Transactions
Entering Transactions
Use the Transaction window to enter your invoices, debit memos, credit memos, and commitments. You can also query and update your transactions in this window and review your transactions and chargebacks in the Transactions Summary window. For a list of fields you can update, see: Maintaining Your Transactions.
From this window, you can also quickly view the balance due on a transaction, and drill down to view more details in the Balances window. See: Viewing Transaction Balances.
When you enter an invoice, Receivables uses your AutoAccounting rules to determine your default general ledger accounts. See: Using AutoAccounting.
You can enter transactions one at a time or in a group called a batch. See: Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval.
Your system administrator determines whether you can delete a transaction. See: Function Security in Oracle Receivables, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Note: You can view the detail accounting lines for existing transactions in the form of a balanced accounting entry (i.e., debits equal credits) by choosing View Accounting from the Tools menu. You can also choose to view the detail accounting as t-accounts.
See: Viewing Accounting Lines.
Note: If you are using Multiple Reporting Currencies (MRC) functionality, then you can use the View Currency Details window to view transaction amounts in both your primary and MRC reporting currencies.
See: Viewing MRC Details for a Transaction.
Previewing Transactions Online
If you use Bill Presentment Architecture (BPA), then you can use the BPA icon to preview completed transactions online. See: Viewing Online Bills, Oracle Bill Presentment Architecture User Guide.
Transaction Types
Transaction types determine whether a transaction updates your open receivables, can be posted to your general ledger, the transaction's creation sign, and whether transactions with this type use natural application only or will allow overapplication. The transaction type also provides the default transaction class, payment term, and printing options for each transaction.
You can set up AutoAccounting to use transaction types when determining your general ledger accounts. If AutoAccounting depends on transaction type and you change this value, Receivables displays a pop-up window asking you if you want to recalculate all of your general ledger accounts. If you choose Yes, Receivables reruns AutoAccounting and makes the appropriate changes to your accounts (unless the transaction is a chargeback). See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Prerequisites
-
Define transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction batch sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define accounting rules (optional), Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Set up document numbering (optional), Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To manually enter an invoice or a debit memo:
-
Enter the transaction batch Source for this transaction. The default is the value of the AR: Transaction Batch Source profile option. If no value exists, then you must enter a source.
The transaction batch source specifies automatic or manual invoice numbering and the transaction type. The transaction batch source also determines which attribute of the Invoice Transaction Flexfield is used to default into the Reference field, although you can override the default. See: Transaction Batch Sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Enter the Date of this transaction. The default date is either the batch date or, if there is no batch information, the current date.
-
If your batch source does not specify Automatic Invoice Numbering, enter a transaction Number. Otherwise, Receivables assigns a number when you save. If you are adding transactions to a batch, the transaction number must be unique within this batch.
Important: Once you save a transaction, you cannot update the transaction number.
-
Enter the GL Date for this transaction. The default date is either the batch date or, if there is no batch information, the current date.
-
Choose the Class of this transaction.
-
Enter the Currency of this transaction. The default currency is either the currency entered at the batch level or your functional currency, but you can change it to any currency that is defined in Receivables. If the currency is different from your functional currency, and you have not defined daily conversion rates, enter exchange rate information. See: Foreign Currency Transactions.
Note: You can optionally account for rounding differences that can occur when you create foreign currency transactions by enabling Header and Line Level Rounding, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Choose a transaction Type.
-
If you are using manual sequence numbering, then enter a unique Document Number. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Select the legal entity for this transaction.
-
Enter the ship-to customer (optional).
-
Enter the customer Bill-to Name and Location for this transaction.
If the bill-to customer has a primary bill-to location, then Receivables defaults the location and address.
If no primary bill-to location exists for the customer, however, then you must select a valid bill-to location from the list of values.
-
Accept the default sold-to customer, or enter a new customer.
-
Accept the default paying customer, or enter a new customer.
Use these fields in conjunction with an automatic receipt method to indicate that this transaction will be paid by automatic receipt.
-
If you are creating an invoice against a commitment, enter the Commitment, or choose one from the list of values.
Note: You can also add a deposit to an invoice that is already completed. See: Using Commitments.
-
Enter the Payment Term for this transaction.
Receivables calculates the Due Date based on the payment term and date of this transaction. If you enter a split payment term, the due date is the date when the first installment is due.
See: Entering Invoices with Installments.
Receivables uses the following hierarchy to determine the default payment terms, stopping when one is found:
-
customer bill-to site level
-
customer account level
-
Transaction Type
-
-
If you want to assign invoicing rules, see: Entering Invoices with Rules.
-
Accept the default receipt method, or select a new receipt method. Receipt methods selected in the Payment Details region indicate that this transaction should be paid by an automatic method, such as by credit card, direct debit, or bills receivable. Transactions paid by automatic methods use Oracle Payments to complete the funds capture process. See: Enabling the Funds Capture Process, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
The receipt method defaults based on the paying customer's receipt method assigned at the site or account level (site takes precedence). If no assigned receipt method exists, then you can select a receipt method from the list of values.
You can select any receipt method from the list of values, as long as the invoice date is within the receipt method active date range and the receipt method has bank accounts in the currency of the invoice, or at least one of its bank accounts has the Multiple Currencies Allowed check box selected.
The selected receipt method automatically defaults the payment method and instrument number.
-
Optionally choose Select Instrument to navigate to the Payment Instrument window. To choose this button, you must first select a receipt method. In the Payment Instrument window, you can select a different payment instrument, or create a new one. You can select any payment instrument that has been assigned to the defaulted payment method at the customer account or site level.
The Payment Instrument window also displays payment instrument details. Oracle Payments populates these fields during the funds capture process.
The fields in this window display differently depending on the payment method that is associated with the receipt method. For example:
-
If the payment method is a bank account transfer payment method, then the Payment Instrument window displays bank account details.
Choose Create/Update Instrument to navigate to the Payment Details page, where you can update existing bank accounts, or add or create a new bank, bank branch, or bank account.
-
If the payment method is a credit card payment method, then the Payment Instrument window displays credit card details.
Choose Create/Update Instrument to navigate to the Payment Details page, where you can update existing credit cards, or add a new credit card.
For both types of payment instruments, use the Payment Details page to indicate the priority level of each payment instrument, if multiple instruments exist, as well as the customer's notification preferences, such as by e-mail or fax.
Note: You can also create payment instruments at the customer account or site level. See: Entering and Updating Account Payment Details and Entering and Updating Account Site Payment Details.
-
-
In the More tabbed region, accept the default territory or select a new one.
-
Enter a Salesperson (optional).
If the system option Require Salespersons is Yes and you did not assign a salesperson to this customer at the customer account or site level, then the default is No Sales Credit. To see how Receivables chooses a default salesperson for your transactions, see: Salespersons, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
For more information about sales credits, see: Entering Revenue Credits.
The More tabbed region also includes other important attributes of the transaction that you are entering. See: More Tabbed Region.
-
Enter the Remit To Address for this transaction. The default is the remit-to address assigned to the country, state, and postal code combination for this customer's address.
-
To enter the goods or services to bill to this customer, choose Line Items, then enter the Item, Quantity, and Unit Price for each item. Receivables automatically calculates the total Amount for each line. See: Lines Field Reference.
Note: You can use standard memo lines instead of items if, for example, you have not installed Oracle Order Management or if you want to enter a line that is not a standard inventory item. To enter a memo line, place your cursor in the Description field, then select a standard memo line from the list of values. (You must use the list of values when entering a standard memo line.) See: Standard Memo Lines, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Receivables displays a default Tax Classification, if one exists. If you upgraded to Release 12 from a previous version of Oracle Receivables, then tax classifications represent your migrated tax codes.
Tip: Oracle Receivables uses Oracle E-Business Tax as its tax engine. E-Business Tax provides a single set of application features that manage tax calculations for Receivables. Additionally, E-Business Tax is the repository of all tax-related data.
E-Business Tax migrates the tax decision making responsibility from your users to the tax experts at your enterprise. Implement E-Business Tax to leverage this powerful central tax solution. If you implement E-Business Tax to automatically calculate taxes based on transaction line content and other tax sources and corresponding rules, then you no longer need to use tax classifications.
See: Setting Up Tax, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
When you select a tax classification, E-Business Tax searches for corresponding tax details to complete the tax calculation. If tax details are insufficient (for example, the associated tax rate is end-dated), then E-Business Tax will not calculate tax for the transaction line.
-
If you entered an inventory item, enter a Warehouse Name to indicate the ship-from location for this item (optional). If AutoAccounting is based on Standard Lines, you can use the inventory item and warehouse name to create accounting flexfield information. For example, you use multiple inventory organizations and set up AutoAccounting to create the Revenue account based on standard lines. AutoAccounting uses the item and warehouse that you enter here to create the Product segment of your Revenue account. See: AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
To review or update tax information for this line, choose Tax. See: Entering Tax Information. To review tax exemption information for this line, choose Lines, then open the Tax Exemptions tabbed region.
Important: You cannot review tax information for a line if the standard line type is Freight or Charges, or if the transaction is a chargeback.
-
To enter Freight information for this transaction, choose Freight. See: Entering Freight Information.
To enter Freight information for an invoice line, select the line, then choose Freight. See: Entering Freight Information.
-
To review or update accounting information, choose Distributions. See: Reviewing Accounting Information.
-
To review or update Sales Credit information, choose Sales Credits. See: Entering Revenue Credits.
-
Save your work. If you are ready to complete this transaction, see: Completing Transactions.
Related Topics
Transactions Window Field Reference
Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval
Importing Transactions Using AutoInvoice
Transactions Window Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of fields in the Transactions window. If a field is in a different window, such as the Transactions Summary or Transaction Batches window, this is noted.
Balance Due: Use this region to view the balance due on a transaction. Choose Details to navigate to the Balances window. Choose Refresh to recalculate the transaction balances without closing the window. See: Viewing Transaction Balances.
Balance Forward Bill Number: Receivables displays two transaction number fields. The first field displays the balance forward bill number that is associated with this transaction. The second field displays the transaction number. You can view all transactions that appeared on a specific balance forward bill by entering a balance forward bill number and performing a query on this field.
Control Amount: (Transaction Batches window) The total amount of invoices in this batch. If you enter invoices in different currencies, enter the total amount irrespective of currency. For example, if you intend to enter two invoices, one for 100 US Dollars and the other for 50 euros, enter 150 here.
Instrument Number: This field is display only. Receivables defaults this value based on the receipt method. Your customers use payment instruments to pay you. For example, a payment instrument can be a credit card or a bank account. You can change the payment instrument by choosing Select Instrument, which opens the Payment Instrument window. From this window, choose Create/Update Instrument to update or create a payment instrument on the Payment Details page.
Invoice Date: Receivables prints the invoice date on your invoice. Receivables calculates the due date from the invoice date and payment terms you assign to this invoice. The default value is the batch date if you entered a batch, or the current date if you did not enter batch information.
If you change the invoice date, Receivables automatically recalculates the due date and the associated tax.
Number: Receivables displays two transaction number fields. The first field displays the balance forward bill number that is associated with this transaction. The second field displays the transaction number.
Partially Purged: (Transaction Batches window) If this box is checked, some of the transactions belonging to this batch have been deleted by the Archive Purge program. When transactions are partially purged, the Control Total section appears out of balance because the Actual Count and Amount fields no longer include the purged transactions.
Paying Customer: This could be different from the billing customer if, for example, you wanted a primary customer to pay for related invoices.
Payment Method: This field is display only. Receivables defaults this value based on the receipt method.
Receipt Method: The receipt method assigned to this transaction.
In this list of values, Receivables displays all eligible receipt methods, and indicates if a receipt method is assigned to the paying customer bill-to address or not.
Receivables uses the following hierarchy to default a value for this field:
-
the primary receipt method of the parent site
-
the primary receipt method of the primary customer
-
the primary receipt method of the bill-to site
-
the primary receipt method of the bill-to customer
Note: If the receipt method that you assigned to the invoice is a credit card receipt method that is not already assigned to the paying customer, then Receivables automatically updates the customer records with this receipt method information.
Period: (Transaction Batches window) The accounting period that corresponds to the batch date you entered in the Date field. Use the Accounting Calendar window to define your accounting periods.
Reference: The transaction batch source for this transaction determines which attribute of the Invoice Transaction Flexfield is used to default into the Reference field. For manual transactions, you can override the default in the Reference field with other information about this transaction, such as a related transaction number or a customer name.
