Setting Up Inbound Product Data Synchronization and Data Quality Management
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Setup Overview of Inbound Product Data Synchronization
- Creating a 1SYNC Target System and Global Location Number
- Creating Match Rules
- Defining Source Systems
- Applying the 1SYNC Library
- Defining Units of Measure for GDSN Attributes
- Mapping Values Between 1SYNC Codes and Oracle Codes
- Mapping Categories Between GPC Alternate Catalogs and Item Catalogs
Setup Overview of Inbound Product Data Synchronization
Oracle Product Information Management uses the Import Workbench to bring product data from disparate systems into a master product information repository, known as the Product Information Management Data Hub (PIMDH).
While importing data into a centralized data model, the Import Workbench identifies and resolves duplicates and errors while at the same time enriching existing data with external information. This process creates a blended record, known as the single source of truth. You can then create business reports and other documents related to the updates.
In order to import data from an external source system, you must define a source system for each data source and create match rules to help match imported data to existing data in the product information repository. If you plan to import item data from the 1SYNC Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN), then you must complete the following additional steps:
-
Create a 1SYNC target system and GLN
See: Creating a 1SYNC Target System and Global Location Number
-
Create suppliers and supplier sites, both with an appropriate GLN
Define the suppliers and supplier sites from whom you intend to receive data through 1SYNC, as well as the Global Location Numbers (GLNs) of the supplier sites. 1SYNC uses the GLN to identify the supplier.
See: Suppliers, Oracle Payables User's Guide.
-
Create structure batches to receive GDSN item data
Create structure batches within a source system. The source system must have the Enable for Data Pool flag set to Yes. View the data sent by the supplier via 1SYNC in the Unconfirmed tab of the batch if no match rules ran automatically.
See: Creating Batches, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide.
-
Apply the 1SYNC library to seed the attributes required to receive item data
-
Define units of measure classes and units of measure for GDSN attributes
-
Create an XSL mapping from 1SYNC UOM classes to the GDSN attribute UOM classes
See: Creating XSL Mappings from 1SYNC UOM classes to GDSN Attribute UOM Classes
-
Create an Item Catalog Category and associate attribute groups to the category for items received by way of 1SYNC
Create an item catalog category (ICC) for the items received through 1SYNC and map the attribute groups created using the ldt file egogdsnag.ldt. This enables you to see the data sent by 1SYNC in the item pages.
See: Defining Item Catalog Categories and Associating Attribute Groups with an Item Catalog Category
-
Create alternate catalog categories with GPC codes
Create alternate catalog categories (ACCs) with the same names as the GPC codes. This enables you to identify the items received from 1SYNC and to map them to appropriate ICCs.
-
Map categories between the GPC alternate catalog and the item catalog
See: Mapping Categories Between GPC Alternate Catalogs and Item Catalogs
Related Topics
Defining Units of Measure for GDSN Attributes
Overview of Inbound Product Data Synchronization and Data Quality Management, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide
Creating a 1SYNC Target System and Global Location Number
GDSN requires each physical location in a company to have a Global Location Number (GLN). The GLN is 13-digit number with a check digit assigned as the last digit. Oracle enables you to assign a GLN to each supplier address using Oracle Payables.
The GLN is not displayed by default, since it is primarily used for the purpose of synchronizing product data. You can display the field using the personalization framework.
To add a GLN to a supplier location
-
From the Home page, select the System Administrator responsibility.
-
From the menu, under Profile, select System.
-
Search for and select the profile option Personalize Self-Service Defn.
-
In the System Profile Values form, Site field, select Yes from the list of values.
-
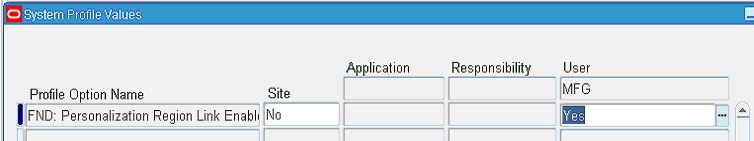
Search for and select the profile option FND: Personalization Region Link Enabled. Enter the User for whom you want to enable personalization as a search criteria.
-
In the System Profile Values form, set the profile option FND: Personalization Region Link Enabled to Yes at the User Level for the user.
Tip: Enter a user with the Payables responsibility and who will update the GLN.
-
Log out, then log on again as the user with the Payables responsibility.
-
Select the Payables responsibility for the Operating Unit under which you plan to update the supplier site GLN.
-
In the menu, under Suppliers, select Entry.
-
Search for and select the supplier for which you plan to update a supplier site with the GLN.
