12 Using Lifecycle Listeners in MAF Applications
This chapter includes the following sections:
12.1 Introduction to Lifecycle Listeners in MAF Applications
Lifecycle listeners contain code that runs in response to specific application events. Review the information about the interfaces to be implemented for communication with event notifications, and how they can create lifecycle listeners.
Lifecycle listeners are useful locations to write code that executes in response to specific events in your application. MAF provides lifecycle listeners where you can write code in response to application or application feature events. A typical implementation of an application lifecycle listener method may be to write code that initializes the database of the application when the application starts, as described in Using the Local SQLite Database, or to update a security configuration from URL parameters, as described in How to Update Connection Attributes of a Named Connection at Runtime.
MAF provides the following two interfaces that you can implement to communicate with event notifications:
-
oracle.adfmf.application.LifeCycleListenerThis interface specifies the following methods that an application lifecycle listener must implement:
-
activate() -
deactivate() -
start() -
stop()
-
-
oracle.adfmf.feature.LifeCycleListenerThis interface specifies the following methods that a feature lifecycle listener must implement:
-
activate() -
deactivate()
-
You create a lifecycle listener by creating a Java class that implements the appropriate interface and registering the implementation in your MAF application, as described in Registering a Lifecycle Listener for a MAF Application or an Application Feature.
A new MAF application that you create implements the oracle.adfmf.application.LifeCycleListener interface through the default creation of the application.LifeCycleListenerImpl.java class in the ApplicationController project in the application , as shown in Figure 12-1.
Figure 12-1 Implementation of Application Lifecycle Listener
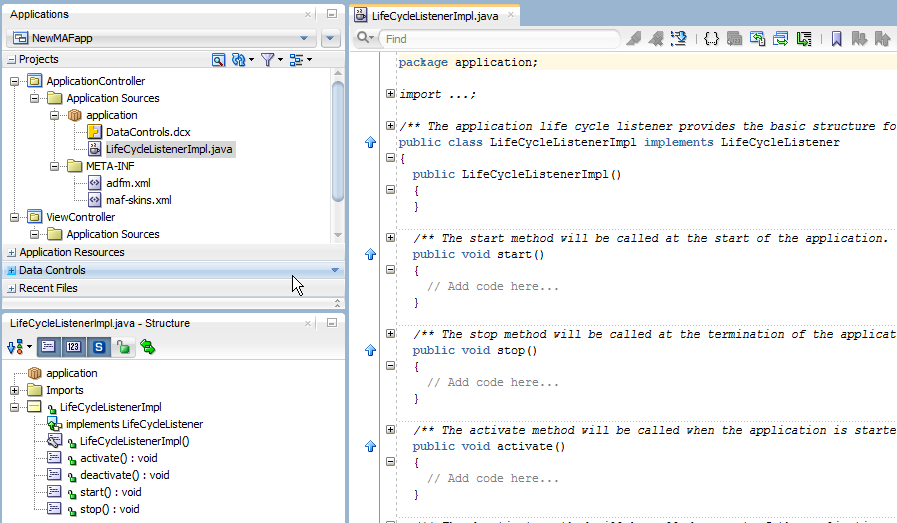
Note that the application lifecycle listener is executed with an anonymous user (that is, there is no user associated with any of its methods and no secure web service is called).
Table 12-1 describes the specific times that MAF invokes application lifecycle methods during an application startup, shutdown, and hibernation.
Table 12-1 Timing of the MAF Invocation of Application Lifecycle Methods
| Method | Timing | When Called | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Called after the MAF application has completely loaded the application features and immediately before presenting the user with the initial application feature or the springboard. This is a blocking call. |
When the application process starts. |
Uses include:
|
|
|
Called as the MAF application begins its shutdown. |
When the application process terminates. |
Uses include:
|
|
|
Called as the MAF application activates from being situated in the background (hibernating). This is a blocking call. |
After the |
Uses include:
|
|
|
Called as the MAF application deactivates and moves into the background (hibernating). This is a blocking call. |
Before the |
Uses include:
|
Table 12-2 describes the specific times that MAF invokes feature lifecycle methods during a feature activation and deactivation.
