Supply Chain Plan Exception Messages
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of Exception Messages
- Viewing Exceptions
- Understanding Exceptions
- Exception Diagnosis and Resolution
Overview of Exception Messages
The planning engine issues exception messages (exceptions) to:
-
Alert you to a situation that may need your intervention, for example, a past due sales order
-
Recommend that you perform an action, for example, change the date of a supply order
The planning engine issues certain exceptions for all plan types and others for only certain plan types.
The planning engine only issues exceptions against items and resources that have exception sets assigned to them.
You can consider exception messages and recommendations when you:
-
Run plans
-
Review plans
When running plans, you can:
-
Set plan options that make your plans consistent with your company business practices.
-
Run them for a single plant or for an entire supply chain.
-
Run them with no material and resource constraints, with some material and resource constraints, and with optimization objectives (for example, profit, inventory turns, customer service, and overloading resources).
When reviewing plans, you can:
-
Search for specific exceptions (for example, exceptions that relate to a specific buyer or item)
-
View exceptions grouped by type
-
Drill down to related exceptions and detailed supply and demand information
-
Run simulations to test improved plan suggestions
-
Use Oracle Workflow to notify employees and trading partners of specific exception and to create automatic resolution actions
Exception Groups and Exception Messages Summary
Oracle Advanced Planning and Scheduling displays exception messages by exception group. An exception group is a group of exception messages that deal with a common issue.
This section lists the exception groups and the exception messages in each exception group.
Late sales orders and forecasts
-
Sales order/forecast at risk
-
Past due sales orders
-
Past due forecast
-
Late replenishment for sales order
-
Late replenishment for forecast
-
Early replenishment for sales order
-
Early replenishment for forecast
Supply problems for late sales orders and forecasts
-
Sales order/forecast at risk due to resource shortage
-
Sales order/forecast at risk due to material shortage
-
Requirement causes resource overload
-
Order causes supplier capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
-
Order with insufficient lead time
-
Requirement with insufficient lead time
-
Order lead time constraint
-
Requirement lead time constraint
-
Demand quantity not satisfied
-
Late supply pegged to forecast
-
Late supply pegged to sales order
-
Order violates a business calendar
Material and resource capacity
-
Material constraint
-
Resource constraint
-
Resource overloaded
-
Supplier capacity overloaded
-
Resource underloaded
-
Batch was started with less than minimum capacity
-
Batch was started with more than maximum capacity
Transportation and distribution
-
Transportation resource constraint
-
Transportation resource's weight overloaded
-
Transportation resource's volume overloaded
Shortages and excess
-
Items with a shortage
-
Items below safety stock
-
Items with excess inventory
Reschedules
-
Past due orders
-
Orders to be rescheduled out
-
Orders to be cancelled
-
Orders to be rescheduled in
-
Orders with compression days
-
Orders scheduled to next inventory point
-
Order is firmed late
-
Requirement is firmed late
-
Order is firmed early
-
Requirement is firmed early
-
Shared supply scheduled late
Substitutes and alternates used
-
Planned order uses alternate BOM/routing
-
Planned order uses substitute components
-
Planned order uses alternate resources
-
Order sourced from alternate facility
-
Order sourced from alternate supplier
-
Demand satisfied using end item substitution
Projects/tasks
-
Items with a shortage in a project/task
-
Items allocated across projects/tasks
-
Items with excess inventory in a project/task
Item exception
-
Items with negative starting on hand
-
Items with expired lot
-
Items with no activity
-
Sourcing split percentage violated
Recommendations
-
Batches
-
Discrete jobs
-
Flow schedules
-
Jobs
-
Purchase requisitions
Exception Sets
Use planning exception sets in the source instance to specify sensitivity controls and exception time periods for exceptions.
The fields in the exception set are not item and resource attributes but they act as if they are. Define as many planning exception sets as you need for your different types of items and resources (use the Planning Exception Sets form). Then, assign exception sets to items and resources.
The planning engine only issues exceptions against items and resources that have exception sets assigned to them.
Sensitivity controls control the quantity and percent thresholds for exception messages. For example, setting Excess Quantity to 3000 limits reporting of excess to situations in which supply exceeds demand by 3000.
Exception time period types control the time period for exceptions. For example, setting shortage exceptions to Planning time fence limits reporting of shortage to those situations in which the shortage is within the planning time fence.
Creating and Updating Exception Sets
Before creating and updating exception sets, study the exception messages. When the description of an exception message indicates that it is subject to exception set values, consider sensitivity controls and time periods that make sense for your business.
To create and update exception sets
-
Navigate to the Planning Exception Sets window.
-
Create or select a planning exception set name.
-
Enter sensitivity controls except User-Defined Time Fence (Days).
-
Select exception time period types.
If you selected User-defined time fence in any of the fields, specify the length of the time fence in days in User-Defined Time Fence (Days).
-
Save your work.
Assigning Planning Exception Sets
To assign a planning exception set to an item, navigate to the Items form, MPS/MRP Planning attribute group, Exception Set field.
To assign a planning exception set to a resource:
-
Navigate to the Departments form, click Resources, and view the Resources form
-
Navigate to the Owned region, Planning tabbed region, Exception set field
-
Assigning Planning Exception Sets
To assign a planning exception set to an item, navigate to the Items form, MPS/MRP Planning attribute group, Exception Set field.
To assign a planning exception set to a resource:
-
Navigate to the Departments form, click Resources, and view the Resources form
-
Navigate to the Owned region, Planning tabbed region, Exception set field
Viewing Exceptions
Overview
View exception messages in the Planner Workbench. For more information, see Overview of Planner Workbench.
To view exceptions
-
In the Navigator pane, choose a plan for which to view exception messages. You can view exception messages at the item level by selecting an item in the Items or Organization tree.
-
In the right pane, navigate to the Actions tabbed region to access the Exception Summary window.
Exception Summary Window
The Exception Summary window displays summary exception message information:
-
Generated by the current planning run
-
Saved from previous simulation runs
It displays the following information:
-
Action Type: The exception group
-
Version
-
Count: The exception message count by exception group
The window orders the exception groups by their typical importance to troubleshooting; for example, late orders are more important than recommendations.
Using the Find window, you can sort, group, or subtotal exceptions according to various criteria, for example, item, supplier, and buyer.
-
Exception Summary Window
The Exception Summary window displays summary exception message information:
-
Generated by the current planning run
-
Saved from previous simulation runs
It displays the following information:
-
Action Type: The exception group
-
Version
-
Count: The exception message count by exception group
The window orders the exception groups by their typical importance to troubleshooting; for example, late orders are more important than recommendations.
Using the Find window, you can sort, group, or subtotal exceptions according to various criteria, for example, item, supplier, and buyer. If you group by organization, item, planner code, resource, category, department, customer, or supplier, the results window displays their column headings. For other group by criteria, the results window displays a generic column heading, for example, Group By 1.
To sort exceptions
-
Navigate to the Exception Summary and select View > Find.
The Find Actions window displays.
-
Select criteria by which to sort exceptions.
-
Select Display Message Count.
-
Click Find.
To view exception details
-
Navigate to the Exception Summary window and place the cursor over the exception group or the exception message.
-
Double click on the entity to access the Exception Details window.
Exception Details Window
The Exception Details window displays information about each exception. If you select one exception type, the window displays information in a folder for that exception type. If you select multiple exception types, the window displays the generic default folder.
Days Late applies to the Late replenishment for forecast and Late replenishment for sales order exception messages.
Quantity Satisfied By Due Date is the portion of a demand that can be satisfied by the due date.
Buttons
On the Exception Details window, you can obtain additional information about certain exceptions by clicking buttons on the bottom. The buttons that appear are unique to the exception.
Right Mouse Options
From the Exception Details window, you can obtain additional information by right-clicking on the exception. The choices in the pop-up menu are unique to the exception. Some choices are:
-
Supply
-
Demand
-
Resource Availability
-
Resource Requirements
-
Sources
-
Destinations
-
Related Exceptions
-
Gantt Chart
-
Horizontal Plan
-
Vertical Plan
-
End Item Supplies
-
End Pegged Supplies
-
Critical Activities
Related Exceptions
If you are working in a constrained or optimized plan, you can use the right mouse option Related Exceptions to obtain further cause and effect information, for example:
-
Is an order late because of a resource, material, or transportation resource constraint.
-
Does a material, resource, or transportation resource issue cause late orders?
From a resource, material, or transportation resource constraint exception message, you drill down to Late replenishment for sales order and Late replenishment for forecast exception messages that the constraint affects.
Exception Message Filters
Use exception message filters to view only the exception messages that you want to. You can create and save queries that specify certain exception messages and certain criteria. When you execute this query, the planning engine displays the exception messages that meet your criteria.
For example, you may want to view the Late replenishment for sales order and Late replenishment for forecast exception messages if the shipment of item A from organization M1 is delayed by more than two days.
You can filter on exception messages issued both by Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning and Oracle Collaborative Planning.
To filter exception messages
-
In the Planner Workbench, click the Queries tabbed region.
-
In Plan, select the plan that you want to query.
-
To create a query for you to use (personal query), right-click Personal Queries and select Create Query. To create a query for you and others to use (public query), right-click Public Queries and select Create Query.
You can also right-click Personal Queries or Public Queries and then click the Create Query icon.
-
In the Create Query window:
Specify the Query Name.
In Query Type, select Exceptions. You can use the other choices to create queries that filter item, resource, and supplier information.
If the query is personal and you want to make it public, in Public, select Yes. If the query is public and you want to make it personal, in Public, select No.
-
In the Exceptions region, select the exception messages that you want to view.
You can filter on most but not all planning engine exception messages. To include Oracle Collaborative Planning exception messages, set profile option MSC: Configuration to APS + CP.
The query results display the exception messages in the order that they appear in this region. If you want to change the order of the exception messages, use the arrows on the right of the region to rearrange them.
-
For some exception messages, you can specify selection criteria. The query selects occurrences of the exception message that match the criteria.
If you want the query to display its results grouped by criteria, select Group By for those criteria. For example, you group the exception message Late replenishment from supplier by supplier. Your query displays the number of Late replenishment from supplier exception messages against each supplier.
To clear the criteria and start over, click Clear.
-
To save the query, click Save or Save as.
To delete existing saved query criteria, click Delete.
-
Click Execute. The query results appear in the right pane.
To view the results of a previously executed query, in Executed Query, select its name.
To re-execute a saved query, search for it in the left pane under Personal Queries and Public Queries.
-
To view exception details, right-click the exception message and select Exceptions All, Exception Action Taken, or Exception No Action Taken. The Exception Details window appears.
To research Oracle Collaborative Planning exception messages, click More Details. To research planning engine exceptions, click the remaining buttons.
Understanding Exceptions
-
The circumstances under which the planning engine issues each exception message
-
Where appropriate, the calculation of key attributes of the exception message
-
Where appropriate, a scenario illustrating the exception message
-
The information shown for each exception message
-
Resolution suggestions for the exception message
The exception message explanations for Constrained - Enforce Due Dates and Constrained - Enforce Capacity Constraints plans assume that both plan options Material Constraints and Capacity Constraints are selected. Note the behavior of constrained and optimized plans that have either or both options cleared:
-
Resource or material capacity does not cause late orders.
-
Lead time still can cause a late order.
-
The planning engine still reports resource and material capacity overloads.
Late Sales Orders and Forecasts Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Sales order/forecast at risk | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Past due sales orders | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3: Past due forecast | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4: Late replenishment for sales order | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5: Late replenishment for forecast | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 6: Early replenishment for sales order | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 7: Early replenishment for forecast | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 8: Late Replenishment for MPP/MPS Demands | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 9: Changes recommended for sales orders | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1: Sales order/forecast at risk
Explanation
This exception message appears when demands are at risk. A demand is at risk when it is pegged to a supply order against which the planning engine has issued certain exception messages. These certain exception messages are in the Supply Problems for Late Sales Orders and Forecasts exception group and you can use them for further information about the sales order or forecast at risk:
-
Sales order/forecast at risk due to resource shortage
-
Sales order/forecast at risk due to material shortage
-
Requirement causes resource overload
-
Order causes supplier capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
-
Order with insufficient lead time
-
Requirement with insufficient lead time
-
Order lead time constraint
-
Requirement lead time constraint
-
Demand quantity not satisfied
-
Late supply pegged to forecast
-
Late supply pegged to sales order
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message all refers to the demand line and is:
-
Order Number
-
End Item
-
End Item Org
-
End Item Description
-
Order Due Date
-
Order Quantity
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Demand Class
Resolution Suggestions
Check for more details from related exceptions in the Supply Problems for Late Sales Orders and Forecasts exception group.
2: Past due sales orders
Explanation
This exception message appears for past due sales order lines. A past due sales order line is a sales order line with a schedule date earlier than the plan horizon start date.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: The sales order line warehouse
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Old Date: The sales order line schedule date
-
Date: The sales order line schedule date
-
Quantity
Resolution Suggestions
Consider revising the sales order line schedule date.
3: Past due forecast
Explanation
This exception message appears for late forecast entries. A late forecast entry is a forecast entry with a date earlier than the plan horizon start date. The planning engine issues this message even if the forecast is totally consumed.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number: The forecast entry line number
-
Old Date: The forecast entry due date
-
Date: The forecast entry due date
-
Quantity: The forecast entry netted quantity
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Deleting the entry from the forecast
-
Revising the forecast due date
4: Late replenishment for sales order
Explanation
This exception message appears in a constrained plan when the planning engine detects that the supplies for a sales order line are due later than the sales order line.
The demand satisfied date is the latest due date of the supplies pegged directly to an end demand. The planning engine issues this exception message against a sales order line when its demand satisfied date is later than its schedule date.
This exception usually occurs because of a material constraint, resource constraint, or planning time fence. It often occurs in Constrained - Enforce capacity constraint plans when the planning engine needs to move supply order due dates to honor capacity constraints.
For example, there is a sales order line on item A due 25 January for quantity 100 in organization D2
The supplies pegged to this sales order line are:
-
Supply 1: Quantity 50 and due date 23 January
-
Supply 2: Quantity 20 and due date 25 January
-
Supply : Quantity 30 and due date 27 January
Demand satisfied date is 27 January (from Supply 3).
Days late is 2.
Quantity satisfied by sales order line schedule date is 70 (from Supply 1 and Supply 2).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: Sales order line warehouse
-
End Item: For the sales order line
-
Quantity: For the sales order line
-
Order Number: For the sales order line
-
Priority: For the sales order line
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Demand Date: Sales order line schedule date
-
Demand Satisfied Date
-
Days Late: Demand Satisfied Date - Demand Date
-
Quantity Satisfied by Due Date: The quantity of on time and early supply orders pegged directly to the sales order line. This appears if you set profile option MSO: Allow Partial Demand Completion to All End Demands or to Sales Orders.
Resolution Suggestions
In the Planner Workbench, Exception Details window, sort the orders by your priority, for example, days late or demand priority.
For each exception, right click on it, select Related Exceptions, and view the constraint.
See Identifying Root Causes of Late Demandfor more information.
Consider:
-
Revising demand priority rules
-
Revising the sales order line demand priority
-
Expediting the supply order
-
Revising the sales order line schedule date or forecast entry date
5: Late replenishment for forecast
Explanation
This exception message appears in a constrained plan when the planning engine detects that the supplies for a forecast entry are due later than the forecast entry.
The demand satisfied date is the latest due date of the supplies pegged directly to an end demand. The planning engine issues this exception message against a forecast entry when its demand satisfied date is later than its schedule date.
This exception usually occurs because of a material constraint, resource constraint, or planning time fence. It often occurs in Constrained - Enforce capacity constraint plans when the planning engine needs to move supply order due dates to honor capacity constraints.
For example, there is a forecast entry on item A due 25 January for quantity 100 in organization D2.