-
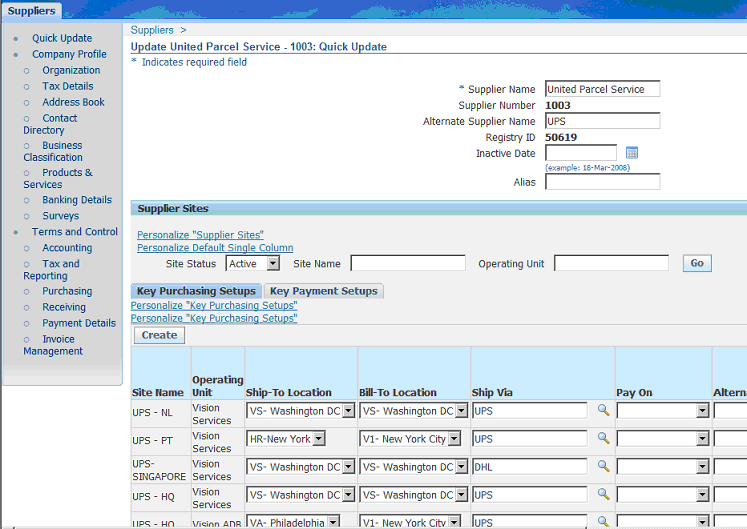
From the Update (supplier name): Quick Update page, select the Company Profile: Address Book link.
-
In the Update (supplier name): Address Book page, find the supplier site. Click Update for the site.
-
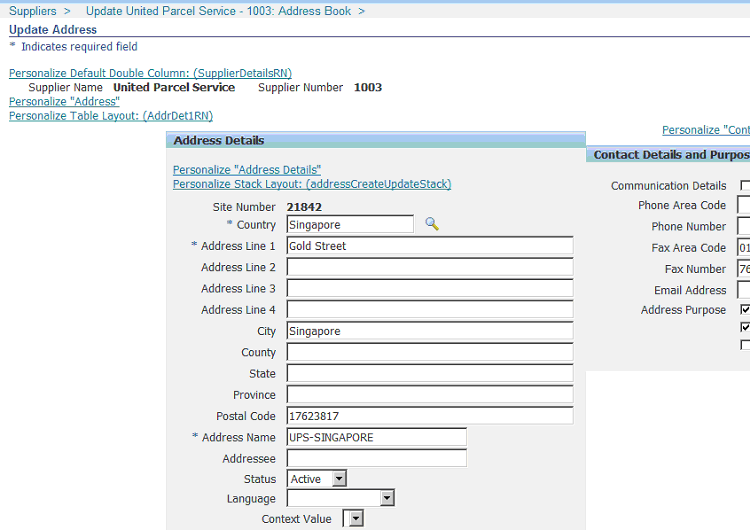
In the Update Address page, click the Personalize "Address" link.
Note: The Global Location Number field does not appear by default on the page. You must personalize it.
-
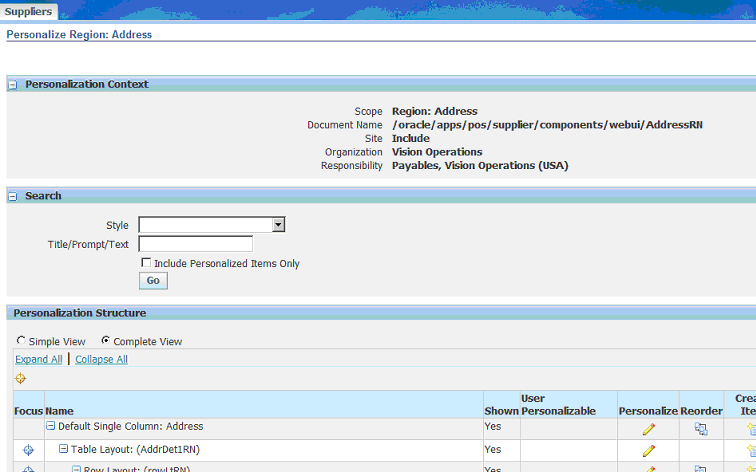
In the Personalize Region: Address page, select Complete View and click Expand All.
-
Find the Global Location Number field and click Update.
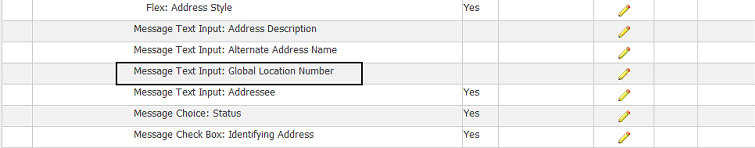
-
In the Personalize Message Text Input: Global Location Number page, find the presentation property Rendered. The Original Definition value is false. Choose whether to update the value to true at the Site, Organization and/or Responsibility level. Click Apply.
