3 Migrating Your Application to MAF 2.1.2
This chapter provides information about migrating applications created using earlier releases of MAF and ADF Mobile to MAF 2.1.2.
This chapter includes the following sections:
3.1 Migrating an Application to MAF 2.1.2
The MAF 2.1.0 release introduced significant changes described in this chapter. Use the information in this chapter if you migrate an application created in a pre-MAF 2.1.0 release to MAF 2.1.2. If you migrate an application to MAF 2.1.2 that was created in MAF 2.1.0 or previously migrated to MAF 2.1.2, MAF will have made already made the changes required by migration to JDK 8, management of Cordova plugins, and a new cacerts file.
MAF 2.1.0 used newer versions of Apache Cordova and Java. It also changed the way that JDeveloper registered plugins in your MAF application. For SSL, it delivered a cacerts file that contains new CA root certificates.
Read the subsequent sections in this chapter that describe how these changes impact the migration of your MAF application to MAF 2.1.0 or later.
Finally, MAF 2.1.0 delivered an updated SQLite database and JDBC driver. Review, and migrate as necessary, any code in your migrated MAF application that connects to the SQLite database. For more information about how to connect to the SQLite database, see the "Using the Local SQLite Database" section in the Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
3.2 Migrating to JDK 8 in MAF 2.1.2
MAF applications that you create in MAF 2.1.0 and later use JDK 8. You specify the location of your JDK 8 installation the first time you start JDeveloper after installing the MAF extension, as described in Section 1.5, "Installing the MAF Extension in JDeveloper."
If you migrate a MAF application that compiled with an earlier version of Java, note that MAF 2.1.0 and later requires JDK 8 and compiles applications using the Java SE Embedded 8 compact2 profile. When you open an application that you migrated from a pre-MAF 2.1.0 release in MAF 2.1.2 for the first time, JDeveloper makes the following changes:
-
Renames the configuration file that specifies the startup parameters of the JVM from
cvm.propertiestomaf.properties. For more information about themaf.propertiesfile, see the "How to Enable Debugging of Java Code and JavaScript" section in Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework. -
Replaces instances (if any) of the following import statement in the application's Java source files:
com.sun.util.logging
With:
java.util.logging
-
Replaces the following entries in the application's
logging.propertiesfile.handlers=com.sun.util.logging.ConsoleHandler .formatter=com.sun.util.logging.SimpleFormatter
With:
.handlers=java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler .formatter=java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter
For more information about the
logging.propertiesfile, see the "How to Configure Logging Using the Properties File" section in Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
3.3 Migrating Cordova Plugins from Earlier Releases to MAF 2.1.2
MAF applications developed using earlier releases of MAF (prior to MAF 2.1.0) registered plugins in the maf-application file. Release MAF 2.1.0 and later registers plugins in the maf-plugins.xml file. JDeveloper makes the following changes to an application from an earlier release that uses plugins when you migrate the application:
-
Comments out entries in the
maf-application.xmlfile that referenced plugins. For example, JDeveloper comments out entries such as the following:<!--<adfmf:cordovaPlugins> <adfmf:plugin fullyQualifiedName="BarcodeScanner" implementationClass="com.phonegap.plugins. barcodescanner.BarcodeScanner" platform="Android" name="BarcodeScanner"> ..... </adfmf:cordovaPlugins>--> -
Registers the plugin in the
maf-plugins.xmlfile, as shown in the following example:<cordova-plugins> ... <cordova-plugin id="c3" pluginId="org.apache.cordova.barcodeScanner"> <platform id="p3" name="ios" enabled="true"/> <platform id="p4" name="android" enabled="false"/> </cordova-plugin> </cordova-plugins>
To complete the migration and make sure that your migrated MAF application can use the plugins it used previously, verify that the:
-
Version of the plugin is supported by MAF.
MAF applications in 2.1.1 use Cordova 3.6.3 on Android and Cordova 3.7.0 on iOS.