The supplies pegged to this forecast entry are:
-
Supply 1: Quantity 50 and due date 23 January
-
Supply 2: Quantity 20 and due date 25 January
-
Supply : Quantity 30 and due date 27 January
Demand satisfied date is 27 January (from Supply 3).
Days late is 2.
Quantity satisfied by forecast entry due date is 70 (from Supply 1 and Supply 2).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: For the forecast entry
-
End Item: For the forecast entry
-
Quantity: Unconsumed quantity for the forecast entry
-
Order Number: Forecast entry line number
-
Priority: For the forecast entry
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Demand Date: Forecast entry date
-
Demand Satisfied Date
-
Days Late: Demand Satisfied Date - Demand Date
-
Quantity Satisfied by Due Date: The quantity of on time and early supply orders pegged to the forecast. This appears if you set profile option MSO: Allow Partial Demand Completion to All End Demands or to Sales Orders.
Resolution Suggestions
See 4: Late replenishment for sales order resolution suggestions in this topic.
6: Early replenishment for sales order
Explanation
This exception message appears in a constrained plan when the planning engine detects that the supplies for a sales order line are due earlier than the sales order line.
The demand satisfied date is the latest due date of the supplies pegged directly to an end demand. The planning engine issues this exception message against a sales order line when its demand satisfied date is earlier than its schedule date.
The planning engine issues the message even if it plans the supply earlier due to constraints.
For example, there is a sales order line on item A due 25 January for quantity 100 in organization D2.
The supplies pegged to this sales order line are:
-
Supply 1: Quantity 50 and due date 19 January
-
Supply 2: Quantity 20 and due date 21 January
-
Supply 3: Quantity 30 and due date 23 January
Demand satisfied date is 23 January (from Supply 3).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: Sales order line warehouse
-
End Item: For the sales order line
-
Quantity: For the sales order line
-
Order Number: For the sales order line
-
Priority: For the sales order line
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Demand Date: Sales order line schedule date
-
Demand Satisfied Date
-
Item Description
Resolution Suggestions
If you are implementing Just-In-Time scheduling, use this exception to help minimize inventory carrying cost by identifying causes of early replenishment, for example:
-
Organization receiving calendar restrictions: For example, supplier delivers once a week.
-
Resource load levelling
-
Firm supplies
7: Early replenishment for forecast
Explanation
This exception message appears in a constrained plan when the planning engine detects that the supplies for a forecast entry are due earlier than the forecast entry.
The demand satisfied date is the latest due date of the supplies pegged directly to an end demand. The planning engine issues this exception message against a forecast entry when its demand satisfied date is earlier than its schedule date.
The planning engine issues the message even if it plans the supply earlier due to constraints.
For example, there is a forecast entry on item A due 25 January for quantity 100 in organization D2.
The supplies pegged to this forecast entry are:
-
Supply 1: Quantity 50 and due date 19 January
-
Supply 2: Quantity 20 and due date 21 January
-
Supply 3: Quantity 30 and due date 23 January
Demand satisfied date is 23 January (from Supply 3).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: Forecast entry organization
-
End Item: For the forecast entry
-
Quantity: For the forecast entry
-
Order Number: Forecast entry line number
-
Priority: For the forecast entry
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Demand Date: Forecast entry date
-
Demand Satisfied Date
-
Item Description
-
Demand Class
Resolution Suggestions
See 4: Early replenishment for sales order resolution suggestions in this topic.
8: Late replenishment for MPP/MPS demands
Explanation
The Late Replenishment for MPP/MPS Demands exception is generated when the MRP detects that the supply is going to miss the required dependent demand due date.
It alerts MRP users when supplies are going to miss due dates driven by the MPS or MPP.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Order Number
-
Item
-
Org
-
Due Date
-
Quantity
Resolution Suggestion
Review the Days Late on this exception. You can opt to:
-
Ignore it if the Days Late is not significant
-
Pull in the supply that is feeding the firmed MPP/MPS supply and resolve the lateness. In order to do this, you may need to add a resource or supplier capacity to make the pull in of this supply a feasible action.
-
Push out the MPP/MPS supply to a later date in the MPP/MPS plan. In the next run of this plan (the MRP Plan), the demand will appear at a later date and will be satisfied on time.
9: Changes recommended for sales orders
Explanation
This exception message is generated each time there is a change in the following entities:
-
Source Organization
-
Material availability date
-
Schedule arrival date
-
Ship method
You can double click on the sales order recommendation provided in the Exception Summary window to open the Demand window for sales order lines with release recommendations.
You can right click from the exception and select the following:
-
Demand
-
Supply/Demand
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item
-
Description
-
Sales order number with reference to line number
-
Customer/customer site
-
Old source organization
-
New source organization
-
Old schedule date (Suggested due date)
-
New schedule date (Demand satisfied date)
-
Old schedule arrival date
-
New schedule arrival date
-
ATP override flag
-
Latest acceptable days
-
Request ship date
-
Request arrival date
-
Promise ship date
-
Promise arrival date
Resolution Suggestion
Release recommendations to execution system.
Supply Problems for Late Sales Orders and Forecasts Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Sales order/forecast at risk due to resource shortage | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| 2: Sales order/forecast at risk due to material shortage | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| 3: Requirement causes resource overload | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 4: Order causes supplier capacity overload | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5: Order causes transportation weight capacity overload | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 6: Order causes transportation volume capacity overload | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 7: Order with insufficient lead time | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 8: Requirement with insufficient lead time | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 9: Order lead time constraint | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 10: Requirement lead time constraint | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 11: Demand quantity not satisfied | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 12: Late supply pegged to forecast | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 13: Late supply pegged to sales order | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 14: Order violates a business calendar | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1: Sales order/forecast at risk due to resource shortage
Explanation
This exception message appears when the scheduled resource capacity in a planning time bucket is overloaded and indicates that end demands may be at risk due to a resource capacity shortage. The planning engine looks at all make supplies within the bucket (according to their operation schedules), finds their end orders and issues this exception message against those end orders.
For example, there is a sales order on Item A for quantity 100 due on 17 January.
An unconstrained plan creates supply to satisfy this demand using lead-times and applying order modifiers. The planned order is on Item B which has a resource requirement on resource R1 for 10 hours on 10-January.
On 10-January, the cumulative available capacity for resource R1 is 1000 hours and the required capacity is 1200 hours (which includes this resource requirement as well as resource requirements from other supplies pegged to end demands). The planning engine issues a Resource overloaded exception message.
The planning engine issues this Order at risk due to resource shortage for the sales order due on 17 January as well as each of the other end demands pegged to resource R1 on 10 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: The supply organization
-
Resource
-
Dept/Line
-
From Date: The start date of the resource overload
-
To-Date: The end date of the resource overload
-
End Order Number: For the end demand
Some of the information fields for this exception message could be blank; this is normal behavior.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting the top level independent demand date
-
Increasing resource availability:
-
Hours available
-
Resource units assigned to the operation
-
Work and non-work days
-
-
Using an alternate resource: Change the resource in the supply order routing.
-
Using an alternate routing for this item
-
Modifying the sourcing rules
-
Subcontracting
-
Using substitute items: Change the supply order bill of material.
-
Change shift pattern
-
Add capacity: For example, additional workday.
-
Levelling the resource
2: Sales order/forecast at risk due to material shortage
Explanation
This exception message appears when the scheduled supplier capacity in a planning time bucket is overloaded and indicates that an end demand is at risk due to a material shortage. The planning engine looks at all buy supplies within the bucket (according to their dock dates), finds their end orders and issues this exception message against those end orders.
For example, there is a sales order on Item A for quantity 100 due on 17 January.
An unconstrained plan creates supply to satisfy this demand using lead-times and applying order modifiers. The planned order is on Item C, dock date 10-January, quantity 150, and supplier SUPP1.
On 10 January, the cumulative available capacity for SUPP1/Item C is 1000 units and the required capacity is 1200 units (which includes this supply as well as other supplies pegged to end demands). The planning engine issues a Supplier capacity overloaded exception message.
The planning engine issues this Order at risk due to material shortage for the sales order due on 17 January as well as each of the other end demands pegged to SUPP1/Item C on 10 January.
Information Displayed
View this exception message from Planner Workbench tree Suppliers.
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: The supply organization
-
Item: The item with the material shortage
-
Date: The end demand due date
-
End Order Number: The end demand order number
-
Supplier
-
Supplier Site
Some of the information fields for this exception message could be blank; this is normal behavior.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting the sales order schedule date
-
Adjusting the supplier capacity: In the Planner Workbench left pane, right-click Supplier and select Supplier Capacity.
-
Using an alternate supplier: Change the supplier in the sourcing rule
-
Using a substitute item: Change the supply order bill of material
-
Increasing the supplier flexfence capacity tolerance percentage
-
Changing end order quantity
-
Modifying the sourcing rule: For example, sourcing percentage
-
Producing the supply order yourself
3: Requirement causes resource overload
Explanation
This exception message appears when, during scheduling a make order, the planning engine detects a resource requirement that causes a resource capacity overload.
This exception message also appears when the setting for the profile option MSO: Maximize Search of Availability Intervals is incorrect. For more details, see MSO Profile Options.
When an operation fails scheduling, the planning engine uses profile options MSO: Pull push base and MSO: Pull push offset to determine the time by which it pulls or pushes the operation when attempting to reschedule. If the planning engine is scheduling:
-
Backwards, it is the time backwards (pulling delay)
-
Forwards, it is the time forwards (pushing delay)
MSO: Pull push base is the numerical base by which the offset is multiplied to get each delay (it has no unit of measure and the default is 1)
MSO: Pull push offset is the numerical offset (it is in minutes and the default is 1440)
The delay is calculated by i * base (i-1) * offset where i is the rescheduling attempt that it is calculating. For example, with backward scheduling and the default values, the pulling delays are:
-
Delay for first rescheduling attempt: 24 hours earlier [1 * 1 * 1440 = 1440 / 60]
-
Delay for second rescheduling attempt: 48 hours earlier [1 * 2 * 1440 = 2880 / 60]
-
Delay for third rescheduling attempt: 72 hours earlier [1 * 3 * 1440= 4320 / 60]
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Supply Order Number: The order number that contains the overloading resource requirement.
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Start Date: The start date of the time bucket in which the overloading activity falls.
-
End Date: The end date of the time bucket in which the overloading activity falls.
-
Resource Requirements: The required capacity of the overloading activity within the time bucket.
-
Resource Overload: The amount by which the resource capacity in the time bucket is overloaded after scheduling the overloading requirement.
-
Resource Name
-
Organization
-
Department
-
Resource Sequence Number: In the routing.
-
Operation Sequence Number: In the routing.
-
Resource Capacity: The resource available capacity in the bucket before scheduling of the overloading requirement.
-
Cause: This contains the cause of the overload. This attribute is only populated when this exception is generated in Enforce Capacity Constraints plans. Valid values are:
-
Exceeded maximum number of attempts to schedule: This means that the planning engine tried for the specified number of attempts set in MSO: Maximum Number of Pushes for Operation. If all the attempts to schedule proved to be unsuccessful, it goes back to the time slot corresponding to the first attempt to schedule, and schedules the activity there with an overload on the resource. Each time the planning engine is required to search for a new spot to schedule, it looks ahead by a certain time period that is dictated by the settings of the profile MSO: Push Pull Base and MSO: Push Pull Offset.
Each unit or bucket in the number of attempts made is determined by using the following formula:
Time Window = N * a*b^N
Where:
N = A value incremented from 1 to MAX in increments of 1 where MAX is the value set in the profile MSO:Max Num of Pushes for Operation.
a = the value set in the profile MSO: Push Pull Offset; measured in minutesa = the value set in the profile MSO: Push Pull Offset; measured in minutes
b = the value set in the profile MSO: Push Pull Base; default is 1. The planning engine searches in intervals of time that increase in a linear fashion.
-
Firm Resource Requirement: If a resource requirement's start/end are firmed, the planning engine is forced to schedule this requirement at the user specified time. This can sometimes cause an overload if this requirement has been firmed at a time where there is no capacity available on the resource. In such cases, the cause column indicates this condition.
-
Pegged to Firm Resource Requirement / Supply: A resource requirement is forced to be scheduled at a certain time because it pegs to another firm order or a resource requirement. This can severely restrict the planning engine's span of search for available capacity to schedule this resource requirement and force an overload.
-
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding increasing available capacity or decreasing required capacity
-
Selecting and implementing options.
4: Order causes supplier capacity overload
Explanation
This exception message appears when, during scheduling a buy order, the planning engine detects an order that causes a supplier capacity overload.
Information Displayed
View this exception message from Planner Workbench tree Suppliers.
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Bucket Start Date: The start date of the time bucket in which the overloading order falls.
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Organization
-
Due Date
-
Dock Date
-
Required Supplier Capacity: The required capacity of the overloading order within the time bucket.
-
Supplier Capacity Overload: The amount by which the cumulative available supplier capacity is overloaded after scheduling the overloading order.
-
Supplier Name
-
Supplier Site
-
Cumulative Available Capacity: The cumulative available supplier capacity before scheduling the overloading order.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding increasing available capacity or decreasing required capacity
-
Selecting and implementing options.
5: Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
Explanation
This exception message appears when, during scheduling a transfer order, the planning engine detects a transportation weight capacity overload.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Bucket Start Date: The start date of the time bucket in which the overloading shipment falls.
-
Supply Order Number
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Ship Date
-
Shipment Weight
-
Shipment Weight UOM
-
Weight Capacity overload: The amount by which this shipment causes the available weight capacity to be overloaded.
-
Ship Method
-
Source Org
-
Destination Org
-
Available Weight Capacity/Day: The available weight capacity on Ship Date before scheduling of the overloading shipment.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding increasing available capacity or decreasing required capacity
-
Selecting and implementing options.
6: Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
Explanation
This exception message appears when, during scheduling a transfer order, the planning engine detects a transportation volume capacity overload.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Bucket Start Date: The start date of the time bucket in which the overloading shipment falls.
-
Supply Order Number
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Ship Date
-
Shipment Weight
-
Shipment Weight UOM
-
Weight Capacity overload The amount by which this shipment causes the available volume capacity to be overloaded
-
Ship Method
-
Source Org
-
Destination Org
-
Available Weight Capacity/Day: The available volume capacity on Ship Date before scheduling of the overloading shipment.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding increasing available capacity or decreasing required capacity
-
Selecting and implementing options.
7: Order with insufficient lead time
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine schedules a supply order within a window whose size is less than the minimum duration of the supply order.
The planning engine issues this message if either of the following situations exist:
-
Constrained Plan - Enforce Due Date and Optimized Plan - Enforce Due Date: Profile option MSO: Lead Time Control is to Violate minimum processing time to meet demand due date and there is not enough lead-time to meet the demand.
-
Constrained Plan - Enforce Due Date, Optimized Plan - Enforce Due Date, Constrained Plan - Enforce Capacity Constraints, and Optimized Plan - Enforce Capacity Constraints: A supply is firmed early and the upstream orders need to be compressed.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Supply Order Number: The order number of the order with insufficient lead-time
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Order Type
-
Supplier: For buy orders.
-
Supplier Site: For buy orders.
-
Source Org: For transfer orders.
-
Ship Method: For transfer orders.
-
Order Start Time: For make orders, the start time; for buy orders, the dock date; and for transfer orders, the ship date.
-
Order Completion Time: The due date.
-
Minimum Lead Time: The minimum lead-time Required to avoid the compression.
-
Actual Lead Time: Order Completion Time - Order Start Time. This represents the compressed duration as seen in the plan output.
-
Minimum Start Time: The minimum start time of this supply order.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
That the supply may be behind schedule
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Either expediting work on the supply or adjusting the demand due date
8: Requirement with insufficient lead time
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine schedules a resource requirement in either of these ways:
-
Within a window whose size is less than the minimum duration of the resource requirement.