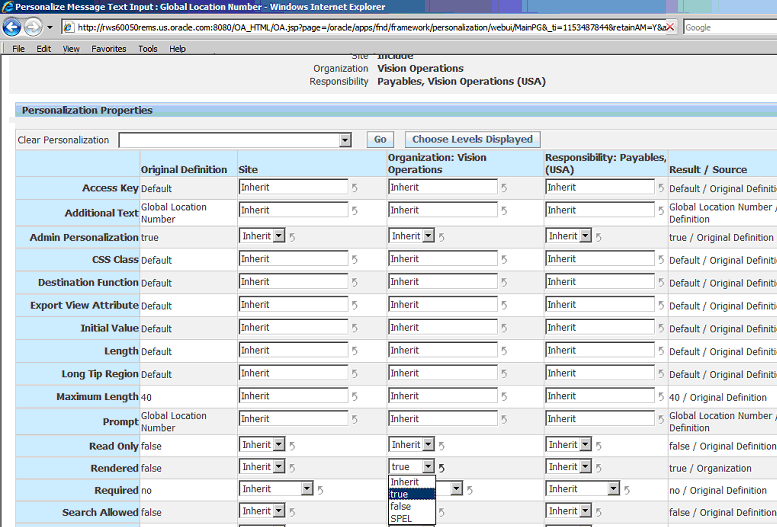
-
In the Personalize Region: Address page, click Return to Application.
-
In the Update Address page, the Global Location Number field now appears. Enter the GLN value, then click Apply.
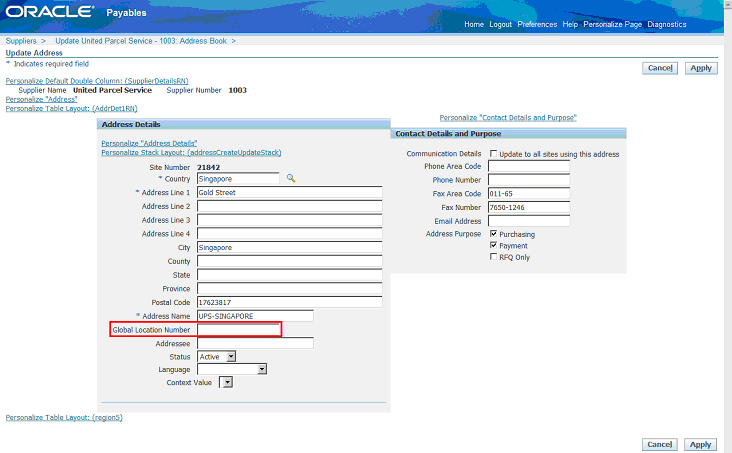
Related Topics
Entering Suppliers Manually, Oracle Payables User's Guide
Creating Match Rules
A match rule defines matching criteria in order to find matches between the incoming external (source system) items and Oracle Product Information Management Data Hub (PIMDH) items. Create match rules at the item catalog level.
After uploading the records into the interface table, PIMDH determines if cross-references for items exist in the production table. If the source system item matches a PIMDH item name, the system confirms the match. At the source system batch level, users can define the default matching rule and choose whether to run the matching rule automatically upon data upload. If you choose to run the matching rule automatically, then a concurrent request launches to find a match using the default matching rule for all unconfirmed records. Alternatively, you can select a match rule and launch the concurrent request to find a match for all unconfirmed items. You can run different matching rules against each batch one at a time while searching to match batch items to the appropriate PIMDH items. The matching process only applies to unconfirmed items. You cannot make changes to the batch while the matching concurrent request executes. The system searches to match source system items against all PIMDH items, including unapproved items.
To create a match rule for an item catalog
-
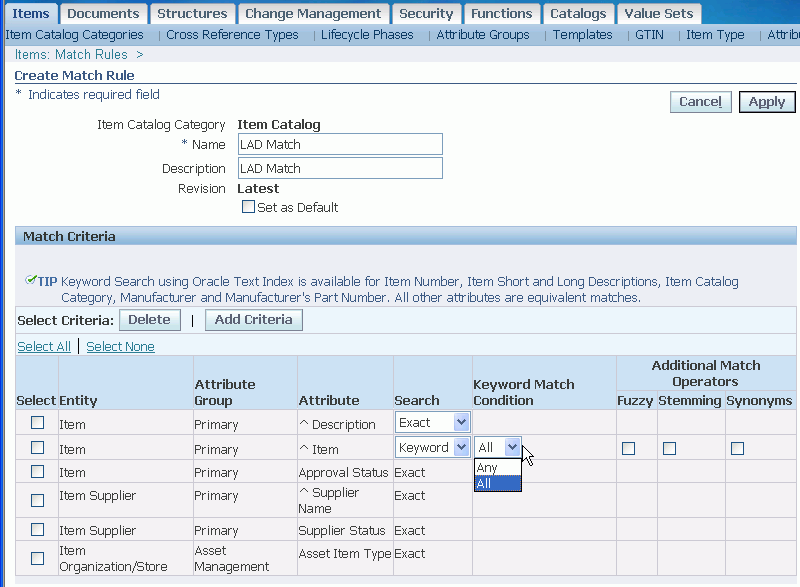
Navigate to the Setup Workbench. From the Items tab, click the Match Rules sub-tab. Click Create.