Sold To Customer: The customer to whom you sold the goods and services. This customer could be different from your ship-to or bill-to customer. The default is the bill-to customer for this transaction, but you can change it.
Status: (Transaction Batches and Transaction Batches Summary windows) The status of your batch. Use batch statuses to implement your batch approval cycle. Receivables provides several standard batch statuses and lets you define additional statuses in the Receivables Lookups window using the lookup type BATCH_STATUS. Receivables treats batch statuses that you create as 'Open.'
More Tabbed Region
Address: The remit-to address for this transaction. The remit-to address is the address to which customers send payments. The default is the remit-to address assigned to the country, state, and postal code for this customer address, but you can change it.
Agreement: If entering an invoice, this is the order agreement this invoice is against. You can only enter this field if you have defined an agreement with the selected customer or customers related to the selected customer. You can associate an agreement with your customer in the Sales Orders window in Oracle Order Management.
If you are entering a commitment, this is the agreement to associate with this commitment. You can only use agreements defined in Oracle Order Management.
Comments: Any comments about this transaction. If this transaction is a credit memo, this field displays information entered in the Comments field of the Credit Transactions window. This text does not appear on the printed transaction.
Cross Reference: The transaction to relate to this invoice. This field is optional. You can choose any transactions that are assigned to your bill-to customer or a selected customer. If you enter a cross reference transaction number and then change your bill-to customer, Receivables will erase the value in this field.
Default Tax: You can enter a value for this field only if the profile option Tax: Allow Override of Customer Exemptions is Yes and the transaction is not a chargeback. Use the default value of 'Standard' if you want tax to be calculated as per the normal procedures set up in Receivables. Enter 'Exempt' to force tax exemption on the invoice lines, and your system option Use Customer Exemptions is set to Yes. Enter 'Require' to force tax calculation on the invoice lines. If you update this field, there will be no effect on existing invoice lines; only new invoice lines will get the new value as a default.
Dispute Amount: The current amount of this invoice, debit memo, or chargeback that is in dispute. Receivables sums up the dispute amounts for each installment of your payment schedule and displays the total in this field. You can either increase or decrease the dispute amount. If you enter 0 (zero), the debit item is no longer in dispute. If your debit item does not have split terms, then you can enter a dispute amount that is between zero and the balance due for this item.
You can review your disputed debit items in the Disputed Invoice Report. For debit items with split terms, you can enter the dispute amount for each installment in the Installments window or you can set it to either the balance due or zero in this field.
Exempt from Late Charges: Use this check box to indicate whether late charges are calculated against this invoice, debit memo, or chargeback. If you select this box, then Receivables calculates late charges according to your customer's credit profile. If you do not select this box, then Receivables does not calculate late charges on this transaction, regardless of the customer's credit profile.
Original Transaction: When you query a chargeback in the Transactions window, this field shows the transaction for which the chargeback was created.
PO Date: The purchase order date for this transaction. Receivables displays a warning message if the purchase order date is later than the transaction date. This field is for reference only and is not validated by Receivables.
PO Number: The purchase order number for this transaction. This field is for reference only and is not validated by Receivables.
PO Revision: The purchase order revision number for this transaction. This field is for reference only and is not validated by Receivables.
Print Date: The date on which this transaction was last printed.
Print Option: The printing option for this invoice. The default is the print option for this transaction type. Choose 'Print' for invoices you want to print. You can choose all new or changed invoices to print at one time. Choose 'Do Not Print' for invoices you do not want to print (for example, if you need to generate an invoice for internal purposes, but you do not want to send the printed invoice to your customer).
Special Instructions: Any special instructions for this transaction. You can enter up to 240 characters. The first 51 characters appear on the printed transaction. If this transaction is a credit memo, this field displays information entered in the Special Instructions field of the Credit Transactions window. You can define additional instructions in the Receivables Lookups window. See: Reviewing and Updating Receivables Lookups, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Status: (Transactions window) The status of this transaction. This is a user maintainable field and you can define values for it in the Receivables Lookups window. Possible values include Open, Pending, Closed, or Void. This field is not used by Receivables, therefore it is not updated automatically when an invoice is paid off, closed, etc. You have to manually update this field.
Territory: The sales territory for this invoice. The default is the value of the Source of Territory in the System Options window (for example, bill-to, ship-to, sales rep, or none).
Notes Tabbed Region
Date: If you are entering a new note, the default is the current date. If this transaction is in dispute, this is the dispute date.
Source: The source of this note. This is a display-only field. If you are entering a new note, the source is Invoice Maintenance.
Memo: Any additional information about this transaction.
Note: The Credit Memo Request workflow uses the information in this field to document a disputed invoice's path through the approval process. See: AME Credit Memo Request Workflow.
Commitment Tabbed Region
See: Entering Commitments.
Reference Information Tabbed Region
Use the fields in this region only for chargebacks and credit memos.
Reason: The reason for this transaction.
-
If this transaction is a credit memo, then this field holds the reason why the credit was requested.
-
If this transaction is a chargeback that resolved a claim, then this field holds the reason for the chargeback.
See: Resolving Claims.
Customer Reference: Additional information from the customer about the reason for this transaction.
Related Topics
Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval
Lines Window Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields in the transaction Lines window. Fields not included in this section are described in Entering Transactions.
Amount Includes Tax: This poplist indicates whether the amount for this line includes a tax. The default is the setting of the Inclusive Tax option of the tax code for this line. You can change this setting if the Allow Override option for this tax code is Yes. If you change this setting, Receivables recalculates the line amount.
Note: The Lines window is a folder form and you can choose to display three additional fields: the Amount Includes Tax, Net Amount, and Net Unit Price. The Amount Includes Tax field indicates whether the tax for this line is inclusive or exclusive. If this is an inclusive tax, the Net Amount and Net Unit Price fields display the amount and unit selling price for this line without tax. To display these fields, choose Show Field from the Folder menu, then select the field to view.
Description: The description for this invoice line. Receivables prints the description on the invoice. You can also choose standard memo lines that you previously defined, such as tax and freight charges. If you wish to update a previously chosen memo line, Receivables will only let you change the memo line to another of the same type. For example, if you have a tax memo line, you can only change it to another memo line of type 'Tax.'
If you entered a freight amount in the Transactions window or if the Allow Freight option for the transaction type associated with this invoice is set to No, standard memo lines with a type of Freight will not appear in the list of values. If the Allow Freight option for the transaction type you selected for this invoice is set to Yes, you can select standard memo lines with a type of Freight. After you select a standard memo line with a type of Freight, you can choose Freight to specify the amount of freight to assign to this line.
You can select standard memo lines with a type of Tax if the profile option Tax: Allow Manual Tax Lines is set to Yes. After you select a standard memo line with a type of Tax, you can choose the Tax button to specify the amount of tax to assign to this line.
Total (Freight): The total amount of freight for this transaction.
Total (Lines): The sum of all lines for this transaction. This amount does not include tax.
Total (Tax): The sum of all applicable tax for your transaction lines. This amount includes any inclusive and exclusive tax.
Total (Transaction): The sum of all lines, tax, and freight amounts for this transaction. This amount includes any inclusive and exclusive tax.
Unit Price: The unit selling price for this invoice line item. If you entered a standard line item, the default is the Unit List Price you entered for this standard line item in the Memo Lines window; there will be no default for System Items. If the currency of the invoice is different from the functional currency, the default unit price will be the Standard Price / Currency Exchange Rate. The default value for this field is zero for Tax and Freight lines. You can accept this price or enter the actual selling price. The unit price can be a positive or a negative number.
Sales Order Tabbed Region
Date: The date you ordered this item. This field is for informational purposes only.
Line: The order line number to which this invoice line refers.
Number: The sales order line number for this invoice line.
Rev: The revision number for this order.
Tax Exemptions Tabbed Region
Certificate: If you enter 'Exempt' in the Tax Handling field (see below), enter a tax exemption Certificate Number. Use the list of values to select an existing tax exemption certificate number.
Reason: If you enter 'Exempt' in the Tax Handling field, enter a Reason for creating this exemption, or select from the list of values. You can define additional exemption reasons in the Receivables Lookups window.
Tax Handling: You can enter a value for this field only if the profile option Tax: Allow Override of Customer Exemptions is Yes and the transaction is not a chargeback. Use the default value of 'Standard' if you want tax to be calculated as per the normal procedures set up in Receivables. Enter 'Exempt' if your system option Use Customer Exemptions is set to Yes and you want to force tax exemption on the invoice lines. Enter 'Require' to force tax calculation on the invoice lines. If you update this field, there will be no effect on existing invoice lines; only new invoice lines will get the new value as a default.
More Tabbed Region
Reason: User-defined lookup code indicates the reason for a credit memo. Defaults from the invoice header level, but you can change it.
Reference: Any additional information about this line item.
Translated Description: A description of the inventory item in an alternate language. You enter this information when defining inventory items.
Warehouse Name: The ship-from location for this item. If AutoAccounting is based on Standard Lines, you can use the inventory item and warehouse you enter to create accounting flexfield information. See: AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Related Topics
Standard Memo Lines, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Entering Tax Information
Oracle Receivables uses Oracle E-Business Tax as its tax engine. E-Business Tax provides a single set of application features that manage tax calculations for Receivables. Additionally, E-Business Tax is the repository of all tax-related data.
E-Business Tax calculates tax according to predefined rules and a universe of data points from your transactions and transaction lines. These rules can be as complex as necessary to meet the specific requirements and exceptions faced by your organization. In this way, E-Business Tax migrates the tax decision making responsibility from your users who enter transactions, to the tax experts at your enterprise.
When you enter transactions, select the Tax button to review the taxes that E-Business Tax calculates. The Detail Tax Lines window displays data directly from the E-Business Tax repository. Manual changes to existing tax lines, as well as the ability to enter new tax lines, are strictly controlled by the E-Business Tax responsibility, profiles, and security.
Prerequisites
-
Set up tax
See: Setting Up Taxes in Oracle E-Business Tax, Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
To enter or review tax information for a transaction or transaction lines:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to view.
-
To enter or review tax information for this transaction, choose Tax.
To enter or review tax information for a specific invoice line, choose Line Items, select the line to view, then choose Tax.
Tip: To enter or review tax information for all of your transaction lines, choose For this Document.
See: Managing Detail Tax Lines, Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
-
Choose Tax Information to navigate to the Additional Tax Determining Factors window.
Use the Additional Tax Determining Factors window to review and enter additional tax information on Receivables transaction lines.
See: Entering Additional Determining Factor Information on Receivables Tax Lines, Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
Related Topics
Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide
Oracle E-Business Tax Implementation Guide
Detail Tax Lines Window Field Reference
The fields in the Detail Tax Lines window are described in the Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
See: Managing Detail Tax Lines, Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
Related Topics
Entering Freight Information
You can assign freight charges to an invoice or to each invoice line. When you assign freight to an invoice, Receivables includes the freight amount in the total amount of the invoice. To assign freight to each invoice line, choose Freight from the Lines window after entering your invoice lines.
You cannot enter or update freight information if the invoice's transaction type has Allow Freight set to No or if the line type is either Tax or Charges.
By default, Receivables does not calculate tax on freight charges. However, you can calculate sales tax on freight by using inventory items to define freight services and entering these items as ordinary invoice lines.
Prerequisites
-
Define freight carriers, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To assign freight charges to a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to view.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the transaction, then choose Open.
-
To enter freight information for this invoice, choose Freight.
To enter freight charges for a specific invoice line, choose Line Items, select the invoice line to which you want to assign freight charges, then choose Freight.
-
Select the freight Carrier from the list of values (optional). There is no default value.
You use the Freight Carriers window to define the values that appear in the list of values.
-
Enter the Amount of freight charges to be collected for this invoice or invoice line. If you are assigning freight to an invoice line and this is a standard freight line, the default Amount is the Unit List Price of the standard memo line adjusted for any currency differences.
To assign freight charges to all of your invoice lines, open the Freight for All Lines tabbed region, then enter the Amount of freight charges for each line. Receivables calculates the Total amount of freight charges for your invoice lines.
-
Enter the freight GL Account. AutoAccounting creates the default freight account. If it cannot create the entire account, Receivables displays a pop-up window so you can complete the account information. See: Using AutoAccounting.
Related Topics
Freight Window Field Reference
Freight Window Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields in the Freight window.
Carrier: The company you use to send product shipments to your customers.
FOB (free on board): The point or location where the ownership title of goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer. Receivables uses the Ship-to FOB and then the Bill-to FOB as the default value when you enter transactions.