-
To start earlier than the earliest start time of its operation according to the planning time fence and other upstream precedence constraints
The planning engine issues this message if either of the following situations exist:
-
Constrained Plan - Enforce Due Date and Optimized Plan - Enforce Due Date: Profile option MSO: Lead Time Control is to Violate minimum processing time to meet demand due date and there is not enough lead-time to meet the demand.
-
Constrained Plan - Enforce Due Date, Optimized Plan - Enforce Due Date, Constrained Plan - Enforce Capacity Constraints, and Optimized Plan - Enforce Capacity Constraints: A supply is firmed early and the upstream requirements need to be compressed.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Supply Order Number: The order number of the supply order that contains this resource requirement with insufficient lead-time.
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Order Type
-
Op-Seq: Operation sequence in the routing.
-
Res-Seq: Resource sequence in the routing.
-
Department: The department of the resource that contains this resource requirement
-
Resource: The resource that contains this resource requirement.
-
Start Time: Of the resource requirement.
-
Completion Time: Of the resource requirement.
-
Minimum Lead Time: Based on the maximum assigned units in the routing.
-
Actual Lead Time: Completion Time - Start Time. Represents the compressed duration of this resource requirement
-
Minimum Start Time: Of the Resource Requirement.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
That the supply may be behind schedule
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Either expediting work on the supply or adjusting the demand due date
9: Order lead time constraint
Explanation
This exception is generated in Enforce Capacity Constraints plans. It is generated when the lead-time of an order is the cause for a demand being satisfied late. The exception specifies the minimum lead-time required for the order as well as the actual lead-time that is available if the demand is to be satisfied on time. The actual lead-time will be less than the minimum lead-time indicating that a lead-time compression is required to meet the demand on time. Since, this is an Enforce Capacity Constraints plan, Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning will not actually compress the lead-time. Instead, it will satisfy the demand late and issue the Order Lead Time Constraint exception. This exception is generated for make orders without a routing, buy orders and transfer orders.
The planning engine:
-
Issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes
-
Does not issue this exception message if the plan planning mode is Constrained (Without Detailed Scheduling)
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Supply Order Number: This is the order number of the supply that has the lead-time constraint.
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Order Type
-
Due Date
-
Supplier: For buy supplies.
-
Supplier Site: For buy supplies.
-
Source Org: For transfer supplies.
-
Ship Method: For transfer supplies.
-
Required Start Time: For make orders, the start time; for buy orders, the dock date; and for transfer orders, the ship date.
-
Required Completion Time: The due date.
-
Minimum Lead Time: The minimum lead-time for this order.
-
Actual Lead Time: Required Completion Time - Required Start Time.
-
Minimum Start Time: The earliest time that this order can start.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
That the supply may be behind schedule
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Either expediting work on the supply or adjusting the demand due date
10: Requirement lead time constraint
Explanation
This exception is generated in Enforce Capacity Constraints plans. It is generated when the lead-time of a resource requirement is the cause for a demand being satisfied late. The exception specifies the minimum lead-time required for the resource requirement as well as the actual lead-time that is available if the demand is to be satisfied on time. The actual lead-time represents the processing time as dictated by the usage specified in the routing definition. The actual lead-time will be less than the minimum lead-time indicating that a lead-time compression is required to meet the demand on time. Since, this is an Enforce Capacity Constraints plan, Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning will not actually compress the lead-time. Instead, it will satisfy the demand late and issue the Requirement Lead Time Constraint exception. This exception is generated for Resource Requirements for Make Orders with Routings specified.
The planning engine issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Supply Order Number: The supply order that contains this resource requirement.
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Order Type
-
Op-Seq: Operation sequence in the routing.
-
Res-Seq: Resource sequence in the routing.
-
Department: The Department of the resource that is on the resource requirement.
-
Resource: The resource that contains this resource requirement.
-
Required Start Time: Of the resource requirement so as to meet the demand on time.
-
Required Completion Time: Of the resource requirement so as to meet the demand on time.
-
Minimum Lead Time: Based on the maximum assigned units in the routing.
-
Actual Lead Time: Required Completion Time - Required Start Time
-
Minimum Start Time: Of the resource requirement.
-
Start Date: The planned start date of the resource requirement.
-
End Date: The planned completion date of the resource requirement.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
That the supply may be behind schedule
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Either expediting work on the supply or adjusting the demand due date
11: Demand quantity not satisfied
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine finds any demand pegged to supplies and the supply quantities are less than the demand quantity. The planning engine issues this exception message for demands at all levels of the supply chain bill of materials.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item: On the supply.
-
Item Description
-
Order Number
-
Organization
-
Demand Quantity
-
Demand Order Type
-
Due Date
-
Demand Class
-
Customer
-
Customer site
-
Quantity Mismatch: Demand quantity - Total pegged supply quantity
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Checking and evaluating the end demand information
-
Finding other sources of supply for the demand or adjusting the demand due date
12: Late supply pegged to forecast
Explanation
This message appears when a supply due date is later than the demand due date to which it is pegged; the demand can be independent demand or dependent demand (which will eventually peg to a forecast). This usually occurs because of lead-times and time fences.
Refer to the example for the Late supply pegged to sales order exception message, the planning engine issues this Late supply pegged to forecast exception message in bucket 15 against the planned order pegged to the dependent demand and forecast in bucket 12.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: For the supply order
-
End Item: Forecast entry item
-
Quantity: For the supply order
-
Order Number: The forecast entry line number
-
Priority
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Due Date: For the supply order
-
Demand Date: The demand due date
-
End Demand Date: The forecast entry due date
-
Days Late: Due Date - Demand Date. This calculation uses calendar days rather than manufacturing calendar working days.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Expediting the late supply
-
Adjusting the forecast entry date
13: Late supply pegged to sales order
Explanation
This message appears when a supply due date is later than the demand due date to which it is pegged; the demand can be independent demand or dependent demand (which will eventually peg to a sales order). This usually occurs because of time fences.
For example, there are forecasts at organization D1 on item A for quantity 50 on day 7 and quantity 30 on day 12.
Organizations D1 and M1 have two days transit time between them.
The planning engine creates dependent demand at organization M1 on item A for quantity 50 on day 7 and quantity 30 on day 12.
There are sales orders at organization M1 on Item A for quantity 50 on day 9 and quantity 30 on day 14.
Total demand at organization M1 on Item A is 160.
There is a discrete job at organization M1 on Item A for quantity 100 on day 5.
Because of lead-times and time fences, the first day available to create a planned order at organization M1 on Item A is day 15.
The planning engine creates a planned order at organization M1 on Item A for quantity 60 on day 15 and pegs it to the:
-
Dependent demand on day 12
-
Sales order on day 12
The planning engine issues a Late supply pegged to sales order exception message with:
-
Due date of Day 15 (supply order)
-
Demand date of Day 12 (sales order)
-
End demand date of Day 12 (sales order)
-
Days late of 3 (Day 15 - Day 12)
The planning engine issues a Late supply pegged to forecast exception message with:
-
Due date of Day 15 (supply order)
-
Demand date of Day 12 (dependent demand)
-
End demand date of Day 14 (forecast)
-
Days late of 3 (Day 15 - Day 12)
Schedule Entity 1 ... 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Org D1: Forecasts - - - - - - 50 - - - - 30 - Org M1: Dependent demand - - - - 50 - - - - 30 - - - Org M1: Sales orders - - - - 50 - - - - 30 - - - Org M1: Supply orders - 100 - - - - - - - - - - Org M1: Planned orders - - - - - - - - - - - - 60
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: For the supply order
-
End Item: Sales order line item
-
Quantity: For the supply order
-
Order Number: For the sales order
-
Priority
-
Customer
-
Customer Site
-
Due Date: For the supply order
-
Demand Date: The demand due date
-
End Demand Date: The sales order line due date
-
Days Late: Due Date - Demand Date. This calculation uses calendar days rather than manufacturing calendar working days.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Expediting the late supply
-
Adjusting the sales order line schedule date
14: Order violates a business calendar
Explanation
The planning engine issues this exception message against buy orders, make orders, transfer orders, sales orders, and forecasts (entities) that have dates that are non-workdays of the following calendars (violates the calendar). For make orders with routings, the planning engine does not issue this exception message for resource requirements that violate calendars:
-
Shipping calendar: The dates that a shipments can start from a supplier or source organization
-
Receiving calendar: The dates that a customer or destination organization can receive shipments
-
Intransit calendar: The dates that a carrier or other shipment service operates
-
Supplier capacity calendar: The dates that a supplier operates and has processing time and capacity available. Start dates and processing times of buy orders must respect this calendar
-
Organization manufacturing calendar: The dates that a work center operates and has capacity available. The order and due dates of make orders must respect this calendar.
Each entity can have only one exception message. If the entity violates multiple calendars, the exception message lists all of the calendars that it violates.
For example, 1 January for organization M is a non-workday on the receiving calendar. There is a purchase order shipment due to organization M on 1 January. When the plan runs, the planning engine issues this exception message against the purchase order shipment.
This exception message is related to exception message Sales order/forecast at risk.
Information Displayed
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Source Organization: For transfer orders.
-
Order Type: For buy orders and transfer orders, Planned Order, Purchase Requisition, or Purchase Order. For make orders, Planned Order or Discrete Job. For sales orders, Sales Order. For forecasts, Forecast.
-
Order Number: For buy orders and transfer orders, planned order, purchase requisition, or purchase order number. For make orders, planned order or discrete job number. For sales orders, sales order number. For forecasts, forecast name.
-
Supplier: For buy orders.
-
Supplier Site: For buy orders.
-
Customer: For sales orders and forecasts.
-
Customer Site: For sales orders and forecasts.
-
Organization: For buy orders, the receiving organization. For transfer orders, the destination organization. For make orders without a routing, the make at organization. For sales orders and forecasts, the shipping organization.
-
Order Date
-
Order Start Date
-
Order Due Date
-
Order Dock Date: For buy orders and transfer orders.
-
Order Ship Date; For forecasts, the forecast date. For sales orders, the suggested ship date. For buy orders, the ship date from the supplier. For transfer orders, the ship date from the source organization.
-
Calendar: All calendars that the entity violates.
-
Order Quantity
-
Ship Method: For sales orders, forecasts, buy orders, and transfer orders.
Resolution Suggestion
Change the date of the entity.
Arrange for work on the non-workday.
Material and Resource Capacity Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
For cells that contain (1), note that orders with compression days and overloaded exceptions (resource overloaded, supplier capacity overloaded, and transportation resource overloaded) are generated for constrained and optimized plans only when there are firm supplies in the plans or if you select the Enforce Demand Due Dates plan option.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Material constraint | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Resource constraint | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3: Resource overloaded (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4: Supplier capacity overloaded (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 5: Resource underloaded | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 6: Batch was started with less then minimum capacity | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 7: Batch was started with more than maximum capacity | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 8: Operation Hard Link Violation | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
1: Material constraint
Explanation
This exception message appears when a demand due date needs to be pushed out due to either:
-
Lead time violation
-
Supplier capacity constraint
If there are also Resource constraint exception messages for this end demand, you may also need to provide adequate resource capacity.
The planning engine:
-
Issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes
-
Does not issue this exception message if the plan planning mode is Constrained (Without Detailed Scheduling)
Lead time violation
It occurs for lead-time violation when there is not enough time to obtain the material. For buy items with lead-times and for make items with no routings and lead-times, the planning engine uses total lead-time. The overload is the quantity.
For example, today is 12-December, there is a demand for 5 on 20-December, and the total lead-time is 10 days.
Supplier capacity constraint
It occurs for supplier capacity constraint when there is not enough supplier capacity to purchase the buy item by a certain date. The certain date is the Latest possible completion time (LPCT) - the item post-processing lead-time, including breaks and delivery calendars.
You can see the amount of supplier capacity that you need to add at different suppliers during different time periods in order to satisfy a demand on time. If there are Resource constraint exception messages for an end demand, you may also need to provide adequate resource capacity.
Supplier capacity is available at 0000 hours each work day according to the owning organization manufacturing calendar. The planning engine accumulates supplier capacity for a plan:
-
From the launch date, if you launch the plan on a work day at 0000 hours
-
From the next working day after the launch date, if you launch the plan on a non-work day or on a work day after 0000 hours
While the horizontal plan accumulates the available and required capacities from the beginning, the exception process begins accumulating them again on the day after it issues an exception message.
Since supplier capacity is global, the planning engine issues these exceptions to the owning organization.
The calculation of overload is Required Quantity - Cumulative Available Quantity.
The calculation for Cumulative Available Quantity is Cumulative supplier capacity - Cumulative quantity already used by other supplies. The amount already used depends on previously scheduled supplies.
For example, supplier capacity is 25 units per day.
The plan start date is 3 January.
The planning engine needs to purchase 100 units on 5 January.
The cumulative available supplier capacity on 5 January is 75 units.
If the planning engine suggested a supply order to meet the demand, it would overload supplier capacity by 25 units (100 required - 75 available). However, an Enforce Capacity Constraints plan with Material selected cannot overload supplier capacity. The planning engine:
-
Moves the supply and dependent demand to a later date where supplier capacity is available
-
Issues this Material constraint exception message with overload of 25 units
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Supplier
-
Supplier Site
-
Supply Order Number
-
Order Type
-
Quantity
-
Due Date
-
Dock Date
-
Bucket Start Date: The date of the overload. (For this exception, there is no end date.)
-
Required Capacity
-
Cumulative Available Capacity: At Bucket Start Date before scheduling.
-
Overload
Resolution Suggestions
Check to see if these exceptions cause Late replenishment for sales order or Late replenishment for forecast exception messages; right click the exception message and select Related Exceptions.
In the Planner Workbench, Exception Details window, sort the Late replenishment for sales order and Late replenishment for forecast exception messages by your priority, for example, days late or demand priority.
Check to see if a resource capacity issue caused early processing of the supply order resulted in the material constraint.
Consider:
-
Adjusting sales order line schedule date
-
Adjusting forecast entry date
-
Adjusting supplier capacity
-
Using an alternate supplier
-
Using a substitute component: In unconstrained plans, make a manual substitution.
-
Arranging and recording new substitute items
-
Increasing supplier flexfences
-
Changing the sales order or forecast quantity
-
Modifying the sourcing rule: For example, change sourcing percentage
-
Changing lead-time
2: Resource constraint
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects unavailability of resource capacity for a specific time period because of the capacity requirements of an end demand. The overload is the amount of resource capacity needed.
The planning engine:
-
Issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes
-
Does not issue this exception message if the plan planning mode is Constrained (Without Detailed Scheduling)
When the planning engine performs resource/task allocation for an order, it first tries to schedule demands backward from the demand due dates. If there is not enough resource availability in a planning time bucket for it to schedule an activity to meet the demand due date, it generates this Resource constraint exception for the planning time bucket.
Since the order failed backward scheduling, the planning engine forward schedules the order from the plan start date to realistically allocate the resources/tasks. Therefore, the actual resource requirements may be later than the dates on the exception.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: When the planning engine determines the window in which it wants to schedule the operation, it schedules the operation in that window with an overload if necessary.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: When the planning engine determines the window in which it wants to schedule the operation, it determines if there would be an overload if it schedules the operation.
If there would not be any resource overload, the planning engine does not issue the exception.
If there would be a resource overload, the planning engine issues the exception and reports the quantity of the resource constraint as the quantity reported in the exception message. For example, an end demand may have the following resource constraints associated with it:
-
Resource 1: Constraint dates 5 January to 6 January, overload 4 hours
-
Resource 2: Constraint dates 7 January to 8 January, overload 2 hours
-
Resource 1: Constraint dates 21 January to 27 January, overload 22 hours
You can see the amount of capacity that you need to add at different resources during different time periods in order to satisfy the demand on time. If there are also Material constraint exception messages for this end demand, you may also need to provide adequate supplier capacity.
Information Displayed
-
Resource
-
Organization
-
Department
-
Supply Order Number: Of the operation and resource.