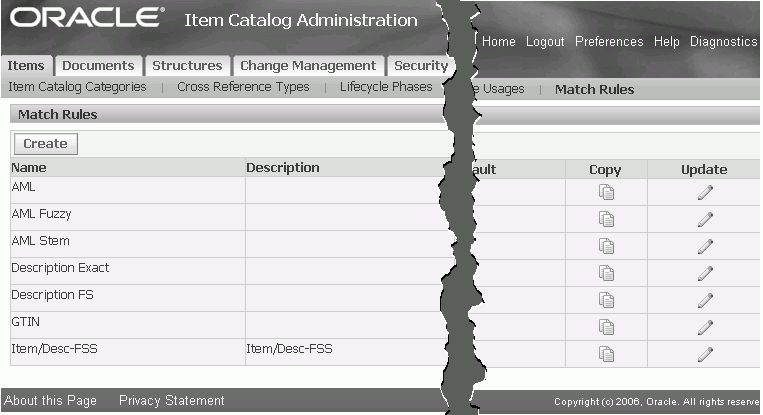
-
Name the match rule and provide a Description. Check Set as Default to have this match rule automatically appear as the default item catalog match rule for source systems. Optionally, you can select another default match rule when defining a source system.
-
Click Add Criteria.
-
Find and select the item attributes for which you want to add criteria using either the Attribute Name, Business Entity, or Attribute Group field. Click Apply.
Choose from the following business entities:
-
Item
-
Item Organization/Store
-
Item Revision
-
Item Supplier
Tip: You can match the following attributes by keywords, using fuzzy, stemming, and synonym searches:
-
item
-
item description
-
item long description
-
item catalog category
-
manufacturer
-
manufacturer part number
-
supplier
-
supplier part number
All other attributes must match exactly. To use synonym searches, you must load a thesaurus into the database and set the site level EGO: Thesaurus for Matching profile option to Yes.
-
-
Once you have added all of the criteria, click Apply.
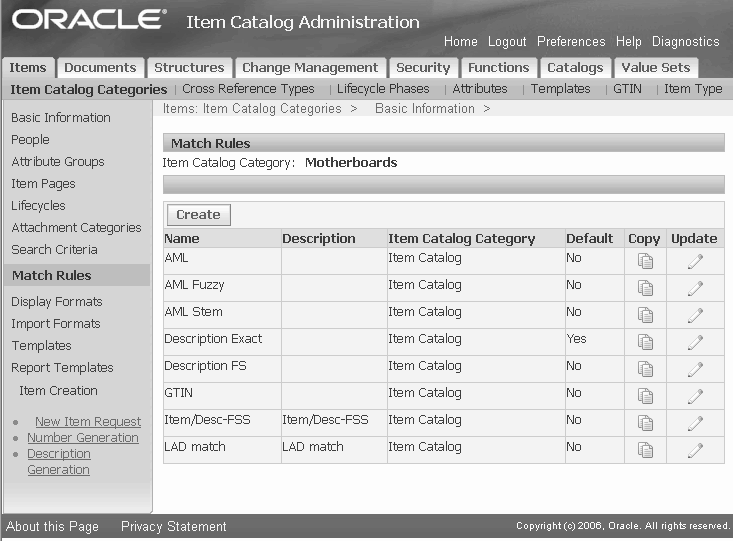
To optionally create a match rule for an item catalog category
After defining match rules at the item catalog level, you can optionally create additional match rules for individual item catalog categories.
-
Navigate to the Setup Workbench. Click the Item Catalog Categories tab. Search for the item catalog category, then click an item catalog category name link.
-
Select Match Rules from the list of options under the Item Catalog Categories sub-tab. From here, follow the same procedure to create match rules for the item catalog category as you did to create match rules for an item catalog.
Note: The item catalog match rules are listed along with the item catalog category match rules, but you cannot update them from within the item catalog category.
Related Topics
Overview of Inbound Product Data Synchronization and Data Quality Management, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide
Defining Source Systems
When importing data from a source other than Oracle Product Information Management Data Hub (PIM Data Hub or PIMDH), you must create a source system within Import Workbench.