Shipping Reference: Any related freight information you want to provide. Receivables does not validate this field.
Related Topics
Freight Carriers, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Reviewing Accounting Information
Receivables uses AutoAccounting to create the revenue accounts for your invoice after you enter your invoice lines. You can review or update the revenue account assignments for your invoice in the Distributions window.
Note: The default accounting that AutoAccounting creates is considered interim accounting only. Receivables integrates with Oracle Subledger Accounting, the E-Business Suite's centralized accounting engine, which accepts the default accounts that AutoAccounting derives without change. However, you can modify the accounting rules in Subledger Accounting to create accounting that meets your business requirements. See: Accounting in Receivables.
If you are reviewing an invoice that uses rules, you must run the Revenue Recognition Program before you can view accounting information in this window. See: Recognizing Revenue.
You can change the Accounting Flexfield for each account, but you cannot create or delete lines in the Distributions window. If you change a row that has already been posted, Receivables does not alter the posted entry; instead, it makes the adjustments through additional entries. For a list of fields you can update, see: Maintaining Your Transactions.
Prerequisites
-
Define AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To review or update the revenue account assignments for your transaction lines:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to view.
Note: You can also view the detail accounting lines in the form of a balanced accounting entry (i.e., debits equal credits) or as t-accounts by choosing View Accounting from the Tools menu.
See: Viewing Accounting Lines.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the transaction, then choose Open.
-
If this invoice uses invoicing rules, you can view the account sets for this invoice by opening the Sets for All Lines tabbed region.
Note: You can also view accounting information by choosing Lines in the Transaction window, and then choosing Distributions.
-
To update the revenue account assignments for this invoice or invoice line, modify the GL Account information for that account.
Note: The default percent amount of each invoice line assigned to an account is 100% unless AutoAccounting is based on Salesperson and the salesperson assignment is split. In this case, the field will reflect the split and you can either accept this percentage or enter another one. If you change the percent, Receivables calculates the Amount.
Related Topics
Distributions Window Field Reference
Technical Perspective: Transactions
Distributions Window Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields in the Distributions window.
Accounting Rule: The accounting rule for this invoice line. Accounting rules are used to recognize revenue over multiple general ledger periods. If you entered an invoicing rule at the invoice header-level, you must enter a value in this field. If you did not enter an invoicing rule, Receivables skips this field. If you have selected a standard memo line or an item with an accounting rule for this invoice line, Receivables defaults this field to that accounting rule.
Distribution Amount: The specific amount of the invoice line to assign to this revenue account.
GL Date: The date that this account will post to your general ledger. The default is the general ledger date you entered for this invoice. You cannot change this date. If you are using invoicing rules, Receivables does not display the general ledger date until you run the Revenue Recognition Program. See: Invoices with Rules.
Percent (%): The percentage of this invoice line to assign to this revenue account.
Related Topics
Transactions Window Field Reference
Creating Accounting Information
From the Transactions workbench, you can create accounting entries in either draft or final mode for a selected transaction. Select Create Accounting from the Tools menu, which submits the Submit Accounting program.
For a description of the program parameters, see: Create Accounting Program, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide.
Alternatively, you can create accounting for a batch of transactions. See: Creating Accounting in Receivables.
Related Topics
Entering Revenue Credits
You can assign revenue and non-revenue sales credits for your invoices, credit memos, and debit memos. You can also split credit among several salespersons for each invoice or invoice line item and assign additional or bonus credit above your invoice amount. You can modify existing sales credit lines as well as create new ones.
You assign default sales credits by specifying a primary salesperson when entering your transactions. You only need to enter or update sales credit information to give sales credit to more than one salesperson and to distribute credit across your invoice lines. If each invoice line has different sales credit, you can enter line-level sales credits.
If you specify a salesperson, then Receivables automatically populates the salesperson's assigned sales group, if one is available. You can change the default.
You can update sales credits before posting to the general ledger. If you have already posted to the general ledger, then you must use the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard to update sales credits.
Note: For rule-based transactions, you cannot use the Transactions workbench to update sales credits or modify salespeople after Revenue Recognition has run, even if the transaction is incomplete. Instead, you must use the RAM wizard. See: Revenue Accounting.
If you modify a transaction's default salesperson, then either save your work or choose the Sales Credits button, Receivables asks if you want to rerun AutoAccounting to recalculate your receivable and freight accounts. If you choose Yes, Receivables reruns AutoAccounting and makes the appropriate changes to your accounts; otherwise, Receivables saves the changes to the sales credit information, but does not rerun AutoAccounting.
Important: If AutoAccounting is based on sales credits and you change this information, a decision window asks if you want to redefault the accounting for this transaction. If you choose No, the links on the distributions to the old sales credit lines are broken. If you choose Yes, the account assignments and account sets for all account classes that are based on sales credits are recreated based on the new sales credits. See: Using AutoAccounting.
Warning: When updating sales credits in the Transactions workbench, do not rerun AutoAccounting if:
-
AutoAccounting is based on salesperson, and
-
The AR: Allow Update of Existing Sales Credits profile option is set to Yes, and
-
You have previously adjusted revenue on this transaction using the RAM wizard.
To safely update sales credits on transactions whose revenue was already adjusted, you should always use the RAM wizard.
Prerequisites
-
Define salespersons, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define customers and assign a primary salesperson
To enter or review sales credit information for your transaction lines:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction.
-
If you are in the Transaction window, go to step 4.
If you are in the Summary window, select the transaction, then choose Open.
-
To update sales credits for this transaction, choose Sales Credits, then enter a new percent of revenue credit for this salesperson.
To enter different sales credits for each invoice line or for all invoice lines, choose Line Items, then choose Sales Credits.
-
To update sales credits for an invoice line, choose For This Line from the menu, then enter the Revenue or Non-Revenue percentage or amount.
To update sales credits for all invoice lines, choose For All Lines from the menu, then enter the Revenue or Non-Revenue percentage or amount for each salesperson.
-
To split sales credit with another salesperson, choose Default from the menu, then perform the following:
a. Update the sales credit Amount or percent for the primary salesperson, then choose New Record.
b. Enter the Name of the new salesperson and the percentage of sales credit they will receive.
Related Topics
Reviewing Accounting Information
Entering Quick Transactions
You can enter transactions with as little or as much information as you want. You can set up your system so that Receivables provides default values for most required transaction information.
For example, you need to enter many transactions but do not have the time or all of the required information to complete them. In this case, you can enter only minimal information, such as transaction source, customer name and location and any invoice lines, then save your work. Then, when you receive more information, you can requery the incomplete transactions, enter any missing data, and complete each one at your convenience.
Prerequisites
-
Define transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction batch sources and choose automatic invoice numbering, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define receipt classes, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define receipt methods, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define payment terms, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define accounting rules (optional), Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Set up your customers. Define addresses, payment terms, receipt methods, collector, primary salesperson, profile class, freight carrier and terms, and payment details for each.
-
Define customer profile classes, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide. Assign primary salesperson, bill-to location, collector, payment terms, late charge information, currency rates and limits.
To enter a transaction with minimal information:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Enter a transaction Source.
-
Enter the Customer Name or Number.
-
Enter the Bill-to Name and Location.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, choose Open.
-
If you are using manual sequence numbering, then enter a unique Document Number. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
To enter invoice lines, choose Line Items, then enter the Item, Description, Quantity, and Unit Price for item (optional).
-
Save your work. If you are ready to complete this transaction, see: Completing Transactions.
Related Topics
Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval
Entering Invoices with Rules
Invoicing rules let you determine when to recognize the receivable for invoices that span more than one accounting period. You can assign invoicing rules to invoices that you manually enter or import into Receivables through AutoInvoice.
Receivables provides the following invoicing rules:
-
Bill in Advance: Use this rule to recognize the receivable immediately.
-
Bill in Arrears: Use this rule to recognize the receivable at the end of the revenue recognition schedule.
Accounting rules determine the number of periods and percentage of total revenue to record in each accounting period. See: Accounting Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Prerequisites
-
Define transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction batch sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Set up document numbering (optional), Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define accounting rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To enter an invoice with rules:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Enter general information for this invoice. See: Entering Transactions.
-
Choose an Invoicing Rule of In Advance or In Arrears. Once you save this invoice, you cannot update this field, even if no value has been entered.
Important: You need to enter an invoicing rule if you want to assign an accounting rule to line items or if you want Receivables to enter a default rule based on the item or memo line that you enter (see next step).
-
Choose Line Items, then enter the Item, Quantity, and Unit Price for this item. Receivables automatically calculates the total Amount.
Note: Receivables saves your invoice information when you choose the Line Items button.
Tip: You can use standard memo lines instead of items if, for example, you have not installed Oracle Order Management or Oracle Inventory. To use memo lines, place your cursor in the Description field, then enter the memo line or select from the list of values. See: Standard Memo Lines, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Open the Rules tabbed region. Enter an Accounting rule, a Duration, and the First Date to start recognizing revenue for this invoice line.
If you enter an accounting rule whose type is either Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods or Daily Revenue Rate, Partial Periods, enter a rule start and end date. Do not enter a duration.
If you enter a accounting rule whose type is Variable Schedule, enter the number of general ledger periods over which you want to distribute revenue for this invoice line in the Duration field.
If you enter an accounting rule whose type is Fixed Schedule, Receivables displays the default duration for this rule.
Note: The period type for the accounting rule must match a period type in the calendar that is assigned to this ledger. See: Defining Period Types, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide.
-
To view the account sets that AutoAccounting has assigned to your invoice lines, choose Distributions.
-
To view the account sets for a single invoice line, choose Sets for this Line from the menu. Or, to view the accounting information for all invoice lines, choose Sets for All Lines.
Note: The Revenue Recognition program uses the account sets to determine your revenue accounts. You must run the Revenue Recognition program to generate the actual distribution lines. See: Recognizing Revenue.
-
To update accounting information, you can modify the GL account codes for all classes in the Account Distribution Sets.
Note: Revenue is the only class that allows distribution lines. If you add additional revenue distribution lines, the total for all revenue distribution lines must equal 100% per invoice line. To update distributions after you run the Revenue Recognition program, you must change the distributions for the specified periods.
Related Topics
Foreign Currency Transactions
When you create a batch or enter a receipt or transaction that is not in your functional currency, Receivables displays a pop-up window to let you enter exchange rate information. Receivables uses this information to convert your foreign currency receipt and transaction amounts to your functional currency.
Tip: You can also define daily conversion rates. Daily conversion rates enable Receivables to automatically calculate exchange rate information when you enter foreign currency receipts and transactions. See: Entering Daily Rates, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide.
Profile Options
The following profile options affect the appearance and behavior of the Exchange Rates window:
-
Journals: Display Inverse Rate
-
Currency: Allow Direct EMU/Non-EMU User Rates
Note: EMU is an acronym for the Economic and Monetary Union and refers to countries within the European Union who share a single currency called the euro.
If the profile option Journals: Display Inverse Rate is No, Receivables calculates the Functional amount as:
Functional Currency = Foreign Currency * Rate
Otherwise it is calculated as:
Functional Currency = Foreign Currency / Rate
The profile option Currency: Allow Direct EMU/Non-EMU User Rates controls whether you can enter an exchange rate when the receipt or transaction you are entering is in an EMU currency but your functional currency is not an EMU currency (or vice versa).
If this profile option is set to No and you specify a Rate Type of User, Receivables displays three additional fields in the Exchange Rates window. Use these fields to enter an exchange rate between your functional currency and the euro. When you do this, Receivables displays both the fixed (euro to EMU) and the derived (EMU to non-EMU) exchange rates. Refer to the section below for more information.
If this profile option is set to Yes and you specify a Rate Type of User, you can enter an exchange rate between your functional currency and the receipt or transaction currency (the additional fields do not appear in this case).
Exchange Rate and Adjust Exchange Rate Field Reference
Rate Date: The date that applies to the exchange rate for your foreign currency. The default is either the batch date (if this receipt is part of a batch) or the receipt date.
Rate Type: Receivables provides the following conversion rate types:
-
Corporate: You define this rate to standardize rates for your company. This is generally a standard market rate determined by senior financial management for use throughout the organization.
-
Spot: Choose this rate to perform conversion based on the rate on a specific date. It applies to the immediate delivery of a currency.
-
User: Choose this rate when you enter a foreign currency for a receipt and you have not defined a daily exchange rate for the foreign currency. If you choose this rate type, you must enter the exchange rate to use. Receivables does not validate rates with a type of User.
