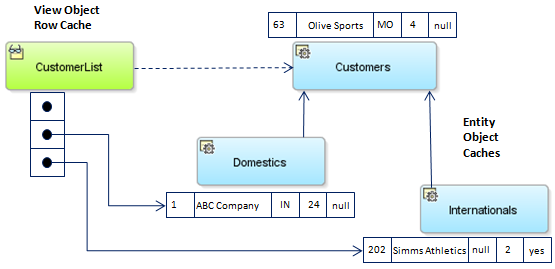
Description of "Figure 7-1 View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage Handles Entity Subtypes "
Note:
The example in this section refers to the oracle.summit.model.polymorphic package in the SummitADF_Examples application workspace.
7.2.1 How to Create a Subtype View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage
The view object that you create with a polymorphic entity usage may inherit one or more of the attributes of the base entity object and the entity subtypes. Attributes that you select from the entity objects will be overridden by the view object attribute definitions. When an entity-based view object references an entity object with a discriminator attribute, then Oracle ADF enforces that the discriminator attribute is included in the query (in addition to the primary key attribute).
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of polymorphic view objects (also called in this section, subtype view objects). For more information, see About Polymorphic View Objects.
You will need to complete these tasks:
-
Create the base entity object and entity subtypes upon which the view objects will be based. For details about creating base entity objects and entity subtypes, see How to Create Entity Objects in an Inheritance Hierarchy.
-
Create an entity-based view object from the base entity object and select the attributes that are common to the subtype view objects. The base view object must contain the superset of attributes represented by each subtype view object. For details about creating an entity-based view object, see How to Create an Entity-Based View Object.
-
In the base view object that you create, select the entity subtype corresponding to each subtype view object that you will create. JDeveloper limits the subtype view objects that you may create to the polymorphic entity usage selections you make.
To select entity subtypes in the base view object:
-
Open the base view object in the overview editor and click the Entity Objects navigation tab.
-
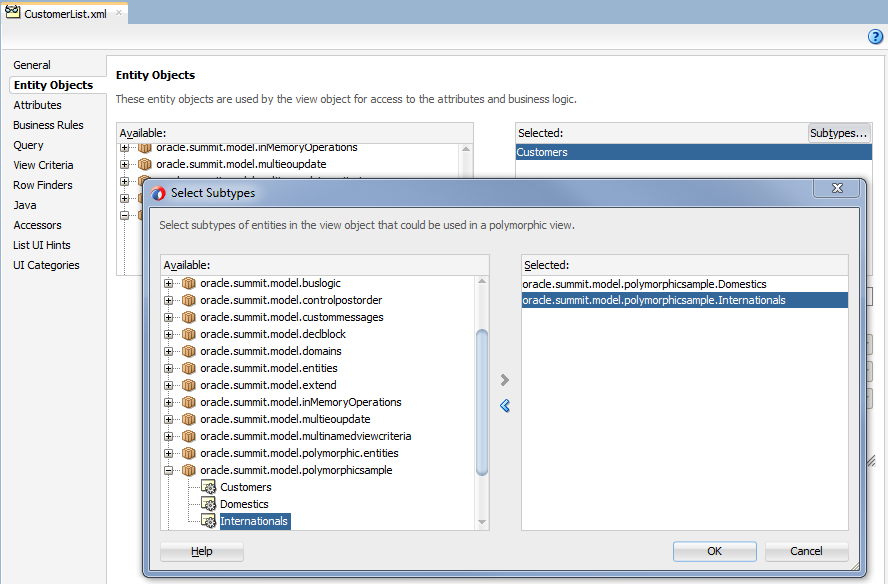
In the Entity Objects page, click Subtypes and in the Select Subtypes dialog, add the entity subtypes to the Selected list.
For example, as Figure 7-2 shows, the entity subtype
DomesticsandInternationalshave been selected to anticipate creating subtype view objects for each.Figure 7-2 Entity Subtypes Define Possible Subtype View Objects
-
To create a subtype view object with a polymorphic entity usage:
-
In the Applications window, right-click your data model project and choose New and then View Object.
-
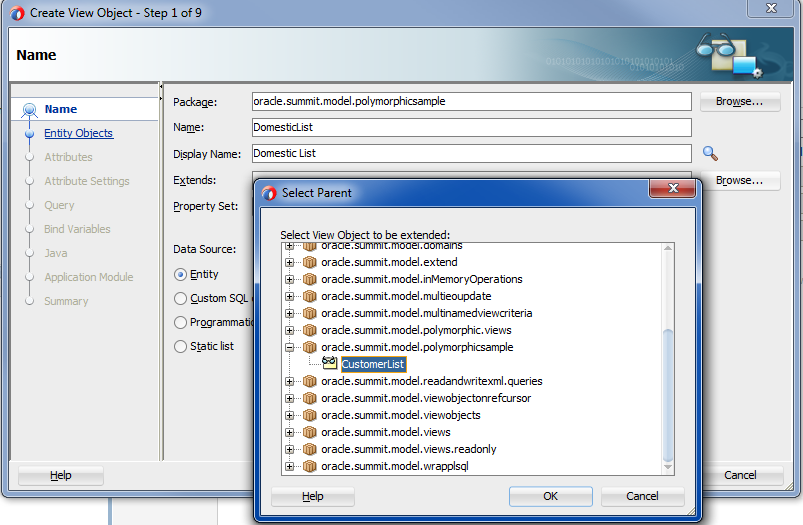
In the Create View Object wizard, name the subtype view object and then next to the Extends field, click Browse.
For example, you might name the subtype view object
DomesticListorInternationalListwhen the subtype view object extends a base view objectCustomerList. In this case, the data model project would define a baseCustomersentity object in order to support the creation of subtype view objects with polymorphic entity usages for theDomesticsandInternationalssubtype entity objects. -
In the Select Parent dialog, select the entity-based view object that you wish to extend and click OK.