To define a source system
-
Navigate to the Import Workbench and select the Source System Setup tab.
-
Click Define Source System to create a new source system.
-
Alternatively, you can search for and view any existing source system item that is enabled only for customer items. Enable it for items.
-
On the Define Source System page, enter the following for the source system:
-
a unique name
-
a unique code
Note: The code can be alphanumeric, but must not contain any spaces. Ensure that the code matches the System Code defined on the System Setup page within the corresponding Oracle Application Integration Architecture (AIA).
Select the Enable For Items check box if you plan to use this source system for item-related data.
Additional Information: Oracle Product Information Management Data Hub uses the same architecture as Oracle Customer Data Hub. The Enable For Items check box communicates that you plan to enter item-related data. You can always uncheck this box at a later time.
Select the Enable for Data Pool check box if the source system is a GDSN data pool. The system can perform certain tasks for GDSN batches, such as:
-
using a group ID to process an entire item hierarchy
-
automatically sending a message to the data pool once data is imported
-
enabling you to send messages to 1SYNC as needed
Additional Information: You can specify a GDSN-enabled source system for both GDSN and non-GDSN batches. However, you cannot specify a non-GDSN source system for a GDSN batch.
For more information about GDSN, see: Overview of the Global Data Synchronization Network.
-
-
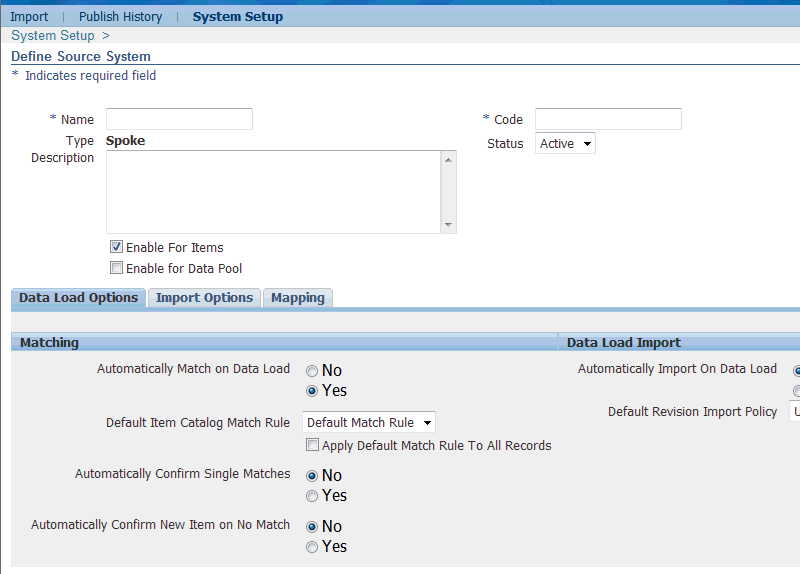
On the Define Source System page, Click the Data Load Options sub-tab.
-
Select Yes by Automatically Match on Data Load if you want to run match rules.
Tip: If you want to load data from a source system and manually inspect it before running match rules, then select No.
-
If you are using match rules, then select a Default Item Catalog Match Rule from the list.
-
Determine whether to check or uncheck Apply Default Match Rule To All Records.
-
Uncheck - The system applies the default item catalog category-level match rule to unconfirmed items with an assigned item catalog category. The system assigns the item catalog level match rule for items with no item catalog category.
Check - The system applies the default item catalog-level match rule to all unconfirmed items.
-
-
Select Yes if you want to Automatically Confirm Single Matches that you find when running match rules for the entire batch. If you select No, then the system tries to match all unconfirmed records using the default match rule.
-
Select Yes if you want to Automatically Confirm New Item on No Match. When you run match rules for the entire batch, this option enables you to automatically confirm an item with no matches as a new item. If you select No, then you must manually move any unmatched items from the Unconfirmed tab to the Confirmed tab, where they are marked with the match status of New.
Note: If the Item Number and Description are not provided, the Source System Item Reference and Description will be used as the Item Number and Description by default.
-
Select the appropriate Import option:
-
Immediately on data load - automatically updates the Oracle Item Master table with matched data.
-
Schedule Data and Time - select the date and time to import the confirmed items or structures in the batch.
-
None - leaves the data in the Import Workbench. You can manually import the data at a later time.
-
-
Select the appropriate Default Revision Import Policy:
-
Create New - creates a new version of the item.
-
Update Latest - updates the latest item revision upon import.