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Op-seq. number
-
Res-Seq number
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the resource is overloaded.
-
To Date: The end date of the planning time bucket in which the resource is overloaded.
-
Resource Requirement
-
Resource Capacity: The available capacity of the resource before scheduling the resource.
-
Overload: Resource Capacity - Resource Requirement after scheduling the resource.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting sales order line schedule date
-
Increasing your resource availability:
-
Increase hours available per unit (overtime)
-
Increase the resource assigned units
-
Increase work days (overtime)
-
Changing shift pattern
-
-
Using an alternate resource
-
Using an alternate routing
-
Modifying the sourcing rules
-
Subcontracting
-
Using substitute items (with different resources)
3: Resource overloaded
Explanation
This exception message appears when, in a planning time bucket, both:
-
The resource required capacity is more than the resource available capacity
-
The load ratio is more than the exception set Over-utilization
The amount of overload is the minimum duration of the operation for the maximum assigned units of the routing. Load ratio is a percent and its calculation is (Required Capacity/Available Capacity) * 100.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: Since the planning engine holds the due dates, the material and resources that support them can contribute to resource overload.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints, the message typically appears only if there are firm supplies or firm operation start or end dates. Typically, these plans change due dates to avoid overloading resources but since the supplies and operation dates are firm, they can contribute to resource overload.
For example, resource R1 has available capacity of 24 hours day (one resource unit for three shifts) on the three daily planning buckets 3 January, 4 January, and 5 January.
The supplies that use resource R1 are:
-
S1: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 3 January 12:00, end 4 January 12:00
Requirements 24 hours
-
S2: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 4 January 0:00, end 4 January 10:00
Requirements 10 hours
-
S3: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 4 January 12:00, end 5 January 12:00
Requirements 24 hours
The exception set Over-utilization for resource R1 is 0 (report load ratios over 100).
Based on the task start and due dates, the planning engine schedules the resource requirements as follows:
-
S1: 12 hours on 3 January and 12 hours on 4 January
-
S2: 10 hours on 4 January
-
S3: 12 hours on 4 January and 12 hours on 5 January
The daily resource requirements are:
-
3 January: 12 hours
4 January: 34 hours
5 January: 12 hours
Required capacity exceeds available capacity on 4 January. The planning engine issues this Resource overloaded exception on 4 January with load ratio 142 ((34 / 24) * 100).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Resource
-
Dept/Line
-
Start Constraint Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the resource is overloaded
-
End Constraint Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket in which the resource is overloaded. As long as Load Ratio remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the End Constraint Date.
-
Load Ratio
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Using resolution suggestions for the Resource constraint exception message
-
Adjusting the exception set Over-utilization
4: Supplier capacity overloaded
Explanation
This exception message appears when, in a planning time bucket, the supplier required capacity is more than the supplier available capacity.
The amount of overload is Required capacity - Cumulative available capacity of that bucket. Load ratio is a percent and its calculation is (Required Quantity/Cumulative Available Quantity) * 100.
Since supplier capacity is global, the planning engine issues these exceptions to the owning organization. You can only view this exception in the plan's owning organization.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Unconstrained: Since unconstrained plans assume infinite capacity, the planning engine may issue many instances of this exception. If profile option MSC: Enable Enhanced Sourcing is Yes, unconstrained plans first exhaust supplier capacity from rank 1 suppliers and then use supplier capacity from rank 2 suppliers.
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: The planning engine issues this exception if overloading the supplier capacity is the only way to meet the demand date.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: The planning engine issues this exception when firm supply orders and their lower-level component firm supply orders overload the supplier capacity.
For example, supplier A available capacity on days 2 through 10 is 1 per day.
Days 6 and 7 are non-work days.
There are planned orders for buy item B which the planning engine sources from supplier A:
-
Dock date day 1, quantity 5
-
Dock date day 3, quantity 12
-
Dock date day 9, quantity 23
The planning engine issues the following Supplier capacity overloaded exception messages:
-
On day 1, the load ratio is 500 (5 * 100) Since there is no available quantity on day 1, this calculation does not include it.
-
On day 3, the load ratio is 200 (12/(1*2) * 100). There are two days of suppler capacity available since the previous Supplier capacity overloaded exception message on day 1 (days 2 and 3).
-
On day 9, the load ratio is 575 (23/(1*4) *100). There are four days of suppler capacity available since the previous Supplier capacity overloaded exception message on day 3 (days 4, 5, 8, and 9).
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization: The owning organization
-
Item
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the supplier capacity is overloaded
-
To Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket in which the supplier capacity is overloaded. As long as Load Ratio remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the To Date.
-
Supplier
-
Supplier Site
-
Load Ratio: The planning engine does not carry supplier capacity overloads from one planning time bucket to the next.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Using resolution suggestions for the Material constraint exception message
-
Adjusting the exception set Over-utilization
5: Resource underloaded
Explanation
This exception message appears when, in a planning time bucket, both:
-
The resource required capacity is less than the resource available capacity
-
The load ratio is the same as or lower then than the exception set Over-utilization.
Load ratio is a percent and its calculation is (Required Quantity/Cumulative Available Quantity) * 100.
For example, resource R1 has available capacity of 24 hours day (one resource unit for three shifts) on the three daily planning buckets 3 January, 4 January, and 5 January.
The supplies that use resource R1 are:
-
S1: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 3 January 12:00, end 4 January 12:00
Requirements 24 hours
-
S2: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 4 January 0:00, end 4 January 10:00
Requirements 10 hours
-
S3: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Start 4 January 12:00, end 5 January 12:00
Requirements 24 hours
The exception set Under-utilization for resource R1 is 60 (report load ratios of 60 or less).
Based on the task start and due dates, the planning engine schedules the resource requirements as follows:
-
S1: 12 hours on 3 January and 12 hours on 4 January
-
S2: 10 hours on 4 January
-
S3: 12 hours on 4 January and 12 hours on 5 January
The daily resource requirements are:
-
3 January: 12 hours
-
4 January: 34 hours
-
5 January: 12 hours
The planning engine detects that on both 3 January and 5 January the load ratio is 50 ((12 / 24) * 100) which is lower than the exception set Under-utilization. It issues this Resource underloaded exception for each of those days.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Resource
-
Dept/Line
-
Start Constraint Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the resource is underloaded.
-
End Constraint Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket in which the resource is underloaded. As long as Load Ratio remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the End Constraint Date.
-
Load Ratio
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting the exception set Under-utilization
-
Increasing the workload
-
Decreasing available capacity
-
Shifting resources to other work centers
-
Processing rework
-
Executing special projects
-
Balancing the loads across planning time buckets
6: Batch was started with less than minimum capacity
Explanation
This exception message appears when the resource has batching parameters.
The planning engine creates batches that meet the resource minimum batch quantity within the batching window. It converts the quantities of all orders into the unit of measure of the batching resource.
If it cannot find enough orders within the batching window whose quantities make up the minimum batch quantity, it creates the batch with less than the minimum quantity and issues this exception.
For example, batching resource R1 has characteristics:
-
Minimum batch capacity: 30
-
Maximum batch capacity: 100
-
Batch capacity unit of measure: M3 (cubic meters)
-
Batching window size: 3 days
-
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 15 KG
-
Volume: 4 F3 (cubic feet)
The planning engine schedules supply orders for item A and its resource R1:
-
S1: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Quantity 100
Volume = 11.34 M3
Needs to be scheduled on 3 January
-
S2: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Quantity 80
Volume 9.07 M3
Needs to be scheduled on 5 January
-
S3: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Quantity 250
Volume 28.35 M3
Needs to be scheduled on 7 January
The planning engine schedules a batch on 3 January with S1.
The batch size is now 11.34 M3.
It schedules S2 as follows:
-
Sets S2's batching window relative to its scheduling date: S2's scheduling date is 5 January so the batching window is from 2 January to 8 January.
-
Searches within the batching window for an existing batch that still has room: The batch with S1 (started on 3 January) is within S2's batching window.
-
Moves in S2 to 3 January and combines it with S1 in the same batch.
The batch size is now 20.41 M3 (11.34 M3 + 9.07 M3).
It schedules S3 as follows:
-
Sets S3's batching window relative to its scheduling date: S3's scheduling date is 7 January so the batching window is from 4 January to 10 January.
-
Searches within the batching window for an existing batch that still has room. There are no existing batches within S3's batching window.
-
Creates a separate batch containing only S3 then continues scheduling other supplies.
There are no other supplies for the planning engine to schedule.
The batch size for the batch started on 3 January is 20.41 and the minimum batch capacity is 30. The planning engine issues this Batch was started with less than minimum capacity exception message against the batch started on 3 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Batch Number
-
Resource
-
Dept/Line
-
Min Capacity: The minimum batch capacity in the unit of measure of the item's volume
-
Max Capacity: The maximum batch capacity in the unit of measure of the item's volume
-
From Date: The batch start date
-
To Date: The batch finish date.
-
Load Ratio: Required Capacity/Maximum Batch Capacity
-
Required Capacity: For all activities in the batch in the unit of measure of the item's volume
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Reducing the number of days in the planning time fence: Rather than creating new batches, the planning engine adds orders to batches and moves in later orders to meet the minimum batch capacity.
-
Increasing the size of the batching window: The planning engine has more candidates from which to select for the batches.
-
Unfirming firm orders: The planning engine does not pre-process them into batches.
7: Batch was started with more than maximum capacity
Explanation
This exception message appears when the resource has batching parameters and the planning engine creates a batch with more than the maximum quantity. It occurs when:
-
There are firm orders
-
The only way to meet a demand due date in a Constrained - Enforce due dates plan is to violate the maximum batch capacity
-
The only way to meet a demand due date in a Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints plan with Resource Constraint selected and Material Constraint cleared is to violate the maximum batch capacity
The planning engine converts the quantities of all orders into the unit of measure of the batching resource.
For example, batching resource R1 has characteristics:
-
Minimum batch capacity: 30
-
Maximum batch capacity: 100
-
Batch capacity unit of measure: M3 (cubic meters)
-
Batching window size: 3 days
-
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 15 KG
-
Volume: 4 F3 (cubic feet)
The planning engine converts item A volume from 4 F3 to 0.1134 M3.
The planning engine schedules supply orders for item A and its resource R1:
-
S1 - firm: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Quantity 600
Volume = 68.04 M3
Needs to be scheduled on 5 January
-
S2 - firm: Operation sequence 10, resource sequence 10
Quantity 600
Volume 68.04 M3
Needs to be scheduled on 5 January
The planning engine schedules a batch on 5 January with S1. It cannot change the date of a firm supply order to move it into another batch.
The batch size is now 68.04 M3.
The planning engine schedules adds S2 to the batch started on 5 January. It cannot change the date of a firm supply order to move it into another batch and cannot start another batch.
The batch size is now 136.08 M3 (68.04 M3 + 68.04 M3).
There are no other supplies for the planning engine to schedule.
The batch size for the batch started on 5 January is 136.08 and the maximum batch capacity is 100. The planning engine issues this Batch was started with more than maximum capacity exception message against the batch started on 5 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Batch Number
-
Resource
-
Dept/Line
-
Min Capacity: The minimum batch capacity in the unit of measure of the item's volume
-
Max Capacity: The maximum batch capacity in the unit of measure of the item's volume
-
From Date: The batch start date
-
To Date: The batch finish date
-
Load Ratio: Required Capacity/Maximum Batch Capacity
-
Required Capacity: For all activities in the batch in the unit of measure of the item's volume
Resolution Suggestions
Consider unfirming some firm orders. Rather than violating the maximum batch capacity, the planning engine will move unfirm orders to another date.
8: Operation Hard Link Violation
Explanation
This exception message appears when a user-defined operation minimum time offset, maximum time offset, or item shelf life days cannot be respected due to firming of requirements or orders. It can also appear when a negative minimum time offset or a negative maximum time offset is violated because of the upstream operation start time boundary.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is: .....
-
From
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Supply order number
-
Operation sequence number
-
Resource sequence number
-
-
To
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Supply order number
-
Operation sequence number
-
Resource sequence number
-
-
Minimum time offset
-
Maximum time offset
-
Shelf life days
-
Actual offset
Resolution Suggestions
Navigate to the Supply/Demand window or the Resource Requirements window to identify causes and possible solutions.
Transportation and Distribution Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
For cells that contain (1), note that orders with compression days and overloaded exceptions (resource overloaded, supplier capacity overloaded, and transportation resource overloaded) are generated for constrained and optimized plans only when there are firm supplies in the plans or if you select the Enforce Demand Due Dates plan option.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Transportation weight constraint | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Transportation volume constraint | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3: Transportation resource's weight overloaded (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4: Transportation resource's volume overloaded (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1: Transportation weight constraint
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects unavailability of transportation weight capacity for a specific time period because of the capacity requirements of supplies pegged to an end demand. The overload is the amount of extra resource capacity needed.
The planning engine issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes.
The plan parameter Resource Capacity includes the transportation resources. In an enforce capacity constraints plan with Resource Constraints cleared and Material Constraints selected, the planning engine may calculate transportation weight load and issue exception messages.
If you do not want to use transportation weight capacity as a constraint, either leave its definitions blank (the planning engine assumes infinite capacity) or enter a large amount. Since a large amount affects plan performance, we recommend leaving its definitions blank.
The calculation for overload is Required Capacity - Available Capacity.
For example, transportation resource TR1 has characteristics:
-
Weight capacity: 100 LB per day
-
Volume capacity = 100 F3 (cubic feet)/day
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 1 LB
-
Volume: 1 F3 (cubic feet)
There is a shipment of item A1 for quantity 1000 on 3 January from organization M1 to organization M2.
The planning engine detects not enough transportation weight capacity on 3 January. In an enforce capacity constraint plan, the planning engine moves the shipment to dates on which there is enough transportation capacity.
The planning engine:
-
Accumulates available transportation weight capacity
-
Schedules the shipment on 13 January
-
Issues this Transportation weight constraint exception message for 3 January with overload 900 (1000 required - 100 available)
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
To Organization: Destination organization
-
From Organization: Source organization
-
Ship Method
-
Constraint Date
-
Overload
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting your transportation resource capacity
-
Using a different ship method
-
Using a different shipping calendar
2: Transportation volume constraint
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects unavailability of transportation volume capacity for a specific time period because of the capacity requirements of supplies pegged to an end demand. The overload is the amount of extra resource capacity needed.
The planning engine issues this exception if profile option MSO: Calculate Constraint Exceptions is Yes.
The plan parameter Resource Capacity includes the transportation resources. In an enforce capacity constraints plan with Resource Constraints cleared and Material Constraints selected, the planning engine may calculate transportation volume load and issue exception messages.
If you do not want to use transportation volume capacity as a constraint, either leave its definitions blank (the planning engine assumes infinite capacity) or enter a large amount. Since a large amount affects plan performance, we recommend leaving its definitions blank.
The calculation for overload is Required Capacity - Available Capacity.
For example, transportation resource TR1 has characteristics:
-
Weight capacity: 100 LB per day
-
Volume capacity = 100 F3 (cubic feet)/day
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 1 LB
-
Volume: 1 F3 (cubic feet)
There is a shipment of item A1 for quantity 1000 on 3 January from organization M1 to organization M2.
The planning engine detects not enough transportation volume capacity on 3 January. In an enforce capacity constraint plan, the planning engine moves the shipment to dates on which there is enough transportation capacity.
The planning engine:
-
Accumulates available transportation capacity
-
Schedules the shipment on 13 January
-
Issues this Transportation volume constraint exception message for 3 January with overload 900 (1000 required - 100 available)
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
To Organization: Destination organization
-
From Organization: Source organization
-
Ship Method
-
Constraint Date
-
Overload
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting your transportation resource capacity
-
Using a different ship method
-
Using a different shipping calendar
3: Transportation resource's weight overloaded
Explanation
This exception message appears when, in a planning time bucket, the transportation resource required weight capacity is more than the transportation resource available weight capacity.
