9 Using Plugins in MAF Applications
This chapter includes the following sections:
9.1 Introduction to Using Plugins in MAF Applications
MAF packages a number of Cordova plugins. A MAF application uses these plugins to interact with the device on which it is deployed. Core plugins are the plugins that MAF provides by default. View these plugins in the MAF Application Editor. Examples include the Email and Contacts plugins that MAF applications use to access email and contact functionality from a device.
View the Cordova versions used by the Android, iOS, and Windows platforms by selecting External Plug-ins in the MAF Application Editor.
Select a plugin in the Core Plugins list, as shown in Figure 9-1, to view a description of the individual plugins. By default, a newly-created MAF application enables only one core plugin (Network Information plugin). You enable these core plugins, as described in Enabling a Core Plugin in Your MAF Application.
Note:
All applications on iOS devices have network access by default. You cannot change this behavior. If an application that is deployed to an Android device does not require network access, disable the Network Information plugin. The Network Information plugin must be enabled to facilitate remote debugging of an application running on an Android emulator or device.
You can register additional plugins if the core plugins that MAF provides by default do not meet the requirements of your MAF application. For more information, see “Introduction to custom Cordova plugin development" at http://blogs.oracle.com/mobile/entry/introduction_to_custom_cordova_plugin and Registering Additional Plugins in Your MAF Application. Once you have either enabled the core plugin or registered any additional plugins for your MAF application, you create content in an application feature that accesses the functionality of the plugin. For more information, see Using a Plugin in a MAF Application.
The deployment of a MAF application may fail, after the registration of additional plugins, for the following reasons:
-
Filename conflicts between plugins that your MAF application uses.
-
The additional plugins that were registered require dependent plugins for proper functioning.
For more information, see Deploying Plugins with Your MAF Application Deploying Plugins with Your MAF Application.
If you want to migrate a MAF application created with an earlier release of MAF, you need to register any plugins your application uses in the MAF Application Editor. For more information, refer to "Migrating Plugins from Earlier Releases." section in .
Figure 9-1 Plugins in the MAF Application Editor
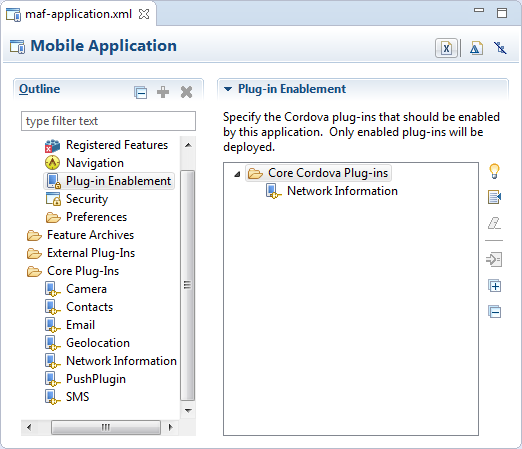
9.2 Enabling a Core Plugin in Your MAF Application
By default, newly-created MAF applications enables only one core plugin (Network Information plugin). Enable or disable additional core plugins so that your MAF application can access the associated device functionality.
9.2.1 How to Enable a Core Plugin in Your MAF Application
You enable a core plugin using the MAF Application Editor.
To enable a core plugin in your MAF application:
9.2.2 What Happens When You Enable a Core Plugin in Your MAF Application
Once you enable a core plugin in the MAF Application Editor the plugin is listed in Plugin Enablement in the editor. You can see which features in the application use the selected plugin in the Registered Features Declaring Usage in the Plugin Enablement area. The example below shows the entries for a MAF application where the Email and Network Information plugins have been enabled. Enabling these plugins is a prerequisite to your MAF application using the device's email client and accessing the internet.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<maf-plugins xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf">
<cordova-plugins>
<core-cordova-plugin id="c1" pluginId="cordova-plugin-network-information"/>
<core-cordova-plugin id="c2" pluginId="com.oracle.maf.email"/>
</cordova-plugins>
</maf-plugins>
9.3 Registering Additional Plugins in Your MAF Application
Register additional plugins in your MAF application when you require functionality in your MAF application not provided by the core plugins that MAF delivers.
9.3.1 How to Register an Additional Plugin
You use the MAF Application Editor to register the additional plugin you want your MAF application to use.
Before you begin, ensure that the application, and the plugin to be registered with the application, are stored on the same drive. If, for example, you store your application on the C: drive in a Windows environment, you must also store the plugin that you want to register with the application on the C: drive. This ensures that OEPE, using a relative path, successfully registers the plugin with your application.