-
-
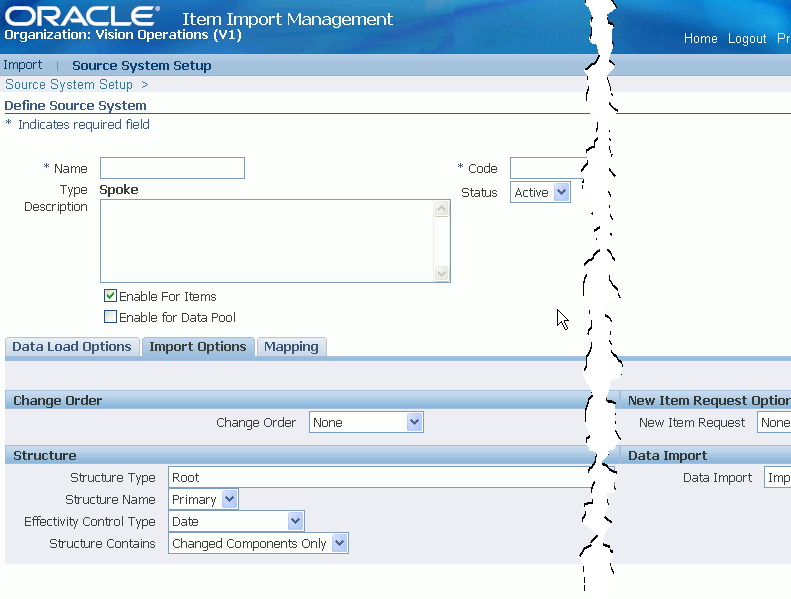
Click the Import Options sub-tab.
Define default import options here. You can change the import options for a particular batch later, if necessary.
-
Select one of the following Change Order options:
-
Add To Existing - associates the imported data with an existing change order.
-
Create New - creates a new change order for the imported data.
Additional Information: When creating a new change order, you have the opportunity to enter or select the following:
-
Change Order Category
-
Change Order Type
-
Change Order Name
-
Change Order Description
Once you select the change order type, depending on the setup, the Change Order Number field is automated or you must manually enter a change order number.
-
-
None - imports the data into PIMDH without going through a change approval process.
-
-
Select one of the following New Item Request options:
-
None - you cannot create any new item requests from this source system. Instead, the system creates draft items. Later, you can navigate to the Item Workbench, further define the draft items, and add it to a new item request. See:
-
One per Item Catalog Category - create one new item request per item catalog category within an imported batch. This new item request can contain multiple line items.
-
One per Item - create one new item request per item.
For more information about new item requests, see: Creating New Item Requests, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide.
-
-
If you are importing structures, select the following default options:
-
Structure Type
Caution: Oracle Product Information Management Data Librarian recommends avoiding the use of the Root structure type. User-defined attributes and import formats are not supported for the Root structure type.
-
Structure Name
-
Effectivity Control Type - choose Date or Model/Unit Number
-
Structure Contains - choose All Components or Changed Components Only
-
-
Select one of the following Data Import options:
-
Import All Data
-
Create Cross References Only - Select this option if you want to create cross-references only. It will not import the data.
-
-
Click the Mapping sub-tab. Select one of the following Mapping Process options:
-
Define in PIMDH - Enables you to define the mapping of attributes between an external source system and PIM Data Hub within PIM Data Hub.
-
External - Enables you to upload an XSLT file containing mapping information between an external source system and PIM Data Hub.
-
None - No mapping occurs.
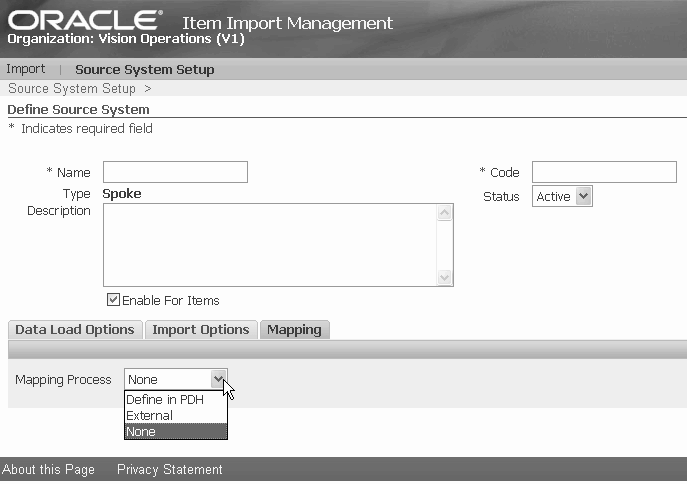
-
Related Topics
Overview of Inbound Product Data Synchronization and Data Quality Management, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide
Applying the 1SYNC Library
Important: This setup step is mandatory if you receive item data from 1SYNC. If you do not receive item data from 1SYNC, you can skip this step.