The plan parameter Resource Capacity includes the transportation resources. In an enforce capacity constraints plan with Resource Constraints cleared and Material Constraints selected, the planning engine may calculate transportation resource load and issue exception messages.
If you do not want to use transportation capacity as a constraint, either leave its definitions blank (the planning engine assumes infinite capacity) or enter a large amount. Since a large amount affects plan performance, we recommend leaving its definitions blank.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Unconstrained: The planning engine issues this exception frequently because unconstrained plans do not consider transportation capacity.
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: The planning engine issues this exception if overloading the transportation resource capacity is the only way to meet the demand date.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: The planning engine issues this exception when firm jobs overload the transportation capacity.
The calculation for:
-
Transportation resource required weight capacity is Shipment quantity * Item weight
-
Utilization percent is (Required Capacity/Available Capacity) * 100
For example, transportation resource TR1 has available weight capacity of 100 LB per day.
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 1 LB
-
Volume: 1 F3 (cubic feet)
There is a shipment of item A1 for quantity 1000 of Item A1 on 3 January from organization M1 to organization M2.
In an unconstrained plan, the planning engine:
-
Schedules this shipment on 3 January to satisfy the demand on time
-
Issues this Transportation resource's weight overloaded exception message with overload is 900 (1000 required - 100 available)
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Constraint Start Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the transportation resource weight constraint occurs.
-
Constraint End Date: The end date of the planning time bucket in which the transportation resource weight constraint occurs.
-
Supply Order Number: Of the transfer supply.
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Ship Date
-
Shipment Weight
-
Shipment Weight UOM
-
Weight Capacity overload
-
Ship Method
-
Source Org
-
Destination Org
-
Available Weight Capacity/Day: The available weight capacity on Ship Date before scheduling of the overloading shipment.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting your transportation resource capacity
-
Using a different ship method
-
Using a different shipping calendar
4: Transportation resource's volume overloaded
Explanation
This exception message appears when, in a planning time bucket, the transportation resource required volume capacity is more than the transportation resource available volume capacity.
The plan parameter Resource Capacity includes the transportation resources. In an enforce capacity constraints plan with Resource Constraints cleared and Material Constraints selected, the planning engine may calculate transportation resource load and issue exception messages.
If you do not want to use transportation capacity as a constraint, either leave its definitions blank (the planning engine assumes infinite capacity) or enter a large amount. Since a large amount affects plan performance, we recommend leaving its definitions blank.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Unconstrained: The planning engine issues this exception frequently because unconstrained plans do not consider transportation capacity.
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: The planning engine issues this exception if overloading the transportation resource capacity is the only way to meet the demand date.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: The planning engine issues this exception when firm jobs overload the transportation capacity.
The calculation for:
-
Transportation resource required volume capacity is Shipment quantity * Item volume
-
Utilization percent is (Required Capacity/Available Capacity) * 100
For example, transportation resource TR1 has available volume capacity of 100 F3 per day.
The physical attributes of item A are:
-
Weight: 1 LB
-
Volume: 1 F3 (cubic feet)
There is a shipment of item A1 for quantity 1000 of Item A1 on 3 January from organization M1 to organization M2.
In an unconstrained plan, the planning engine:
-
Schedules this shipment on 3 January to satisfy the demand on time
-
Issues this Transportation resource's volume overloaded exception message with overload is 900 (1000 required - 100 available)
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Constraint Start Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the transportation resource volume constraint occurs.
-
Constraint End Date: The end date of the planning time bucket in which the transportation resource volume constraint occurs.
-
Supply Order Number: Of the transfer supply.
-
Order Type
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Ship Date
-
Shipment Volume
-
Shipment Volume UOM
-
Volume Capacity overload
-
Ship Method
-
Source Org
-
Destination Org
-
Available Volume Capacity/Day: The available volume capacity on Ship Date before scheduling of the overloading shipment.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Adjusting your transportation resource capacity
-
Using a different ship method
-
Using a different shipping calendar
Shortages and Excess Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Items with a shortage | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Items below safety stock | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3: Items with excess inventory | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1: Items with a shortage
Explanation
This exception message appears when projected available balance for a planning bucket is negative and is within the exception set Shortage Exceptions exception time period. Projected available balance is Previous bucket projected available balance + Sum of supply quantities with due date in this planning time bucket - Sum of demand quantities with due date (excluding safety stock demand) in this planning time bucket.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Unconstrained: The planning engine can peg late supplies to demands at any level in the supply chain. Therefore, you can see item shortages in several levels of the supply chain bill of material.
-
Unconstrained, Constrained - Enforce due dates, Optimized - Enforce due dates: The planning engine can compress lead-times and violate planning time fences to meet demands. Item shortages typically occur when there are firm orders whose due dates are too late to meet the demand.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: The demands are most likely independent (because the planning engine pushes out dependent demand due dates). Due to lead-time, planning time fence, resource capacity constraints, or supplier capacity constraints, the supply due dates are later than the end demand due date.
For example, item A1 in organization M1 has the following demands and supplies in daily buckets:
-
3 January
Beginning available (on hand) balance 0.
Planned order 1: Quantity 100
Planned order 3: Quantity 200
Discrete job 1: Quantity 300
Planned order demand 1 (dependent demand): Quantity 250
Forecast demand 1: Quantity 200
-
4 January
Planned order 4: Quantity 100
Planned order demand 2 (dependent demand): Quantity 250
Forecast demand 2 = 200
-
5 January
No demands or supplies
-
6 January
Planned order 5: Quantity 200
This table shows the horizontal view of this scenario.
| Schedule Entity | Beg | 3 January | 4 January | 5 January | 6 January |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirements | - | 450 | 450 | 0 | 0 |
| Supply orders | - | 300 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Planned orders | - | 300 | 100 | 0 | 200 |
| Projected available balance | 0 | 150 | (200) | (200) | 0 |
The planning engine issues this Item with a Shortage exception message for quantity -200 from 4 January to 5 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Quantity: Projected available balance
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the negative projected available balance occurs.
-
To Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket in which the negative projected available balance occurs. As long as Quantity remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the To Date.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Expediting the late supply
-
Adjusting the sales order schedule date
2: Items below safety stock
Explanation
This exception message appears when projected available balance for a planning bucket is below the specified safety stock level for the planning bucket. Projected available balance is Previous bucket projected available balance + Sum of supply quantities with due date in this planning time bucket - Sum of demand quantities with due date in this planning time bucket. See Safety Stock.
The planning engine does not consult the exception set for the item.
For example, there are sales orders at organization M1 on item A for quantity 200 past due and quantity 150 in bucket 4.
Item A has safety stock level 73 for buckets 1 to 3 and 45 for bucket 4.
There is a planned order for item A for 395 in bucket 4.
The planning engine creates an Items below safety stock exception for buckets 1 to 3. The planned order in bucket 4 meets the sales order demands and the safety stock.
| Schedule Entity | Past | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Org M1: Sales orders | 200 | - | - | - | 150 |
| Org M1: Safety stock level | - | 73 | 73 | 73 | 45 |
| Org M1: Planned orders | - | - | - | - | 395 |
Information Displayed
The information displayed for the exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket with projected available balance below safety stock.
-
To Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket with projected available balance below safety stock. As long as Quantity remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the To Date.
-
Quantity: Projected Available Balance - Specified Safety Stock
Resolution Suggestions
Consider expediting supply orders.
3: Items with excess inventory
Explanation
The planning generates this message when projected available balance for a bucket is greater than the exception set Excess Quantity value for the item and within the exception set Excess Exceptions exception time period. Projected available balance is Previous bucket projected available balance + Sum of supply quantities with due date in this planning time bucket - Sum of demand quantities with due date in this planning time bucket.
For example, item A1 in organization M1 has exception set information:
-
Excess Quantity: 0
-
Excess Exceptions Time Period: 5 days
This table shows a horizontal view of item A1.
| Schedule Entity | Beg | 3 January | 4 January | 5 January | 6 January |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirements | - | 450 | 450 | 0 | 0 |
| Supply orders | - | 300 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Planned orders | - | 300 | 100 | 0 | 200 |
| Projected available balance | 0 | 150 | (200) | (200) | 0 |
The planning engine issues this Item with excess inventory exception message for quantity 150 on 3 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Item Description
-
Quantity: Projected Available Balance - Exception set Excess Quantity
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket with excess projected available balance
-
To Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket with excess projected available balance. As long as Quantity remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the To Date.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Canceling unneeded supply orders
-
Transferring the material to another facility
Reschedules Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
For cells that contain (1), note that orders with compression days and overloaded exceptions (resource overloaded, supplier capacity overloaded, and transportation resource overloaded) are generated for constrained and optimized plans only when there are firm supplies in the plans or if you select the Enforce Demand Due Dates plan option.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Past due orders | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2: Orders to be rescheduled out | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 3: Orders to be cancelled | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 4: Orders to be rescheduled in | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5: Orders with compression days (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 6: Orders scheduled to next inventory point | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 7: Order is firmed late | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 8: Requirement is firmed late | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 9: Order is firmed early | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 10: Requirement is firmed early | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 11: Shared supply scheduled late | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
The planning engine follows these rules when it recommends rescheduling purchase orders and purchase requisitions:
-
Purchase orders, reschedule out: The planning engine may not reschedule out purchase orders because of lead-time constraints, of insufficient capacity between plan start date and the dock date, or the order date or start date is past due. It may reschedule out purchase orders that are pegged to demands whose due dates have moved out.
-
Purchase orders, reschedule in: The planning engine may not reschedule in purchase orders within supplier lead-time or that are past due. It may reschedule in purchase orders outside supplier lead-time but the new order date must not be past due. The planning engine does not consider capacity.
-
Purchase requisitions, reschedule out: The planning engine may reschedule out purchase requisitions because of lead-time constraints, of insufficient capacity between plan start date and the dock date, the order date or start date is past due, or pegging to demands whose due dates have moved out.
-
Purchase requisitions, reschedule in: The planning engine may not reschedule in purchase requisition within supplier lead-time or are past due. It may reschedule in purchase orders outside supplier lead-time but the new order date must not be past due and the requisition must have sufficient accumulated capacity.
The planning engine must compress the lead-time for subsequent supplies and may recommend rescheduling in Constrained - Enforce demand due date plans or when a requirement for this item results from a firmed supply.
1: Past due orders
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine detects supply orders and planned orders which have order (start) dates and due dates in the past (before the planning horizon start date).
For non-firmed supply orders, the planning engine also issues an Orders to be rescheduled out exception message.
The planning engine schedules all operations of a past due order beyond the planning horizon start date. If the order is firm, the planning engine retains the order's firmed duration as it schedules all its operations beyond the planning horizon start date.
There may be dependent demand resulting from past due orders. If you clear plan option Lot for Lot, the planning engine groups the demand which results by item and creates one planned order per item (or more depending on the plan options) to meet it. If you select it, the planning engine creates one planned order for each dependent demand.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Old Date: The current due date
-
Date: The suggested due date. It is usually the planning horizon start date but it can be later if the schedules receipt is not firm and is not needed until a later planning time bucket.
-
Quantity
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Check the end item demand which causes the supply order.
Consider:
-
Changing the demand due date
-
For supply orders, expediting
-
For supply orders, cancelling
2: Orders to be rescheduled out
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine suggests that you reschedule an existing supply order (scheduled receipt) to a later date to avoid carrying excess inventory. It occurs when the planning engine detects a non-firm existing supply order with a due date that is earlier than it suggests (suggested due date).
The planning engine does not issue this recommendation for firm existing supply orders.
The planning engine continues to plan lower bill of material levels as if you accept the suggestion.
For example, item A1 at organization M1 has the following demand and supply:
-
A non-firm discrete job for quantity 100 due on 5 January
-
A sales order line for quantity 100 due on 8 January
The planning engine issues this Orders to be rescheduled out exception against the discrete job and suggests a new date of 8 January.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
From Date: The current due date
-
To Date: The suggested due date
-
Quantity
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider reviewing the recommendations for the item and then rescheduling the order out. The planning engine continues to plan lower level bills of material as if you accept the suggestion.
3: Orders to be cancelled
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine suggests that you cancel an existing supply order.
It occurs when the planning engine detects a non-firm existing supply order that you do not need to satisfy demand or safety stock requirements.
The planning engine continues to plan lower bill of material levels as if you accept the suggestion.
The following diagram shows a scenario in organization M1:
-
There is a sales order at organization M1 on Item A for quantity 100 in bucket 3.
-
There is a forecast at organization M1 on item A for quantity 100 in bucket 4.
-
There are discrete jobs at organization M1 for item A for quantity 150 in bucket 1, 50 in bucket 5, and 100 in bucket 8.
-
The planning engine pegs 100 of the supply of 150 in bucket 1 to the sales order for 100 in bucket 3. It creates an Early replenishment for sales order exception message against the supply of 150 in bucket 1.
-
The planning engine pegs 50 of the supply of 150 in bucket 1 to the forecast for 100 in bucket 4.
-
The planning engine pegs the entire supply of 50 in bucket 5 to the forecast for 100 in bucket 4. It creates an Order to be rescheduled in exception message against the supply of 50 in bucket 5 from bucket 5 to bucket 4.
-
The planning engine cannot find any demand to which to peg the supply of 100 in bucket 8. It creates an Orders to be cancelled exception message against the supply of 100 in bucket 8.
Schedule Entity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Org M1: Sales orders - - 100 - - - - - Org M1: Forecasts - - - 100 - - - - Org M1: Supply orders 150 - - - 50 - - 100
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider reviewing the recommendations for the item and then cancelling the order. The planning engine continues to plan lower level bills of material as if you accept the suggestion.
4: Orders to be rescheduled in
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine suggests that you reschedule an existing supply order to an earlier date. It occurs when the planning engine detects a non-firm existing supply order with a due date that is later than it suggests (suggested order date).
The planning engine continues to plan lower bill of material levels as if you accept the suggestion.
For example, there is a sales order at organization M1 on Item A for quantity 100 in bucket 3.
There is a forecast at organization M1 on item A for quantity 100 in bucket 4.
There are discrete jobs at organization M1 for item A for 150 in bucket 1, 50 in bucket 5, and 100 in bucket 8.
The planning engine pegs 100 of the supply of 150 in bucket 1 to the sales order for 100 in bucket 3. It creates an Early replenishment for sales order exception message against the supply of 150 in bucket 1.
The planning engine pegs 50 of the supply of 150 in bucket 1 to the forecast for 100 in bucket 4.
The planning engine pegs the entire supply of 50 in bucket 5 to the forecast for 100 in bucket 4. It creates an Order to be rescheduled in exception message against the supply of 50 in bucket 5 from bucket 5 to bucket 4.
The planning engine cannot find any demand to which to peg the supply of 100 in bucket 8. It creates an Orders to be cancelled exception message against the supply of 100 in bucket 8.
| Schedule Entity | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Org M1: Sales orders | - | - | 100 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Org M1: Forecasts | - | - | - | 100 | - | - | - | - |
| Org M1: Supply orders | 150 | - | - | - | 50 | - | - | 100 |
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
From Date: The current due date
-
To Date: The suggested due date
-
Quantity
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider reviewing the recommendations for the item and then rescheduling the order in. The planning engine continues to plan lower level bills of material as if you accept the suggestion.
5: Orders with compression days
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine detects that a supply order needs to be completed in less time that its minimum processing time in order for it to meet a demand. If the planning engine plans the order according to its lead-time, it would start in the past (before the planning horizon start date). The compression days represents all of the following:
-
The number of days of work that you need to make up on the order to respect its due date.
-
The number of days that the order would be scheduled in the past (before the planning horizon start date).
-
The number of days that the order needs to be compressed if its start date is the planning horizon start date.
