Observação:
- Este tutorial requer acesso ao Oracle Cloud. Para se inscrever e obter uma conta gratuita, consulte Conceitos Básicos do Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- Ele usa valores de exemplo para credenciais, tenancy e compartimentos do Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Ao concluir seu laboratório, substitua esses valores por valores específicos do seu ambiente de nuvem.
Execute suas análises no OCI Data Flow usando o notebook interativo OCI Data Science
Introdução
O Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Data Flow é um serviço de big data totalmente gerenciado que permite executar aplicativos Apache Spark em qualquer escala sem praticamente nenhuma administração. O Spark se tornou a principal estrutura de processamento de big data e o OCI Data Flow é a maneira mais fácil de executar o Spark no Oracle Cloud porque não há nada para que os desenvolvedores instalem ou gerenciem.
Objetivo
O objetivo deste tutorial é orientá-lo pela configuração necessária para acessar as sessões do OCI Data Flow por meio da sessão de notebook OCI Data Science. Essas sessões permitem que você execute cargas de trabalho interativas do Spark em um cluster de Fluxo de Dados duradouro por meio de uma integração do Apache Livy.
Além disso, depois que a sessão do OCI Data Flow Spark for criada, passaremos por algum código de amostra para executar operações do Spark no OCI Object Storage e no Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse.
Tarefa 1: Configurar o notebook OCI Data Science com o OCI Data Flow
Criar e configurar o ambiente Conda do OCI Data Flow
-
Crie buckets obrigatórios.
a. Crie um bucket chamado dataflow-logs em sua tenancy.
b. Crie um bucket chamado dataflow-warehouse em sua tenancy.
-
Crie um grupo dinâmico em um compartimento específico.
ALL {resource.type='dataflowrun', resource.compartment.id='<compartment_id>'} ALL {resource.type='datasciencenotebooksession', resource.compartment.id='<compartment_id>'} Any {resource.type = 'datacatalogmetastore'} -
Crie uma política para gerenciar recursos do OCI do OCI Data Flow e do OCI Data Science.
-
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP <df-dynamic-group> TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ANY {target.bucket.name='<bucket_name>',target.bucket.name ='dataflow-logs,target.bucket.name='dataflow-warehouse'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<ds-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE dataflow-family in compartment '<your-compartment-name>' -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<df-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE data-catalog-metastores IN TENANCY -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<dcat-hive-group>' TO READ buckets IN TENANCY -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<dcat-hive-group>' TO MANAGE object-family IN TENANCY WHERE ANY { target.bucket.name = '<bucket_name>',target.bucket.name = '<managed-table-location-bucket>',target.bucket.name = '<external-table-location-bucket>'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<ds-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ALL {target.bucket.name='ds-conda-env'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<df-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ALL {target.bucket.name='ds-conda-env'}
-
-
Crie projeto e sessão do OCI Data Science.