To register an additional plugin for a MAF application:
9.3.2 What Happens When You Register an External Plugin for Your MAF Application
Once you select the source files for the plugin you want your MAF application to use, OEPE edits the application's maf-plugins.xml file with entries that identify the enabled plugins in your MAF application. The example below shows the entries in a maf-plugins.xml file where the Globalization plugin shown in Figure 9-2 has been registered with the MAF application.
Figure 9-2 Additional Plugin in the MAF Application Editor
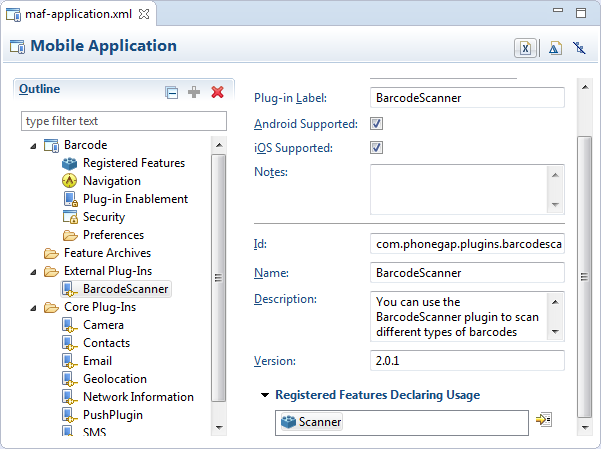
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<maf-plugins xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf">
<cordova-plugins>
<core-cordova-plugin id="c1" pluginId="cordova-plugin-network-information"/>
<cordova-plugin id="c2" pluginId="cordova-plugin-globalization"
path="../../../../CordovaPlugins/cordova-plugin-globalization/">
<platform id="p1" name="android" enabled="true"/>
<platform id="p2" name="ios" enabled="true"/>
<platform id="p3" name="windows" enabled="true"/>
</cordova-plugin>
</cordova-plugins>
</maf-plugins>
9.4 Deploying Plugins with Your MAF Application
The deployment of a plugin with your MAF application depends on the chosen method of deployment.
Deployment to a FAR
A deployment to a FAR includes a copy of the maf-plugins.xml file of the application named jar-maf-plugins.xml. It is identical to the maf-plugins.xml file of the application with the exception that the path attribute value of each plugin is an empty string. A FAR deployment does not include the source files for the plugin.
Deployment to a Mobile Application Archive File
A deployment to a Mobile Application Archive File includes a copy of the maf-plugins.xml file of the application with all path attributes set to an empty string.
Deployment Using an Android, iOS, or Windows Deployment Configuration
During deployments using an Android, iOS or Windows deployment configuration, OEPE invokes tools that build and deploy the application. These tools, in turn, invoke the Cordova plugman tool to install the configured plugins from their source location to the deployment folder.
Resolving Naming Conflicts Between Plugins
Deployment can fail due to naming conflicts if more than one plugin used by your MAF application contains resource files with the same name. For example, deployment fails if a MAF application uses two plugins that both have a resource file name arrays.xml.
To resolve these naming conflicts, rename the resource file in the plugin that conflicts with the resource file name in the other plugin. Update the reference to the resource file in the plugin.xml file of the first plugin. In our example, this requires you to rename the array.xml resource file name of the first plugin to pluginone_arrays.xml and edit the plugin.xml file of the plugin as follows:
<source-file src="src/android/LibraryProject/res/values/pluginone_arrays.xml"
target-dir="res/values"/>
Adding Missing Dependent Plugins
Deployment can fail if an additional plugin that your MAF application uses does not locate the plugins that it requires (dependent plugins). This scenario can arise if you work behind a firewall. At deployment time, OEPE invokes the tools of Apache Cordova to manage plugins dependencies. These tools may fail to download dependent plugins if their proxy settings are not configured to allow the download of dependent plugins. To work around this scenario, download the missing dependent plugin, and add it to your MAF application. You add the missing dependent plugin the same way as other plugins that you want to add to your MAF application. For more information, see Registering Additional Plugins in Your MAF Application. After you add the dependent plugin, make sure that it appears before the plugin that requires it in the maf-plugins.xml file, as demonstrated in the example below.
<maf-plugins xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf">
<cordova-plugins>
....
<cordova-plugin id="c2" pluginId="com.example.dependent.dependentPlugin"
path="../../../../../plugins/Dependent-Plugin-Required-By-PluginWithID_c3/">
...
<cordova-plugin id="c3" pluginId="com.example.plugin"
path="../../../../../plugins/AdditionalPlugin/">
...