The view object you select is the base view object which defines the superset of attributes and is the view object that the subtype view object extends. For example, you select the base view object
CustomerListto extend when you want to create the subtype view objectDomesticList, as shown in Figure 7-3.Figure 7-3 Subtype View Object Extends Base View Object
-
In the Create View Object wizard, make sure that Entity is selected as the data source and click Next.
-
In the Entity Objects page, in the Available list, locate the entity subtype that you want to define as the polymorphic entity usage for the subtype view object and click Add.
The list of available entity subtypes is defined in the inheritance hierarchy of the base entity object, as explained in the prerequisites for this procedure. For example, when you create the subtype view object
DomesticListfor the base view objectCustomerList, you would addDomesticsas the entity subtype from the Available list, as shown in Figure 7-4.Figure 7-4 Subtype View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage Selection
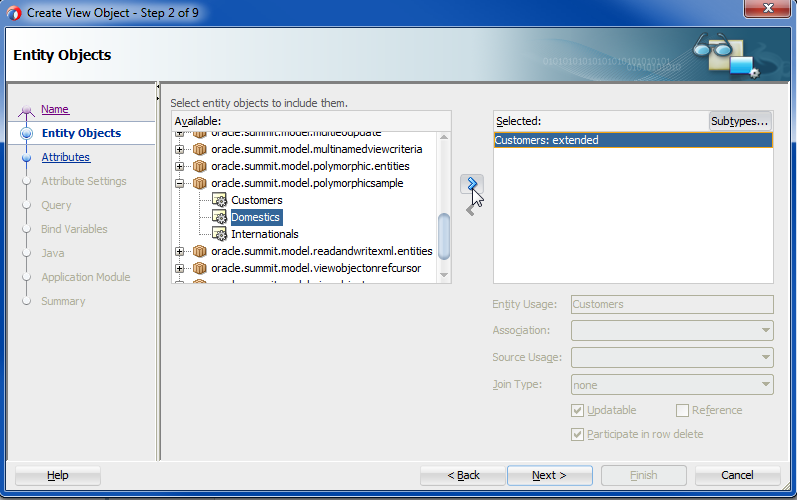
Description of "Figure 7-4 Subtype View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage Selection" -
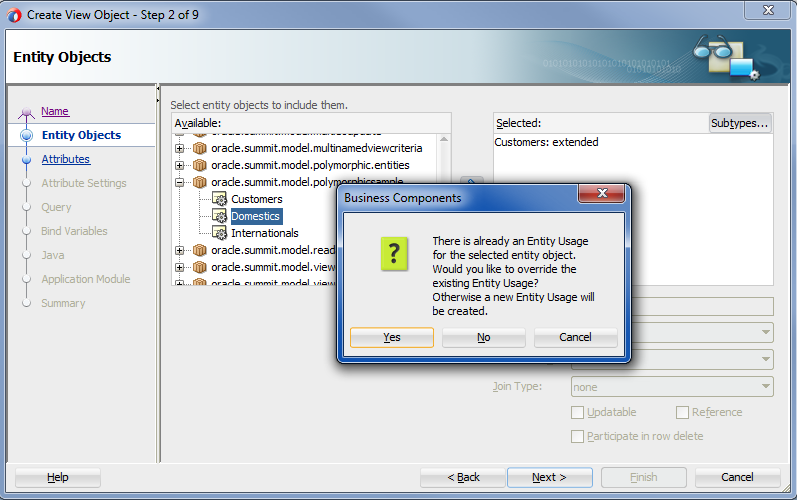
In the Business Components dialog, click Yes to override the entity usage for your subtype view object with the desired polymorphic entity usage.
The Business Components dialog warns you that you will override the attributes of the base entity usage with the entity subtype, as shown in Figure 7-5.
Note that clicking No in the dialog will add an additional usage without overriding the attributes of the base entity usage. Normally, you click Yes to override the base entity usage with the desired entity subtype.
Figure 7-5 Polymorphic Entity Usage Overrides Subtype View Object
-
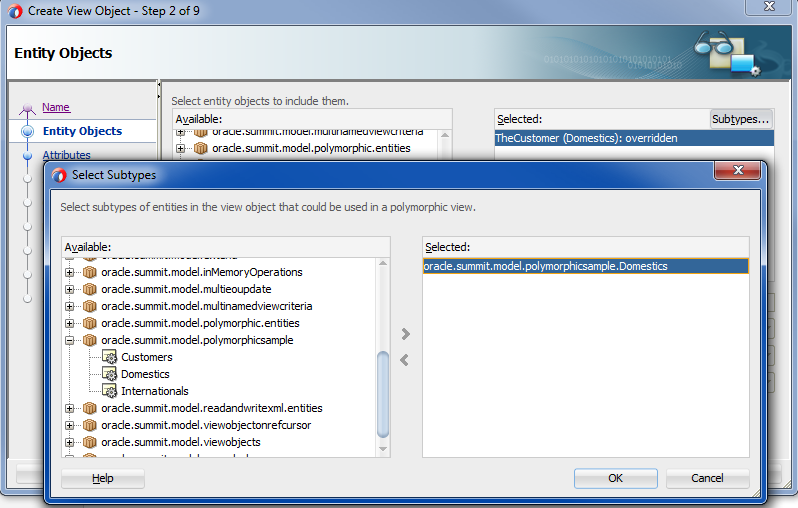
In the Selected list, select the overridden entity usage and click Subtypes.
-
In the Select Subtypes dialog, use the shuttle buttons to leave only the desired polymorphic entity subtype in the Selected list and click OK.