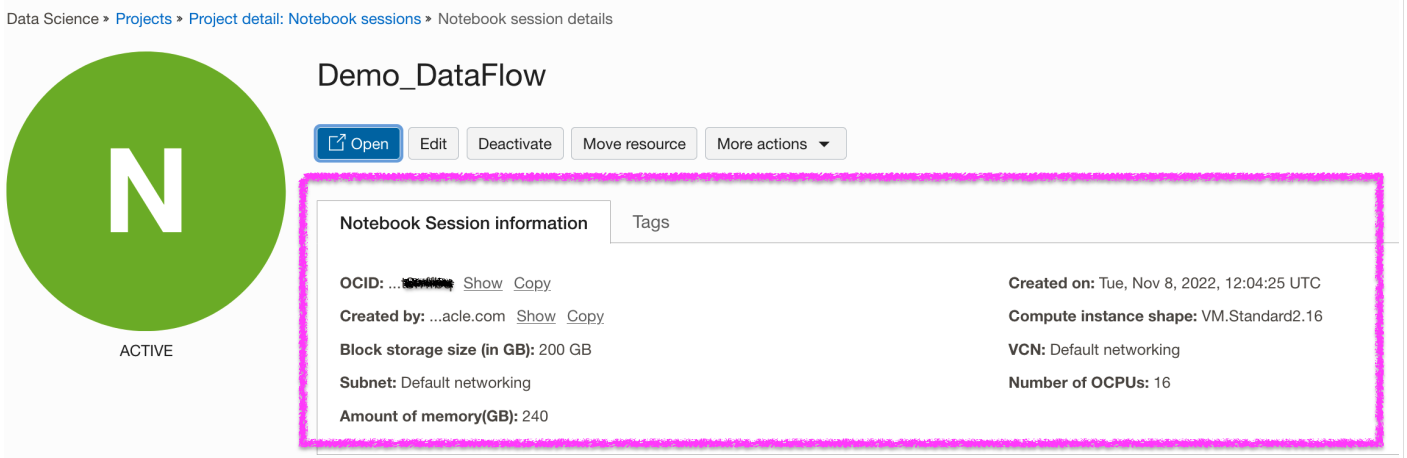
-
Abra uma nova sessão do OCI Data Science. No menu Arquivo, selecione Novo Acionador e clique em Terminal.
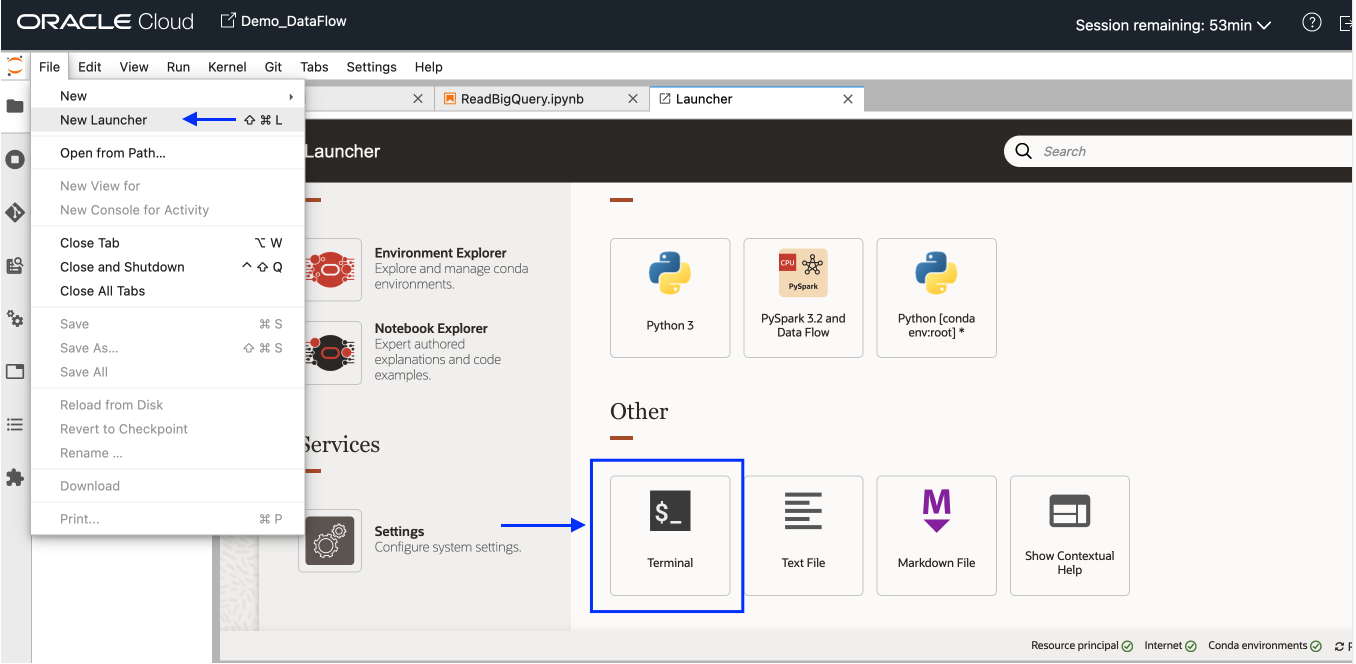
-
Instale e ative o ambiente Conda
pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1no seu terminal.odsc conda install -s pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1 source activate /home/datascience/conda/pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1 -
Depois que o Conda for ativado, vá para a guia Novo Iniciador e clique em Definições. Digite as informações necessárias sobre o armazenamento de objetos no qual o pacote Conda será submetido a upload e salvo.

