Release 2 (9.0.2)
Part Number A92171-02
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle9i Application Server Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.0.2) Part Number A92171-02 |
|
This chapter introduces the Oracle9i Application Server administration tools.
It contains the following topics:
This chapter introduces the tools you can use to manage your Oracle9iAS environment. The primary tool for managing Oracle9iAS--as well as your entire Oracle environment--is Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Many Oracle users are familiar with the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, which is designed to reduce the complexity of managing your Oracle Database Server as well as the network components, software, and hardware that support your Oracle environment.
With Oracle9iAS Release 2, Oracle introduces the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site, which is designed specifically to help you manage Oracle9i Application Server.
Together, the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site provide a complete set of efficient tools to reduce the cost and complexity of managing your enterprise.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site provides Web-based management tools designed specifically for Oracle9iAS. Using the Web site, you can monitor and configure the components of your Oracle9i Application Server installations. You can deploy applications, manage security, and create and manage Oracle9i Application Server clusters.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site consists of:
These Web pages provide you with a high-level view of your Oracle9i Application Server environment. For more information, see "Introducing the Enterprise Manager Home Pages" on page 3-3.
These technologies automatically perform many management tasks. For example, they discover the components of each application server instance, gather and process performance data, and provide access to application configuration information. For more information, see "About the Underlying Technologies" on page 3-17.
Oracle9iAS provides a wide variety of software solutions designed to help you run all aspects of your business. As a result, you will want to manage Oracle9iAS from different levels of detail. At times, you may want to manage a set of application server instances to compare their performance; or, you may find it efficient to combine multiple instances into an Oracle9iAS cluster.
At other times, you will want to manage an individual application server instance or a specific component--or even a specific Web application used to run your business or support your customers.
Further, different administrators may specialize in managing specific aspects of your Oracle9iAS environment. One administrator may monitor your J2EE application deployments. Another may be responsible for managing your implementation of Oracle9iAS Portal.
To support these multiple levels of management, Oracle introduces the Oracle Enterprise Manager Home Pages. Each Home Page provides the information you need to monitor the performance and availability of Oracle9iAS from a particular level of management detail. Selected Home Pages also provide tools for configuring your Oracle9iAS components.
From each Home Page, you can obtain high-level information or you can drill down to get more specific information about an instance, component, or application.
Consider the following Home Pages that are available when you use the Oracle Enterprise Manager:
To view the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site, click Log on to Oracle Enterprise Manager on the Oracle9iAS Welcome page.
You can access the Welcome Page by pointing your browser to the HTTP Server URL for your installation. For example, the default HTTP Server URL is:
http://hostname:7777
You can also go directly to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site using the following instructions:
http://hostnanme:<port_number>/
For example, if you installed Oracle9i Application Server on a host called SYS12, you would enter the following address in your Web browser:
http://SYS12:1810
|
Note: Experienced administrators can modify the default port, but in most cases, the port specified for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site is 1810. |
The username for the administrator user is ias_admin. The password is defined during the installation of Oracle9iAS.
Depending upon the components you configured and the choices you made during the Oracle9iAS installation, Enterprise Manager displays the appropriate Home Page.
The initial Home Page varies depending upon whether or not you installed an Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. For more information about the options available when installing Oracle9iAS, see the Oracle9i Application Server Installation Guide.
Table 3-1 describes the Enterprise Manager Home Pages that might be used as a starting point when you first browse to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site.
| Enterprise Manager Home Page | Description |
|---|---|
|
Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page |
Use this Home Page to monitor and configure a single application server instance. For more information, see "Using the Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page" on page 3-5. The Instance Home Page is the first page you see if you have installed a single application server instance that is not associated with an Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. |
|
Oracle9iAS Farm Home Page |
Use this Home Page to view a list of all the application server instances associated with a particular Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. For more information, see "Using the Oracle9iAS Farm Home Page" on page 3-7. The Farm Home Page is the first page you see if you have installed one or more application server instances that are associated with a common Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. The Farm Home Page is also the first page you see when you view the Web site on a host where the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure has been installed. |
|
Application Servers Home Page |
Use this page to view a list of the application server instances installed on the current host. Click the name of an instance to drill down and display the Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page, or--if the instance you select is associated with an Oracle9iAS Infrastructure--click Farm to display the Oracle9iAS Farm Home Page. This is the first Home Page you see if you have installed more than one application server instance on the host and one or more of the instances are not associated with an infrastructure. |
From the Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page (Figure 3-1), you can start and stop the application server instance, monitor the overall performance of the server, and review the components of the server. You can also drill down and examine the performance of a particular component and configure the component.