The Select Subtypes dialog lets you specify the entity subtype to be referenced by the usages you have defined in the Entity Objects page of the Create View Object wizard. The list of available entity subtypes is defined by the base view object, as explained in the prerequisites for this procedure. Normally, you will pick the same entity subtype as the one you choose to override (as shown in Figure 7-5).
For example, when you create the subtype view object
DomesticList, you would selectDomesticsas the single entity subtype of the base entity objectCustomers(and deselectInternationalsfrom the Selected list), as shown in Figure 7-6.Figure 7-6 Subtype View Object with a Single Polymorphic Entity Usage Applied
-
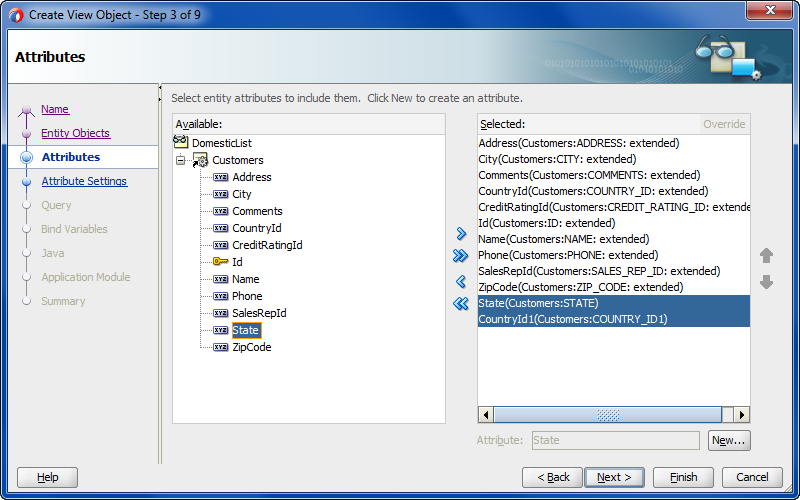
In the Create View Object wizard, in the Entity Objects page, click Next and on the Attributes page of the wizard, shuttle the desired attributes from the entity subtype to the Selected list.
For example, for the
DomesticListview object you would select theStateattribute from the entity subtypeDomestics, as shown in Figure 7-7.Figure 7-7 View Object with a Entity Subtype Attribute Addition
-
In the Attributes page, remove the primary key attribute so the extended view object defines a single primary key attribute and then select the discriminator attribute and click Override and click Next.
For example, for the
DomesticListview object you would remove theCountryIdattribute from the subtype view object's selected list and override theCountryIdattribute, as shown in Figure 7-8.Figure 7-8 View Object with the Overridden Discriminator Attribute
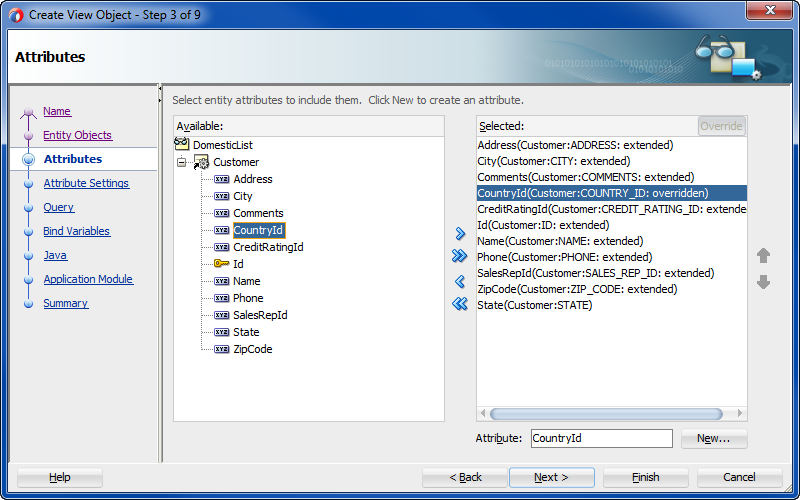
Description of "Figure 7-8 View Object with the Overridden Discriminator Attribute" -
In the Attributes Settings page, select the discriminator attribute from the dropdown and enter the Default Value that defines the subtype and click Finish to complete the wizard.
For example, for the
DomesticListview object you would enterDOMESTIC, as shown in Figure 7-9.Figure 7-9 View Object with the Overridden Discriminator Attribute
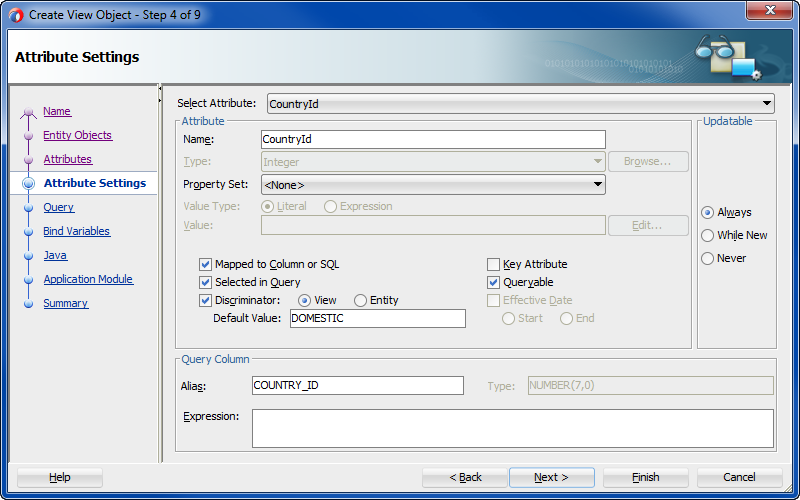
Description of "Figure 7-9 View Object with the Overridden Discriminator Attribute" -
Repeat this procedure to create additional subtype view objects with unique polymorphic entity usages.