If you select a Rate Type of Spot or Corporate, Receivables verifies that a rate exists for the date you enter and you cannot update the exchange rate.
Rate: The exchange rate for this receipt. If you entered a Rate Type of User, enter an exchange rate. You can have multiple currency exchange rates for the same date. Otherwise, the rate type you entered provides the default rate. You define your non-user exchange rates in the Daily Rates window. If you entered a Rate Type other than User, Receivables verifies that a rate exists for the Rate Date you entered.
Important: The Exchange Rates window displays the following fields instead of the Rate field if certain conditions are met. For more information, see: Profile Options in Oracle General Ledger, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
<functional currency> To EUR: Enter the exchange rate between your functional currency and the euro.
EUR To <transaction/receipt currency>: The fixed exchange rate between the euro and the EMU currency. This is a display-only field.
<functional currency> To <transaction/receipt currency>: The exchange rate between your functional currency and the transaction or receipt currency. This is a display-only field.
Note: The profile option Journals: Display Inverse Rate determines in which order the currencies in these field prompts appear.
Related Topics
Viewing Exchange Rate Information for a Receipt or Transaction
Adjusting an Exchange Rate
You can change the rate type, rate date, and exchange rate of a foreign currency receipt, even if it has been transferred to your general ledger.
You cannot adjust the exchange rate of a foreign currency transaction once it has been posted or has had a receipt applied to it. To use a different exchange rate, you must reverse the transaction (delete it, credit it, or change the transaction type to one that has Open Receivable and Post to GL set to No), then recreate the transaction at the new rate.
Prerequisites
-
Define daily conversion rate types, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide
-
Enter a foreign currency receipt or transaction
To adjust the exchange rate information for a foreign currency receipt:
-
To adjust the rate for a receipt, navigate to the Receipts or the Receipts Summary window.
-
Query the receipt.
-
Select the receipt, then choose Adjust Exchange Rate from the Tools menu.
-
Enter the GL Date and New Rate Date for this exchange rate adjustment (optional). The default for the New Rate Date and GL Date is the current date, but you can enter a new date. If the current date is not in an open period, the default GL Date is the last date of the most recent open period.
-
Enter the New Rate Type to convert your foreign currency amounts into your functional currency. See: Foreign Currency Transactions.
-
If you entered a Rate Type of 'User', enter the New Rate to convert your foreign currency amounts to your functional currency. Otherwise, Receivables determines the rate from the Rate Type and Rate Date.
If three additional fields appear, enter the exchange rate between your functional currency and the euro. See: Exchange Rate and Adjust Exchange Rate Field Reference.
-
Choose Adjust. Receivables saves this adjustment and updates the amount of this receipt in your functional currency.
-
To view the functional currency gain or loss resulting from the currency exchange rate adjustment of the receipt, choose Receipt History.
Viewing Exchange Rate Information for a Receipt or Transaction
You can view exchange rate information for a receipt from either the Receipts or Receipts Summary window. You can view exchange rate information for a transaction from either the Transactions or Transaction Summary window.
To view exchange rate information for a receipt:
-
Navigate to the Receipts or the Receipts Summary window.
-
Query the receipt.
-
If you are in the Receipts window, choose Exchange Rate from the Tools menu.
If you are in the Receipts Summary window, select the receipt, then choose Exchange Rate from the Tools menu.
-
To adjust the exchange rate, see: Adjusting an Exchange Rate.
To view exchange rate information for a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transactions or the Transaction Summary window.
-
Query the transaction.
-
If you are in the Transactions window, choose Exchange Rate from the Tools menu.
If you are in the Transaction Summary window, select the transaction, then choose Exchange Rate from the Tools menu.
-
To update the exchange rate, enter a new Rate Type (if the Rate Type is Corporate or Spot). If the Rate Type is User, enter a new Rate, then choose Ok.
Entering Invoices with Installments
You can let your customers make invoice payments in multiple installments by using a split payment term. When you assign a split payment term to an invoice, Receivables automatically creates the payment schedules based on the invoice date and the payment terms that you define. For example, your split payment term might specify that 40 percent of the invoice is due in 30 days after the invoice date with the remainder due in 60 days.
You define your split payment term in the Payment Terms window. You can enter due dates for each installment and specify discounts to assign to each line of your payment terms. You can also apply the tax and freight for the invoice to the first installment or prorate tax and freight over all of the installments.
Receivables lets you review invoice installments if the status of the invoice is Complete. You can review invoice installments in the Installments window. You can update the transaction due date in the Installments window if the profile option AR: Update Due Date is set to Yes.
Prerequisites
-
Define split payment terms, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To enter an invoice with split payment terms:
-
Navigate to the Transactions window.
-
Enter general information for this invoice. See: Entering Transactions.
-
Enter a split payment term in the Payment Term field, or select a payment term from the list of values.
-
Save your work. If you are ready to complete this invoice, see: Completing Transactions.
Related Topics
Invoices with Rules
Invoicing and accounting rules let you create invoices that span several accounting periods. Accounting rules determine the accounting period or periods in which the revenue distributions for an invoice line are recorded. Invoicing rules determine the accounting period in which the receivable amount is recorded.
You can assign invoicing and accounting rules to transactions that you import into Receivables using AutoInvoice and to invoices that you create manually in the Transactions window.
Accounting Rules
Use accounting rules to determine revenue recognition schedules for your invoice lines. You can assign a different accounting rule to each invoice line. Accounting rules let you specify the number of periods and the percentage of the total revenue to recognize in each period.
-
You can specify whether accounting rules use a fixed or variable revenue recognition schedule. Accounting rules of Fixed Schedule span a predefined number of periods. Accounting rules of Variable Schedule let you define the number of periods during invoice entry.
-
If your enterprise requires the precise recognition of revenue for a schedule that includes both full and partial accounting periods, then you can use an accounting rule of either Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods or Daily Revenue Rate, Partial Periods. These accounting rules let you meet strict revenue accounting standards by using a daily rate to calculate revenue for partial periods. You can recognize the exact amount of revenue for multiple periods in a schedule at a very granular level.
-
You can also create rules that will defer revenue to an unearned revenue account. This lets you delay specifying the revenue recognition schedule until the exact details are known. When these details are known, you use the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard to manually recognize the revenue, or leverage the Revenue Adjustment API.
See: Deferred Accounting Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide and Revenue Accounting.
See: Using Rules.
Invoicing Rules
Use invoicing rules to determine when to recognize your receivable for invoices that span more than one accounting period. You can only assign one invoicing rule to an invoice.
Receivables provides the following invoicing rules:
-
Bill In Advance: Use this rule to recognize your receivable immediately.
-
Bill In Arrears: Use this rule if you want to record the receivable at the end of the revenue recognition schedule.
Important: With Cash Basis Accounting, you only recognize revenue when payment is received. Invoices with rules are therefore not applicable for this method of accounting, as they are designed to distribute revenue over several periods before receipt of payment. If you import invoices into a cash basis accounting system, lines with associated invoicing and accounting rules will be rejected by AutoInvoice.
Bill in Advance Accounting Entries
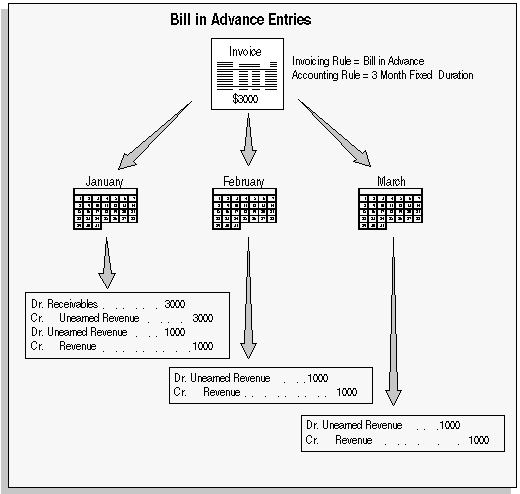
For a text description of this graphic, see Text Description of the Bill in Advance Accounting Entries Graphic.
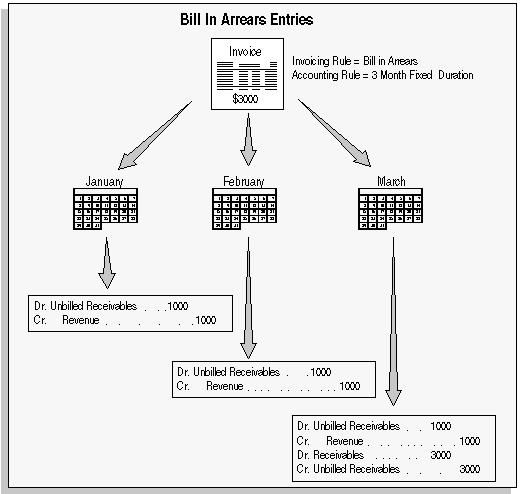
For a text description of this graphic, see Text Description of the Bill in Arrears Accounting Entries Graphic.
Account Sets
Account sets are templates used to create revenue and offset accounting distributions for individual invoice lines with accounting rules. These account sets enable you to split revenue for a line over one or more revenue or offset accounts. To meet your business requirements, you can change account sets before the Revenue Recognition program is run. After the Revenue Recognition program is run, you can change the individual GL distribution lines and Receivables automatically creates reversing GL entries. AutoAccounting creates the initial revenue and offset account sets for your invoice.
Revenue Recognition
The Revenue Recognition program identifies all new transactions and creates the revenue distributions for those transactions. The distributions are created for all periods, even in periods whose status is Not Open, using the rules associated with the transactions. See: Recognizing Revenue.
Related Topics
Accounting Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Using Rules
This section provides you with an overview of how Receivables uses invoicing and accounting rules.
Define Accounting Rules
Use the Accounting Rules window to define an unlimited number of accounting rules. See: Accounting Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Define accounting rules using the following rule types:
-
Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods
Use rules of this type if you want Receivables to use a daily revenue rate to accurately calculate the revenue distributions across all accounting periods, including both full and partial periods. A partial period is an accounting period whose start date is not the first day of the period, or whose end date is not the last day of the period.
Tip: This accounting rule type provides you with the most precise revenue recognition schedule possible. Use rules of this type in cases where you must meet strict revenue accounting standards for partial accounting periods.
Rules of this type require the specification of an accounting rule start and end date during invoice entry. If the invoice is imported with a rule of this type, then both dates are required by AutoInvoice.
Receivables uses the total revenue amount for the line in conjunction with the number of days in the rule duration period (including both start and end dates) to calculate the daily revenue rate:
Daily Revenue Rate = Total Revenue / Number of Days (Total Rule Duration Period)
Using the daily revenue rate, Receivables can accurately calculate the revenue for each period in the revenue recognition schedule:
Revenue Amount = Daily Revenue Rate * Days in Period
-
Daily Revenue Rate, Partial Periods
Use rules of this type if you want Receivables to use a daily revenue rate to accurately calculate the revenue for only partial periods. This rule provides you with an even, prorated revenue distribution across the schedule's full periods.
Similar to the Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods rule type, rules of this type also require an accounting rule start and end date to enable the calculation of the daily revenue rate.
-
Fixed Schedule
For accounting rules with a fixed schedule, you specify the period (such as weekly or monthly) and the number of periods over which the revenue is recognized. The revenue is then evenly divided across the periods. The percentage can be updated if necessary, but must always total 100. For example, if you define an accounting rule with a period type of monthly, spanning 4 periods, and you accept the default, prorated revenue distribution, Receivables will recognize 25 percent of the transactions revenue for each of 4 months.
Fixed schedule rules also let you set specific GL dates on which to recognize revenue, when you select Specific Date as your period type. When you specify a date for a period, then all other periods for this accounting rule must also be assigned a date.
-
Variable Schedule
When defining accounting rules with a variable schedule, you must enter a period type, but not the number of periods. The number of periods is defined when you manually enter an invoice in the Transaction window. If the invoice is imported, the number of periods is passed through AutoInvoice.
When defining a variable schedule accounting rule, you can optionally specify what percentage of revenue you want to recognize in the first period. The remaining revenue will be prorated over the number of periods you specify during invoice creation.
