5 Defining the Content Type of MAF Application Features
This chapter describes using the MAF Application Editor and MAF Features Editor to define the display behavior of the mobile application's springboard and navigation bar and how to designate content by embedding application features.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 5.1, "Introduction to Content Types for an Application Feature"
-
Section 5.2, "Defining the Application Feature Content as Remote URL or Local HTML"
-
Section 5.3, "Defining the Application Feature Content as a MAF AMX Page or Task Flow"
-
Section 5.4, "What You May Need to Know About Selecting External Resources"
5.1 Introduction to Content Types for an Application Feature
The content type for an application feature describes the format of the user interface, which can be constructed using MAF AMX components or HTML(5) tags. An application feature can also derive its content from remotely hosted pages that contain content appropriate to a mobile context. These web pages might be a JavaServer page authored in Apache Trinidad for smartphones, or be comprised of ADF Faces components for applications that run on tablet devices. The application features embedded in a MAF application can each have different content types.
While a MAF application includes application features with different content types, applications features themselves may have different content types to respond to user- and device-specific requirements. For information on how the application feature delivers different content types, see Chapter 22, "Setting Constraints on Application Features." Adding a child element to the <adfmf:content> element, shown in Example 5-1, enables you to define how the application feature implements its user interface.
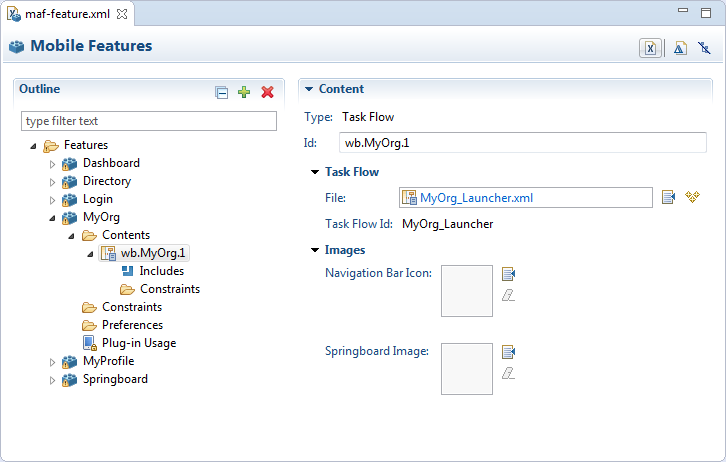
The Content tab of the MAF Features Editor, shown in Figure 5-1, provides you with dropdown lists and fields for defining the target content-related elements and attributes shown in Example 5-1. The fields within this tab enable you to set constraints that can control the type of content delivered for an application feature as well as the navigation and springboard icon images that it uses.
5.2 Defining the Application Feature Content as Remote URL or Local HTML
The Content tab of the overview editor, shown in Figure 5-1, provides you with dropdown lists and fields for defining the target content-related elements and attributes shown in Example 5-1. The fields within this tab enable you to set constraints that can control the type of content delivered for an application feature as well as the navigation and springboard icon images that it uses.
Before you begin:
Each content type has its own prerequisites, as follows:
-
Remote URL—A reference to a web application. You can enhance an existing web application for mobile usage and extend device services. Remote content can complement both MAF AMX and local HTML content by providing a local data cache and a full set of server-side data and functionality. The remote URL implementation requires a valid web address. For more information, see Chapter 20, "Implementing Application Feature Content Using Remote URLs."
-
Local HTML—Reference a HTML page that is packaged within your MAF application. Such HTML pages can reference JavaScript, as demonstrated by the HelloWorld sample application described in MAF Sample Applications. Consider using this content type to implement application functionality through usage of the Cordova JavaScript APIs if the MAF is not best suited to implementing your application's functionality. For more information about JavaScript APIs and the MAF, see Appendix B, "Local HTML and Application Container APIs."
To define the application content as Remote URL or Local HTML:
-
Right-click an application feature listed in the MAF Features Editor and select Add.
-
In the New Object dialog, either Local URL or Remote HTML and click OK.
-
Define the content-specific parameters:
-
For local HTML content, enter the location of the local bundle or create the HTML page by clicking Add in the URL field, and entering a name for the HTML file in the New Mobile HTML Page dialog, and then building the page using OEPE's HTML editor. Because this is an application feature, this page is stored within the ViewContent folder of the view project.
-
For remote URL content, select the connection that represents address of the web pages on the server (and the location of the launch page).
You can create this connection by first clicking Add and then completing the Create URL Connection dialog. This connection is stored in the
connections.xmlfile.
-
-
If needed, do the following:
-
Enter constraints that describe the conditions under which this content is available to users. For more information, see Chapter 22, "Setting Constraints on Application Features."
-
Select navigation bar and springboard images.
-
5.3 Defining the Application Feature Content as a MAF AMX Page or Task Flow
The Content tab of the Overview editor, shown in Figure 5-1, provides you with dropdown lists and fields for defining the target content-related elements and attributes shown in Example 5-1. The fields within this tab enable you to set constraints that can control the type of content delivered for an application feature as well as the navigation and springboard icon images that it uses.