For example, the
InternationalListview object is a second subtype that extendsCustomerList. It supplies the valueINTERNATIONALfor theCustomerTypeCodediscriminator attribute.
After creating the subtype view object, you must define the list of subtypes that participate in the view object polymorphism, as described in Updating the Application Module to Expose Subtype Usages. For example, the CustomersModule application module with view instance CustomerList1 must be configured to name the subtype view objects DomesticList and InternationalList.
7.2.2 What Happens When You Create a Subtype View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage
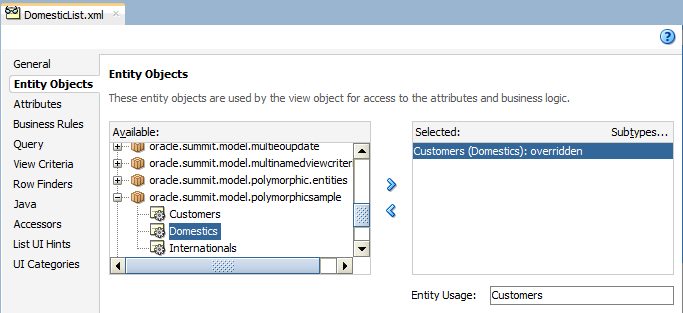
The Entity Objects page of the overview editor identifies the selected entity object with the entity usage override. For example, the overview editor for the DomesticList view object identifies the overridden entity usage Customers (Domestics): overridden with the overriding subtype in parenthesis, as shown in Figure 7-10.
Figure 7-10 View Object Editor Shows Entity Usage is Overridden
When you create an entity-based view object with a polymorphic entity usage, JDeveloper adds information about the allowed entity subtypes to the base view object's XML document. For example, when creating the CustomerList view object, the names of the allowed subtype entity objects are recorded in an <AttrArray> tag. The XML property DiscrColumn identifies CountryTypeCode as the base view object's polymorphic discriminator attribute like this:
<ViewObject Name="CustomerList" ... >
<EntityUsage
Name="Customers"
Entity="oracle.summit.model.polymorphics.entities.Customers" >
</EntityUsage>
<AttrArray Name="EntityImports">
<Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.entities.Domestics" />
<Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.entities.Internationals" />
</AttrArray>
...
<ViewAttribute
Name="CountryTypeCode"
PrecisionRule="true"
EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode"
EntityUsage="Customers"
AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE"
DiscrColumn="true">
</ViewAttribute>
...
</ViewObject>
Then, when you create a subtype view object with a polymorphic entity usage, JDeveloper adds information about the base view object to the subtype view object's XML document. For example, The following example shows the DomesticList subtype view object with the name of the base view object recorded in the Extends property. The XML property DiscrColumn identifies the overridden CountryTypeCode attribute as the polymorphic discriminator attribute, with a subtype value of DOMESTIC. Only the additional attribute State, specific to the subtype view object, appears in the XML document.
<ViewObject Name="DomesticList" Extends="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.views.CustomerList" ...> <EntityUsage Name="Customers" Entity="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.entities.Domestics"/> <AttrArray Name="EntityImports"> <Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphicsample.Domestics"/> </AttrArray> <ViewAttribute Name="CountryTypeCode" PrecisionRule="true" DiscrColumn="true" EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE" DefaultValue="DOMESTIC"> <DesignTime> <Attr Name="_OverrideAttr" Value="true"/> </DesignTime> </ViewAttribute> <ViewAttribute Name="State" PrecisionRule="true" EntityAttrName="State" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="STATE"/> </ViewObject>
Similarly, the XML document for the InternationalList subtype view object names the same CustomerList base view object in the Extends property of its XML document, but defines the polymorphic discriminator attribute with a subtype value of INTERNATIONAL and the additional attribute Language specific to its subtype like this:
<ViewObject Name="InternationalList" Extends="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.views.CustomerList" ... > <EntityUsage Name="Customers" Entity="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.entities.Internationals"/> <AttrArray Name="EntityImports"> <Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphicsample.Internationals"/> </AttrArray> <ViewAttribute Name="CountryTypeCode" PrecisionRule="true" DiscrColumn="true" EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE" DefaultValue="INTERNATIONAL"> <DesignTime> <Attr Name="_OverrideAttr" Value="true"/> </DesignTime> </ViewAttribute> <ViewAttribute Name="Language" PrecisionRule="true" EntityAttrName="Language" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="LANGUAGE"/> </ViewObject>
Note the <AttrArray> tag in the subtype view object definition identifies the allowed entity object for each subtype. Each subtype view object should therefore name a single subtype entity object. If the <AttrArray> tag of a subtype view object definition names more than one entity object, you may remove the unused one. This situation arises when using the Create View Object wizard to create the subtype view object but not reducing the list of default subtype entity objects in the Select Subtypes dialog, as shown in Figure 7-6. By default the dialog makes all subtype entity objects selected.
7.2.3 What You May Need to Know About Polymorphic Entity Usages
When you derive view objects from polymorphic entity usages, you will want to follow these best practices to allow the discriminator attribute to filter the query to only contain the expected subtypes.
7.2.3.1 Your Query Must Limit Rows to Expected Entity Subtypes
If your view object expects to work with only a subset of the available entity subtypes in a hierarchy, you need to include an appropriate WHERE clause that limits the query to only return rows whose discriminator column matches the expected entity type. You should not rely solely on the discriminator attribute to perform subtype filtering in the query. Without the addition of attributes to limit the query, the view object will effectively query all rows and cause the client to discard rows that do not match any discriminator values.