-
Publicar ambiente Conda.
odsc conda publish -s pyspark3_2anddataflowv1_0Observação: a publicação levará algum tempo. Uma vez concluído, você poderá observar que o pacote Conda foi submetido a upload no bucket do Object Storage.
Configurar e criar sessão do OCI Data Flow Spark usando o Livy Service
Abra o Notebook usando "PySpark e DataFlow" como kernel do novo Launcher e execute os seguintes comandos para configurar e criar a sessão do OCI Data Flow Spark usando o Livy Service:
-
Configurar Autenticação usando o ADS.
import adsads.set_auth("resource_principal") # Supported values: resource_principal, api_key -
Carregar Extensão.
%load_ext dataflow.magics -
Crie a sessão do OCI Data Flow Spark usando o serviço Livy por meio do notebook OCI Data Science.
import json command = { "compartmentId": "ocid1.compartment.oc1..xxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "displayName": "Demo_DataFlow_Spark_v1", "sparkVersion": "3.2.1", "driverShape": "VM.Standard.E3.Flex", "executorShape": "VM.Standard.E3.Flex", "driverShapeConfig":{"ocpus":1,"memoryInGBs":16}, "executorShapeConfig":{"ocpus":1,"memoryInGBs":16}, "numExecutors": 1, "logsBucketUri": "<oci://bucket@namespace/>", "archiveUri": "<oci://bucket@namespace/archive.zip>" "configuration":{"spark.archives":"<oci://bucket@namespace/>#conda", "spark.oracle.datasource.enabled":"true"} } command = f'\'{json.dumps(command)}\'' print("command",command) #"configuration":{ # "spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"true", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.shuffleTracking.enabled":"true", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors":"1", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors":"4", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.executorIdleTimeout":"60", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.schedulerBacklogTimeout":"60", # "spark.dataflow.dynamicAllocation.quotaPolicy":"min" }}' %create_session -l python -c $command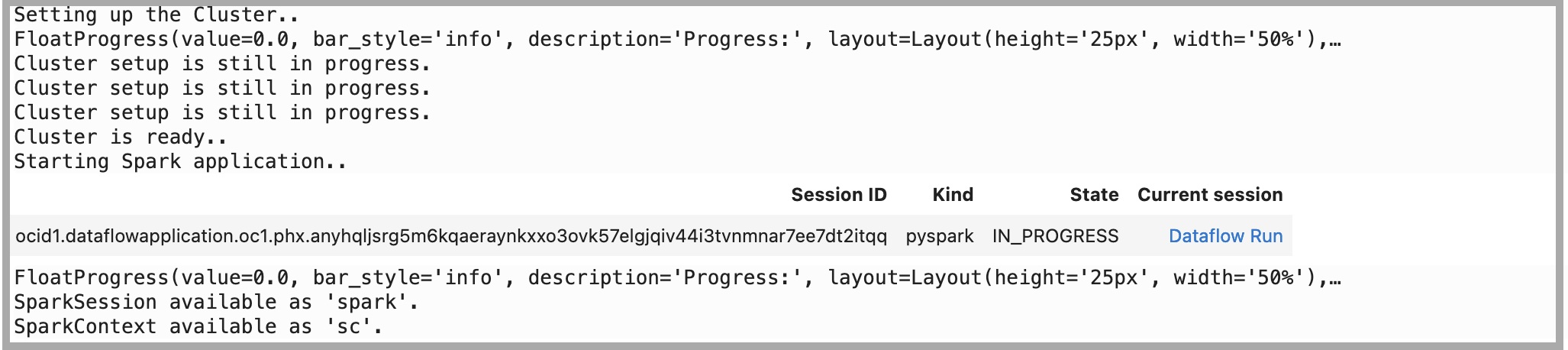
Tarefa 2: Executar operações do Spark no OCI Object Storage usando o código de amostra
-
Importe bibliotecas dependentes na sessão.