You must maintain the item data sent by 1SYNC in PIM. Create the appropriate attribute groups and attributes in the setup pages. Apply the item attributes specified in 1SYNC by applying an ldt file containing these seeded values to PIM.
To create the attributes for receiving item data from 1SYNC
-
Create the value sets by applying the value set ldt file egogdsnvs.ldt.
-
Create the attributes by applying the attribute group ldt file egogdsnag.ldt.
Note: If necessary, remove attributes not require. For example, attributes for an industry vertical (such as electronics) not supported by the customer.
Defining Units of Measure for GDSN Attributes
Important: This setup step is mandatory if you receive item data from 1SYNC that contains the GDSN attributes listed below. If you do not receive item data from 1SYNC, you can skip this step.
Oracle Product Information Management includes 150+ GDSN Attributes. Some of these attributes do not have pre-defined units of measure (UOMs), though, so that you can tailor the attribute UOMs to fit your business needs.
Important: You must set up UOMs for these attributes before accepting inbound attribute values from 1SYNC. If you accept an inbound attribute value for these attributes before setting up the UOM, you cannot set up the UOM later. If this happens, clear the values for those attributes (for all items), and then set up the UOM.
The following table lists the attributes that need UOM classes and UOMs assigned to them.
| Attribute Group Name | Attribute Name |
|---|---|
| Trade Item Pack Hierarchy | Composition Width |
| Material Information | Weight |
| FMCG: Measurements | Fat Percent In Dry Matter |
| Size | Size Dimension |
| Hardlines | Nesting Increment |
| GDSN Industry: Hardlines | Out Of Box Depth |
| GDSN Industry: Hardlines | Out Of Box Height |
| GDSN Industry: Hardlines | Out Of Box Width |
| Handling Information | Non GTIN Pallet Height |
| Handling Information | Non GTIN Pallet Gross Weight UOM |
| Handling Information | Maximum Stacking Weight |
| Temperature Information | Storage Handling Temperature Maximum |
| Temperature Information | Storage Handling Temperature Minimum |
| Temperature Information | Delivery To Distribution Center Temperature Minimum |
| Temperature Information | Delivery To Market Temperature Maximum |
| Temperature Information | Delivery To Distribution Center Temperature Maximum |
| Temperature Information | Delivery To Market Temperature Minimum |
| Storage Handling Humidity | Minimum Humidity |
| Storage Handling Humidity | Maximum Humidity |
| Hazardous Information | Flash Point Temperature |
| Trade Item Measurements | Depth |
| Trade Item Measurements | Height |
| Trade Item Measurements | Width |
| Trade Item Measurements | Diameter |
| Trade Item Measurements | Volume |
| Trade Item Measurements | Gross Weight |
| Trade Item Measurements | Net Weight |
| Trade Item Measurements | Drained Weight |
| Trade Item Measurements | Peg Horizontal |
| Trade Item Measurements | Peg Vertical |
| Trade Item Measurements | Product Strength Basis |
| Trade Item Measurements | Generic Ingredient Strength |
| Order Information | Order Sizing Factor |
| Order Information | Order Lead Time |
| Ordering Information | Goods Pick up Lead Time |
| Packaging Material Information | Packaging Material Composition |
| Price Date Information | List Price Basis Per Unit |
| Price Date Information | Suggested Retail Price Basis Per Unit |
| Price Comparison Measurement | Comparison Measurement |
Related Topics
Mapping Values Between 1SYNC Codes and Oracle Codes
Note: When using Oracle UOM codes that have corresponding 1SYNC UOM codes, map the UOM codes to each other using UNIT_OF_MEASURE_DVM.xml.
Defining Unit of Measure Classes, Oracle Inventory User's Guide
Defining Units of Measure, Oracle Inventory User's Guide
Mapping Values Between 1SYNC Codes and Oracle Codes
You must create a map to link the following Oracle codes to the corresponding 1SYNC codes:
-
Country
-
Currency
-
Item Processing
-
Language
-
Trade Item Descriptor
-
Unit of Measure
Use domain-value map (DVM) files to map Oracle codes to 1SYNC codes. Each DVM file has 2 columns, GDSN, and EBIZ. Each row in the file maps a 1SYNC code value to the corresponding code used in Oracle eBusiness Suite. The Oracle Enterprise Service Bus documentation provides specific steps to load a DVM file and to create DVM records. See: Creating and Populating Domain-Value Maps, Oracle Enterprise Service Bus Developer's Guide 10g (10.1.3.3.0).
Verify the presence of the following DVM files in the directory <soa-suite-home>\Bpel\system\xmllib\m4u\config after you inflate the cln_bpel_xmllib.jar from $APPL_TOP/cln/12.0.0/patch/115/jar/bpel to <soa-suite-home>\bpel\system\xmllib\.