7.2.3.2 Exposing Selected Entity Methods in View Rows Using Delegation
By design, clients do not work directly with entity objects. Instead, they work indirectly with entity objects through the view rows of an appropriate view object that presents a relevant set of information related to the task as hand. Just as a view object can expose a particular set of the underlying attributes of one or more entity objects related to the task at hand, it can also expose a selected set of methods from those entities. You accomplish this by enabling a custom view row Java class and writing a method in the view row class that:
-
Accesses the appropriate underlying entity row using the generated entity accessor in the view row, and
-
Invokes a method on it
For example, assume that the Customers entity object contains a performCustomerFeature() method in its CustomersImpl class. To expose this method to clients on the CustomerList view row, you can enable a custom view row Java class and write the method, as shown in the following example.
// In CustomerListRowImpl.java
public void performCustomerFeature() {
getTheCustomer().performCustomerFeature();
}
JDeveloper generates an entity accessor method in the view row class for each participating entity usage based on the entity usage alias name. Since the alias for the Customers entity in the CustomerList view object is "TheCustomer", it generates a getTheCustomer() method to return the entity row part related to that entity usage.
The code in the view row's performCustomerFeature() method uses this getTheCustomer() method to access the underlying CustomersImpl entity row class and then invokes its performCustomerFeature() method. This style of coding is known as delegation, where a view row method delegates the implementation of one of its methods to a corresponding method on an underlying entity object. When delegation is used in a view row with a polymorphic entity usage, the delegated method call is handled by appropriate underlying entity row subtype. This means that if the CustomersImpl, DomesticsImpl, and InternationalsImpl classes implement the performCustomerFeature() method in a different way, the appropriate implementation is used depending on the entity subtype for the current row.
After exposing this method on the client row interface, client programs can use the custom row interface to invoke custom business functionality on a particular view row. The following example shows the interesting lines of code from a TestEntityPolymorphism class. It iterates over all the rows in the CustomerList view object instance, casts each one to the custom CustomerListRow interface, and invokes the performCustomerFeature() method.
CustomerList customerlist = (CustomerList)am.findViewObject("CustomerList");
customerlist.executeQuery();
while (customerlist.hasNext()) {
CustomerListRow customer = (CustomerListRow)customerlist.next();
System.out.print(customer.getEmail()+"->");
customer.performCustomerFeature();
}
Running the client code in the previous example produces the following output:
austin->## performCustomerFeature as Domestics hbaer->## performCustomerFeature as Internationals : sking->## performCustomerFeature as Domestic :
Rows related to Customers entities display a message confirming that the performCustomerFeature() method in the CustomersImpl class was used. Rows related to Domestics and Internationals entities display a different message, highlighting the different implementations that the respective DomesticsImpl and InternationalsImpl classes have for the inherited performCustomerFeature() method.
7.2.3.3 Creating New Rows With the Desired Entity Subtype
In a view object with a polymorphic entity usage, when you create a new view row it contains a new entity row part whose type matches the base entity usage. To create a new view row with one of the entity subtypes instead, use the createAndInitRow() method.
The following example shows two custom methods in the CustomerList view object's Java class that use createAndInitRow() to allow a client to create new rows having entity rows either of Domestics or Internationals subtypes. To use the createAndInitRow(), as shown in the example, create an instance of the NameValuePairs object and set it to have an appropriate value for the discriminator attribute. Then, pass that NameValuePairs to the createAndInitRow() method to create a new view row with the appropriate entity row subtype, based on the value of the discriminator attribute you passed in.
// In CustomerListImpl.java
public CustomerListRow createCustomersRow() {
NameValuePairs nvp = new NameValuePairs();
nvp.setAttribute("CustomerTypeCode","DOMESTIC");
return (CustomerListRow)createAndInitRow(nvp);
}
public CustomerListRow createInternationalsRow() {
NameValuePairs nvp = new NameValuePairs();
nvp.setAttribute("CustomerTypeCode","INTERNATIONAL");
return (CusotmersListRow)createAndInitRow(nvp);
}
If you expose methods like this on the view object's custom interface, then at runtime, a client can call them to create new view rows with appropriate entity subtypes. The following example shows the interesting lines relevant to this functionality from a TestEntityPolymorphism class. First, it uses the createRow(), createDomesticsRow(), and createInternationalsRow() methods to create three new view rows. Then, it invokes the performCustomerFeature() method from the CustomerListRow custom interface on each of the new rows.
// In TestEntityPolymorphism.java CustomerListRow newCustomer = (CustomerListRow)CustomerList.createRow(); CustomerListRow newDomestic = Customerlist.createDomesticsRow(); CustomerListRow newInternational = Customerlist.createInternationalsRow(); newCustomer.performCustomerFeature(); newDomestic.performCustomerFeature(); newInternational.performCustomerFeature();
As expected, each row handles the method in a way that is specific to the subtype of entity row related to it, producing the results:
## performCustomerFeature as Customer ## performCustomerFeature as Domestic ## performCustomerFeature as International
7.3 Working with Polymorphic View Rows
ADF Business Components allows you to configure a view object to have polymorphic view rows. This allows the client to access different view row types with specific view row interfaces.
In the example shown in Working with Polymorphic Entity Usages, the polymorphism occurs "behind the scenes" at the entity object level. Since the client code works with all view rows using the same CustomerListRow interface, it cannot distinguish between rows based on a Domestics entity object from those based on a Customers entity object. The code works with all view rows using the same set of view row attributes and methods common to all types of underlying entity subtypes.
If you configure a view object to support polymorphic view rows, then the client can work with different types of view rows using a view row interface specific to the type of row it is. By doing this, the client can access view attributes or invoke view row methods that are specific to a given subtype as needed. Figure 7-11 illustrates the hierarchy of view objects that enables this feature for the CustomerList example considered above. DomesticList and InternationalList are child view objects that extend the base (or parent) CustomerList view object. Notice that each one includes an additional attribute specific to the subtype of Customers they have as their entity usage. DomesticList includes an additional State attribute, while InternationalList excludes the State attribute and includes the Language attribute. When configured for view row polymorphism, a client can work with the results of the CustomerList view object using:
-
CustomerListRowinterface for view rows related to customers -
DomesticListRowinterface for view rows related to domestic customers -
InternationalListRowinterface for view rows related to international customers
As you'll see, this allows the client to access the additional attributes and view row methods that are specific to a given subtype of view row.