%%spark #Import required libraries. import json import os import sys import datetime import oci import pyspark.sql from pyspark.sql.functions import countDistinct from delta.tables import * -
Execute a operação de Leitura do Spark no Object Storage. Leia o arquivo do Object Storage usando
spark.readda Sessão Livy.%%spark -o df_Bronze_Insurance_Data #Read Claim Insurance files from OCI Object Storage in Spark Dataframe. df_Bronze_Insurance_Data = spark.read.format("csv").option("header", "true") \ .option("multiLine", "true").load("oci://test-demo@OSNamespace/insur_claim/claim.csv*") print("df_RawZone_Data",df_Bronze_Insurance_Data) df_Bronze_Insurance_Data.show(5) -
Execute a operação de Gravação do Spark no Object Storage.
%%spark df_Bronze_Insurance_Data.write.format("json").option("mode","overwrite").save("oci://test-demo@OSNamespace/insur_claim/claim_curated")
Tarefa 3: Executar operações de Leitura e Gravação no Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse usando o código de amostra
-
Carregue dados no Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse usando o Vault Secreto para Wallet. Copie o código a seguir como está. Para obter mais informações, consulte: amostra GitHub.
%%spark def get_authenticated_client(token_path, client, file_location=None, profile_name=None): """ Get an an authenticated OCI client. Example: get_authenticated_client(token_path, oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient) """ import oci if not in_dataflow(): # We are running locally, use our API Key. if file_location is None: file_location = oci.config.DEFAULT_LOCATION if profile_name is None: profile_name = oci.config.DEFAULT_PROFILE config = oci.config.from_file(file_location=file_location, profile_name=profile_name) authenticated_client = client(config) else: # We are running in Data Flow, use our Delegation Token. with open(token_path) as fd: delegation_token = fd.read() signer = oci.auth.signers.InstancePrincipalsDelegationTokenSigner( delegation_token=delegation_token ) authenticated_client = client(config={}, signer=signer) return authenticated_client def get_password_from_secrets(token_path, password_ocid): """ Get a password from the OCI Secrets Service. """ import base64 import oci secrets_client = get_authenticated_client(token_path, oci.secrets.SecretsClient) response = secrets_client.get_secret_bundle(password_ocid) base64_secret_content = response.data.secret_bundle_content.content base64_secret_bytes = base64_secret_content.encode("ascii") base64_message_bytes = base64.b64decode(base64_secret_bytes) secret_content = base64_message_bytes.decode("ascii") return secret_content def get_delegation_token_path(spark): """ Get the delegation token path when we're running in Data Flow. """ if not in_dataflow(): return None token_key = "spark.hadoop.fs.oci.client.auth.delegationTokenPath" token_path = spark.sparkContext.getConf().get(token_key) if not token_path: raise Exception(f"{token_key} is not set") return token_path def get_temporary_directory(): if in_dataflow(): return "/opt/spark/work-dir/" else: import tempfile return tempfile.gettempdir() def in_dataflow(): """ Determine if we are running in OCI Data Flow by checking the environment. """ if os.environ.get("HOME") == "/home/dataflow": return True return False def download_wallet(spark, wallet_path): """ Download an Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse/ATP wallet file and prepare it for use in a Data Flow application. """ import oci import zipfile # Get an object store client. token_path = get_delegation_token_path(spark) object_store_client = get_authenticated_client( token_path, oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient ) # Download the wallet file. from urllib.parse import urlparse parsed = urlparse(wallet_path) bucket_name, namespace = parsed.netloc.split("@") file_name = parsed.path[1:] response = object_store_client.get_object(namespace, bucket_name, file_name) temporary_directory = get_temporary_directory() zip_file_path = os.path.join(temporary_directory, "wallet.zip") with open(zip_file_path, "wb") as fd: for chunk in response.data.raw.stream(1024 * 1024, decode_content=False): fd.write(chunk) # Extract everything locally. with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_file_path, "r") as zip_ref: zip_ref.extractall(temporary_directory) # Distribute all wallet files. contents = "cwallet.sso ewallet.p12 keystore.jks ojdbc.properties sqlnet.ora tnsnames.ora truststore.jks".split() spark_context = spark.sparkContext for file in contents: spark_context.addFile(os.path.join(temporary_directory, file)) return temporary_directory -
Defina os seguintes parâmetros relacionados à Instância e à Wallet do Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse.