Obtain a newer version of the plugin if the plugin was created using an earlier release of Cordova.
-
Set the relative path to the plugin so that the MAF application's
maf-plugins.xmlfile correctly references the plugin. For more information, see the "Registering Additional Plugins in Your MAF Application" section in Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.If the
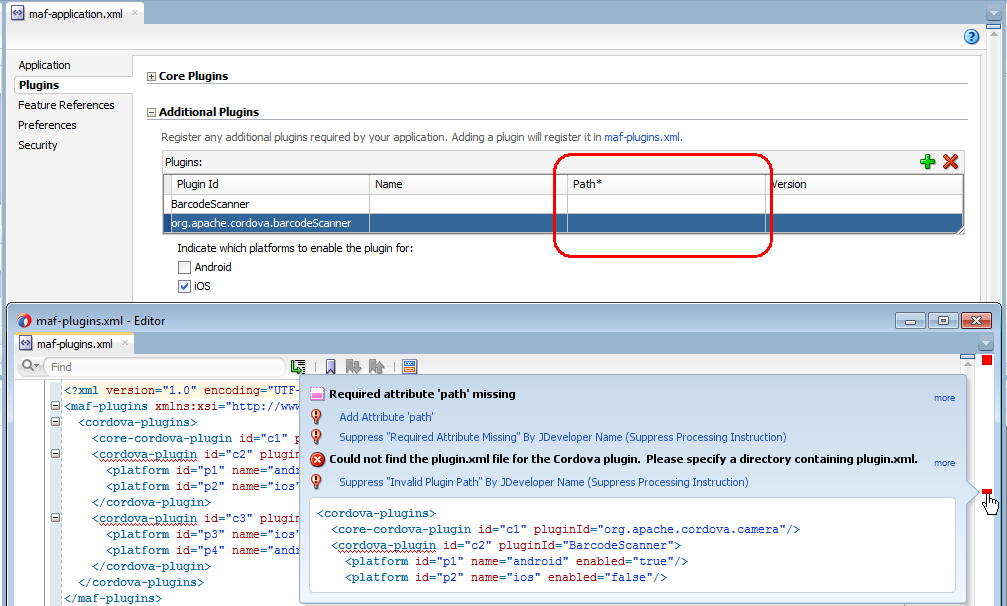
maf-plugins.xmlfile does not correctly reference a plugin using a relative path, the overview editor for themaf-application.xmlfile's Path* field which requires a value is empty and themaf-plugins.xmldisplays a validation failure, as shown in Figure 3-1.
3.4 Migrating ADF Mobile Applications
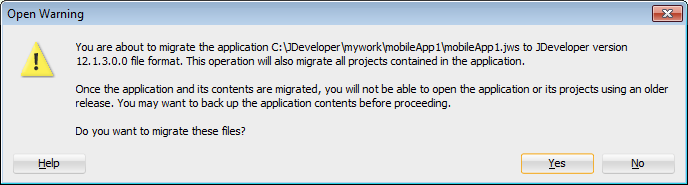
MAF automatically migrates the configuration of applications written in Versions 11.1.2.3.0 and 11.1.2.4.0 of ADF Mobile. After you open the workspace (.jws) file of an ADF Mobile application, MAF alerts you that the application is not the current version by presenting the Open Warning dialog (illustrated in Figure 3-2), that prompts you to continue with the migration, or dismiss the dialog and close the file.