Note:
MAF also provides another interface (oracle.maf.api.feature.FeatureLifeCycleListener) that extends oracle.adfmf.feature.LifeCycleListener and provides additional methods to write code before and after your restart an application feature, as described in Restarting an Application Feature in a MAF Application.Table 12-2 Timing of the MAF Invocation of Feature Lifecycle Methods
| Method | Timing | When Called | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Called before the current application feature is activated. |
Called when a user selects the application feature for the first time after launching a MAF application, or when the application has been re-selected (that is, brought back to the foreground). |
Uses include:
|
|
|
Called before the next application feature is activated, or before the application feature exits. |
Called when the user selects another application feature. |
You can, for example, use the |
For more information about the oracle.adfmf.application.LifeCycleListener, oracle.adfmf.feature.LifeCycleListener, and oracle.maf.api.feature.FeatureLifeCycleListener interfaces, see Java API Reference for Oracle Mobile Application Framework.
The LifecycleEvents sample application demonstrates declaring listener classes that implement both the application and feature interfaces. It registers these listener classes in the maf-application.xml of the MAF application and maf-feature.xml files. For more information about this and other sample applications, see MAF Sample Applications.
12.2 Registering a Lifecycle Listener for a MAF Application or an Application Feature
Use the procedure to register an application lifecycle listener using the overview editor for the mafapplication.xml file, and register a feature lifecycle listener using the overview editor for the maf-features.xml file.
You register an application lifecycle listener by using the overview editor for the maf-application.xml file and a feature lifecycle listener using the overview editor for the maf-features.xml file.
To register an application lifecycle listener:
-
In the Applications window, expand the Application Resources panel.
-
In the Application Resources panel, expand Descriptors and then ADF META-INF.
-
Double-click maf-application.xml.
-
In the Application navigation tab, specify the Java class that implements the
oracle.adfmf.application.LifeCycleListenerinterface in the Lifecycle Event Listener field. By default, this is set toapplication.LifeCycleListenerImpl.If you want to package the application lifecycle listener in a JAR library that will be distributed for use elsewhere, you might use a custom class different from the default implementation provided by MAF.
To register an application feature lifecycle listener:
- In the Applications window, expand the ViewController project, Application Sources, and then META-INF.
- Double-click the
maf-feature.xmlfile. - In the Features list, select the feature for which you want to register a feature lifecycle listener.
- In the Lifecycle Event Listener field, specify the Java class that implements the
oracle.adfmf.feature.LifeCycleListenerinterface.
12.3 What Happens When You Register a Lifecycle Listener
The application.LifeCycleListenerImpl.java class in the ApplicationController project, which is registered by the listener-class attribute in the maf-application.xml file, implements the lifecycle listener.
By default, a MAF application that you create implements an application lifecycle listener through the creation of the application.LifeCycleListenerImpl.java class in your application's ApplicationController project. The listener-class attribute in the maf-application.xml file registers this class, as shown in the following example.
<adfmf:application xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:adfmf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf"
version="1.0" name="NewMAFapp" id="com.company.NewMAFapp"
appControllerFolder="ApplicationController" listener-class="application.LifeCycleListenerImpl">
...
</adfmf:application>
JDeveloper writes an entry to the maf-feature.xml file for the listener-class attribute when you register a feature lifecycle listener. The following example shows an entry in the LifecycleEvents sample application described in MAF Sample Applications.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<adfmf:features xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:adfmf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf">
<adfmf:feature id="Feature1" name="Feature1" listener-class="mobile.Feature1Handler">
<adfmf:description>This is a sample feature to show the feature lifecycle handlers.
</adfmf:description>
<adfmf:content id="Feature1.1">
<adfmf:amx file="Feature1/feature1.amx"/>
</adfmf:content>
</adfmf:feature>
...
</adfmf:features>