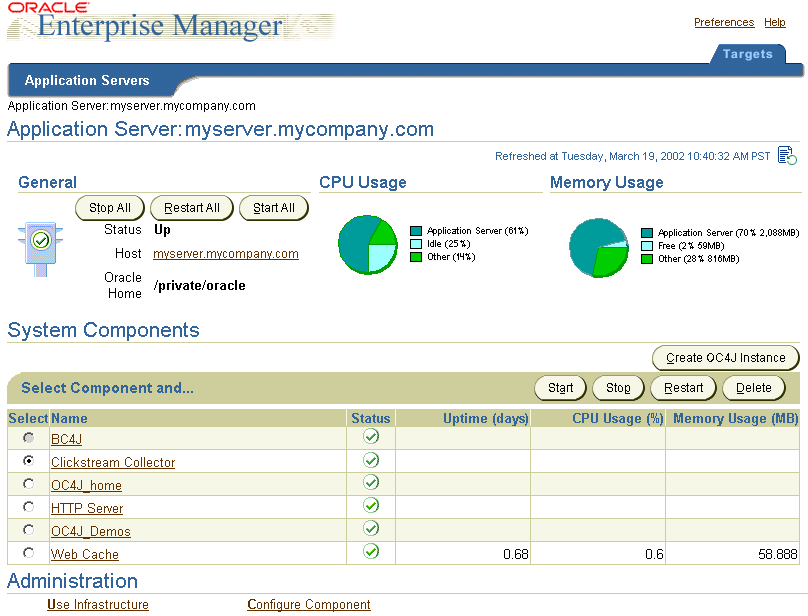
If you scroll down the page, the Home Page provides a table that lists the components of the application server. From this table, you can also get a snapshot of how each individual component is performing.
From the System Components table, you can display a Home Page for each component of the application server.
Depending upon the options you have installed, the Administration section of the Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page provides additional features that allow you to perform the following tasks:
For more information, click Help at the top of the Oracle9iAS Instance Home Page.
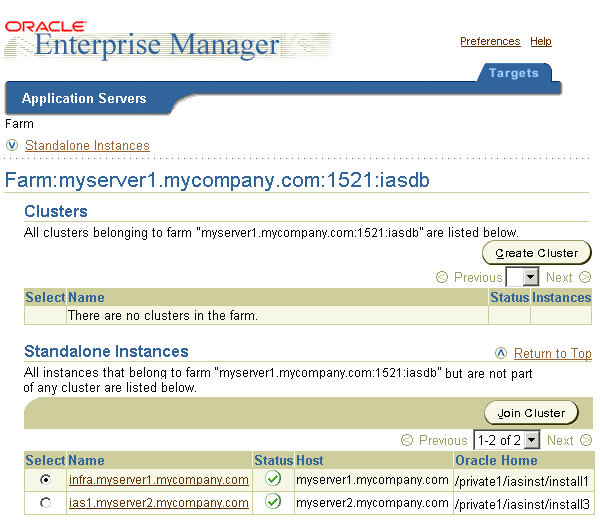
If your application server instance is associated with an Oracle9iAS Infrastructure, your start page for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site is the Oracle9iAS Farm Home Page (Figure 3-2).
For more information about installing the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure, see the Oracle9i Application Server Installation Guide.
The Farm Home Page displays a list of the standalone application server instances and Oracle9iAS clusters associated with your Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. Standalone instances are application server instances that are not part of an Oracle9iAS cluster.
Using the Farm Home Page, you can perform the following tasks:
Chapter 14, "Application Server Clustering" for more information about Oracle9iAS clusters
See Also:
Oracle9iAS component Home Pages vary from one component to another. That is because each component has different monitoring and configuration requirements. However, most of the component Home Pages has the following common elements:
For more information about monitoring Oracle9iAS components, see Chapter 9, "Monitoring HTTP Server, OC4J, and Web Cache". For information about configuring Oracle9iAS components, see Chapter 6, "Configuring HTTP Server, OC4J, and Web Cache".