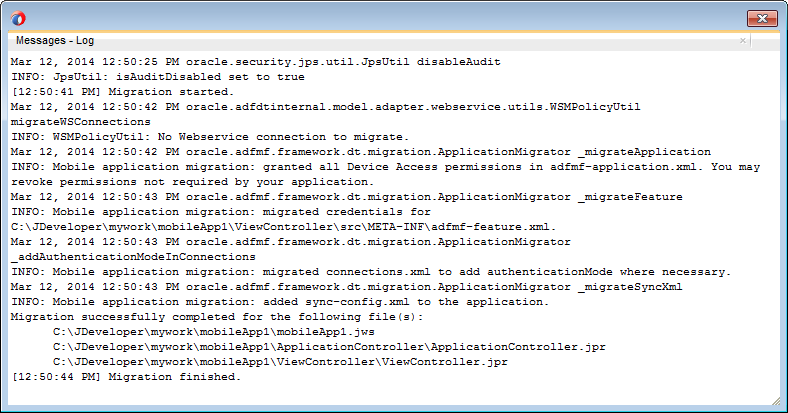
MAF writes the status of the migration to the Log window, as illustrated by Figure 3-3. The migration process also logs the following warning if it detects that the application to migrate uses the old configuration service API.
The MAF 2.0 Configuration Service API is not backwards compatible with previous versions and cannot be migrated automatically. Refer to Section 9.3 "Migrating the Configuration Service API" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework 2.0. for information on migrating to the new API.
For more information, see the "Migrating the Configuration Service" section in Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
3.4.1 What Happens When You Migrate an ADF Mobile Application
Table 3-1 describes how migration affects ADF Mobile artifacts.
Table 3-1 Migration of ADF Mobile Artifacts and Configuration
| File Name | Change |
|---|---|
|
|
The migration makes the following changes:
|
|
|
The migration renames the file as |
|
|
The migration removes the secure SOAP web service connections defined by the |
|
|
The migration renames the file as <skin-family>mobileAlta</skin-family> <skin-version>v1.1</skin-version> |
|
|
The migration renames the file as |
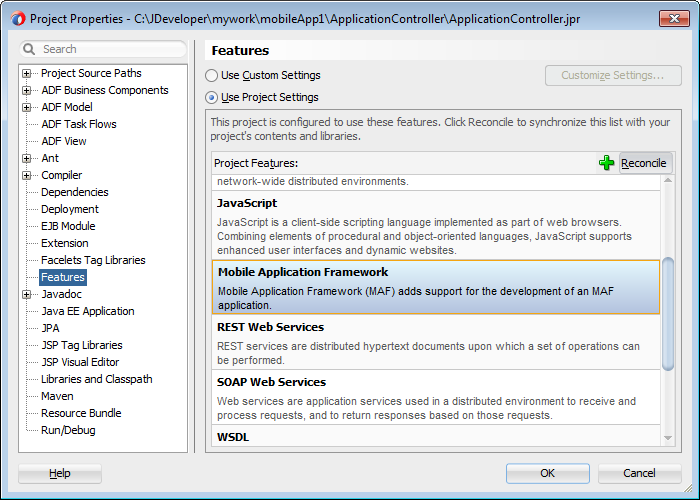
The application migrates from the ADF Mobile Framework technology to use the Mobile Application Framework technology as a project feature. Figure 3-4 shows the Features page for an application controller project that uses the Mobile Application Framework technology. Choose Project Properties > Features to view this dialog.
MAF does not override the icon, splash screen, or navigation bar images created for the ADF Mobile application; the image files within the application controller's resources file are retained. Likewise, any images used for application features are also retained.
3.4.1.1 About Migrating Web Service Policy Definitions
MAF stores web service policy definitions in the wsm-assembly.xml file. ADF Mobile applications store this information in the connections.xml file. Example 3-1 illustrates oracle/wss_username_token_client_policy by the <policy-references> element in the connections.xml file.
Example 3-1 The connections.xml File
<policy-references xmlns="http://oracle.com/adf">policy-reference category="security"
uri="oracle/wss_username_token_client_policy"
enabled="true"
id="oracle/wss_username_token_client_policy" xmlns=""/>
</policy-references>
Example 3-2 illustrates the policy defined in the wsm-assembly.xml file.
3.4.2 What You May Need to Know About FARs in Migrated Applications
MAF does not migrate the adfmf-feature.xml file packaged within a Feature Archive (FAR) file. You replace the ADF Mobile FARs used by a migrated application to make sure that the credentials attribute has been replaced by securityEnabled=true in the FAR's maf-feature.xml file.