To calculate compression days, the planning engine:
-
Uses the organization's manufacturing calendar
-
Backward schedules orders using item lead-time offset (for unconstrained plans) or routing level processing times (for constrained plans)
-
Finds the number of days between the order (start) date and the planning horizon start date.
A supply order with compression days at a higher level of the supply chain bill of material leads to supply orders with compression days at lower levels of the supply chain bill of material. The planning engine calculates the lower level compression days as follows:
-
For unconstrained plans: It sets each lower level dependent demand due on the planning horizon start date and backward schedules its supply order from that date. The compression days for each supply order represents the amount of compression time needed for that order alone.
-
For constrained plans: It sets each lower level dependent demand due on the start date of the supply which caused it (which is prior to the planning horizon start date) and backward schedules its supply order from that date. The compression days for each supply order represents the time difference between the order start date and the planning horizon start date. This method calculates compression for an order in relation to its higher level supply orders.
-
For example, C pegs to B which pegs to A which pegs to end demand. Lead time offset is 3 for A, B, and C. The supply order for A has 1 compression day.
In an unconstrained plan, the supply order for B has 3 (day 0 - 3 days lead-time) compression days and the supply order for C has 3 (day 0 - 3 days lead-time) compression days.
In a constrained plan, the supply order for B has 4 (day -1 - 3 days lead-time) compression days and the supply order for C has 7 (day -4 - 3 days lead-time) compression days.
There are differences among the plan types:
-
Unconstrained: The planning engine may compress existing supplies that need to be rescheduled in and planned orders if there is not enough time between the planning horizon start date and the demand date.
-
Constrained - Enforce capacity constraints and Optimized - Enforce capacity constraints: The planning engine moves out demands (other than those from firm supplies) to avoid compression the supplies pegged to the demands. It creates Late replenishment for sales orders and Late replenishment for forecast exception messages.
-
Constrained - Enforce due dates and Optimized - Enforce due dates: The planning engine may compress existing supplies and planned orders during the scheduling process while trying to meet the demand due date. In some cases, it may schedule supplies within the planning time fence.
For example, launch an unconstrained plan with plan start date of Wednesday.
The planning engine detects an unsatisfied demand for Friday and creates a planned order due on Friday.
It calculates lead-time offset for the item as three days and calculates the order date for Tuesday.
It sets the order date to Wednesday and issues this exception with one compression day.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order number
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Compression days
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider changing the demand due date to a later date. The planning engine continues to plan as if you accept the suggestion.
If the exception occurs on a transfer order, use the Supply/Demand window for visibility into the destination organization. You can take action either at the source or destination organization.
6: Orders scheduled to next inventory point
Explanation
This exception message appears for plans:
-
With items that have item attribute Planned Inventory Point selected
-
With plan option Move Jobs to PIP selected
-
In which orders are created to move inventory to the next planned inventory point
When the planning engine finds excess supply that needs to be cancelled at an upstream point that is not a planned inventory point, it:
-
Creates an order to move this supply to the downstream planned inventory point
-
Issues this Orders scheduled to next inventory point exception message
If the excess supply does not meet the criteria for this exception message, the planning engine issues an Orders to be cancelled exception.
For example, item A uses one component (C).
There are three discrete jobs on item C for quantity 50 due in bucket 10.
There are two MDS entries on item A for quantity 50 in buckets 12 and 13.
The planning engine pegs two of the discrete jobs to the MDS entries.
Since item A is a planned inventory point, the planning engine schedules the third job to item A rather than cancelling it.
| Schedule Entity | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Org M1, Item C: Discrete jobs | 50 50 50 |
- | - | - | - |
| Org M1, Item A: MDS | - | - | 50 | 50 | - |
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item: In the created order
-
Planned Inventory Point: The item marked as a PIP item at the point to which the order is scheduled
-
Date: The order due date
-
Quantity
-
Department/Line
-
Order Number
-
Resource: The resource on which the supply order is scheduled
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
This exception message is for information.
7: Order is firmed late
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine is scheduling activity Unconstrained Latest Possible Completion Times (ULPCTs) for a supply order and finds a firm supply that does not fit in with the scheduling of the non-firm operations to that point.
This diagram shows an example of the situation.
Order/requirement firmed late example
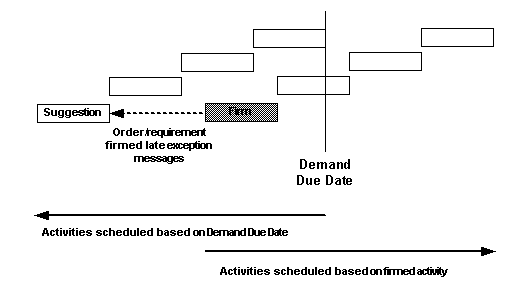
In Enforce demand date plans with profile option MSO: Lead Time Control set to Violate minimum processing times to meet demand due date, the planning engine violates precedence constraints between the firm supply and its next downstream supply.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Firm Supply Item
-
Firm Supply Item Description
-
Firm Supply Order Number
-
Firm Supply Organization
-
Source Organization: For transfer supplies.
-
Supplier: For buy supplies.
-
Supplier Site: For buy supplies.
-
Firming Type: Firm Start Date, Firm End Date, Firm Start Date and End Date, or Firm All.
-
Days Late: The number of days by which the firm supply is late according to the ULPCT calculation.
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Researching the situation that resulted in the original firming
-
Evaluating the supply schedule and the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding changing the firmness of the activity, changing the firm date of the activity, or dealing with other activities that fall outside of minimum start time and of demand due date.
-
Selecting and implementing options.
8: Requirement is firmed late
Explanation
This exception message appears in the same circumstances as exception message Order is firmed late.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Firm Supply Item
-
Firm Supply Item Description
-
Firm Supply Order Number
-
Firm Supply Organization
-
Source Organization: For transfer supplies.
-
Firm Supply Operation Sequence Number: If operation firming leads to the exception message.
-
Firm Supply Resource Sequence number: If resource firming leads to the exception message.
-
Firming Type: Firm Start Date, Firm End Date, Firm Start Date and End Date, or Firm All.
-
Days Late: The number of days by which the firm supply is late according to the ULPCT calculation.
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Researching the situation that resulted in the original firming
-
Evaluating the supply schedule and the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding changing the firmness of the activity, changing the firm date of the activity, or dealing with other activities that fall outside of minimum start time and of demand due date.
-
Selecting and implementing options.
9: Order is firmed early
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine is scheduling activity Unconstrained Earliest Possible Start Time (UEPSTs) for a supply order and finds a firm supply that does not fit in with the scheduling of the non-firm operations to that point.
This diagram shows an example of the situation.
Order/requirement firmed early example
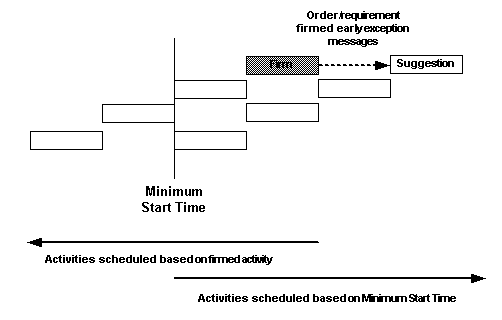
In Enforce demand date plans with profile option MSO: Lead Time Control set to Violate minimum processing times to meet demand due date, the planning engine violates precedence constraints between the firm supply and its next downstream supply.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Firm Supply Item
-
Firm Supply Item Description
-
Firm Supply Order Number
-
Firm Supply Organization
-
Source Organization: For transfer supplies.
-
Supplier: For buy supplies.
-
Supplier Site: For buy supplies.
-
Firming Type: Firm Start Date, Firm End Date, Firm Start Date and End Date, or Firm All.
-
Days Late: The number of days by which the firm supply is late according to the UEPST calculation.
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Researching the situation that resulted in the original firming
-
Evaluating the supply schedule and the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding changing the firmness of the activity, changing the firm date of the activity, or dealing with other activities that fall outside of minimum start time and of demand due date.
-
Selecting and implementing options.
10: Requirement is firmed early
Explanation
This exception message appears in the same circumstances as exception message Order is firmed early.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Firm Supply Item
-
Firm Supply Item Description
-
Firm Supply Order Number
-
Firm Supply Organization
-
Source Organization: For transfer supplies.
-
Firm Supply Operation Sequence Number: If operation firming leads to the exception message.
-
Firm Supply Resource Sequence number: If resource firming leads to the exception message.
-
Department
-
Resource
-
Firming Type: Firm Start Date, Firm End Date, Firm Start Date and End Date, or Firm All.
-
Days Late: The number of days by which the firm supply is late according to the UEPST calculation.
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Researching the situation that resulted in the original firming
-
Evaluating the supply schedule and the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding changing the firmness of the activity, changing the firm date of the activity, or dealing with other activities that fall outside of minimum start time and of demand due date.
-
Selecting and implementing options.
11: Shared supply scheduled late
Explanation
This exception appears when shared supplies get fixed at the beginning of the current slice and need to be treated as firm when scheduling demands within the current slice.
The planning engine calculates it only if profile options:
A shared supply is similar to a firm supply because, at the beginning of scheduling a slice, the planning engine treats shared supplies from previous slices as firm. A shared supply is different from a firm supply because the planning engine considers all lower level supplies of a shared supply as shared. Therefore, a shared supply can cause lateness but cannot cause compression.
For more information, see Plan Shared Supplies.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Shared Supply Item
-
Shared Supply Organization
-
Shared Supply Item Description
-
Shared Supply Order Number
-
Shared Supply Order Type
-
Supply Quantity
-
Due Date
-
Source Organization
-
Ship Method
-
Supplier
-
Supplier Site
-
Days Late: The number of days by which the shared supply is late according to the ULPCT calculation.
-
Schedule Ship Date
-
Schedule Arrival Date
-
Request Ship Date
-
Request Arrival Date
-
Promise Ship Date
-
Promise Arrival Date
Resolution Suggestions
Consider
-
Evaluating the supply schedule and the end demand information
-
Collecting and evaluating available options regarding firming the activity or splitting and rearranging supply orders to avoid a shared supply.
-
Selecting and implementing options.
Substitutes and Alternates Used Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
For cells that contains (2), note that these exceptions are not a result of decisions made by the planning engine. They are only visible in an unconstrained plan if a planner manually chosen this alternative, for example, by firming a planned order or selecting an alternate routing.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Planned order uses alternate BOM/routing | Yes (2) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Planned order uses substitute components | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3: Planned order uses alternate resources | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4: Order sourced from alternate facility | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 5: Order sourced from alternate supplier | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 6: Demand satisfied using end item substitution | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
1: Planned order uses alternate BOM/routing
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine, in a constrained or cost-based optimized plan:
-
Under the direction of a decision rule, assigns an alternate bill of material and routing to a planned order
-
Detects a firm a planned order with an alternate bill of material and routing
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Alternate BOM
-
Alternate Routing
Resolution Suggestions
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
2: Planned order uses substitute components
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine, in a constrained or cost-based optimized plan:
-
Under the direction of a decision rule, assigns a substitute component to a planned order.
-
Detects a firm a planned order with a substitute component.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Date: The due date
-
Substitute Component
-
Quantity: Of the substitute component
-
Order Number
Resolution Suggestions
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
3: Planned order uses alternate resources
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine, in a constrained or cost-based optimized plan:
-
Assigns an alternate resource to an operation of a planned order in a constrained or cost-based optimized plan
-
Detects a firm planned order that uses an alternate resource
The situation usually occurs when the primary resource becomes overloaded. The resource can exist either in the primary routing or in an alternate routing.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Dept./Line
-
Resource: The alternate
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Order Number
Resolution Suggestions
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
4: Order sourced from alternate facility
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine, in a constrained or cost-based optimized plan:
-
Under the direction of a decision rule, assigns a planned order to an alternate facility
-
Detects a firm planned order with an alternate facility assigned
An alternate facility is an organization and is not a supplier site.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: The destination organization
-
Item
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Source Org: The alternate facility
-
Supplier
-
Supplier Site
Resolution Suggestions
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
5: Order sourced from alternate supplier
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine:
-
In an unconstrained plan where profile option MSC: Enable Enhanced Sourcing is Yes, plans orders using supply capacity from rank 2 suppliers
-
In a constrained or cost-based optimized plan, under the direction of a decision rule, assigns a planned order to an alternate supplier (supplier with rank other than 1)
-
In a constrained or cost-based optimized plan, detects a firm planned order with an alternate supplier assigned
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: The owning organization
-
Item
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Source Org
-
Supplier: The alternate
-
Supplier Site: The alternate
Resolution Suggestions
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
6: Demand satisfied using end item substitution
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine plans to satisfy an end item demand using a supply order with a substitute item. The planning engine substitutes items:
-
For cost-based optimized plans
-
For any plans under the direction of substitution rules
-
If the plan option Decision Rules, End Item Substitution is selected
If the planning engine satisfies a demand with multiple planned orders, it issues an exception for each supply order with the substitute item.
For example, the substitution chain is PSS7001 > PSS7002 > PSS7003 > PSS7004. The planning engine can satisfy demand for:
-
PSS7001 using PSS7002, PSS7003, or PSS7004
-
PSS7002 using PSS7003 or PSS7004
-
PSS7003 using PSS7004
For more information, see End-Item-Level Substitution.
The planning engine calculates the quantity of the substitute using the information in the Item Relationships, Oracle Inventory User's Guide form.
For example, there is demand for PSS7002 in organization M1 for 100.
The planning engine satisfies this demand with inventory of item PSS7004 in organization M2.
The demand organization is M1 and the substitute organization is M2. The demand item is PSS7002 and the substitute item is PSS7004.
The substitute organization is the most upstream organization in the supply pegging tree of the substitute item. For example, the planning engine can:
-
Peg on hand at organization M2 to a planned order demand arising from a transfer from organization M2 to organization M1
-
Peg the transfer order to sales order demand at organization M1
Since the on hand supply is the most upstream supply, its organization is the substitute organization.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org: The demand organization
-
Item: The demand item
-
Quantity: The demand quantity
-
Order Number: If the end demand is a sales order, the sales order number; if the end demand is a forecast, blank
-
Substitute Org
-
Substitute Item
-
Substitute Qty: As specified in the item relationship.
-
Date: The due date
-
Demand class
-
Customer
-
Customer site
Resolution Suggestions
Release the substitute item to the sales order through Planner Workbench.
To enable release of substitute items, navigate to Planner Workbench Preferences window, Other tab and select Include Sales Orders.
To release substitute items:
-
Navigate to the Supply/Demand window.
-
The field Action is Release.
-
The status of the sales order does not matter for the release to happen.
-
After you release the substitution, concurrent process Release sales order recommendations runs in the source instance to make the change to the sales order.
Monitor the volume and frequency of occurrences. Many occurrences bear investigation as alternates and substitutes are often more expensive or more difficult to obtain.
Projects/Tasks Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Items with a shortage in a project/task | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2: Items allocated across projects/tasks | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 3: Items with excess inventory in a project/task | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
1: Items with a shortage in a project/task
Explanation
This exception message appears in the same circumstances as the Items with a shortage except that the planning engine only uses the supplies and demands belonging to a project and task.
If there is both a project manager and a task manager, the planning engine sends the exception message to the task manager through the exception workflow.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Date: The start date of the planning time bucket with negative project projected available balance
-
Quantity: The projected available balance
-
Planning Group
-
Project
-
Task
Resolution Suggestions
Consider reviewing and correcting supply and demand imbalances with the project and task mangers.
2: Items allocated across projects/tasks
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects a supply belonging to one project/task which is pegged to a demand belonging to another project/task. It occurs when the two projects are in the same planning group.
If there is both a project manager and a task manager, the planning engine sends the exception message to the task manager through the exception workflow.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Date: The due date
-
Quantity
-
Planning Group
-
Project: The supply project
-
Task: The supply task
-
To Project: The demand project
-
To Task: The demand task
Resolution Suggestions
This exception message is for information.