At any time while using the Enterprise Manager Web site, you can click Help at the top of the page to get more information. In most cases, the Help window displays a help topic about the current page. Click Help Contents in the Help window to browse the list of help of topics or to search for a particular word or phrase.
To use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Home Pages, you must start the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site. The Web site is automatically started after you install the application server. You must start it manually after each system reboot, or create a script to automatically start it during system boot.
The following sections describe how to:
Before you start the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site, you must be sure that the X Server software on your UNIX system is properly configured. Specifically, you must define the DISPLAY environment variable. This variable is required for the X Server software.
In most cases, the X Server software will be configured properly, but if you need to set the DISPLAY variable, use the following instructions:
If you are using ksh or sh, issue the following commands:
$ DISPLAY=hostname:0.0; export DISPLAY
If you are using csh or tcsh, issue the following commands:
% setenv DISPLAY hostname:0.0
In the examples, replace hostname with the name of a valid host running the X Server software.
You allow remote access by entering the following command:
% xhost +
If you need to start or stop the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site on a UNIX system, use the commands shown in Table 3-4.
The emctl command is available in the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory after you install Oracle9iAS.
You can verify the Enterprise Manager Web site is started by pointing your browser to the Web site URL. For example:
http://hostname:1810
If you have trouble stopping the Enterprise Manager Web site, you can use the following procedure to locate and stop the Enterprise Manager Web site process on your UNIX system. For example, use this procedure if you have changed the ias_admin password and you do not have the original password:
$ /usr/ucb/ps auxww | grep EMDROOT
$ kill <process_number>
To start or stop the Enterprise Manager Web site on Windows, use the Services control panel. The name of the service is in the following format:
OracleORACLE_HOMEEMwebsite
For example, if the name of the Oracle Home is OraHome902, the service name is:
OracleOraHome902EMWebsite
The Services control panel shows you the status of the service and indicates the method used to start the service. You can then select the service name and use the controls on the Services window to start and stop the service. When you stop the service, the Services control panel displays a dialog box asking for the ias_admin password.
You can also start or stop the service using the following command line:
net start WEB_SITE_SERVICE_NAME
For example:
net start OracleOraHome902EMWebsite
The ias_admin password is required to use the Enterprise Manager Web site. You can change the ias_admin user password in the following ways:
If you use an infrastructure, you must adhere to the Oracle Internet Directory password policy when setting the ias_admin password. This is because, even though the ias_admin password is not stored in Oracle Internet Directory, it may be used to set component passwords within Oracle Internet Directory. The default password policy is a minimum of five characters, with at least one numeric character. For more information see "Password Policies".
Warning:
To change the ias_admin user password using Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site:
ias_admin password for all application server installations on the host.
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 9.
To change the ias_admin user password using a command-line tool:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl set passwordnew_password (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\bin\emctl set passwordnew_password
For example:
(UNIX)ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl set password m5b8r5(Windows)ORACLE_HOME\bin\emctl set password m5b8r5
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 9.
Oracle strongly recommends that you use the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol and HTTPS for all connections to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site. There are two methods for setting up the Enterprise Manager Web site for secure connections:
The following sections describe these methods in detail.
|
Note: The emctl command used in the following procedures is located in the following directory:
(Windows) |
In your testing or development environment, you can enable SSL for the Enterprise Manager Web site without performing any significant configuration steps. However, this method of enabling security is based on a standard SSL Server Identity that is not trustworthy. Consider this method of setting up SSL if you are investigating SSL for the first time. This method of setting up security is not recommended for production systems.
To enable SSL for the Enterprise Manager Web site in your testing environment:
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 3-9
emctl command:
emctl set ssl test
https://server_name:1810
To disable SSL in your testing environment:
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 3-9.
emctl command:
emctl set ssl off
http://server name:1810
For your production systems, Oracle strongly recommends that you set up security for the Enterprise Manager Web site using a valid security certificate. For more information about security certificates, see the Oracle9i Application Server Security Guide.
To set up SSL for Enterprise Manager Web site in your production environment:
emctl gencertrequest
Enterprise Manager generates a Certificate Request, stores the request in a file called server.csr, and shows you the location of this file. The content of the file looks similar to the output shown in Example 3-1.