After you migrate the application:
-
Choose Application Properties > Libraries and Classpath.
-
Select the FAR and click Remove.
-
Import the FAR containing the migrated view controller.
-
Migrate the ADF Mobile application that contains the view controller project that was packaged as a FAR.
Note:
A FAR cannot include both anadfmf-feature.xmlfile and amaf-feature.xmlfile.-
Deploy the view controller project as a FAR.
-
Import the FAR into the migrated application.
-
For more information about how to import a FAR into an application, see the "How to Use FAR Content in a MAF Application" section of Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
3.5 Migrating to New cacerts File for SSL in MAF 2.1.2
MAF 2.1.0 delivered a new cacerts file for use in MAF applications. Make sure that the cacerts file packaged in the MAF application that you publish for your end users to install contains the same CA root certificates as the HTTPS server that end users connect to when they use your MAF application.
You may need to import new certificates to your MAF application's cacerts file if the HTTPS server contains certificates not present in your MAF application's cacerts file. Similarly, system administrators for the HTTPS servers that your MAF application connects to may need to import new certificates if your MAF application uses a certificate not present on the HTTPS server.
Use JDK 8's keytool utility to view and manage the certificates in your MAF application's cacerts file. The following example demonstrates how you might use JDK 8's keytool utility to display the list of certificates in a cacerts file:
JDK8install/bin/keytool -list -v -keystore dirPathToCacertsFile/cacerts –storepass changeit | grep "Issuer:"
For more information about using the JDK 8's keytool utility to manage certificates, see http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/#security. For example, to use the keytool utility on Windows, see http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/windows/keytool.html. For UNIX-based operating systems, see http://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/unix/keytool.html.
For more information about the cacerts file and using SSL to secure your MAF application, see the "Supporting SSL" section in Developing Mobile Applications with Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
Example 3-3 lists the issuers of CA root certificates included in MAF 2.1.0's cacerts file. Use JDK 8's keytool utility, as previously described, to manage the certificates in this file to meet the requirements of the environment where your MAF application will be used.
Example 3-3 CA Root Certificate Issuers in MAF 2.1.0 cacerts File
Issuer: CN=DigiCert Assured ID Root CA, OU=www.digicert.com, O=DigiCert Inc, C=US Issuer: CN=TC TrustCenter Class 2 CA II, OU=TC TrustCenter Class 2 CA, O=TC TrustCenter GmbH, C=DE Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=premium-server@thawte.com, CN=Thawte Premium Server CA, OU=Certification Services Division, O=Thawte Consulting cc, L=Cape Town, ST=Western Cape, C=ZA Issuer: CN=SwissSign Platinum CA - G2, O=SwissSign AG, C=CH Issuer: CN=SwissSign Silver CA - G2, O=SwissSign AG, C=CH Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=server-certs@thawte.com, CN=Thawte Server CA, OU=Certification Services Division, O=Thawte Consulting cc, L=Cape Town, ST=Western Cape, C=ZA Issuer: CN=Equifax Secure eBusiness CA-1, O=Equifax Secure Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=SecureTrust CA, O=SecureTrust Corporation, C=US Issuer: CN=UTN-USERFirst-Client Authentication and Email, OU=http://www.usertrust.com, O=The USERTRUST Network, L=Salt Lake City, ST=UT, C=US Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=personal-freemail@thawte.com, CN=Thawte Personal Freemail CA, OU=Certification Services Division, O=Thawte Consulting, L=Cape Town, ST=Western Cape, C=ZA Issuer: CN=AffirmTrust Networking, O=AffirmTrust, C=US Issuer: CN=Entrust