%%spark PASSWORD_SECRET_OCID = "ocid1.vaultsecret.oc1.phx.xxxxxxx" TARGET_TABLE = "ADMIN.TB_NAME" TNSNAME = "demolakehouseadw_medium" USER = "admin" WALLET_PATH = "oci://bucketname@osnamespace/Wallet_DemoLakeHouseADW.zip" # Download and distribute our wallet file. wallet_path = download_wallet(spark, WALLET_PATH) adw_url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@{}?TNS_ADMIN={}".format(TNSNAME, wallet_path) -
Obtenha a senha usando o serviço secreto.
%%spark # Get our password using the secret service. print("Getting wallet password") token_path = get_delegation_token_path(spark) password = get_password_from_secrets(token_path, PASSWORD_SECRET_OCID) print("Done getting wallet password") # Save the results to the database. print("Saving processed data to " + adw_url) properties = { "driver": "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver", "oracle.net.tns_admin": TNSNAME, "password": password, "user": USER } -
Leia a tabela de amostra do Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse.
%%spark SOURCE_TABLE = "ADMIN.RETAILPOS" df_RetailPOS_15min = spark.read.jdbc(url=adw_url, table=SOURCE_TABLE, properties=properties) -
Carregue o Dataframe acima no Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse.
%%spark #Load into Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse: TARGET_TABLE = "ADMIN.RETAILPOS_15MINUTES" print("TARGET_TABLE : ",TARGET_TABLE) # Write to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse. print("Write to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse : ") df_RetailPOS_15min.write.jdbc(url=adw_url, table=TARGET_TABLE, mode="Append", properties=properties) print("Writing done to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse : ")
Próximas Etapas
-
Com o OCI Data Flow, você pode configurar notebooks do OCI Data Science para executar aplicativos interativamente no serviço Data Flow. Assista ao vídeo tutorial sobre como usar o Data Science com o Data Flow Studio.
-
Consulte também a documentação do SDK do Oracle Accelerated Data Science para obter mais informações sobre a integração do serviço Data Science e Data Flow.
-
Mais exemplos estão disponíveis em GitHub com amostras do serviço Data Flow e amostras do serviço Data Science.
-
Para começar hoje mesmo, inscreva-se na Avaliação Grátis do Oracle Cloud ou acesse sua conta para experimentar o OCI Data Flow. Experimente o tutorial sem necessidade de instalação de 15 minutos do Data Flow para ver a facilidade do processamento Spark com o Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Links relacionados
Aquisições
Autor - Kumar Chandragupta (OCI Sr. Cloud Engineer)
Mais Recursos de Aprendizagem
Explore outros laboratórios no site docs.oracle.com/learn ou acesse mais conteúdo de aprendizado gratuito no canal YouTube do Oracle Learning. Além disso, visite education.oracle.com/learning-explorer para se tornar um Oracle Learning Explorer.
Para obter a documentação do produto, visite o Oracle Help Center.
Perform your analytics on OCI Data Flow using OCI Data Science interactive notebook
F79466-01
March 2023
Copyright © 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.