For more information about certificate authorities, see the Oracle9i Application Server Security Guide.
The Certificate Authority returns to you two certificate files. One is the Certificate Authority Certificate and the other is the SSL Server Site Certificate. The content of each Certificate file looks similar to the one shown in Example 3-2.
emctl installcert -ca certificate_authority_certificate_path
For example:
emctl installcert -ca /home/myfiles/cacertificate.cer
If the certificate is installed successfully, the following message appears:
OC4J keystore was updated at $ORACLE_HOME/sysman/j2ee/server/keystore.secure
emctl installcert -cert SSL_Server_Site_Certificate_path
For example:
emctl installcert -cert /home/myfiles/ssl_certificate.cer
If the SSL Site Certificate is installed successfully, the following message appears:
OC4J keystore was updated at $ORACLE_HOME/sysman/j2ee/server/keystore.secure OC4J keystore is ready for SSL.
Steps 1 through 4 establish the material needed for the Enterprise Manager Web site to act as a unique and trustworthy SSL Server Site. Oracle recommends that you protect this material with a password. The initial default password is "welcome". To modify the password, enter the following command:
emctl set ssl password old_password new_password
For example:
emctl set ssl password welcome manchester123
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 3-9.
emctl command:
emctl set ssl test
https://server_name:1810
-----BEGIN NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST----- MIIBpzCCARACAQAwZzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNhbGlmb3JuaWExDDAKBgNVBAcT A0VNRDEMMAoGA1UEChMDRU1EMQwwCgYDVQQLEwNFTUQxGTAXBgNVBAMTEFRFU1QgQ0VSVElGSUNB VEUwgZ8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADgY0AMIGJAoGBAM1saVui7S/f+bFLMBmP2nFhHcAf/RNMViWg 5-MRTBBCIanSPTtABle54VOrTEXPACbmbedDIeMbr+585=wjC+MHaJoEtEXSUVrOYin4OP-XOX-H I2GfwYnYf4G6ZmbvopKPYx9NxfKdqathbiR8ayG+TH92YsoOJdsyry2nnDltAgMBAAGgADANBgkq hkiG9w0BAQQFAAOBgQClZmkgwhQUjmFMaFCx2+wMZQNpQ0AQEtaz3MNQeChIIVkZLeGRoZ0g4HFX CL1SOp2Jl2+dKuW4N+xa9y9Vo0vVtAAY7l7a4r83CyotaMOLXW70YuxRxzs6a3OxwlH1AUFr3KUY xyr/IjOxYRyMOnk4INLK6EC1ght+BnYHo77imw== -----END NEW CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIB4jCCAYygAwIBAgIQUcmat1ccRQmg8ZuXwne+qTANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFADA5 MR4wHAYDVQQKFBVPcmFjbGUgU2VjcmV0IFNlcnZpY2UxFzAVBgNVBAMUDkRldmVs b3BtZW50IENBMB4XDTAyMDIwNTIxMzM1MVoXDTAyMDgwNDIxMzM1MVowZzELMAkG A1UEBhMCVVMxEzARBgNVBAgTCkNhbGlmb3JuaWExDDAKBgNVBAcTA0VNRDEMMAoG A1UEChMDRU1EMQwwCgYDVQQLEwNFTUQxGTAXBgNVBAMTEFRFU1QgQ0VSVElGSUNB VEUwgZ8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADgY0AMIGJAoGBAM1saVui7S/f+bFLMBmP2nFh HcAf/RNMViWgpKgCsN8JyFJXwLOIqd8i+Ggf0VT9wfGkI4+8oSIvdhiLJdZ431VB agbDGpf03nmj4NNCnxNkrG+yI2GfwYnYf4G6ZmbvopKPYx9NxfKdqathbiR8ayG+ TH92YsoOJdsyry2nnDltAgMBAAEwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQADQQCcGj+eRsUrg6Pt typn6q25ZlfpZw3VMLqf8wQ+uEjGw6Y+Bd5f7tAoPXsjxdzVdB2GG+eHZI0eipA9 VIRtwZM1 -----END CERTIFICATE-----
The Enterprise Manager Web site relies on various technologies to discover, monitor, and administer the Oracle9iAS environment.