Import each of the DVM files from the <soa-suite-home>\Bpel\system\xmllib\m4u\config into your Enterprise Service Bus Console. Once you import these files, edit the DVMs from the ESB console to create new mapping records.
DVM Files
-
COUNTRY_DVM.xml
Map between country codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and 1SYNC target market codes.
Country Code Example
The target market code for United States of America is US in the 1SYNC XML file. Oracle E-Business Suite defines the United States of America country code as USA. To map these two values, create a record in COUNTRY_DVM.xml with the value USA in the EBIZ column and the value US in the GDSN column.
-
CURRENCY_DVM.xml
Map between currency codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and 1SYNC currency codes.
-
ITEM_PROCESSING_CODES_DVM.xml
Map between the SyncItemPublicationLine processing codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and the 1SYNC CatalogueItemNotification codes. There is no requirement to define additional records after importing ITEM_PROCESSING_CODES_DVM.xml since this map is predefined.
-
LANGUAGE_DVM.xml
Map between the language codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and the 1SYNC language codes.
Language Code Example
The 1SYNC language code for American English is "en". Oracle defines American English as "US". To map these two values, create a record in LANGUAGE_DVM.xml with the value US in the EBIZ column and the value en in the GDSN column.
-
TRADE_ITEM_DESCRIPTOR_DVM.xml
Map between the tradeItemDescriptor codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and the 1SYNC ProductType codes.
Trade Item Descriptor Code Example
You can choose to define a TRADE_ITEM_DESCRIPTOR code of BASE_UNIT_OR_EACH to represent a product type EACH in Oracle E-Business Suite. 1SYNC uses the ProductType EA to identify EACH items. To map these two values, create a record in TRADE_ITEM_DESCRIPTOR_DVM.xml with the value BASE_UNIT_OR_EACH in the EBIZ column and the value EA in the GDSN column.
-
UNIT_OF_MEASURE_DVM.xml
Map between the UOM codes used in the Oracle E-Business Suite and the 1SYNC UOM codes.
Unit of Measure Code Example
Define a UOM code of KILOG to represent the unit of measure kilogram in Oracle E-Business Suite. 1SYNC uses the UOM code KG to identify kilograms. To map these two values, create a record in UNIT_OF_MEASURE_DVM.xml with the value KILOG in the EBIZ column and the value KG in the GDSN column.
-
Primary_UOM_Code_DVM.xml
Map between the PrimaryUOMCode codes used in Oracle E-Business Suite and the 1SYNC ProductType codes.
Note: You can also update the Oracle codes Item Description, Lifecycle ,Lifecycle Phase, and Status from 1SYNC codes. The following bullets explain how:
-
The 1SYNC code "Short Description" defaults to the Oracle code "Item Description". If "Short Description" is null, then the 1SYNC code "Product Description" defaults. If "Product Description" is also null, then the 1SYNC code "Item Number" (GTIN Name) defaults to the Oracle code "Item Description".
-
To default values from 1SYNC to Oracle for the Oracle code Item Lifecycle, Lifecycle Phase, and Status, you have the option to use the user hook EGO_IMPORT_USER_HOOKS.Default_LC_and_Item_Status. You can write custom code to update the Item Open Interface table (MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE) from this user hook. Data in the interface table is imported during the item import process. See: Managing Item Imports, Oracle Product Information Management User's Guide.
Related Topics
For a list of 1SYNC code values, refer to 1SYNC_Data_Recipient_XML_Guide_R6.1v2.pdf, available for download from 1SYNC. Contact 1SYNC at http://www.1sync.org/home.html.
Mapping Categories Between GPC Alternate Catalogs and Item Catalogs
Map the alternate catalog category (ACC) to the item catalog category (ICC) that you created to maintain the items received from 1SYNC. When the items are received from 1SYNC, BPEL uses this mapping to identify the ICC to which the items belong in PIM. This also enables you to run the match rules defined for the ICC.
-
Navigate to the Setup Workbench. Click the Item Catalog Categories tab.
-
Click the Catalog Category Mapping link.
-
Click Create to create a new mapping.
-
Enter the Name of the mapping.
-
Specify the Source Catalog. This is the Catalog that has the alternate catalog category with GPC codes.
-
Specify the Item Catalog as the Target Catalog.
-
Check the Enabled flag. This activates the mapping.
-
In the Mappings region, click Add Another Row.
-
Specify the From Category. This is the alternate catalog category with GPC codes.
-
Specify the To Category. This is the ICC that has the attribute groups and pages created for 1SYNC items.
-
If you want to map more alternate categories to different/same ICCs, click Add Another Row and repeat the previous two steps.
-
Click Apply.