1 Introduction to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 1.1, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Overview"
-
Section 1.2, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Business Processes"
-
Section 1.3, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Integrations"
-
Section 1.4, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Implementation"
1.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Overview
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting system from Oracle provides a foundation for managerial accounting and activity-based costing. The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting foundation includes fully integrated building blocks that are designed around business processes.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to analyze data using traditional cost accounting, activity-based costing, or a combination of the two. You can combine traditional cost accounting and activity-based costing for greater flexibility in managing a business.
Traditional accounting and activity-based costing differ in that activity-based costing is not required to follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principals (GAAP). In activity-based costing, debits do not have to equal credits. You can focus on a segment of the business instead of the entire business.
Typically, you use activity-based costing when a more accurate allocation of indirect expense-to-cost object is required.
In general, cost objects are divided into two major categories: customer and product. You can determine the level of detail for customer and product based on the needs of the business.
Managerial accounting provides the information that managers of economic organizations use to plan and control their operations. It analyzes an organization at the profit center level rather than at the organizational level used in financial accounting. For example, managerial accounting analyzes customer and product information rather than organizational levels such as marketing, administration, and manufacturing.
In managerial accounting systems, traditional financial accounting systems provide databases that are used in modeling, simulation, and "what-if" analyses. Allocations are run over indirect cost pools to assign all revenues and expenses to the profit center level. This process provides the information that is necessary to make high-level decisions about product lines, customer profitability, marketing strategies, reorganizations, and cost reduction projects.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting addresses the reporting needs for managerial decision-making. For example, by producing unique views of financial information, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting demonstrates that the same sales volume can have vastly different profit margins because of shipment size, special packaging, special requirements, and product mix.
To address these needs, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to:
-
Capture financial information within the cost analyzer table for further analysis.
-
Track and assign transactions using cost objects.
-
Capture quantity information.
-
Reassign costs based on cost drivers.
Activity-based costing enables you to identify and capture direct or indirect costs for specific products or customers by using cause-and-effect relationships. JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to collect, track, and assign activities to specific cost objects.
This table lists features of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting:
| Feature | Usage |
|---|---|
| Cost object tracking | Enables you to directly assign transactions to their original cost objects. Cost objects are the lowest level at which costs are calculated or tracked. Examples of cost objects include customers, item numbers, and sales numbers. |
| Cost analyzer | Enables you to arrange and analyze managerial accounting information without affecting financial accounting information. |
| Detailed product costs | Enables you to capture detailed product costs when you create automatic journal entries. Use detailed product costs to analyze costs for material, labor, or overhead. |
| Driver calculations | Enables you to calculate volumes that are based on transaction information. For example, you can calculate the number of sales order lines by customer. Driver volumes are used to reassign indirect costs to cost objects. |
| Cost assignments and allocations | Enables you to process calculations for activity-based costing, as well as managerial accounting, over the Cost Analyzer Balances table (F1602). You can define allocations according to your business needs. The system provides an audit trail of the calculations and provides separate balances for amounts that are transferred from and to original balances. |
| Activity-based costing | Enables you to define cost objects, activities, and processes, and to create relationships between them. It also enables you to analyze business process costs. |
1.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Business Processes
This diagram illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting business processes:
Figure 1-1 Advanced Cost Accounting process flow
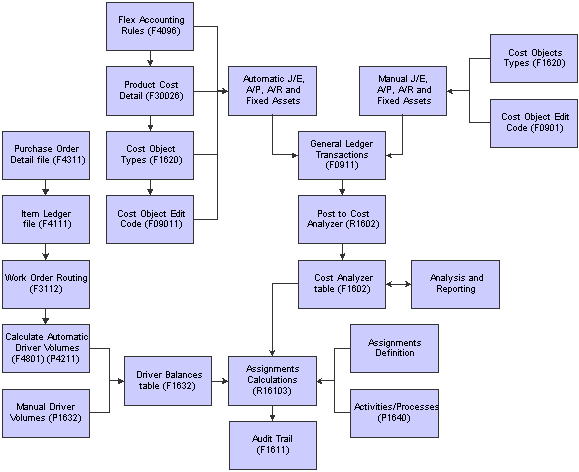
Description of ''Figure 1-1 Advanced Cost Accounting process flow''
We discuss these business processes in the business process chapters in this implementation guide.
1.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Integrations
When you process transactions in other systems, you can capture information that is relevant to activity-based costing or managerial accounting by using flex accounting rules or cost object rules, based on the setup method for the application.
|
Note: You should use the Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAI) setup method for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Manufacturing and Distribution systems from Oracle. If you use another method, you must ensure that it is correct for that system. |
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting system works with other JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems to ensure that all information is fully integrated into the general ledger. We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters in this implementation guide. Supplemental information about third-party application integrations is located on the My Oracle Support web site.
This table lists the systems with which the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting system integrates:
| Application | Integration |
|---|---|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to either enter cost objects manually or let the system determine how to automatically supply the cost object information. You can enter information in cost object fields that are available when the Activate Cost Objects field in the Cost Management Constants table (F1609) is active.
You use flex accounting rules to determine how the system automatically completes the cost object fields when creating offset entries during the pre-post voucher and payment processes. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to enter cost objects in manual transactions. The cost object fields are available when the Activate Cost Objects field in the Cost Management Constants table (F1609) is active. |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Inventory Management | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to use the Item Cost Component Add-ons table (F30026) to determine inventory-related costs and retrieve information by cost type. If the Product Cost Detail field in the Inventory Constants table (F41001) is active, you must use the standard cost (07) cost method. If the Product Cost Detail field is not active, you can use cost methods 01 through 06 and 08. The system calculates costs based on the Item Cost File table (F4105).
You use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when creating automatic journal entries. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Manufacturing Accounting | You use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when creating automatic journal entries. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Product Costing | You use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when you create automatic journal entries. If the Product Cost Detail field is not active, you can use cost methods 01 through 06 and 08. The system calculates costs by using the Item Cost File table (F4105). The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement Management | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting enables you to enter cost objects in manual transactions. The cost object fields are available when the Activate Cost Objects field in the Cost Management Constants table (F1609) is active. You can use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when creating automatic journal entries. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management | You use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when creating journal entries. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management enables you to use the Item Cost Component Add-ons table (F30026) to determine inventory-related costs and retrieve information by cost type. If the Product Cost Detail field in the Inventory Constants table (F41001) is active, you must use the standard cost (07) cost method. If the Product Cost Detail field is not active, you can use cost methods 01 through 06 and 08. The system calculates costs based on the Item Cost File table (F4105). |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Transportation Management | You use flex accounting rules to determine how to complete the cost object fields when creating journal entries. The system reviews the flex accounting rules when these factors apply:
|
1.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting Implementation
This section provides an overview of the steps that are required to implement the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting system.
In the planning phase of your implementation, take advantage of all JD Edwards EnterpriseOne sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting, use the EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant. EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant, a Java-based tool, reduces the time required to search and download ESUs by 75 percent or more and enables you to install multiple ESUs at one time.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Software Updates Guide.
1.4.1 Global Implementation Steps
This table lists the suggested global implementation steps for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Advanced Cost Accounting system:
-
Set up companies, fiscal date patterns, and business units.
-
Set up accounts, and the chart of accounts.
-
Set up the General Accounting constants.
-
Set up multicurrency processing, including currency codes and exchange rates.
-
Set up ledger type rules.
-
Enter address book records.
-
Setting up Constants
See Setting Up Constants.
-
Setting Up Cost Object Types
-
Setting Up Activities