37 Offsetting GST Input Tax Credit and Calculating Duty Liability (Release 9.1 Update)
This chapter discusses these topics:
37.1 Understanding the GST Credit Offset Process
As a manufacturer or provider of goods and services, you receive credit for paying input tax when you procure goods and services to run your business. You are liable to pay output tax on the sales done in your business. You can offset the output tax against the input tax that you have paid.
You can utilize the input tax credit (ITC) for one GST type to recover the tax liability (output tax) for another GST type. However, you must follow the order of priority prescribed by the government to offset the ITC against the tax liability of other GST types. For example:
| Input Tax Credit | Utilize for Liability Payment (in the order listed below) |
|---|---|
| IGST | 1. IGST
2. CGST 3. SGST |
| CGST | 1. CGST
2. IGST |
| SGST | 1. SGST
2. IGST |
In the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, you complete these tasks to offset the ITC against the liability amounts:
-
Set up GST offset rules along with the priority order.
-
Specify the GST unit, period, and year for which you want to adjust the tax liability with the ITC.
37.2 Setting Up Rules to Offset the GST ITC
You use the GST Credit Distribution Setup program (P75I830) to create GST offset rules. The system stores the offset rules in the GST Credit Distribution Setup table (F75I830).
To set up GST offset rules:
-
From the GST Module, click GST System Setup (G75IGST4H), and then GST Credit Distribution Setup.
-
On the Work With GST Credit Distribution Setup form, click Add.
-
On the GST Credit Distribution Setup form, complete the following header fields:
-
Expiration Date
-
From Tax Type
Enter the GST type (CGST, IGST, SGST, or GCESS) from which you want to utilize the ITC to adjust the tax liability.
-
-
For a particular From Tax Type and Expiration Date, enter multiple To Tax Type lines in the grid. Complete the following fields in the grid:
-
To Tax Type
Enter the GST type (CGST, IGST, SGST, or GCESS) for which you want to adjust the tax liability with the ITC.
-
Priority
The system follows the order of priority that you set up in this field when distributing the available ITC to adjust tax liability.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you set up the priority for each GST type according to the order prescribed by the Indian government. If you do not set up the priority according to the prescribed order, the ITC distribution might not be accurate.Example: Priority when the From Tax Type is IGST:
From Tax Type To Tax Type Priority IGST IGST 1 IGST CGST 2 IGST SGST 3 Example: Priority when the From Tax Type is CGST:
From Tax Type To Tax Type Priority CGST CGST 1 CGST IGST 2 Example: Priority when the From Tax Type is SGST:
From Tax Type To Tax Type Priority SGST SGST 1 SGST IGST 2
-
37.3 Offsetting and Distributing ITC
You select the GST unit, period, and year for which you want to offset the ITC against the liability amounts in the GST Credit Distribution program (P75I831).
The system uses the payment date specified in the Payment Date processing option for the P75I831 program and:
-
Retrieves the effective offset rule that has an expiration date equal to or nearest to the payment date
For example, if the payment date is March 15, 2017, and two offset rules exist with expiration dates in that period: March 20, 2017, and March 31, 2017. The system uses the offset rule with the expiration date of March 20, 2017.
-
Offsets the available ITC against the liability amounts based on the order of priority set up in the retrieved offset rule
Consider an example of three transactions (an interstate purchase, an interstate sale, and an intrastate sale) that originated from a business unit in Karnataka state. The ITC and the liability amounts are illustrated according to the transaction types in the table below. All the amounts are in INR.