Figure 7-11 Hierarchy of View Object Subtypes Enables View Row Polymorphism
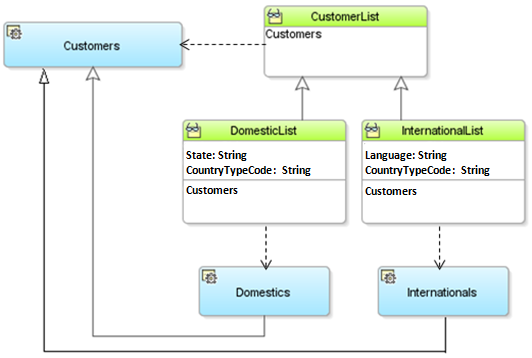
Note:
The example in this section refers to the oracle.summit.model.polymorphicvo package in the SummitADF_Examples application workspace.
7.3.1 How to Create a View Object with Polymorphic View Rows
The view object that you create with polymorphic view rows may inherit one or more of the attributes from a hierarchy of view objects, each with their own base entity object. Attributes that you select from the extended view objects will be overridden by the polymorphic view row definitions in the parent view object.
To create a view object with polymorphic view rows:
-
In the Application Navigator, double-click the view object that you want to be the base view object in the inheritance hierarchy.
For example, the
CustomerListview object is the base forDomesticListview object. -
In the overview editor for the view object, click the Attributes navigation tab and select the discriminator attribute that distinguishes which view row interface to use for the view row, and then click the Edit selected attribute(s) button.
For example, the
CustomerTypeCodeis the discriminator attribute forCustomerList. -
In the Edit Attribute dialog, select the Discriminator checkbox, enter a Default Value, and click OK.
You must supply a value for the Default Value field that matches the attribute value for which you expect the base view object's view row interface to be used. For example, in the
CustomerListview object, you would mark theCustomerTypeCodeattribute as the discriminator attribute and supply a default value ofCUSTOMER. -
In the overview editor for the view object, in the Attributes page, delete all attributes that are specific to the subtype view object.
For example, the attribute
Stateswould be removed from the base view object since it is used exclusively by theDomesticListsubtype view object. -
In the overview editor, click the Java navigation tab, and enable a custom view row class for the base view object, and expose at least one method on the client row interface. This can be one or all of the view row attribute accessor methods, as well as any custom view row methods.
-
Create the subtype new view object that extends the base view object:
-
In the Application Navigator, right-click the base view object and choose New Extended Object, and in the Create Extended Object dialog, name the subtype view object.
In this example, the
CustomerListview object is the base and the subtype view object is namedDomesticList. -
In the overview editor for the subtype view object, click the Attributes navigation tab and choose Add Attribute From Entity from the Add button dropdown, and then, in the Attributes dialog, add the attributes that are specific to the subtype view object and click OK.
In this example, the subtype
DomesticListdefines the additional attributeState. -
In the Attributes page of the overview editor, select the discriminator attribute for the view row, and click Override and then click the Edit selected attribute(s) button.
-
In the Edit Attribute dialog, give the discriminator attribute a distinct Default Value to define the subtype of the extended view object and click OK.
For example, the
DomesticListview object provides the valueDOMESTICfor theCustomerTypeCodediscriminator attribute. -
In the overview editor, click the Java navigation tab, and enable a custom view row class for the extended view object.
If appropriate, add additional custom view row methods or override custom view row methods inherited from the parent view object's row class.
-
Repeat to add additional extended view objects as needed.
For example, the
InternationalListview object is a second one that extendsCustomerList. It supplies the valueINTERNATIONALfor theCustomerTypeCodediscriminator attribute.
-
After setting up the view object hierarchy, you must define the list of view object subtypes that participate in the view row polymorphism, as described in Updating the Application Module to Expose Subtype Usages. For example, the CustomersModule application module with view instance CustomerList1 must be configured to name the subtype view objects DomesticList and InternationalList.
7.3.2 What Happens When You Create a View Object With Polymorphic View Rows
When you create the base view object that you use to define child view objects with polymorphic view row definitions, JDeveloper adds information about the discriminator attribute to the base view object's XML document. For example, when creating the CustomerList view object, the XML property DiscrColumn identifies CountryTypeCode as the base view object's polymorphic discriminator attribute, with a subtype value of CUSTOMER like this:
<ViewObject
Name="CustomerList" ... >
<EntityUsage
Name="Customers"
Entity="oracle.summit.model.polymorphics.entities.Customers" >
</EntityUsage>
...
<ViewAttribute
Name="CountryTypeCode"
PrecisionRule="true"
EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode"
EntityUsage="Customers"
AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE"
DiscrColumn="true"
DefaultValue="CUSTOMER">
</ViewAttribute>
...
</ViewObject>
Then, when you create a child view object with a polymorphic view row definition, JDeveloper adds information about the view row definition to the child view object's XML document. For example, The following example shows the DomesticList child view object with the name of the base view object recorded in the Extends property. The XML property DiscrColumn identifies the overridden CountryTypeCode attribute as the polymorphic discriminator attribute, with a subtype value of DOMESTIC. Only the additional attribute State, specific to the subtype, appears in the XML document of the child view object.