Root Certification Authority, OU="(c) 2006 Entrust, Inc.", OU=www.entrust.net/CPS is incorporated by reference, O="Entrust, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=UTN-USERFirst-Hardware, OU=http://www.usertrust.com, O=The USERTRUST Network, L=Salt Lake City, ST=UT, C=US Issuer: CN=Certum CA, O=Unizeto Sp. z o.o., C=PL Issuer: CN=AddTrust Class 1 CA Root, OU=AddTrust TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE Issuer: CN=Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2, OU="(c) 2009 Entrust, Inc. - for authorized use only", OU=See www.entrust.net/legal-terms, O="Entrust, Inc.", C=US Issuer: OU=Equifax Secure Certificate Authority, O=Equifax, C=US Issuer: CN=QuoVadis Root CA 3, O=QuoVadis Limited, C=BM Issuer: CN=QuoVadis Root CA 2, O=QuoVadis Limited, C=BM Issuer: CN=DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA, OU=www.digicert.com, O=DigiCert Inc, C=US Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=info@valicert.com, CN=http://www.valicert.com/, OU=ValiCert Class 1 Policy Validation Authority, O="ValiCert, Inc.", L=ValiCert Validation Network Issuer: CN=Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1, O=Equifax Secure Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=GeoTrust Universal CA, O=GeoTrust Inc., C=US Issuer: OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=thawte Primary Root CA - G3, OU="(c) 2008 thawte, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Certification Services Division, O="thawte, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=thawte Primary Root CA - G2, OU="(c) 2007 thawte, Inc. - For authorized use only", O="thawte, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=Deutsche Telekom Root CA 2, OU=T-TeleSec Trust Center, O=Deutsche Telekom AG, C=DE Issuer: CN=Buypass Class 3 Root CA, O=Buypass AS-983163327, C=NO Issuer: CN=UTN-USERFirst-Object, OU=http://www.usertrust.com, O=The USERTRUST Network, L=Salt Lake City, ST=UT, C=US Issuer: CN=GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority, O=GeoTrust Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=Buypass Class 2 Root CA, O=Buypass AS-983163327, C=NO Issuer: CN=Baltimore CyberTrust Code Signing Root, OU=CyberTrust, O=Baltimore, C=IE Issuer: OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=Baltimore CyberTrust Root, OU=CyberTrust, O=Baltimore, C=IE Issuer: OU=Starfield Class 2 Certification Authority, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=Chambers of Commerce Root, OU=http://www.chambersign.org, O=AC Camerfirma SA CIF A82743287, C=EU Issuer: CN=T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3, OU=T-Systems Trust Center, O=T-Systems Enterprise Services GmbH, C=DE Issuer: CN=VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5, OU="(c) 2006 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 2, OU=T-Systems Trust Center, O=T-Systems Enterprise Services GmbH, C=DE Issuer: CN=TC TrustCenter Universal CA I, OU=TC TrustCenter Universal CA, O=TC TrustCenter GmbH, C=DE Issuer: CN=VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G4, OU="(c) 2007 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3, OU="(c) 1999 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=XRamp Global Certification Authority, O=XRamp Security Services Inc, OU=www.xrampsecurity.com, C=US Issuer: CN=Class 3P Primary CA, O=Certplus, C=FR Issuer: CN=Certum Trusted Network CA, OU=Certum Certification Authority, O=Unizeto Technologies S.A., C=PL Issuer: OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=GlobalSign, O=GlobalSign, OU=GlobalSign Root CA - R3 Issuer: CN=UTN - DATACorp SGC, OU=http://www.usertrust.com, O=The USERTRUST Network, L=Salt Lake City, ST=UT, C=US Issuer: OU=Security Communication RootCA2, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP Issuer: CN=GTE CyberTrust Global Root, OU="GTE CyberTrust Solutions, Inc.", O=GTE Corporation, C=US Issuer: OU=Security Communication RootCA1, O=SECOM Trust.net, C=JP