These technologies include:
The Enterprise Manager Web site uses DMS to gather performance data about your Oracle9iAS components. To learn more about DMS, see the Oracle9i Application Server Performance Guide.
While you can use Oracle HTTP Server and OC4J to deploy your own applications, the Enterprise Manager Web site also uses HTTP Server and OC4J to deploy its management components. When you start the Web site for the first time, you will notice that several default OC4J instances are reserved for Oracle management applications. For more information, see the topic "About the Default OC4J Instances" in the Enterprise Manager Web site online help.
OPMN manages Oracle HTTP Server and OC4J processes within an application server instance. It channels all events from different component instances to all components interested in receiving them.
|
See Also:
Chapter 13, "High Availability" for more information about OPMN |
DCM manages configurations among application server instances that are associated with a common Infrastructure (members of an Oracle9iAS farm). It enables Oracle9iAS cluster-wide deployment so you can deploy an application to an entire cluster, or make a single host or instance configuration change applicable across all instances in a cluster. The Enterprise Manager Web site uses DCM to make configuration changes and to propagate configuration changes and deployed applications across the cluster.
|
See Also:
Chapter 14, "Application Server Clustering" and Appendix F, "DCM Command-Line Utility (dcmctl)" for more information on DCM |
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site provides all the tools you need to manage your application server instances, farms, clusters, and system components. However, if you have an environment that includes other Oracle products and applications in addition to Oracle9iAS, consider using the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, when used with the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site, provides a wider view of your Oracle environment beyond Oracle9iAS. Use the Console to automatically discover and manage databases, application servers, and Oracle applications across your entire network.
The Console offers advanced management features, such as an Event system to notify administrators of changes in your environment and a Job system to automate standard and repetitive tasks, such as executing a SQL script or executing an operating system command.
The following sections describe:
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console is part of the Oracle Enterprise Manager three-tier framework. Unlike a two-tier client-server structure, where a client tier is responsible for the presentation of information and accesses data from a server, Oracle Enterprise Manager utilizes a three-tier architecture:
For a more complete description of the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
The following sections describe how to install the Enterprise Manager three-tier framework so you can use the Console to manage your Oracle environment.
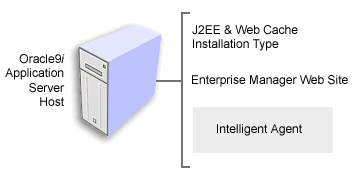
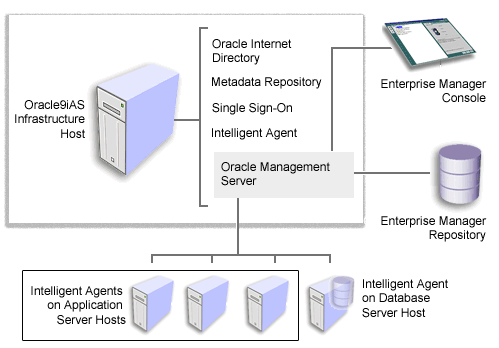
The Oracle Intelligent Agent is installed whenever you install Oracle9iAS on a host computer. For example, if you select the J2EE and Web Cache installation type, the Oracle Universal Installer installs Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site and the Oracle Intelligent Agent, along with the J2EE and Web Cache software (Figure 3-3). This means the Intelligent Agent software is always available if you decide to use the Console and the Management Server to manage your Oracle9iAS environment.
For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Intelligent Agent on UNIX" on page 3-21.
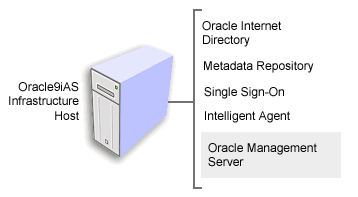
The Console and Management Server are installed as part of the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure. In most cases, you install the Infrastructure on a dedicated host that can be used to centrally manage multiple application server instances. The Infrastructure includes Oracle Internet Directory, Single Sign-On, the metadata repository, the Intelligent Agent, and Oracle Management Server (Figure 3-4).
On UNIX systems, use the agentctl utility to start and stop the Agent. The agentctl command is available in the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory after you install the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure.