<ViewObject Name="DomesticList" Extends="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.views.CustomerList" ...> <ViewAttribute Name="CountryTypeCode" PrecisionRule="true" DiscrColumn="true" EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE" DefaultValue="DOMESTIC"> <DesignTime> <Attr Name="_OverrideAttr" Value="true"/> </DesignTime> </ViewAttribute> <ViewAttribute Name="State" PrecisionRule="true" EntityAttrName="State" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="STATE"/> </ViewObject>
Similarly, the XML document for the InternationalList child view object names the same base view object in the Extends property of its XML document, but defines the polymorphic discriminator attribute with a subtype value of INTERNATIONAL and the additional attribute Language specific to its subtype like this:
<ViewObject Name="InternationalList" Extends="oracle.summit.model.polymorphic.views.CustomerList" ... > <ViewAttribute Name="CountryTypeCode" PrecisionRule="true" DiscrColumn="true" EntityAttrName="CountryTypeCode" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="COUNTRY_TYPE_CODE" DefaultValue="INTERNATIONAL"> <DesignTime> <Attr Name="_OverrideAttr" Value="true"/> </DesignTime> </ViewAttribute> <ViewAttribute Name="Language" PrecisionRule="true" EntityAttrName="Language" EntityUsage="Customers" AliasName="LANGUAGE"/> </ViewObject>
Note that unlike the polymorphic entity usage example described in What Happens When You Create a Subtype View Object with a Polymorphic Entity Usage, view instances with polymorphic view rows use inheritance and overriding attributes to distinguish, for example, between rows based on a Domestics entity object from those based on a Customers entity object. Thus, the definition of allowed subtype entity objects is absent from the XML document of the view objects in the polymorphic view row case (but defined in <AttrArray> tags in the polymorphic entity usage case).
7.3.3 What You May Need to Know About Polymorphic View Rows
When you work with polymorphic view rows, you can interact with the row types to customize the attributes to display or to delegate to methods specific to the entity subtypes of the view rows.
7.3.3.1 Selecting Subtype-Specific Attributes in Extended View Objects
When you create an extended view object, it inherits the entity usage of its parent. If the parent view object's entity usage is based on an entity object with subtypes in your domain layer, you may want your extended view object to work with one of these subtypes instead of the inherited parent entity usage type. Two reasons you might want to do this are:
-
To select attributes that are specific to the entity subtype
-
To be able to write view row methods that delegate to methods specific to the entity subtype
In order to do this, you need to override the inherited entity usage to refer to the desired entity subtype. To do this, perform these steps in the overview editor for your extended view object.
To override the entity usage for the view object:
When you have performed these steps, the Selected list updates to reflect the overridden entity usage. For example, for the DomesticList view object, after overriding the Customers-based entity usage with the Domestics entity subtype, it updates to show: TheCustomer (Domestics): overridden.
After overriding the entity usage to be related to an entity subtype, you can then use the Attributes tab of the editor to select additional attributes that are specific to the subtype. For example, the DomesticsList view object includes the additional attribute named State that is specific to the Domestics entity object.
7.3.3.2 Delegating to Subtype-Specific Methods After Overriding the Entity Usage
After overriding the entity usage in an extended view object to reference a subtype entity, you can write view row methods that delegate to methods specific to the subtype entity class.
The following example shows the code for a performInternationalFeature() method in the custom view row class for the InternationalList view object. It casts the return value from the getTheCustomer() entity row accessor to the subtype InternationalsImpl, and then invokes the performInternationalFeature() method that is specific to Internationals entity objects.
// In InternationalListRowImpl.java
public void performInternationalFeature() {
InternationalsImpl international = (InternationalsImpl)getTheCustomer();
international.performInternationalFeature();
}
Note:
You need to perform the explicit cast to the entity subtype here because JDeveloper does not yet take advantage of the JDK feature called covariant return types that would allow a subclass like InternationalListRowImpl to override a method like getTheCustomer() and change its return type.
7.3.3.3 Working with Different View Row Interface Types in Client Code
The following example shows the interesting lines of code from a TestViewRowPolymorphism class that performs the following steps:
-
Iterates over the rows in the
CustomerListview object.For each row in the loop, it uses Java's
instanceofoperator to test whether the current row is an instance of theDomesticListRowor theInternationalListRow. -
If the row is a
DomesticListRow, then cast it to this more specific type and:-
Call the
performDomesticFeature()method specific to theDomesticListRowinterface, and -
Access the value of the
Stateattribute that is specific to theDomesticListview object.
-
-
If the row is a
InternationalListRow, then cast it to this more specific type and:-
Call the
performInternationalFeature()method specific to theInternationalListRowinterface, and -
Access the value of the
Languageattribute that is specific to theInternationalListview object.
-
-
Otherwise, just call a method on the
CustomerListRow
// In TestViewRowPolymorphism.java
ViewObject vo = am.findViewObject("CustomerList");
vo.executeQuery();
// 1. Iterate over the rows in the CustomerList view object
while (vo.hasNext()) {
CustomerListRow Customer = (CustomerListRow)vo.next();
System.out.print(Customer.getEmail()+"->");
if (Customer instanceof DomesticListRow) {
// 2. If the row is a DomesticListRow, cast it
DomesticListRow mgr = (DomesticListRow)Customer;
mgr.performDomesticFeature();
System.out.println("State: "+domestic.getState());
}
else if (Customer instanceof InternationalListRow) {
// 3. If the row is an InternationalListRow, cast it
InternationalListRow international = (InternationalListRow)Customer;
international.performInternationalFeature();
System.out.println("Speaks English: "+international.getLanguage());
}
else {
// 4. Otherwise, just call a method on the CustomerListRow
Customer.performCustomerFeature();
}
}
Running the code in the previous example produces the following output:
daustin->## performInternationalFeature called English spoken: Yes hbaer->## performCustomerFeature as Customer : sking->## performDomesticFeature called State: CA :
This illustrates that by using the view row polymorphism feature the client was able to distinguish between view rows of different types and access methods and attributes specific to each subtype of view row.