Issuer: CN=AffirmTrust Commercial, O=AffirmTrust, C=US Issuer: CN=TC TrustCenter Class 4 CA II, OU=TC TrustCenter Class 4 CA, O=TC TrustCenter GmbH, C=DE Issuer: CN=VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority, OU="(c) 2008 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=GlobalSign, O=GlobalSign, OU=GlobalSign Root CA - R2 Issuer: CN=Class 2 Primary CA, O=Certplus, C=FR Issuer: CN=DigiCert Global Root CA, OU=www.digicert.com, O=DigiCert Inc, C=US Issuer: CN=GlobalSign Root CA, OU=Root CA, O=GlobalSign nv-sa, C=BE Issuer: CN=thawte Primary Root CA, OU="(c) 2006 thawte, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Certification Services Division, O="thawte, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=Starfield Root Certificate Authority - G2, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", L=Scottsdale, ST=Arizona, C=US Issuer: CN=GeoTrust Global CA, O=GeoTrust Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=Sonera Class2 CA, O=Sonera, C=FI Issuer: CN=Thawte Timestamping CA, OU=Thawte Certification, O=Thawte, L=Durbanville, ST=Western Cape, C=ZA Issuer: CN=Sonera Class1 CA, O=Sonera, C=FI Issuer: CN=QuoVadis Root Certification Authority, OU=Root Certification Authority, O=QuoVadis Limited, C=BM Issuer: CN=AffirmTrust Premium ECC, O=AffirmTrust, C=US Issuer: CN=Starfield Services Root Certificate Authority - G2, O="Starfield Technologies, Inc.", L=Scottsdale, ST=Arizona, C=US Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=info@valicert.com, CN=http://www.valicert.com/, OU=ValiCert Class 2 Policy Validation Authority, O="ValiCert, Inc.", L=ValiCert Validation Network Issuer: CN=AAA Certificate Services, O=Comodo CA Limited, L=Salford, ST=Greater Manchester, C=GB Issuer: CN=America Online Root Certification Authority 2, O=America Online Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=AddTrust Qualified CA Root, OU=AddTrust TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE Issuer: CN=KEYNECTIS ROOT CA, OU=ROOT, O=KEYNECTIS, C=FR Issuer: CN=America Online Root Certification Authority 1, O=America Online Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3, OU="(c) 1999 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=AddTrust External CA Root, OU=AddTrust External TTP Network, O=AddTrust AB, C=SE Issuer: OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G3, OU=(c) 2008 GeoTrust Inc. - For authorized use only, O=GeoTrust Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=GeoTrust Primary Certification Authority - G2, OU=(c) 2007 GeoTrust Inc. - For authorized use only, O=GeoTrust Inc., C=US Issuer: CN=SwissSign Gold CA - G2, O=SwissSign AG, C=CH Issuer: CN=Entrust.net Certification Authority (2048), OU=(c) 1999 Entrust.net Limited, OU=www.entrust.net/CPS_2048 incorp. by ref. (limits liab.), O=Entrust.net Issuer: OU=ePKI Root Certification Authority, O="Chunghwa Telecom Co., Ltd.", C=TW Issuer: CN=Global Chambersign Root - 2008, O=AC Camerfirma S.A., SERIALNUMBER=A82743287, L=Madrid (see current address at www.camerfirma.com/address), C=EU Issuer: CN=Chambers of Commerce Root - 2008, O=AC Camerfirma S.A., SERIALNUMBER=A82743287, L=Madrid (see current address at www.camerfirma.com/address), C=EU Issuer: OU=Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority, O="The Go Daddy Group, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=AffirmTrust Premium, O=AffirmTrust, C=US Issuer: CN=VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3, OU="(c) 1999 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=VeriSign Trust Network, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: OU=Security Communication EV RootCA1, O="SECOM Trust Systems CO.,LTD.", C=JP Issuer: OU=VeriSign Trust Network, OU="(c) 1998 VeriSign, Inc. - For authorized use only", OU=Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2, O="VeriSign, Inc.", C=US Issuer: CN=Go Daddy Root Certificate Authority - G2, O="GoDaddy.com, Inc.", L=Scottsdale, ST=Arizona, C=US