Transaction Originated From Destination State Transaction Type ITC on IGST Liability on CGST Liability on SGST Liability on IGST Karnataka Tamil Nadu Purchase 13,000 Karnataka Maharashtra Sale 10,000 Karnataka Karnataka Sale 4,000 5,000 The system offsets the ITC on IGST against the liability amounts in this order according to the offset rule:
-
IGST ITC of 13,000 is utilized to offset the IGST liability of 10,000
Balance IGST ITC = 3,000
Balance IGST liability = 0
Balance IGST payment to be made to the government= 0
-
Balance IGST ITC of 3,000 is utilized to offset the CGST liability of 4,000
Balance IGST ITC = 0
Balance CGST liability = 1,000
Balance CGST payment to be made to the government= 1,000
When CGST liability of 1,000 is paid to the government, balance CGST liability = 0
-
Because there is no balance IGST ITC to offset the SGST liability of 5,000,
SGST liability = 5,000
Balance SGST payment to be made to the government= 5,000
When SGST liability of 5,000 is paid to the government, balance SGST liability = 0
This example illustrates how the ITC for IGST is used to offset the liability according to the recommended offset rule for IGST. This example does not include ITC for CGST and SGST. But if they exist, then the rules for CGST and SGST will also be applied, and the system will utilize the ITC on each GST type in this order:
-
ITC on IGST
-
ITC on CGST
-
ITC on SGST
-
The GST Credit Distribution Setup program passes amount and account details to create a pair of credit and debit entries in the Account Ledger table (F0911) for the amounts being distributed. The system decreases the ITC closing balances and increases the TL and CL closing balances in the F75I804 table, and also updates the ITC, TL, and CL ledgers in the F75I823 table using a single batch number for the credit and debit entries.
|
Note: If the processing option for the Work With GST Credit Distribution program (P75I831) is set to display an error due to insufficient balance in the GST cash ledger, an error is displayed when there is insufficient balance to adjust the GST credit distribution amount. |
Figure 37-1 Ledgers, Tables, and Accounts Updated After Credit Distribution
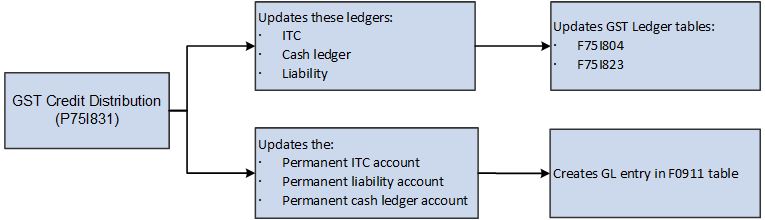
Description of ''Figure 37-1 Ledgers, Tables, and Accounts Updated After Credit Distribution''
The system creates GL distribution journal entries in the F0911 table, crediting the permanent ITC account, crediting the permanent cash ledger account, and debiting the permanent liability account.
37.3.1 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section:
-
Set up offset rules in the GST Credit Distribution Setup program (P75I830).
-
Set up the processing options for the GST Credit Distribution program (P75I831).
On the Default tab of the processing options form, you specify the payment date.
On the G/L tab of the processing options form, you specify the:
-
Remark
-
Version of the P0900049 that the system uses to retrieve additional processing options
-
Document type for the G/L entries created by the Work With GST Credit Distribution program.
-
37.3.2 Offsetting the ITC Against the Liability
To offset the liability with the available ITC:
-
From the GST Module, click GST System Setup (G75IGST4H), and then GST Credit Distribution Setup.
The system launches the Work With GST Credit Distribution form that displays the opening and closing balances for CGST, IGST, SGST, and CESS in the Input Tax Credit ledger, Tax Liability ledger, and Cash Ledger for each GST unit, period, and year combination.
-
On the Work With GST Credit Distribution form, select the record of the GST unit, period, and year for which you want to offset and distribute the ITC amounts. Then, click Select.
The system offsets the available ITC amounts against the liability amounts based on the effective offset rule in the F75I830 table and displays the updated amounts in the GST Credit Distribution form.
-
On the GST Credit Distribution form, review the following:
-
ITC amounts
-
Liability amounts
-
ITC amounts that are utilized to offset the liability
-
Balance liability amounts and the balance ITC amounts
-
Payment amounts that you must pay to the government so that the balance liability is zero (0). This is the amount for which the system creates vouchers.
Initially, the Payment fields are populated with the balance GST amounts that you must pay to the government, and the Balance Liability fields have a value of zero (0) for all the tax types. When you reduce the payment amount, the balance liability increases for that tax type. You can make a payment less than or equal to the default payment amount that the system populates after applying the offset rules. For example, if CGST payment amount is 1,000 INR, then you can make a payment of 1,000 INR or less and not more than that.
-
-
To clear the updates you made and to reset the values that the system has calculated using the effective offset rule, click Reset.