For example, suppose you bill a contract for $900, which starts January 14 and ends April 13 (90 days), and the accounting period is Monthly. In this contract period, January and April are partial periods, and February and March are full periods. This table illustrates the various revenue recognition schedules that Receivables calculates, depending on the accounting rule type:
| GL Date | Period | Days in Period | Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods | Daily Revenue Rate, Partial Periods | Fixed Schedule | Variable Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 14 | January | 18 | 180 | 180 | 225 | 180 |
| February 14 | February | 28 | 280 | 295 | 225 | 240 |
| March 14 | March | 31 | 310 | 295 | 225 | 240 |
| April 13 | April | 13 | 130 | 130 | 225 | 240 |
The above example illustrates the following:
-
If the accounting rule is Daily Revenue Rate, All Periods, then Receivables calculates the daily revenue rate ($900 / 90 days = $10) and uses the rate to calculate the revenue in each period. Receivables uses the final period to catch up with any rounding issues.
-
If the accounting rule is Daily Revenue Rate, Partial Periods, then Receivables uses the daily revenue rate to calculate the revenue for only the partial periods. The full periods receive equal revenue distributions.
-
If the accounting rule is Fixed Schedule, then Receivables uses the rule definition and divides the revenue equally across the number of periods specified in the rule.
-
If the accounting rule is Variable Schedule, then you specify the number of periods during invoice entry, and optionally specify the percentage of revenue to recognize in the first period. Receivables evenly distributes the revenue balance over the remaining periods.
In this example, 20% of the total revenue is recognized in the first period out of a total of four periods.
Assign Invoicing and Accounting Rules
For invoices that you enter manually, you can assign an invoicing rule in the Transactions window. You can assign a default invoicing and accounting rule to your items in the Master Item window (Invoicing tabbed region) and to your Standard Lines in the Standard Memo Lines window.
This table shows where you can assign a default invoicing rule:
| Assigned To | Window | Tabbed Region |
|---|---|---|
| Invoice | Transaction | Main |
This table shows where you can assign an accounting rule:
| Assigned To | Window | Tabbed Region |
|---|---|---|
| Invoice Line | Transaction | Additional Line Information |
| Items | Define Items | Item (Invoicing Attributes) |
| Standard Lines | Standard Memo Lines | Not Applicable |
If you are entering an invoice manually, you must enter an invoicing rule on the invoice header or you will not be able to associate accounting rules with the invoice lines. If you enter an invoicing rule and include items or standard memo lines that have associated accounting rules, the accounting rules default for the invoice line. You can change or manually enter the accounting rules for these invoice lines if there has been no activity against the invoice.
Note: You can also assign invoicing rules to items and standard lines, but these will not be used during manual invoice entry. This is because the invoicing rule assigned at the invoice header will override the invoicing rules defined for the item or standard line.
If you import invoice data from an external system, you must populate the correct columns in the AutoInvoice tables if you want AutoInvoice to generate invoices with rules.
This table shows which column to populate if you want AutoInvoice to generate invoicing rules:
| Column | Populate if: |
|---|---|
| INVOICING_RULE_ID | Your batch source validates rules by ID. |
| INVOICING_RULE_NAME | Your batch source validates rules by value. |
This table shows which column to populate if you want AutoInvoice to generate accounting rules:
| Column | Populate if: |
|---|---|
| ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION | You are passing a variable schedule rule. |
| ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID | Your batch source validates rules by ID. |
| ACCOUNTING_RULE_NAME | Your batch source validates rules by value. |
| RULE_START_DATE and RULE_END_DATE (or ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION if no RULE_END_DATE) ACCOUNTING_RULE_NAME or ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID AMOUNT |
Your are passing a rule that requires the calculation and use of a daily revenue rate. |
Note: If no rules are passed with the invoice lines in the interface tables, AutoInvoice will not try to derive the invoice and accounting rules from the associated items or standard lines.
AutoInvoice uses the invoicing rules assigned to the invoice lines to group lines into invoices. An invoice can only have one invoicing rule, hence lines imported with an invoicing rule of Bill in Arrears will not be grouped with lines with a Bill In Advance invoicing rule when creating an invoice.
Accounting rules, however, require no special grouping, as an invoice may contain a different accounting rule for each invoice line.
Determine the Invoice and GL Dates
When importing invoices, AutoInvoice determines the invoice GL date and the transaction date as follows:
-
If you use Bill in Advance as the invoicing rule, AutoInvoice uses the earliest start date of the accounting rules associated with your invoice lines as the GL date of the invoice.
-
If you use Bill in Arrears as the invoicing rule and the invoice line has a Fixed Schedule accounting rule and a period of Specific Date, AutoInvoice sets the GL date and transaction dates equal to the latest Specific Date of the accounting rule.
For all other accounting rules using the Bill in Arrears invoicing rule, AutoInvoice first computes an ending date for each invoice line based on the accounting rule, accounting rule start date, and duration. AutoInvoice then uses the latest specific date for both the invoice GL date and the transaction date.
When creating invoices with rules manually, the GL date of the invoice is entered during invoice entry. If you use Bill in Advance as the invoicing rule, this date will remain equal to the GL date of the invoice.
However, Receivables overrides this date for an invoicing rule of Bill in Arrears when you save the invoice after completing invoice lines. Receivables uses the same method to derive the new GL date as it does for imported invoices. This method is explained in detail above. Receivables will warn you that it is updating the GL date of the invoice when you save the record. You can then change this date if it does not meet your requirements.
Note: Receivables updates the GL date, even if the date falls in a period whose status is Not Open.
Determine Accounting Rule Start Dates
The first GL date (or accounting rule start date) for an accounting rule can be different from the GL date of the invoice. When the Revenue Recognition program is run, then if the accounting rule start date is different from the invoice start date, the accounting rule will modify the invoice start date and the period in which you recognize your receivable based on whether the invoicing rule is Advanced or Arrears. For example, the GL date of the invoice is January 10, and the First GL Date of the accounting rule for the line is February 15. When the Revenue Recognition program is run in January, the GL date of the invoice is changed to February 15 and the entire schedule moved accordingly. Depending on whether the invoicing rule is Advanced or Arrears, the receivable is recognized either in February or in the last month of the schedule.
When entering invoices manually, you must set the date that you want to start recognizing revenue for an invoice line. Use the First Date field in the Lines window to enter the start date.
When importing invoices, AutoInvoice determines the accounting rule start dates as follows:
-
If your invoice has an accounting rule with a type Fixed Schedule and a period of Specific Date, AutoInvoice uses the earliest accounting rule date as your rule start date. For example, if your accounting rule dates are 10-JUN-93, 10-JUL-93, and 10-AUG-93, AutoInvoice uses 10-JUN-93 as your rule start date.
-
If you elected to derive the rule start date, AutoInvoice first uses the ship date in the interface table. If the ship date does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the sales order date. If the sales order date does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the date you entered in the Run AutoInvoice window.
-
If your invoice does not use a Fixed Schedule accounting rule with a specific date period, or you have not elected to derive the rule start date, then AutoInvoice uses the default date you specified in the Run AutoInvoice window.
If you are using a deferred accounting rule, you can use a different GL start date than the one that you entered on the transaction line in the Revenue Accounting and Sales Credits window. See: Deferred Accounting Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
View and Update Account Sets
Account sets for invoices with rules are created by AutoAccounting. You can manually update the account sets for both imported and manually created invoices in the Distributions window off the Transactions Workbench.
For each account set, Receivables specifies the account and percent of the line total assigned to each account. In the Sets for this Line and Sets for All Lines regions of the Distributions window, you can update account sets to split revenue or offset amounts over multiple accounts any time before running the Revenue Recognition program. This lets you ensure that revenue is distributed to the correct accounts, regardless of how account structures may change. Receivables always ensures that the entered percents total 100.
In the Sets for All Lines region, you can view account sets for all lines. You can also use this region to update the account assignment for a given line, but you must use the Sets for this Line region to update the percent assigned to the account.
To update an account set, specify the account set class that contains the account sets. Valid Account Set Classes include:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Offset | This account set type includes the suspense accounts to be used during your revenue recognition cycle. If your invoicing rule is Bill in Arrears, the offset account set is Unbilled Receivables. If your invoicing rule is Bill in Advance, the offset account set is Unearned Revenue. |
| Revenue | This account set type includes your revenue accounts. |
| Tax | This type of account set is used for tax lines. |
After the Revenue Recognition program is run, the names of the regions of the Distributions window change to the Accounts for This Line and the Accounts for All Lines regions. Use these regions to review and update the actual distributions that were generated using the account set that you specified.
Recognize Revenue
Invoicing and Accounting rules are used to schedule how and when you want to recognize revenue and receivable amounts for selected invoices. However, the distributions are not created until you run the Revenue Recognition program. See: Recognizing Revenue.
The Revenue Recognition program is run automatically whenever you transfer records to your General Ledger using the Submit Accounting program. This ensures that the revenue for invoices with rules is recognized before you post and close the period. Alternatively, you can submit the Revenue Recognition program manually at any time from the Run Revenue Recognition window. The Revenue Recognition program will not create duplicate distribution records even if the program is run several times within the same period.
Credit Invoices with Rules
You can adjust the account assignments of invoices that you wish to credit in three ways: LIFO, Prorate, and Unit. The Last In First Out (LIFO) method backs out revenue starting with the last GL period of the invoice revenue. This method reverses revenue recognition from prior periods until it has backed out an amount of revenue that is equal to the amount of your credit memo line. The Prorate method credits an equal percentage of all of your invoice's account assignments. The Unit method lets you reverse the revenue for the number of units you specify from an original line of the invoice. For example, if an invoice line has a quantity of 10 units, and you credited 2 units, then Receivables would reverse 20% of the revenue starting with the period you specify in the additional line information tabbed region, and continuing until the entire amount of the credit is given. You can specify any of these credit memo methods when you create credit memos through either the Transaction window or by running AutoInvoice.
Note: Note: If you use the Unit method, then you cannot enter a credit quantity that is greater than the quantity on the target invoice line.
Related Topics
Entering Commitments
Receivables lets you create two types of commitments:
-
Deposits: Create a deposit to record a customer's prepayment for goods or services that you will provide in the future.
-
Guarantees: Create a guarantee to record a contractual agreement with your customer to conduct business over a specified period of time.
Use the Transaction window to enter or update your customer commitments. Receivables lets you update certain information depending on the commitment status. For a list of fields you can update, see: Maintaining Your Transactions.
You define a commitment and then specify the debit and credit accounts. When your customers invoice or credit against their commitments, Receivables automatically adjusts the commitment balance and generates reversing accounting entries.
Note: You can also add a deposit to an invoice that is already completed. See: Using Commitments.
You can assign sales revenue and non-revenue credit as a percentage of the commitment total. If you do assign sales revenue credit, Receivables ensures that you assign 100% of your commitment total. To assign additional or bonus credit for certain sales, use non-revenue sales credits.
Note: You can specify in the transaction type whether you want to include tax and freight when applying a deposit to a transaction. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Prerequisites
-
Define payment terms, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction batch sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define salespersons, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To enter a customer commitment:
-
To enter a commitment, follow the same procedure that you used when entering transactions. See: Entering Transactions.
The following steps are unique, however, to entering commitments.
-
Choose a transaction Class of Deposit or Guarantee.
-
Enter the payment Terms if this commitment is a deposit.
You cannot enter installment payment terms if the commitment is a guarantee.
-
Open the Commitment tabbed region.
-
Enter a range of Effective Dates for this commitment (optional). If you do not assign an end date, Receivables lets you enter invoices and credit memos against this commitment indefinitely until the amount due becomes zero. If you enter an end date, Receivables verifies that all existing invoices against this commitment are included in this date range.
-
Enter the Amount of this commitment.
Note: You can never use more than the original deposit amount, or increase the deposit amount.
-
Enter either an Item or a Memo Line for this commitment, or select from the list of values.
If AutoAccounting depends on standard line items, Receivables uses the revenue account associated with this item or memo line along with your AutoAccounting setup to determine the default revenue, AutoInvoice Clearing, Unbilled Receivable, Unearned Revenue, and Receivable accounts for this commitment.
-
Enter a brief Description for this commitment.
-
To review or update accounting information, choose Distributions. See: Reviewing Accounting Information.
Note: Use the AR: Deposit Offset Account Source profile option to indicate how you want to derive the offset account for deposits. Receivables can use either AutoAccounting or the deposit's transaction type as the accounting source for the offset account.
Related Topics
Technical Perspective: Transactions
Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval
If you group your invoices and debit memos into batches, you can view the difference between your control and actual batch totals as you enter transactions. These differences alert you to data entry errors, missing or lost transactions, or duplicate entries. In addition, by grouping your related transactions in a batch, transactions can share default attributes such as transaction type, transaction source, and payment terms.
You can only delete a batch if it does not contain any transactions.