The relevant agentctl commands are listed in Table 3-3.
| If you want to... | Enter the command... |
|---|---|
|
Start the Agent |
|
|
Stop the Agent |
|
|
Verify the status of the Agent |
|
On Windows systems, use the Services control panel to start and stop the Agent. The name of the service is in the following format:
OracleORACLE_HOMEAgent
For example:
OracleOraHome902Agent
The Services control panel shows you the status of the service and indicates the method used to start the service. You can then select the service name and use the controls on the Services window to start and stop the service.
You can also start or stop the service using the following command line:
net start AGENT_SERVICE_NAME
For example:
net start OracleOraHome902Agent
For more information about configuring and controlling the Intelligent Agent, see the Oracle Intelligent Agent User's Guide.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant is launched as a configuration tool at the end of the Oracle9iAS installation. The configuration assistant runs silently in the background and automatically configures Oracle Management Server to use the Metadata Repository of the Infrastructure you are installing.
If you do not configure the Management Server as part of the Infrastructure installation, you can run the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant later. When you run the Assistant later, you can configure Oracle Management Server so it uses the metadata repository, or you can configure the server to use another database on your network.
The following sections describe:
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant guides you through the steps to configure Oracle Management Server. For example, you use the Configuration Assistant to:
For a complete description of the tasks performed by Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
To start the Configuration Assistant at any time, enter the following command:
emca
The emca command is available in the following directory after you install Oracle9iAS Infrastructure:
(UNIX)ORACLE_HOME/bin(Windows)ORACLE_HOME\bin
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide contains detailed instructions about running the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant and configuring Oracle Management Server.
In addition, click Help at any time while running the Configuration Assistant to display the Oracle Enterprise Manager online help. Use the icons in the Help window toolbar to display the Enterprise Manager online help table of contents or to search for a word or phrase in the online help.
When you install the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure, the installation procedure automatically creates a default schema, user, and password for the Enterprise Manager repository. When you run the Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant, you can choose to use this existing repository, or you can create a new repository.
The following instructions describe how to manually configure the management server so it uses the default schema, user, and password:
When you select these options, the Configuration Assistant creates the omsconfig.properties file, which is a file required by the Oracle Management Server.
OEM_REPOSITORY
oem_repository
<host:port:sid>
OEM_REPOSITORY is the default Enterprise Manager schema. When you installed Oracle9iAS infrastructure, the OEM_REPOSITORY database user was created and the necessary Enterprise Manager schema was loaded. Oracle recommends that you do not change this user. You can however, change the default password. The repository username and password are stored in the omsconfig.properties file. The configuration assistant will encrypt the repository password in this file.
The connection information includes the name of the host where the metadata repository resides, the port for the database (usually 1521), and the system identifier (SID) for the database. For example:
mysystem:1521:iasdb
To start or stop Oracle Management Server on a UNIX system, use the commands shown in Table 3-4.
The oemctl command is available in the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory after you install the Oracle9iAS Infrastructure.
For complete instructions on obtaining the status of the Management Server, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
On Windows systems, use the Services control panel to start and stop the management server. The name of the service is in the following format:
OracleORACLE_HOMEManagementServer
For example:
OracleOraHome902ManagementServer
The Services control panel shows you the status of the service and indicates the method used to start the service. You can then select the service name and use the controls on the Services window to start and stop the service. When you stop the management server, the Services control panel displays a dialog box that prompts you for the user name and password. The default user name is sysman. The default password is oem_temp.
You can also start or stop the service using the following command line:
net start AGENT_SERVICE_NAME
For example:
net start OracleOraHome902ManagementServer
For more information about configuring and controlling the management server, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
The following sections describe how to get started using Oracle Enterprise Manager Console.
After you have configured and started Oracle Management Server, you can start the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console. To start the console:
The default Enterprise Manager administrator name is sysman and its password is oem_temp.
The Management Server host that you specify in the Login dialog box must already be configured with the repository you want to access. To select an existing Management Server, click the icon next to the Management Server field.
If this is the first time you are starting the Console, Enterprise Manager displays a dialog asking you for a new password to replace the default oem_temp password. Enter a new password and click OK.
Enterprise Manager displays the Console main window.
Oracle Enterprise Manager provides a Discovery Wizard for identifying hosts and populating the Console Navigator tree with these discovered hosts and the targets on those hosts. The discovered targets, such as databases and listeners, can then be administered with Enterprise Manager.