</cordova-plugins>
</maf-plugins>
9.5 Importing Plugins from a Feature Archive File
When you import a FAR that contains a jar-maf-plugins.xml file to your application, the content in the jar-maf-plugins.xml file merges with the maf-plugins.xml file of the consuming application. OEPE logs information about the merge to its Messages window.
If the plugin to import from the FAR already exists in the maf-plugins.xml file of the consumer application, OEPE logs a message that the plugin exists in the application, and will not be merged.
If the plugin to import from the FAR does not exist in the maf-plugins.xml file of the consumer application, OEPE adds the plugin to the maf-plugins.xml file of the application. In this scenario, you need to set the path to the newly-imported plugin, as described in Registering Additional Plugins in Your MAF Application.
9.6 Using a Plugin in a MAF Application
Once you register a plugin or enable a core plugin in your MAF application, you can create content in the MAF application that uses the plugin.
See "Integrating a custom Cordova plugin into a MAF app" at http://blogs.oracle.com/mobile/entry/integrating_a_custom_cordova_plugin for information about how you can invoke a plugin from Java, from a MAF AMX page, and from local HTML.
The BarcodeDemo sample application also demonstrates how you can accomplish this task.
Figure 9-3 Platform-Specific Content To Access a Plugin
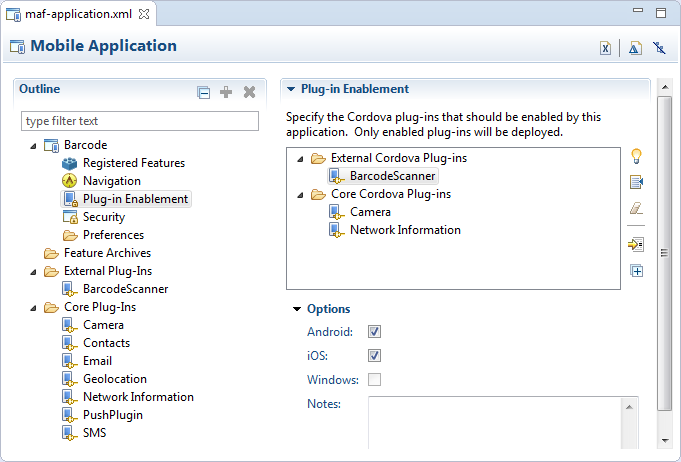
Figure 9-3 shows a button (Scan) in the MAF AMX page that the BarcodeDemo sample application renders on the end user's device at runtime. This button invokes a managed bean method and the managed bean method invokes a JavaScript function that calls the BarcodeScanner plugin.
Figure 9-4 Command Button Invoking Managed Bean Method to Access Plugin
The example below shows a number of code extracts from the BarcodeDemo sample application.
Other sample applications, apart from the BarcodeDemo sample application, that demonstrate how to use additional plugins in MAF applications are BeaconDemo, and DatePicker. For information about how to access and use these sample applications, see MAF Sample Applications.
<!-- The following code snippet from the scanner.amx file shows how the Scan button invokes the scanBarcode method in the managed bean -->
<amx:commandButton text="Scan" id="cl2" actionListener="#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.scanBarcode}"/>
<!-- The following code snippet from the BarcodeBean.java file shows how the scanBarcode managed bean method invokes a JavaScript function -->
public void scanBarcode (ActionEvent event)
{
// Invokes a JavaScript function named “scanBarcodeFromJavaBean"
AdfmfContainerUtilities.invokeContainerJavaScriptFunction(AdfmfJavaUtilities.getFeatureId(),
"scanBarcodeFromJavaBean",
new Object[] { });
}
<!-- The following code snippet from the scanner.js file shows how the JavaScript function accesses the barcode scanner and sets the resulting value in a managed bean field.-->
function scanBarcodeFromJavaBean(options)
{
cordova.plugins.barcodeScanner.scan(
function(result)
function onSuccess(result) {
adf.mf.api.setValue( { "name": "#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.barcodeError}",
"value": ""},
function() {},
function() {});
adf.mf.api.setValue( { "name": "#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.barcodeResult}",
"value": result.text},
function() {},
function() {});
adf.mf.api.setValue( { "name": "#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.barcodeFormat}",
"value": result.format},
function() {},
function() {});
adf.mf.api.setValue( { "name": "#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.barcodeCancelled}",
"value": result.cancelled == 1 ? "Yes" : "No"},
function() {},
function() {});
}
function onError(error) {
adf.mf.api.setValue( { "name": "#{viewScope.BarcodeBean.barcodeError}",
"value": "ERROR: " + error.text},
function() {},
function() {});
}
// Callable externally
scanBarcodeFromJavaBean = function() {
cordova.plugins.barcodeScanner.scan(onSuccess, onError);
}