Prerequisites
-
Define transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define transaction batch sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Set up document numbering, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Batch Statuses
A batch has a status that indicates whether it is complete. A batch can have one of the following statuses:
New: This is a new batch, and it has not yet been saved. After you save, you can change the status to Out of Balance, Open, or Closed.
Out of Balance: The actual count and amount of transactions in this batch do not equal the control count and amount.
Open: The actual count and amount equal your control count and amount.
Closed: The actual count and amount match the control count and amount.
Important: Receivables does not update the batch status automatically. After you enter transactions, navigate to the Status field in the Transaction Batches window and enter a status, or select one from the list of values.
To create a batch of transactions:
-
Navigate to the Transaction Batches or the Transaction Batches Summary window.
-
Enter the transaction batch Source. Batch sources control invoice and invoice batch numbering and the default transaction types for transactions you add to this batch.
-
If Automatic Batch Numbering for this batch source is No, enter a unique batch Name. Otherwise, Receivables assigns a batch name when you save.
-
Enter the Batch and GL Date for this batch. The default batch date is the current date, but you can change it. The default GL Date is the current date. However, if the current date is not in an open period, the default is the last date of the most recent open period. The GL Date you enter must be in an Open or Future period. The batch and GL dates provide default dates for transactions that you add to this batch.
-
Enter the batch Currency. The default is your functional currency, but you can change it. If you change the batch currency and you have not defined daily conversion rates, enter exchange rate information. See: Foreign Currency Transactions.
-
Enter the total number of transactions in this batch in the Control Count field, then enter the total dollar amount of transactions in this batch in the Control Amount field.
-
To add transactions to this batch, choose Transactions or Transaction Summary. See: Entering Transactions. Receivables saves your batch information.
Related Topics
Completing Transactions
Before you can complete a transaction in Receivables, you must ensure that all required information for that transaction type has been entered.
After you enter all required information, you can change a transaction's status to Complete in the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window. When you complete an invoice, Receivables creates payment schedules based on the payment terms and invoice date you specified and includes the invoice in the standard aging and collection process if the transaction type has Open Receivables set to Yes.
Important: If you change the transaction type of a completed invoice to a type in which Open Receivable is set to No, Receivables no longer includes this invoice in the standard aging and collection process.
If you update a completed invoice by changing values on which AutoAccounting depends (for example, salesperson), and AutoAccounting fails, Receivables displays a warning message and changes the status of the invoice to Incomplete. This is also true if you modify values that Receivables uses to calculate tax (for example, ship-to address).
Use the Complete button in the Transactions or Transaction Summary window to complete transactions. Use the Complete check box when the form is in Query mode to indicate the status of transactions you want to view.
Prerequisites
Validation for completing a standard transaction
-
The invoice must have at least one line.
-
The GL date of the invoice must be in an Open or Future period.
-
The invoice sign must agree with the creation sign of the transaction type.
-
The sum of distributions for each line must equal the invoice line amount.
-
If the Calculate Tax field for the transaction type is set to Yes, tax is required for each line (except lines of type Charges).
-
If freight was entered for this transaction, you must specify a freight account.
-
If the system option Require Salesreps is Yes, salespersons must be assigned to each line.
-
If salespeople are assigned to each line, the total revenue sales credit percentage must equal 100%.
-
All the activity date ranges for the setup values (for example, payment terms) must be valid for the invoice date.
-
If this transaction uses an automatic receipt method, you must enter Customer bank, branch, and account information.
Validation for completing an invoice with rules
-
Each line must have an accounting rule and a rule start date.
-
Valid account sets must exist for each invoice line.
-
Valid account sets must exist for tax that is calculated or entered.
Validation for completing a standard credit memo
-
You must enter at least one credit memo line and specify revenue account assignments for each memo line.
-
You must specify a valid receivable account.
-
If your credit memo is crediting tax, you must specify valid tax accounts.
-
If your credit memo is crediting freight, you must specify valid freight accounts.
Note: You cannot change the status of a credit memo that you entered against an invoice, debit memo, or commitment from Complete to Incomplete if you entered another credit memo against this item after the initial memo.
Also, you cannot change the status of a credit memo that you entered against an invoice, debit memo, or commitment from Incomplete to Complete if you entered and completed another credit memo against this item after the initial memo.
To complete a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to complete.
-
Verify that all requirements for completing this type of transaction are met (see above).
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the transaction, then choose the Complete button.
If you are in the Transactions window, choose the Complete button.
Note: When you complete a transaction, the button name changes from Complete to Incomplete. If you click on the button again, Receivables changes the transaction status back to Incomplete (unless the transaction was posted to GL or now has activity, such as a receipt application, against it; in this case, you cannot change the status).
Related Topics
Voiding Transactions
Receivables lets you make a debit memo, credit memo, on-account credit, invoice, or chargeback invalid by updating the transaction type.
You can void a transaction only if the following are true:
-
it does not have any activity against it
-
it has not been processed by the Revenue Recognition program
-
it has not been posted to your general ledger
Prerequisites
-
Define a transaction type of 'void' (set Open Receivables to No), Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To void a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transaction or the Transaction Summary window.
-
Query the transaction.
-
Change the transaction Type to your 'void' transaction type.
Viewing Transactions
Receivables lets you view detailed or summary information about your invoices, receipts, credit memos, debit memos, and commitments that have outstanding balances.
Use the Account Details window to view the status, due date, number of days late, dispute amount, and the balance due for a specific transaction. You can view more detailed information about a transaction by choosing the Details button. Use this window to view details about receipts, as well.
Note: The Account Details window does not display receipts, credit memos, on-account credits, adjustments, and debit items that have a transaction type with Open Receivables set to No. Transactions assigned to a transaction type with Open Receivables set to No do not update your customer balances and therefore are not included in the standard aging and collection process.
You can update the due date for a transaction in this window if the AR: Update Due Date profile option is set to Yes.
Note: You cannot update the due date of an invoice included in a draft or final balance forward bill regardless of the setting of the AR: Update Due Date profile option. Allowing update to the due date of individual invoices of a balance forward bill causes problems with aging.
To view information for a specific transaction, such as customer bill-to and ship-to addresses, payment terms, due date, status and invoice lines, choose the Transaction Overview button.
Tip: To automatically display receipts at risk and include them when calculating a customer's past due balance, set the profile option AR: Include Receipts at Risk in Customer Balance to Yes. See: Overview of Receivables User Profile Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
If this profile option is set to No, you can include receipts at risk by choosing Include Receipts at Risk in Customer Balance from the Tools menu and then re-executing your query.
To review detailed information about a specific transaction:
-
Navigate to the Account Details window.
-
To limit your query, enter selection criteria in the Find Account Details window. For example, enter a Transaction Number, a range of Due Dates, a Bill-to Customer Name, transaction Class, Status, or low and high values of Balances Due to select only those transactions. Leave a field blank if you do not want to limit your query to transactions matching that criteria.
-
Choose Find.
-
Select the item to view, then choose Details.
Note: When you navigate to either the Receipts or Transactions workbench from the Account Details window, you cannot view the next transaction by pressing the Down Arrow key. To display the next transaction, return to the Account Details window, select the transaction to view using either the mouse or Down Arrow key, then choose Details again.
To view open activities against a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Account Details window.
-
To limit your query, enter selection criteria in the Find Account Details window.
-
Choose Find.
-
Select the transaction to view, then choose Activities.
You can also view activities for a receipt. See: Reviewing Receipts and Applications.
To view all relevant information for a specific transaction:
-
Navigate to the Account Details window.
-
To limit your query, enter selection criteria in the Find Account Details window.
-
Choose Transaction Overview.
-
To view additional information about this transaction, open the More tabbed region.
Note: The Lines and Transaction Total fields in the Transaction Overview window do not include any inclusive or exclusive tax amounts for the transaction you are viewing. However, the Unit Price and Amount fields for the individual transaction lines will include tax if the tax code or tax group for this line is tax inclusive.
Viewing Transaction Balances
Receivables lets you view complete information for a specific transaction in the Balances window. The Balances window displays the original transaction amount, the total amount of receipts, credit memos, adjustments, and late charges applied to this transaction and any discounts taken.
Note: If Bills Receivable is enabled, then the Balances window also displays information about your bills receivable assignments.
The Balances window also indicates at what level a receipt, credit, or discount was applied to this transaction and the type of adjustments that were created. For example, you may have created two types of adjustments for a single transaction; one of type 'Charges' and another of type 'Freight'. Similarly, more than one credit memo may have been applied; one at the Line level and one at the Tax level.
Receivables displays the total amount of each action affecting this transaction in the 'Total' column and displays how the line, tax, freight, and late charges balances were affected in the 'Balance' row.
Use the Line Number field to view line-level balances for a transaction, after a receipt application has been made. See: Applying Receipts in Detail.
By default, the Balances window displays transaction balances in the currency in which they were entered, but you can view amounts in your functional currency (if different from the entered currency) by checking the Functional Currency box.
To view current balances for a transaction:
-
In the Account Details window, query a transaction and choose Balances.
-
In the Transactions window, query a transaction and, in the Balance Due region, choose Details.
-
In the Transactions Summary window, query a transaction and choose Balances from the Tools menu.
Related Topics
Account Details Field Reference
Account Details Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields in the Account Details window.
Balance Due: The balance of the transaction. If this item is an invoice, debit memo, deposit, guarantee, or chargeback, the remaining amount is the amount due. If this item is a receipt or on-account credit, the remaining amount is the amount not yet applied to debit items.
Class: The transaction class of a transaction or receipt. Classes include invoices, receipts, credit memos, chargebacks, guarantees, deposits, and debit memos.
Cumulative Balance: If you select a range of transactions, then the Cumulative Balance field displays the balance for the selected items. With your mouse, use the Shift key to select a range of transactions, or the Control key to select specific transactions. If you do not select transactions, then the cumulative and total balances are equal. If you select transactions with different currencies, then only the Functional column displays the cumulative balance.
Note: The Account Details window lets you view transactions across operating units. If the transactions displayed in the Account Details window belong to different ledgers, then a cumulative balance will not be displayed in your functional currency. This is because ledgers can have different functional currencies.
Dispute Amount: The amount of the transaction that is in dispute or has pending adjustments against it.
Placing an Item In Dispute
If your customer disagrees about the outstanding balance for an item, you can mark that item or a specific amount due as 'in dispute.' Amounts that are in dispute appear in collections reports. Oracle Receivables does not prevent you from applying payments to disputed transactions.
You can place transactions in dispute from Oracle Advanced Collections or from Oracle iReceivables by requesting a credit using the Credit Memo Workflow. See: AME Credit Memo Request Workflow.
If you are using Oracle Trade Management to track your customers' invoice short payments, then you can also place transactions in dispute by creating a claim. See: Applying Receipts.
In Receivables, you can also place items in dispute or take them off of dispute in these windows:
-
Account Details
-
Installments (accessed from the Transactions or Transactions Summary window)
-
Transactions (More tab)
You can choose whether to calculate late charges on disputed items by selecting the Disputed Transactions option at the customer profile class, customer account, or site level. See: Defining Customer Profile Classes, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide and Adding and Updating Account Late Charges.
To place an item in dispute in Receivables:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to place in dispute.
-
Select the transaction, then choose Installments.
-
Enter the Dispute Amount and Dispute Date.
You can also place an item in dispute by entering a dispute amount and date in the Account Details window or in the Transactions window, on the More tab.
To mark an item as no longer in dispute:
-
Navigate to the Account Details, Installments, or Transactions window.
-
Query the transaction.
-
Change the Dispute Amount to 0 (zero).
-
Change the Dispute Date to today's date.
Viewing Items in Dispute
Review items in dispute by creating the Disputed Invoice Report. See: Disputed Invoice Report.
Related Topics
Disputing Invoices, Oracle Advanced Collections User Guide
Oracle iReceivables Implementation Guide
Copying Invoices
The Copy Transactions window lets you automatically create invoices for goods or services that you regularly provide to your customers. For example, you need to bill your customers for services or products provided once a month for two years, but do not want to manually create a new invoice every month. By creating invoice copies, you can quickly create a group of invoices that share the same characteristics. All of the dates for the copied invoices (for example, invoice date, GL date, and due dates) are determined using the copy rule that you specify.
When you copy invoices, Receivables does not derive the exchange rates and tax rates from the copied invoice date. Instead, it derives the exchange rate and tax rate from the date of your first copied invoice. Consequently, if you are copying invoices in a foreign currency, or have tax rates that change over time, you may need to manually update the exchange rate and tax rate. (Receivables calls the tax engine to recalculate tax when you copy invoices.) You can use the Transactions window to update the tax rates for your copied invoices.