During startup of the Console, any manageable targets on the machine where the Management Server is running are automatically discovered if the Intelligent Agent is installed and running on that Management Server machine. The Console Navigator then displays all those discovered targets. For more information, see "Starting and Stopping the Intelligent Agent on UNIX" on page 3-21.
To start the Discovery Wizard, choose Discover Nodes from the Navigator menu.
For more information about using the Console to manage Oracle9iAS, see "Using the Console with the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web Site" on page 3-28.
Besides offering you a wider view of your Oracle9iAS environment, the Console also provides two important features for administrators: jobs and events.
The Jobs system allows you to automate standard and repetitive tasks, such as executing a SQL script or executing an operating system command. With the Job system, you can create and manage jobs, share jobs with other administrators, schedule execution of jobs, and view information about the jobs. Jobs can be scheduled on a single node or multiple nodes in the network, provided that the node has an Intelligent Agent running on it.
The Event system allows you to monitor your network for specific conditions, such as loss of service or lack of storage, that may occur in your managed environment. You select tests to run on managed targets (databases, nodes, listeners, or other services), then set the threshold parameters for which you want to be notified. You can share events with other administrators, in addition to being able to notify specific administrators when an event condition occurs. For some event tests, you can also choose to execute a fixit job that automatically corrects the problem.
The Console includes several events that are specific to Oracle9iAS. For more information about the Oracle9iAS events, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Addendum to Event Test Reference Manual.
To learn more about creating jobs and events using the Console, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
For information about starting, configuring, and using the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, see the following documentation on your Oracle9i Application Server Documentation Library CD-ROM:
The Console also provides extensive online help. To display the Console online help, click the Help button on a particular dialog box or property page, or select a command from the Console Help menu.
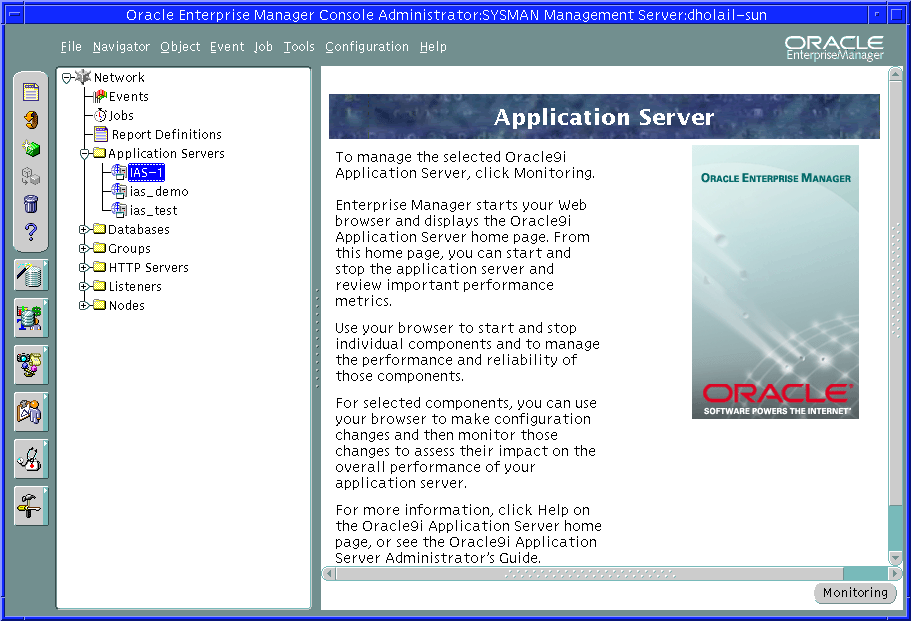
The Console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Web site are designed to work together. For example, suppose you use the Console to discover a host computer where Oracle9iAS has been installed. As long as the Intelligent Agent on that host is up and running, the application server instances on that host appear in the Console navigator pane.
To display the Enterprise Manager Home Page for an application server instance:
The Console displays an information panel describing the Oracle9iAS management tools (Figure 3-6).
Oracle Enterprise Manager opens your default browser and displays the appropriate Oracle Enterprise Manager Home Page for the selected application server instance.
|
Note: To display the Enterprise Manager Home Page, you must have a default browser identified in the PATH environment variable. |
|
|
 Copyright © 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|