3: Items with excess inventory in a project/task
Explanation
This exception message appears in the same circumstances as the Items with excess inventory except that the planning engine only uses the supplies and demands belonging to a project and task.
If there is both a project manager and a task manager, the planning engine sends the exception message to the task manager through the exception workflow.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which there is an excess
-
Quantity: Projected Available Balance - Exception set Excess Quantity
-
Planning Group
-
Project
-
Task
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Cancelling unneeded supply orders
-
Transferring the material to another project
Item Exceptions Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Items with negative starting on hand | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2: Items with expired lot | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 3: Items with no activity | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4: Sourcing split percentage violated | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5: Items with forecast over consumptions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 6: End item minimum remaining shelf life violation | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
1: Items with negative starting on hand
Explanation
This exception message appears when the planning engine detects an item with negative beginning on-hand balance.
It usually occurs because of a recent inventory backflushing transaction or an incorrect inventory balance.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Quantity: The beginning on-hand balance
-
Date
-
Item Description
-
Lot Number
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Releasing the planned order
-
Investigating the item to rule out incorrect inventory balance or to correct an incorrect inventory balance
2: Items with expired lost
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects a potential expired lot. A potential expired lot is a lot that:
-
Has lot expiration date during the planning horizon
-
Is not pegged to a demand that results in its use before its lot expiration date
It occurs against items under lot control Full Control. The calculation for lot expiration date is Lot Receipt Date + Shelf Life Days.
In addition to issuing this exception message, the planning engine plans for you to flush the inventory on its lot expiration date so that you cannot use it after its lot expiration date to satisfy demands.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
To Organization: The organization holding the inventory
-
Item
-
Quantity
-
Item Description
Resolution Suggestions
Consider creating or modifying an actual demand to use the material.
3: Items with no activity
Explanation
This exception appears when the planning engine detects an item in an organization with no demand and no supply throughout the planning horizon. It usually occurs for:
-
Substitute components
-
Components on alternate bills of material
-
End item substitutes
Typically, these items do not have other sources of demand and the planning engine does not need to use them during the planning horizon.
If the item has no activity in multiple organizations, the planning engine issues this exception message for each organization.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
Item Description
Resolution Suggestions
Consider changing the item planning method to Not planned.
4: Sourcing split percentage violated
Explanation
This exception message appears for days when the percentages of the actual sourcing among rank 1 suppliers is different from the percentages in the sourcing rule for rank 1 suppliers. The planning engine issues the exception:
-
Against suppliers whose percentage is not satisfied
-
Only if the deviation of split percentages between the planned values and the values defined in the sourcing rule is greater than the value specified in MSC: Sourcing Variance Tolerance
The planning engine uses profile option MSO: Sourcing Allocation Window to determine the reference period of time for the variance.
The formula for calculating the actual sourcing percentage for a supplier is (Cumulative quantity sourced from supplier/Cumulative quantity sourced from rank 1 suppliers) * 100.
For example, a sourcing rule for item A1 lists two suppliers, both rank 1 with a 50%-50% split.
One supplier has a capacity of 60 units per day and the other supplier has a capacity of 40 units per day. A demand for the item is 200.
This table shows a horizontal view of item A1.
| Schedule Entity | 3 January | 4 January | 5 January | 6 January | 7 January |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier 1 capacity | 60 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Supplier 2 capacity | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Planned orders using supplier 1 | 60 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Planned orders using supplier 2 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Demand | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 200 |
| Total supply | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Projected available balance | 100 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 0 |
The planning engine issues this Sourcing split percentage violated exception message from 3 January to 4 January with a percent variation of 10%.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item
-
Supplier: The supplier name
-
Supplier Site
-
From Date: The start date of the planning time bucket in which the which the actual sourcing percentage does not satisfy the sourcing rule split percentage
-
To Date: The start date of the last planning time bucket in which the which the actual sourcing percentage does not satisfy the sourcing rule split percentage. As long as Percent Variation remains the same in successive planning time buckets, the planning engine uses the same exception and extends the To Date.
-
Allocated Percentage: The sourcing rule split percentage
-
Actual Percentage: The actual split percentage
-
Percent Variation: Actual Percentage - Allocated Percentage
Resolution Suggestions
Consider:
-
Changing the suggested suppliers on the purchase requisitions and purchase orders
-
Reviewing supplier agreements, splitting, history, and capacity to detect a capacity constraint or optimization issue
5: Items with forecast over consumptions
Explanation
This exception message appears for each occurrence of forecast overconsumption and belongs to the Item Exceptions group.
You can right click from the exception and select the following:
-
Demand
-
Sources
-
Destination
-
Horizontal plan
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item
-
Forecast name or Demand Planning scenario name
-
Forecast date (schedule ship or request date)
-
Original quantity
-
Current quantity
-
Over consumed quantity
Resolution Suggestion
You can take corrective action to increase the forecast or talk to the person responsible for forecasting.
6: End item minimum remaining shelf life violation
Explanation
This exception message appears when a product is going to violate the required shelf life criteria when it arrives at a customer site.
The system uses this formula: (Material Available Date + Shelf Life Days - Planned Arrival Date) < Minimum Remaining Shelf Life.
Example
Consider a prescription that must be stocked on drugstore shelves with at least three months (90 days) of remaining shelf life until expiration.The shelf life of this product is 120 days. Based on a plan run the Material Available Date for a supply of this product is February 1, 2007 and the Planned Arrival Date is March 6, 2007.
Therefore, Material Available Date + Shelf Life Days - Planned Arrival Date is: February 1, 2007 + 120 - March 6, 2006 = 120 - 33 = 87.
Because 87 < 90 the exception is generated.
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Item
-
Organization
-
Demand order number
-
Customer
-
Customer site
-
Material available date
-
Planned arrival date
-
Shelf life days
-
Minimum remaining shelf life
This is the requirement specified by the user in the destination side in the Item-Org Mass Maintenance screen.
-
Minimum remaining shelf life planned
This is the left-hand side of the inequality calculated by the plan. In the example above, this is equal to 87 days.
-
Minimum remaining shelf life shortfall
This is equal to (minimum remaining shelf life - minimum remaining shelf life planned). In the example above, minimum remaining shelf life shortfall = 90 - 87 = 3 days.
These hidden fields can be displayed through folder functionality:
-
Category
-
Planner
-
Priority
-
Demand Class
-
Demand Quantity
-
Demand Due Date
-
Old Due Date
-
Suggested Ship Date
Resolution Suggestion
This exception enables planner to identify products that will violate the required shelf life criteria when it arrives at the customer site.
Transportation Management Exceptions Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Order will be delivered later than scheduled | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2: Order will be delivered earlier than scheduled | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
1: Order will be delivered later than scheduled
Explanation
The planning engine issues this exception when Updated Arrival Date is later than:
-
For purchase requisitions and internal requisitions, Dock Date
-
For internal sales orders, Scheduled Arrival Date
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Current Date
-
Updated Arrival Date
-
Quantity
-
Planner
-
Product Family
-
Item Category
-
Supplier (for purchase order and internal requisition only)
-
Supplier Site (for purchase order and internal requisition only)
-
Source Organization (for internal sales order only)
Resolution Suggestion
Run either an online replan or a batch replan. The planning engine issues related exceptions when the new arrival time has an effect on demand satisfaction—late replenishment, early replenishment, order at risk
2: Order will be delivered earlier than scheduled
Explanation
The planning engine issues this exception when Updated Arrival Date is earlier than:
-
For purchase requisitions and internal requisitions, Dock Date
-
For internal sales orders, Scheduled Arrival Date
Information Displayed
The information displayed for this exception message is:
-
Organization
-
Item
-
Order Number
-
Current Date
-
Updated Arrival Date
-
Quantity
-
Planner
-
Product Family
-
Item Category
-
Supplier (for purchase order and internal requisition only)
-
Supplier Site (for purchase order and internal requisition only)
-
Source Organization (for internal sales order only)
Resolution Suggestion
Run either an online replan or a batch replan. The planning engine issues related exceptions when the new arrival time has an effect on demand satisfaction—late replenishment, early replenishment, order at risk
Recommendations Exception Group
This table shows the exceptions in this exception group and states whether the planning engine issues the exception for each plan type.
| Exception Message | Available In Unconstrained Plans | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Demand Dates | Available In Constrained Plans with Enforce Capacity Constraints | Available In Optimized Plans | Available In Inventory Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batches | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Discrete Jobs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Flow Schedules | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Jobs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Purchase Requisitions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Explanation
Recommendations are suggestions to the planner to release planned orders. The planned orders become:
-
Batches: Oracle Process Manufacturing
-
Discrete jobs: Oracle Work in Process
-
Flow schedules: Oracle Flow Manufacturing
-
Jobs: Oracle Project Manufacturing, Oracle Shopfloor Management (OSFM)
-
Purchase requisitions: Oracle Purchasing
Information Displayed
The information displayed in the Supply/Demand window is:
-
Org
-
Item
-
For Release: Checkbox for releasing the planned order
-
Firm: Checkbox for firming the planned order
-
Order Type
-
Sugg Due Date
-
Orig Qty
-
Order Number
-
Action: The recommendation
-
New Date: New firm date specified by planner
-
New Qty: New firm quantity specified by planner
If you right click the exception, you can view other key information; calculations for some key terms are:
-
Suggested Due Date = Date material is needed in inventory
-
Suggested Dock Date = Due date - Postprocessing lead Time
-
Suggested Start Date = Dock date - Processing Lead Time
-
Suggested Order date = Start date - Preprocessing Lead time. The earliest Suggested Order Date allowed is the current day and no compression days are allowed.
Resolution Suggestions
Consider firming or releasing the planned order. For more information, see Implementing Planning Recommendation
Exception Diagnosis and Resolution
Overview
This section explains how to diagnose and resolve exception messages. It includes:
-
Workflow notifications and activities
-
Exception information
-
Identifying the root causes of late demand (enhanced exceptions)
-
Resolution suggestions
-
Online simulation
-
Identifying differences between plans
-
Implementing plan changes
You typically resolve the:
-
Most constrained (bottleneck) resource before the least constrained resource
-
High priority demands before low priority demands
Workflow Notifications and Activities
You can automatically forward exceptions (using Oracle Workflow) to your trading partners. They can research and respond to exceptions through self-service web applications including forecast maintenance, supplier capacity update, ATP, and a secured version of the Planner Workbench. Trading partner responses can trigger other workflow activities such as a notification or an automatic reschedule of a purchase order or sales order. For more information, see Review Workflow Notifications.
Exception Information
The section Understanding Exceptions describes the circumstances under which the planning engine issues the exceptions and the information that it displays.
The section Viewing Exceptions describes how to obtain additional information about exceptions by using buttons, right mouse options, and related exceptions.
Using Constraint Exceptions
Use the constraint exceptions to find situations in which the planning engine is not able to plan within your constraints.
Overload Related Exceptions
The overload-related constraint exception messages are:
-
Requirement causes resource overload
-
Order causes supplier capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
The planning engine issues these exception messages when a specific resource requirement or a supply order causes overload on a production resource (for make items), a supplier capacity (for buy items), or a transportation resource (for transfer items).
Lead Time Related Exceptions
The lead-time-related constraint exception messages are:
-
Requirement with insufficient lead time
-
Order with insufficient lead time
The planning engine issues these exception messages when it schedules a resource requirement or supply order for less than its minimum duration. Minimum duration depends on order type; for example, a resource requirement minimum duration is the processing time required when using the resource maximum assigned units and usage quantity.
Enforce Capacity Constraints Related Exceptions
The constrained plan-related constraint exception messages are:
-
Resource constraint
-
Material constraint
-
Transportation weight constraint
-
Transportation volume constraint
-
Order lead time constraint
-
Requirement lead time constraint
The planning engine issues these exceptions in:
-
Constrained plans
-
Plan option Enforce Capacity Constraint
-
Either or both Material Constraints and Resource Constraints is Yes
It issues them whenever it must satisfy a sales order line or a forecast entry late. They help show the resource overloads, supplier capacity overloads, and lead-time violations that need to occur for you to satisfy the order on time.
These exception messages from Constrained plans-Enforce capacity constraints mirror overload and lead-time exceptions from Constrained plans-Enforce demand due dates:
-
Resource constraint mirrors Requirement causes resource overload
-
Material constraint mirrors Order causes supplier capacity overload
-
Transportation weight constraint mirrors Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
-
Transportation volume constraint mirrors Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
-
Order lead time constraint mirrors Order with insufficient lead time
-
Requirement lead time constraint mirrors Requirement with insufficient lead time
Firming Related Exceptions
The firming-related constraint exception messages are:
-
Order is firmed early
-
Order is firmed late
-
Requirement is firmed early
-
Requirement is firmed late
The planning engine issues these exceptions against firmed resource requirements and supply orders when it thinks they are firmed with either of the following effects:
-
Too early: It cannot properly schedule upstream tasks--using minimum duration--to start after the plan start date.
-
Too late: It cannot properly schedule downstream tasks--using minimum duration--to finish before the demand due date.
Other Exceptions
The other constraint exception messages are:
-
Shared supply scheduled late: A shared supply is scheduled too late to satisfy one of its end demands. The planning engine issues this exception if profile option MSO: Generate Shared Supply Exceptions is Yes.
-
Demand quantity is not satisfied: There is no supply for this demand; the demand is satisfied at the end of the planning horizon.
-
Sales order/forecast at risk: The sales order line or forecast entry is likely to be late. The reasons for the lateness are in the exception group Supply Problems for Late Sales Orders/Forecasts.
Related Exceptions
The following exception messages relate to the exception message Sales order/forecast at risk:
-
Requirement causes resource overload
-
Order causes supplier capacity overload
-
Order is firmed late
-
Order is firmed early
-
Requirement is firmed late
-
Requirement is firmed early
-
Order causes transportation weight capacity overload
-
Order causes transportation volume capacity overload
-
Order with insufficient lead time
-
Requirement with insufficient lead time
The following exception messages relate to the exception message Late replenishments for sales orders/forecasts:
-
Resource constraint
-
Material constraint
-
Order is firmed late
-
Order is firmed early
-
Requirement is firmed late
-
Requirement is firmed early
-
Transportation weight constraint
-
Transportation volume constraint
-
Order lead time constraint
-
Requirement lead time constraint
-
Demand quantity not satisfied
-
Shared supply scheduled late
Identifying Root Causes of Late Demand
-
Late demands: The planning engine process for identifying and scheduling late demands
-
Late demand root cause information: Information you need to know to research the causes of late demands
-
Viewing late demand information: The windows that you can use to see late demand information
Late Demands
The exception messages that are critical relative to late demands in constrained and optimized plans with enforce capacity constraints are:
The process that the planning engine uses that can result in these exception messages is:
-
Start from the demand due date, backward schedule the operations for the demand to determine the latest time that activities should start to meet the demand on time. This is the latest possible start time (LPST).
-
If the LPST is in the past, find the earliest possible start time (EPST) for the first operation and forward schedule the operations for the demand to determine the earliest possible completion time (EPCT) for the demand.
The LPST and EPCT depend on resource availability, resource precedence constraints, planning time fence restrictions, and item lead-times.
-
Start from the EPCT, backward schedule the operations for the demand to minimize work in process and inventory.
Late Demand Root Cause Information
This section describes:
-
Terms and types of information that you may encounter in researching the root cause of late demands
-
Potential causes of late demands
In general, the regular behavior of the planning engine can highlight late demands caused by:
-
Environmental circumstances: For example, a downstream resource suffering from capacity overutilization or from supplier capacity overload on one of its supplies.
-
Data circumstances: For example, an item with inaccurate lead-times or a resource with inaccurate available hours.
The descriptions in this section use a manufactured table as an example. The table consists of four legs and a top, each of which have operations.