Important: If the invoice you are copying has lines that use inclusive tax codes and a tax rate has changed, the line amounts for your copied invoice(s) will also be different from the original transaction. This is because the line amount for a line assigned to a tax inclusive tax code includes tax. If the tax rate for any of the original invoice's lines has changed, the line, tax, revenue, and sales credit amounts for the copied invoice(s) will be different from the original transaction.
During the copy process, Receivables ignores the value of the Tax Calculation box on the original invoice's transaction type, to preserve the tax calculation.
Receivables uses the invoice amount from your model invoice on your copied invoices. Therefore, even if the model invoice has been credited, adjusted, or paid, the amount for all copied invoices is equal to the original invoice amount.
Receivables also uses the accounting distributions from your model invoice on your copied invoices. If your model invoice failed collectibility analysis for automatic revenue recognition, then the copied invoices inherit the model invoice's unearned revenue distributions. Once the copied transactions are completed, you should review the accounting distributions and use the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard to make changes as appropriate. See: Revenue Accounting and Event-Based Revenue Management.
When copying an invoice, Receivables retains the original salesperson and sales group. You can optionally modify this sales information.
You can copy invoices as often as you want and create copies from any existing invoice, even if it is closed.
You create, review, and update copied invoices in the Transaction window.
Copy Rules
You can use one of the following rules to copy an invoice:
Annually: This rule creates an invoice once a year on the same day and month of each year. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, then the invoice date of your first copied invoice is January 1, 1992. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at one-year intervals.
Semiannually: This rule creates an invoice every six months on the same day.
Quarterly: This rule creates an invoice every three months on the same day. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, then the invoice date of your first copied invoice is April 1, 1991. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at three-month intervals.
Monthly: This rule creates an invoice every month on the same day. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, then the invoice date of your first copied invoice is February 1, 1991. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at one-month intervals.
Bimonthly: This rule creates an invoice every other month on the same day. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, then the invoice date of your first copied invoice is March 1, 1991. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at two-month intervals.
Weekly: This rule creates an invoice every seven days. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, then your first copied invoice is January 8, 1991. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at seven-day intervals.
Single Copy: This rule creates one copy of your model invoice for the day you enter in the First Invoice Date field.
Days: This rule creates an invoice based on the number of days you specify. For example, if your model invoice has an invoice date of January 1, 1991, and you enter 20 in the Number of Days field, the invoice date of your first copied invoice is January 21, 1991. All subsequent invoice dates are calculated at 20-day intervals.
To copy an invoice:
Prerequisites
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or the Copy Transactions window.
-
Query the invoice to use as a model for your copied invoices.
Note: You must select a completed invoice.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the invoice, then choose Copy.
-
Choose a copy Rule.
-
Enter the number of copies to create in the Number of Times field.
-
If your copy rule is Days, enter the Number of Days between your copied invoice dates.
-
If the Post to GL flag of the model invoice's transaction type is Yes, enter the First GL Date for the copied invoice. This date must be in an open, future, or never opened period.
Note: If you choose a date in a never opened period, Receivables will create these invoices as incomplete. To complete these invoices, open the period and query the invoice in the Transactions Summary window, then choose the Complete button. However, if you are using the Bill in Arrears invoicing rule, the invoice will be created as complete even if its GL date is in a never opened period.
-
Enter the First Transaction Date to create the copied invoice. The default is the invoice date of the first copied invoice (determined by the copy rule you entered), but you can change it.
-
If you are using manual sequence numbering, enter a unique document Number for each copied invoice. Otherwise, Receivables assigns document numbers when you save. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Save your work. Receivables submits a concurrent process to create your copied invoices and generates a unique Request ID number. You can use this number to review the status of your request in the Concurrent Requests Summary window.
Receivables also creates the Recurring Invoice Program report when you save. Use this report to review all revenue distributions created for the specified period for invoices that use invoice and accounting rules. See: Recurring Invoice Program Report.
Related Topics
Recurring Invoice Program Report
This report contains information about your model invoice and the new, copied invoices that you created in the Copy Transactions window. Receivables automatically generates this report when you submit a request to create copied invoices.
Important: Your new, copied invoices will be created as not complete if the First GL Date was in a never opened period when they were created. To complete these invoices, you must open the never opened period, query each invoice in the Transactions window, and check the Complete check box. However, if you are using the Bill in Arrears invoicing rule, the invoice will be created as complete even if its GL date is in a never opened period.
Related Topics
About Adjustments
Receivables lets you make either positive or negative adjustments to your invoices, debit memos, chargebacks, on-account credits, deposits, and guarantees. You can approve adjustments that are within your approval limits and give pending statuses to adjustments that are outside your approval limits. You can automatically write off debit items that meet your selection criteria.
Adjustment Status
An adjustment has a status that indicates whether it is complete. Receivables provides the following adjustment statuses:
Approved: This adjustment has been approved. Receivables updates the debit or credit item amount and status to reflect the adjustment.
Research Required: This adjustment is on hold because you are either researching the debit or credit item, or are requesting additional information about the adjustment.
Rejected: You have rejected this adjustment. Adjustments with this status do not update the balance of the credit or debit item.
Pending Approval: The adjustment amount is outside the approval limits of the user who entered the adjustment. Adjustments with this status can only be approved by a user with the appropriate user approval limits.
You can define other adjustment statuses by updating the Receivables lookup 'Approval Type'. See: Reviewing and Updating Receivables Lookups, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Adjustment Activities
You use receivables activities to default accounting information for your miscellaneous receipt, late charge, and adjustment transactions. You can define as many receivables activities as you need. Define adjustment activities in the Receivables Activities window. See: Receivables Activities, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Adjustment Types
You can create an adjustment at the invoice header level, but cannot adjust specific elements of an invoice, debit memo, credit memo, or chargeback. See: Creating an Adjustment.
Validation
When you create an adjustment, Receivables verifies that it is within your adjustment approval limits before approving the adjustment. If you enter an adjustment that is within your assigned approval limit for the currency of that item, Receivables updates your customer's balance to reflect the adjustment. If you enter an adjustment that is outside your approval limits, Receivables creates a pending adjustment with a status of Pending Approval. See: Approval Limits, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
If the transaction type does not allow over-application, you cannot enter an amount that would reverse the sign of the balance of the debit item.
If you specify Invoice Adjustments as your type of adjustment, Receivables requires that your adjustment amount be the exact amount to close the item you are adjusting, and enters this amount in the Amount field.
Approving Adjustments
A pending adjustment must be approved before it affects the remaining balance of a transaction. You control adjustment approvals by creating individual approval limits. You define adjustment approval limits in the Approval Limits window by specifying a minimum and maximum approval amount for each user and currency. See: Approval Limits, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
You can overapply an adjustment if the transaction type of the item you are adjusting has Allow Overapplication set to Yes. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Use the Adjustments or the Approve Adjustments window to review and approve your pending adjustments. To review your adjustments and their statuses, see: Adjustment Approval Report. To review only adjustments with a status of 'Approved,' see the: Adjustment Register.
Adjustment Numbering
Receivables automatically generates and assigns a unique adjustment number when you create adjustments.
Related Topics
Creating Automatic Adjustments
Entering Manual Adjustments
Use the Adjustments window to create your adjustments. When you assign an activity to your adjustment, Receivables automatically uses the accounts assigned to that activity for the adjustment.
A transaction must have a status of Complete before you can adjust it.
Prerequisites
-
Define your user approval limits, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To create a manual adjustment:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the transaction to adjust.
-
Select the transaction, then choose Adjust.
-
If this transaction has multiple installments, select the installment to adjust, then choose Adjust.
-
Enter the adjustment.
-
Enter an Activity Name and choose the Type of adjustment you are creating. Valid adjustment types include Invoice, Charges, Freight, and Tax.
-
Enter the Amount of this adjustment. If you specify 'Invoice' as your adjustment type, Receivables requires that the amount of your adjustment be at least enough to close the item you are adjusting, and displays this value in the Amount field. If the amount of this adjustment is outside your approval limits, Receivables sets the status of the adjustment to Pending Approval when you save (unapproved adjustments do not update the balance due for an item).
Important: You can enter an amount greater than the balance due only if the transaction type's Allow Overapplication option is set to Yes. For more information, see: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Enter the GL Date for this adjustment (optional). The default is the later of either the transaction GL date or the current date. However, if this date is not in an open period, the default GL Date is the last date of the most recent open period. The GL date must be later than or equal to the GL date of the debit item you are adjusting and must be in an open or future-enterable period.
-
Enter the Adjustment Date (optional). The default is the current date, but you can change it.
-
Open the Account IDs tabbed region, then enter the GL Account for this adjustment (optional). The activity name provides the default GL account, but you can change it.
-
If you are using manual document numbering, enter a unique Document Number for this adjustment. If you are using automatic document numbering, Receivables assigns a document number when you save. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Open the Comments tabbed region, then enter a Reason for creating this adjustment. Receivables prints your reasons on the Adjustment Register.
Note: An adjustment reason is optional unless you set the AR: Require Adjustment Reason profile option to Yes. See: Overview of Receivables User Profile Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Update the Status of this adjustment (optional). If this adjustment is within your user approval limits, you can choose any status. If you are reviewing a previously approved adjustment, Receivables skips this field.
-
Save your work. Receivables generates a unique number for this adjustment.
Related Topics
Creating Automatic Adjustments
Adjustments Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields in the Adjustments window.
Adjustment Date: The date to apply your adjustment to the item you have selected. The default value for this field is the later of either the GL date of the transaction or the current date. The application date for an adjustment must be later than or equal to the transaction date of the item you are adjusting.
Balance: The balance due of the installment for this invoice, debit memo, or chargeback in the entered currency. The balance due for the debit item is the original amount less any activity, such as payments, credit memos, or adjustments.
Pending Adjustments: The total amount of adjustments that are pending for this item. Pending adjustments are adjustments that you have neither approved nor rejected, and have a status of either Pending Approval or More Research.
Status: (Comments tabbed region) The status of this adjustment. Receivables assigns a status when you save this adjustment.
Related Topics
Creating Automatic Adjustments
Creating Automatic Adjustments
Run AutoAdjustment to automatically adjust the remaining balances of all open invoices, debit memos, credit memos, and chargebacks. You can adjust specific transactions by entering selection criteria such as remaining amount, due date, transaction type, customer name, or customer number.
When you run AutoAdjustment, Receivables automatically creates your pending or approved adjustments based on your approval limits, and prints preview and audit reports for your AutoAdjustment processes.
If you enter a Remaining Amount range that exceeds your adjustment approval limits, Receivables displays a warning message and your approval limits when you submit. If you choose to continue, Receivables creates adjustments with a status of Pending Approval.
If the Remaining Amount range you specify is within your adjustment approval limits, Receivables automatically approves your adjustment.
Prerequisites
To automatically adjust the remaining balances of your open debit items:
-
Navigate to the Create Autoadjustments window.
-
Enter the Invoice Currency of transactions to adjust. The default is your functional currency, but you can change it.
-
Specify the transactions to adjust by entering selection criteria. Enter the Low and High range of Remaining Amounts or Percentages, Due Dates, Transaction Types, or Customer Names to adjust only transactions matching that criteria. Leave a field blank if you do not want to limit adjustments to transactions matching that criteria.
-
Enter an adjustment Activity, or select from the list of values. The adjustment activity determines which account your adjustment debits.
-
Enter the Type of adjustments to create. You can create adjustments of type Lines, Freight, Charges, Tax, or Invoice.
-
Enter the date to post your adjustments to your general ledger in the GL Date field. The default is the current date, but you can change it. If the current date is not in an open period, the default is the last date of the most recent open period. The GL date must be later than or equal to the GL date of the debit item you are adjusting and must be in an open or future-enterable period.
-
Enter a Reason for creating this adjustment, or select from the list of values.
-
Choose one of the following Autoadjustment Options:
Generate Report Only: This option prints the AutoAdjustment Preview Report and lets you see the effects of your adjustments without actually updating your items. This option lets you analyze the adjustments that would be created and decide if you want to modify your selection criteria before actually performing the adjustment.
Create Adjustments: This option creates the approved and pending adjustments, closes the appropriate items, and prints the AutoAdjustment Audit Report.
-
If you do not want to adjust the items of related customers, uncheck the Adjust Related Invoices check box.