7.4 What You May Need to Know About the Discriminator Attribute
You can choose to include or exclude a discriminator attribute in the query that an ADF view object uses to reference an entity object.
When a view object references an entity object with a discriminator attribute, you can decide whether or not that discriminator attribute should be included in the query (in addition to the primary key attribute) by selecting the Polymorphic Discriminator checkbox for the inherited discriminator attribute in the Details tab on the Attributes page of the overview editor for the view object.
When you decide to enable the checkbox, you can then use the Polymorphic Discriminator options in the Details tab to configure whether or not the view object is defined as a subtype view object:
-
Enabling the option View means you want to enable polymorphic view rows.
-
Enabling the option Entity means you want to ignore the discriminator capability of the view row and will instead instantiate the attribute with a default value.
The Entity option is useful in situations where a discriminator attribute is inherited by an entity-based view object with multiple backing entity objects and yet polymorphic view rows are not desired.
Figure 7-12 shows the Details tab for the DomesticList view object enables its CustomerTypeCode discriminator attribute inherited from the Customers entity object. The View selection indicates that this discriminator attribute participates in view object polymorphism and the value DOMESTIC determines the subtype view object's row type.
Figure 7-12 Discriminator Attribute Selection Enables View Row Polymorphism
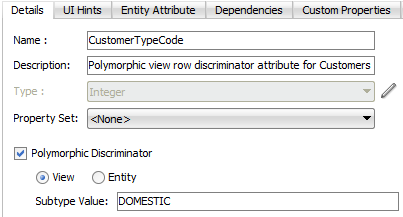
Description of "Figure 7-12 Discriminator Attribute Selection Enables View Row Polymorphism"
7.5 Updating the Application Module to Expose Subtype Usages
You can specify the list of view object subtypes for the base view object instance in an ADF application module definition.
After creating the view object hierarchy using either view row polymorphism or entity object polymorphism, you need to define the list of view object subtypes that participate in the view object polymorphism at runtime. To accomplish this, you update the application module definition to specify the subtype view objects for the base view instance. At runtime, ADF creates polymorphic view rows based on the definitions of the invoked view instance's named subtypes.
7.5.1 How to Expose Subtype Usages on the Data Model
After creating the view object hierarchy using either view row polymorphism or entity object polymorphism, you need to define the list of view object subtypes that participate in the view object polymorphism. To accomplish this, you update the application module definition to specify the subtype view objects for the base view instance.
As Figure 7-13 shows, the data model that exposes the base view object usage CustomerList1 remains unchanged, while the Select Subtypes dialog is used to define the possible polymorphic view object usages of the base view object.
Figure 7-13 Updating the Application Module Definition with Subtype View Objects
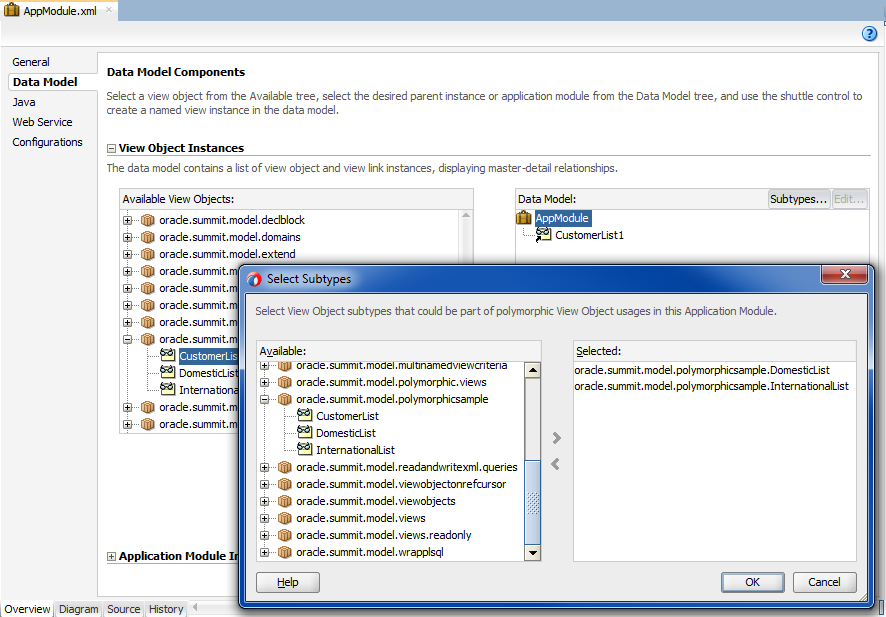
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of polymorphic view objects. For more information, see Working with Polymorphic View Rows.
When you want to create subtype view objects based on polymorphic entity usages, which the view objects derive from the inheritance of the entity subtypes, create the subtype view objects that extend the base entity-based view object. For more information, see Working with Polymorphic Entity Usages.
When you want to create subtype view objects based on polymorphic view rows, which derive from a view object hierarchy that you define, create the subtype view objects with polymorphic discriminator attribute. For more information, see Working with Polymorphic View Rows.
To add subtype view objects to the application module definition:
7.5.2 What Happens When You Add Subtype View Objects to the Application Module
When you add a subtype view object to the application module, JDeveloper adds information about the allowed view subtypes to the application module's XML document. For example, when defining a view instance CustomerList1 with two possible subtype usages, the names of the allowed subtype view objects are recorded in an <AttrArray> tag like this:
<AppModule
...
<ViewUsage
Name="CustomerList1"
ViewObjectName="oracle.summit.model.polymorphicsample.CustomerList"/>
<AttrArray Name="ViewImports">
<Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphicsample.DomesticList"/>
<Item Value="oracle.summit.model.polymorphicsample.InternationalList"/>
</AttrArray>
</AppModule>