Latest Possible Start Time
The latest possible start time (LPST) is the time that the activities need to start to meet the demand on time. If the latest possible start time is in the past, the planning engine cannot schedule to meet the demand on time.
This diagram shows the table assembly and its subassemblies backward scheduled from an independent demand due date. The schedule shows each job finishing just in time for its next use; therefore, the beginning of each job is its latest possible start time. The latest possible start time for the tabletop is in the past.
Latest Possible Start Date Example
Earliest Dates
The earliest possible start time (EPST) is the earliest time that the planning engine can schedule the operations to start.
The earliest possible completion time (EPCT) is the earliest date that the operations are complete if they start at the earliest possible start time.
This diagram shows the table assembly and its subassemblies backward scheduled from the demand due date. Since the tabletop latest possible start time is in the past, the planning engine forward schedules each subassembly from the current date (as material and resources are available). The result is the demand satisfied by date for the table assembly which is later then the demand due date. Since the legs subassembly has a shorter lead-time than the tabletop assembly, it is finished sooner than the tabletop assembly. The completed legs subassembly remains in work in process or moves to inventory until the table assembly needs it.
Earliest Demand Satisfied Date Example
Earliest Order Date
The earliest order date is the earliest possible date that you can start the order, given plan constraints. It is the earliest possible date that can appear as the suggested order date and usually corresponds to the following dates:
-
Make order: Suggested start date
-
Buy order: Suggested dock date
-
Transfer order: Suggested ship date
Even for supplies on the critical path, the suggested order date is usually after the earlier order date because the planning engine right-justifies it to the next order which has its own set of constraints.
If the suggested order date is later than earliest order date, it is usually because there are more constraining supplies at the same level. If this supply started on earliest order date, it would wait on the other constrained supplies (buy items or subassemblies). The planning engine sets the suggested order date later (delays the order start) to avoid work in process and inventory build-up.
This diagram shows three supplies (S1, S2, and S3) pegged to supply S4. The planning engine forward scheduled the supplies and set the suggested order date for each one to be the same as the earliest order date
Earliest Order Date Example
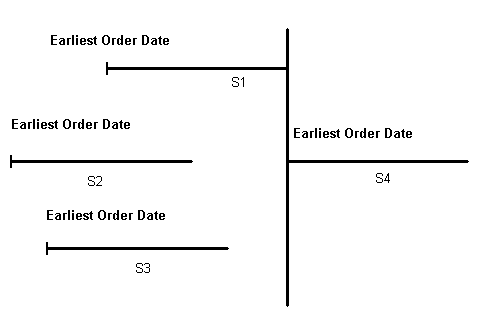
In this diagram, the planning engine has backward scheduled all of the supplies from the due date of S4 to minimize work in process and inventory. This aligns the due date of the subassemblies with the start date of S4. The suggested order dates for S2 and S3 are later than their earliest order dates.
Suggested Order Date Shifted Example
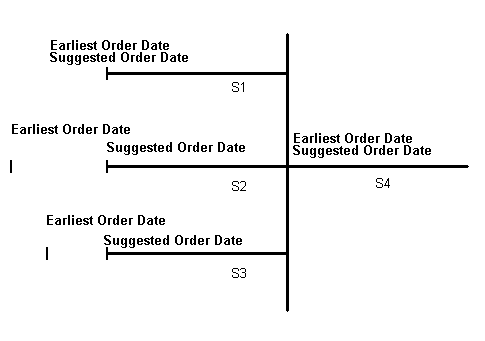
Earliest Completion Date
The earliest completion date is the date that the order can finish if you start it on earliest order date. It is the earliest possible date that can appear as the suggested due date.
If suggested order date is the same as earliest order date, then the field suggested due date is the same as earliest completion date.
If suggested order date is different from earliest order date, the time between earliest order date and suggested start date may not be the same as the time between earliest completion date and suggested due date. Breaks in the capacity profile (for example, holidays) may create capacity availability breaks that result in the operations stretching as they fit in around these breaks.
This diagram shows a supply that has two operations; operation 10 lasts three days and operation 20 lasts two days. The planning engine can schedule the operations with no breaks. Since there is no difference between suggested order date and earliest order date, there is no difference between suggested due date and earliest completion date.
Earliest Possible Times Example
This diagram shows the supply when the planning engine must schedule the operations with breaks. Since there is a difference between suggested order date and earliest order date, there difference between suggested due date and earliest completion date. However, the differences are not the same:
-
The difference between suggested order date and earliest order date is one day
-
The difference between suggested due date and earliest completion date is three days
Actual Times Example
Earliest Possible Demand Satisfied Date
The earliest demand satisfied date is the same as the earliest possible completion time of its supply order. The planning engine reschedules the operations backwards from the earliest possible completion date to minimize work in process and inventory.
This diagram shows the table assembly and its subassemblies backward scheduled from the demand satisfied by date. This aligns the due date of the subassemblies with the start date of the table assembly. The planning engine has scheduled the legs subassembly to start later than the forward scheduling suggested. The completed legs subassembly does not need to remain as long in work in process or in inventory before the table assembly needs it.
Earliest Demand Satisfied Date with Minimum Work in Process Example
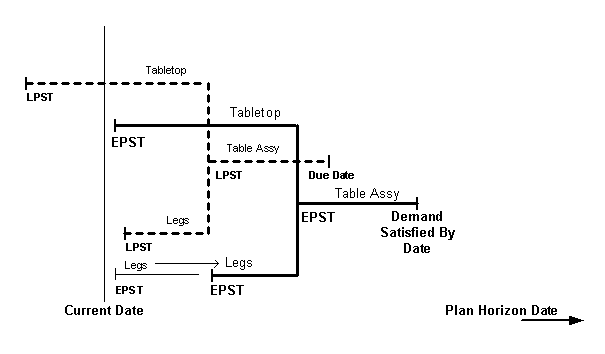
Actual Times
The actual start date and end dates are:
-
Buy orders (planned orders, purchase orders, purchase requisitions): Actual start date = Dock Date, Actual end date = Due Date
-
Make orders (planned orders, discrete jobs, batches, jobs, flow schedules): Actual start date = Start Date, Actual end date = Due Date
-
Transfer orders (planned orders, internal sales orders, internal requisitions): Actual start date = Ship Date, Actual end date = Due Date
Critical Activities
A critical activity is an entity that is:
-
Pegged to a late demand.
-
One of several activities which are at the same bill of material or pegging level.
-
The most constraining at its level. The most constraining activity is the one that most restricts the lower (earliest) bound of the earliest order date of the next highest level supply.
It can be a:
-
Specific activity of a resource
-
Buy supply
-
Transfer supply
This diagram shows three supplies (S1, S2, and S3) pegged to supply S4. The planning engine forward scheduled the supplies. Among the subassemblies, S1 is the critical supply since it determines the earliest order date of supply S4 (the next highest level supply).
Critical Activity Example

The critical supply does not always have to have its suggested order date and earliest order date the same. In this diagram, the first resource that supply S4 needs is not available until 30 June. Therefore, this resource, rather than supply S1 is the critical activity that determines the earliest order date for supply S4.
Resource Constraint on Assembly Example
This diagram shows the final schedule after the planning engine has backward scheduled from the demand satisfied date of supply S4 to minimize work in process and inventory. The planning engine still considers supply S1 as the critical activity.
Final Schedule for Assembly Example
Resource Utilization Profile
The resource utilization profile information includes:
-
All the resources required to complete the operation
-
Required hours and available hours
-
Overload or underload conditions
-
Firmed indications
-
Percent resource utilization
-
Precedence constraints
-
All the tasks being worked on by the resource grouped into orders with the same, higher, and lower priority than the one you are researching
Constrained Times
Constrained Earliest and Actual Times represent the earliest that an activity can start considering resource capacity constraints, supplier capacity constraints, and resource precedence constraints (the earliest that an activity can start is dependent of the earliest time that the previous activity can complete).
Resource Precedence Constraints
Resource precedent constraints are constraints that cause an activity associated with the late demand to wait for a resource when it is otherwise ready to be worked on. They cause the earliest possible completion time to be later and delay satisfaction of the late demand.
Use the resource utilization profile information to identify resource precedent constraints on the late demand:
-
All the levels of resources and operations that satisfy the late demand and their precedence relationships
-
Availability of the upstream resources; if one upstream resource has low availability, it will tend to make all downstream operations later
-
Availability of the downstream resource; since the planning engine backward schedules late demand operations to be just-in-time, a downstream activity that is late because of resource unavailability results in late scheduled upstream operations.
Demands constrained by resources also receive a Resource constraint exception message and you use that exception message to find addition information about the resources.
This diagram shows the operations and resource schedule for a tabletop. Operation 10 Sawing takes 400 minutes and uses resources Chipper for 250 minutes and Lathe for 150 minutes. Operation 20 Painting takes 200 minutes and uses resource Spray painter. The capacity consumption profiles for the resources show that the resources are not always available. Therefore, the:
-
Schedule for this supply is delayed while waiting for the resource Spray painter
-
Due date of the supply is later than it would be if the resource was available when the tabletop assembly was ready for it
Precedence Constraints and Resource Availability
Min Possible Days Late
For supplies, this indicates how late the end demand would be if this supply was the only late supply.
The calculation for Min Possible Days Late is Earliest Completion Date - Need by Date.
The supply Need by Date is the demand Due Sate. Since the planning engine calculates Need By Date from the item fixed and variable lead-times, the Need By Date may be different than the Suggested Due Date from detailed scheduling.
Planning Level
For operations, this indicates its level on the supply chain routing. The higher the number, the lower the operation is on the routing.
For example, if the end item assembly has operations 10, 20, and 30, the level of:
-
Operation 10 is 3
-
Operation 20 is 2
-
Operation 30 is 1
Item Lead Time Constraints
Item lead times can cause delays in demand satisfaction.
For example:
-
Tabletops are buy items with the item lead-time of 60 days. For buy items, the order date is offset from the dock date by the pre-processing lead-time plus either the default supplier lead-time or by the default the item lead-time.
-
If there is no supplier assigned with a specific lead-time, the forward scheduling process on the late demand supply order schedules the dock date for the tabletop 60 days from the plan start date.
If checking determines that this is the reason for the delay of the order, the planner should correct and firm the scheduled dock date for the planned order and consider adjusting the item and default supplier information for the future.
Dependent Demand Material and Resource Constraints
Late demands can be due to material and resource constraints on dependent demand items. Look for the following situations:
-
Supplier capacity for buy dependent demand items: For example, if there is no supplier capacity for purchased tabletops before day 100, then all the planned orders for tabletops are scheduled from day 100 and all other orders downstream and upstream are realigned with them.
-
The downstream operations for the dependent demand need resource capacity: For example, a downstream resource is available from day 0 to day 100. Since there is no available capacity from day 101 to the plan horizon, the planning engine must schedule the operation after the plan horizon date (where it assumes infinite capacity). This pushes out the downstream operation, its work order, and the corresponding dependent demand.
Planning Time Fence Constraints
The planning time fence also imposes certain constraints on the scheduling. Planning time fence is the point in time in the scheduling process that marks a boundary inside of which changes to the schedule may adversely affect component schedules, capacity plans, customer deliveries and cost. Therefore, planned orders outside the planning time fence can be changed by the system planning logic, but changes within the planning time fence must be manually changed by the master scheduler or planner. Therefore, if the planning time fence is too large, then the demands cannot be rescheduled within the time fence and may be delayed. The planner should be able to see a 'Reasons for Lateness' report, which details the effect of the planning time fence on the lateness of the order.
Other Late Demand Causes
When researching late demands, also look for the following situations:
-
Item fixed and variable lead-times that do not accurately reflect the length of the routing process. This can result in less optimal pegging which can indirectly cause lateness. It is especially a problem for buy orders with no supplier lead-time and for transfer orders whose source organization is not planned.
-
Transportation resource availability inaccurate
-
In-transit duration setup between organizations inaccurate
-
Many units of a resource are available but the resource assigned units specified on a routing is a lower number. The planning engine uses the routing assigned units as an upper limit on the number of resource units it schedules.
-
Preprocessing lead-time inaccurate
-
For buy orders, supplier lead-time and postprocessing lead-times
-
For transfer orders, the intransit and postprocessing lead-times
Researching Late Demands Example
A sales order line for item A has due date 7 September. The item receives a Late replenishment for sales order exception message for the 7 September demand with demand satisfied date 30 September.
Check the critical path for completion of the demand. The gaps between levels on the critical path are the best indicator of the constraints, even more than the difference between actual times.
A gap is usually caused by a combination of several constraints, for example, the precedence with the previous level and resource constraints on the current level.
Determine that the reason for the late demand is a precedence constraint on a subassembly; the EPST of the subassembly is 20 September.
Determine the cause of EPST of subassembly is resource availability of RES1.
Check earliest possible start time (EPST) and earliest possible completion date (EPCT) for one of the tasks scheduled on RES1 on 18 September.
Check resource utilization profile for RES1 to determine tasks on RES1 for 18 September.
Identify tasks of the same priority, higher priority, and lower priority.
Check material constraints that might cause a bottleneck to the operation.
Check other late demand causes, for example, item lead-times and planning time fence constraints.
Viewing Late Demand Information
To obtain more information about the root causes of a late demand, use the following Planner Workbench windows:
-
Gantt Chart Orders View: A graphical interface of the late demand with all the supplies pegged to it, start and end times, and critical activities contending for capacity.
-
End Pegged Supplies: Supplies pegged to the late demand including the supplies for the independent demand and for all the dependent demands.
-
Critical Activities: The activities that lie in the critical path of meeting the end demand. If you focus on expediting these, you should see the most improvement in the demand satisfied date.
If the critical path encounters a firm discrete job, firm planned order, or firm operation), it displays information until the last activity of the firmed supply. It does not consider the following as critical:
-
All operations of the firmed supply
-
Components pegging to the firmed supply
To access root cause information
-
Access any of the following windows:
-
Exception Details window for Late replenishment for sales order or Late replenishment for forecasts.
-
Exception Details window for Material constraint or Resource constraint. Right-click and exception and select Related Exceptions. View Late replenishment for sales orders and Late replenishment for forecasts.
-
Supply/Demand window or Demand window for an item. Select a late demand.
-
-
Right-click on a late demand.
For the Gantt Chart, Order view, select Gantt Chart, then select Order view.
For more information on the Gantt chart, see The Order - Centric View
Online Simulation
You can simulate different ways to resolve exceptions before you make permanent changes by modifying information.
Supplier capacity:
-
Add supplier capacity
-
Modify dates and quantities
Resource availability:
-
Add resource availability
-
Modify dates and quantities
-
Add new shifts
Supplies:
-
Add planned orders
-
Firm planned orders, discrete jobs, and purchase orders
-
Modify quantities, dates, sources, and alternates
Demands:
-
Add Manual MDS
-
Modify order priority
Plan Options: Modify objectives
In this process, you may eliminate one exception but create another. For example, if you decide to offload some operations to a different resource, you may overload it.
Identifying Differences Between Plans
If you rerun a plan or run a new plan after making changes or simulated changes, you can compare two plans to find out why the two plans differ. This is useful for determining if:
-
Actions taken by a planner to solve a specific problem have the desired overall effect
For example, a planner may choose to address a late sales order by increasing the priority of the sales order, and then replanning (generating a new plan in the process). By comparing the new plan to the original plan, the planner can see whether the problem sales order is now on time, and whether any other sales orders may have been pushed out as a result of pulling in the problem sales order.
-
Plan setup changes led to changes in key indicator performance. You can compare the plan option settings for two plans.
To compare plans, use the Plan Comparison Report. See Plan Comparison Report.
Implementing Plan Changes
Based on the results of your analysis, online simulations, and plan comparisons, you can implement changes in the execution system:
-
Make most changes in the source instance, including changes to sourcing rules defined in the source.
-
Make cross-instance planning sourcing rule changes in the destination instance.