Each content type has its own prerequisites, as follows:
-
AMX Page—The default content type for application features. For more information about MAF AMX pages, see Chapter 11, "Creating MAF AMX Pages."
An application feature implemented as MAF AMX requires a view (that is, a single MAF AMX page) or a bounded or unbounded task flow. Including a JavaScript file provides rendering logic to the MAF AMX components or overrides the existing rendering logic. Including a style sheet (CSS) with selectors that specify a custom look and feel for the application feature, one that overrides the styles defined at the MAF application level that are used by default for application features. In other words, you ensure that the entire application feature has its own look and feel.
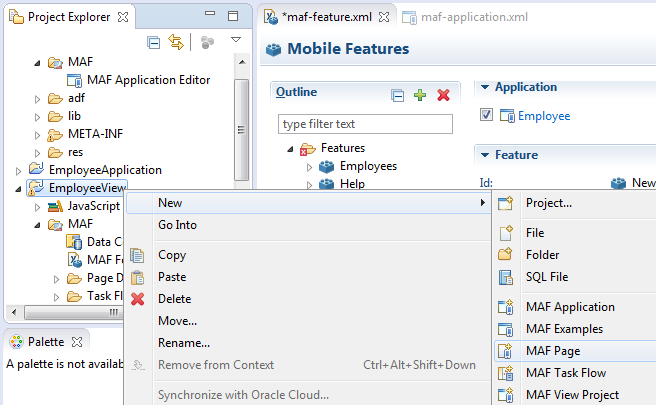
If you create the MAF AMX pages as well as the MAF application that contains them, you can create both using the wizards in the New Gallery. You access these wizards from File > New. Alternatively, you can create an MAF AMX page using the context menu shown in Figure 5-2 that appears when you right-click the view project in the Project Explorer and then choose New.
Note:
When manually editing references to task flows, MAF AMX pages, CSS and JavaScript files in MAF Features Editor, keep in mind that file systems used on devices may enforce case-sensitivity and may not allow special characters. To ensure that these files can be referenced, check the mobile device specification. -
Task Flow—Provides a modular approach to defining control flow in your application feature. Use a task flow to define a collection of activities that make up a task. Examples of activities that you can include in a task flow are views (use to display MAF AMX pages), method calls (use to invoke managed bean methods), and task flow calls (use to call other task flows). For more information about task flows, see Section 11.2, "Creating Task Flows."
To use a MAF AMX page or task flow as application feature content:
-
Select an application feature listed in the Outline of the MAF Feature Editor.
-
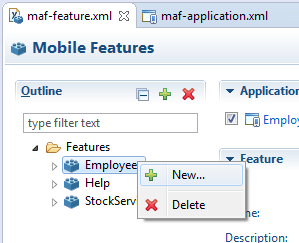
Click the right mouse button and select New, as shown in Figure 5-3.
-
In the New Object dialog, expand the Content node, if necessary and choose one of the following content types and click OK:
-
AMX Page
-
Task Flow
-
-
Define the content-specific parameters:
-
For an AMX Page, click Browse to specify an existing page, or click Create to open the New MAF Page dialog and select the parent folder for your new AMX page.
-
For a Task Flow, click Browse to specify an existing page, or click Create to open the New MAF Task Flow dialog.
-
-
Give your page a descriptive name that will make it easier to identify when working on your mobile application.
-
Click Finish to save the page.
Note:
The images, style sheet, and JavaScript files must reside within the ViewContent folder to enable deployment. See Section 5.4, "What You May Need to Know About Selecting External Resources."5.4 What You May Need to Know About Selecting External Resources
To enable deployment, all resources referenced by the following attributes must be located within the ViewContent folder of the view project.
-
The
iconandimageattributes for<adfmf:feature>(for example,<adfmf:feature id="PROD" name="Products" icon="feature_icon.png" image="springboard.png">). See also, Section 3.4, "Setting Display Properties for an Application Feature." -
The
iconandimageattributes for<adfmf:content>(for example,<adfmf:content id="PROD" icon="feature_icon.png" image="springboard_image.png">). See also Section 5.1, "Introduction to Content Types for an Application Feature." -
The
fileattribute for<adfmf:amx>(for example,<adfmf:amx file="PRODUCT/home.amx" />). See also Section 5.1, "Introduction to Content Types for an Application Feature." -
The
urlattribute for <adfmf: localHTML> (for example,<adfmf:localHTML url="oracle.hello/index.html"/>). See also Section 5.1, "Introduction to Content Types for an Application Feature" and Section 29.6.4.2, "The Custom Login Page." -
The file attribute defined for
type=stylesheetandtype=JavaScriptin<adfmf:includes>(for example,<adfmf:include type="JavaScript" file="myotherfile.js"/>or<adfmf:include type="StyleSheet" file="resources/css/stylesheet.css" id="i3"/>). See also Chapter 7, "Skinning MAF Applications."
MAF does not support resources referenced from another location, meaning that you cannot, for example, enter a value outside of the ViewContent directory using ../ as a prefix.