-
Choose Submit. Receivables displays a Request ID number for your concurrent process and creates the AutoAdjustment Execution report. See: AutoAdjustment Reports. You can use the request ID number to check the status of your request in the Concurrent Requests Summary window.
Related Topics
Monitoring Requests, Oracle Applications User's Guide
AutoAdjustment Reports
Use the AutoAdjustment Preview or AutoAdjustment Execution report to review the total value of automatic adjustments, the number of debit items adjusted, supporting detail on pending and approved adjustments, and final debit item balances.
You can run the AutoAdjustment Preview report prior to creating AutoAdjustments to preview the effect of your adjustments. Receivables generates this report when you choose the Generate Report Only option in the Create Autoadjustments window.
Receivables automatically generates the AutoAdjustment Execution report when you choose the Create Adjustments option in the Create Autoadjustments window.
Report Headings
Adjustment Type: The adjustment type you specify.
Approval Limits: The adjustment approval limits for the person who submits your AutoAdjustment process.
Create Adjustments/Generate Report Only: The appropriate report subtitle based on the AutoAdjustment option you specify. This allows you to differentiate between a preview of possible adjustments and the actual results of an AutoAdjustment process.
Currency: The currency code for the debit items you select to adjust. You can run the AutoAdjustments Report for one currency at a time.
Column Headings
Adjust Amount in Foreign Currency: The adjustment amount for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback in the currency that the debit item was entered. The adjustment amount is determined by the remaining amount range or remaining percent range you specify.
Adjust Amount in Functional Currency: The adjustment amount for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback in your functional currency. The adjustment amount is determined by the remaining amount range or remaining percent range you specify.
Adjustment Status: The adjustment status for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback in your AutoAdjustment process. Valid adjustment statuses are: Approved and Pending Approval.
Balance Due Amount in Foreign Currency: The balance due for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback in the currency that the debit item was entered.
Balance Due Amount in Functional Currency: The balance due for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback in your functional currency.
Invoice Type: The transaction type for each invoice, debit memo, and chargeback. Receivables lets you review reports for a specific transaction type or for all types.
Row Headings
Approved Adjustments Count: The number of approved adjustments in your AutoAdjustment process.
Approved Adjustments Total: The total adjustments and balance due in both foreign and functional currencies for all approved adjustments in your AutoAdjustment process.
Pending Adjustments Count: The number of pending adjustments in your AutoAdjustment process.
Pending Adjustments Total: The total adjustments and balance due in both foreign and functional currencies for all pending adjustments in your AutoAdjustment process.
Total Approved Adjustments Count: The grand total count for all approved adjustments.
Total Approved Adjustments in Functional Currency: The grand total amount and balance due in your functional currency for all approved adjustments.
Total Pending Adjustments Count: The grand total count for all pending adjustments.
Total Pending Adjustments in Functional Currency: The grand total amount and balance due in your functional currency for all pending adjustments.
Related Topics
Creating Automatic Adjustments
Approving Adjustments
When you create an adjustment that is outside of your approval limits, Receivables creates a pending adjustment with a status of Pending Approval. Pending adjustments must be approved before Receivables will update the balance of the transaction.
Note: An adjustment that is pending approval does not reserve the transaction from updates by other types of activity, such as cash or credit memo applications.
You can approve a pending adjustment only if the adjustment amount is within your approval limits. However, you can review adjustment histories, record your comments, and create all other actions (such as assign a status of More Research or Rejected), even if the adjustment is outside your approval limits. See: Approval Limits, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
You can approve an adjustment that has been selected and approved for automatic receipt generation only if the user profile option AR: Invoices with Unconfirmed Receipts is set to Adjustment or Adjustment and Credit.
When you approve an adjustment that is within your approval limits, Receivables automatically updates the balance of the transaction.
Prerequisites
To approve a pending adjustment:
-
Navigate to the Approve Adjustments window.
-
To limit your display to only certain adjustments, enter selection criteria. For example, enter a Creator, Adjustment Number, Currency, range of Amounts, or adjustment Status. Open the More tabbed region to enter selection criteria for a specific transaction, customer, or adjustment. Leave a field blank if you do not want to limit your query to adjustments matching that criteria.
You can control how Receivables displays your adjustments by choosing the Order By Amount or Status option.
-
Choose Find.
Note: You can view the detail accounting lines for an adjustment in the form of a balanced accounting entry (i.e., debits equal credits) by choosing View Accounting from the Tools menu. You can also choose to view the detail accounting as t-accounts.
See: Viewing Accounting Lines.
-
To approve an adjustment, enter a Status of Approved.
To review information about this adjustment, including the date this adjustment was created, who created this adjustment, and any related comments, choose Action History.
Related Topics
Creating Automatic Adjustments
XML Receivables Documents
You can use Oracle XML Gateway to send Receivables documents to your customers. Currently, XML receivables documents include invoices, debit memos, credit memos, chargebacks, and deposits. The largest proportion of XML documents transmitted to customers are customer invoices.
Oracle uses the Open Applications Group Process Invoice DTD called 171_process_invoice_002.dtd (version 7.2.1). Your customers must comply with this standard to ensure that their payables departments can properly accept and process the XML invoice documents that you send.
Your customers can set up their systems to automatically send confirmation messages back to you. These Payables confirmation messages indicate the import status of your XML documents an the reason codes for rejected invoices. XML Gateway processes these confirmation messages and initiates the appropriate Receivables actions and notifications for documents rejected by your customers.
Use the Document Transfer request set to run the Document Transfer Scheduling program and the Document Transfer program to initially send XML documents to your customers. Or you can separately run these two programs in sequence to schedule and then process the document transfer. To review import statuses and, if necessary, retransmit XML documents, use the Document Transfer Summary page and the Document Transfer page.
Open Applications Group (OAG) Standards
This feature conforms to the Open Applications Group Integration Specification (OAGIS) Release 7.2.1 standards. Please refer to the OAG web site at www.openapplications.org for more information on the OAGIS standard.
XML Invoices Process Flow
The following diagram shows the complete XML invoices process flow, including the validation of invoice import by your customer's payables system and the resolution of errors.
XML Invoices Process Flow
XML Messages
XML invoice documents always use this XML message:
-
Process Invoice: This XML message contains information for your customers' invoices, debit memos, credit memos, chargebacks, and deposits.
In addition, your customers can set up their systems to send this XML message back to you:
-
Confirm Business Object Document (Confirm BOD): Your customer can send this XML message to tell you if your XML invoice document import was successful. This is the standard OAG Confirm BOD XML message.
Related Topics
XML Transactions Mapping, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide
Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide
Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide
OAG web site: www.openapplications.org
Implementation Considerations
You can set up your system to handle XML invoice documents to best meet the needs of your organization and your customers.
Before you can transfer and receive XML messages with a customer, you and your customer must agree to and implement the following:
-
OAG standard and version 7.2.1 of the DTDs.
-
Invoice information defined in the user area section of the XML DTDs.
-
Invoice import status codes, other than those seeded in Oracle Payables, used in confirmation messages.
-
Unique trading partner identifier, such as the Source Trading Partner Location code in XML Gateway.
-
Oracle Transport Agent (OTA). Alternatively, your customer can implement a program that understands the OTA protocol.
For more information see the Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide.
Before you set up this feature, consider the following questions:
-
Will your customers send a Confirm BOD to you? If so, will they send one every time or only when they encounter import errors with your XML document?
-
Do you want notifications to be sent by e-mail, Oracle Workflow worklist, or both?
-
Do you want to adjust the timeout default values in the workflow? Set the timeout value for the Confirm BOD message only if you expect your customers to send you a confirmation every time you send an XML transaction message. The default value is 10 minutes.
Review the XML Invoices Process Flow to see how these decisions affect how the workflow manages your XML invoice document process.
Setting Up Your System for XML Invoice Documents
The following table lists the cross-product steps necessary to set up XML invoice documents.
| Step | Performed by | Application | Task | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Receivables user | Receivables | Define customer bill-to sites | Required |
| 2 | Implementer | XML Gateway | Define system profile values | Required |
| 3 | Implementer | XML Gateway | Verify seeded transactions | Required |
| 4 | Implementer | XML Gateway | Define customer bill-to sites as trading partners | Required |
| 5 | Implementer | XML Gateway | Test the Oracle Transport Agent server to server connection | Required |
| 6 | Implementer | Workflow | Define Workflow roles for users | Required |
| 7 | Implementer | Workflow | Adjust any timeout values that you will use | Optional |
| 8 | Implementer | Workflow | Modify any of the standard messages | Optional |
| 9 | Implementer | Workflow | Start Workflow agent listener using the following parameters: ECX_INBOUNDECX_TRANSACTIONWF_DEFERREDWF_ERROR | Required |
| 10 | Implementer | Oracle Transport Agent | Set any security options | Optional |
| 11 | Implementer | Your e-mail system | Set up e-mail server to receive e-mail workflow notifications | Optional |
To set up XML invoice documents:
-
In Receivables, define bill-to sites for your customers.
-
In XML Gateway, define system profile values:
-
ECX log file path for XML message and processing file
-
ECX XSLT file path for XSLT style sheets
-
Oracle XML Gateway system administrator e-mail address
-
ECX_OAG_LOGICALID to identify the sender's information system
-
-
In XML Gateway, verify transactions seeded for XML invoice documents.
-
Party type=Customer
-
Transaction type=AR
-
Transaction subtype:
-
Process invoice messages
PROCESS_INVOICE
PROCESS_DEBIT_MEMO
PROCESS_CREDIT_MEMO
PROCESS_CHARGE_BACK
PROCESS_DEPOSIT
-
Confirm BOD messages
CONFIRM_BOD
-
-
-
In the XML Gateway Trading Partner Setup window, define customer bill-to sites as trading partners in XML Gateway.
Important: To disable the delivery of XML invoice documents for a customer, simply remove the customer's bill-to site from the Trading Partner Setup window in XML Gateway.
Enter the following:
-
Trading Partner Type: Customer
-
Trading Partner Name: customer name
-
Trading Partner Site: customer bill-to site
-
Company Admin E-mail: e-mail address for the message recipient
In XML Gateway, in the Trading Partner Details region of the Trading Partner Setup window, select transactions that will be used in the XML Gateway execution engine, and provide trading partner details. This setup identifies the queue from which to retrieve inbound messages or in which to place outbound messages.
-
(Required) Set up the Process Invoice message transaction details, including:
-
Transaction Type: AR
-
Transaction Subtype:
-
PROCESS_INVOICE
-
PROCESS_DEBIT_MEMO
-
PROCESS_CREDIT_MEMO
-
PROCESS_CHARGEBACK
-
PROCESS_DEPOSIT
Note: When you select a Transaction Type and Transaction Subtype pair, values for the Standard Code, External Transaction Type, External Transaction Sub Type, and Direction fields are automatically populated.
-
-
Map: 171_process_invoice_002
-
Protocol Type: HTTPS
-
In the Connection/Hub field, enter the appropriate value. See: Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide.
-
In the Username, Password, and Protocol Address fields, enter the appropriate values. Obtain these values from your customer's system administrator.
-
In the Source Trading Partner Location Code field, enter the unique value that you have agreed upon with your customer.
-
(Optional) If your customer will send confirmation that they received your XML message, then enable the inbound Confirmation BOD message. In the Document Confirmation, enter:
-
0: if your customer does not send the Confirm BOD to you
-
1: if your customer sends the Confirm BOD to you only when there is an import error
-
2: if your customer always sends the Confirm BOD to you
See: How to Implement the OAG Confirmation Business Object Document, Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide.
-
-
-
(Optional) Set up the Confirm BOD message transaction details, including:
-
Transaction Type: AR
-
Transaction Sub Type: CONFIRM_BOD
-
Map: 002_confirm_bod_004
-
-
-
Test the HTTPS server-to-server connection.
-
In Oracle Workflow, define workflow roles for the users who process invoice documents at your organization so that they can receive notifications. See: Setting Up an Oracle Workflow Directory Service, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
-
(Optional) In Oracle Workflow, adjust any timeout values you will use.
-
(Optional) In Oracle Workflow, modify any of the standard messages.
-
Start Oracle Workflow agent listener.
-
(Optional) In Oracle Transport Agent, set any security options that you plan to use. For more information about Oracle Transport Agent, see the Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide.
-
(Optional) Set up e-mail server to receive e-mail workflow notifications.
Note: You can run the XML Gateway engine in debug mode to generate a detail log file. To generate a detail log file, you must modify the event subscription that runs the XML Gateway engine process. In Oracle Workflow, navigate to the Find Event Subscription window and find the Receivables XML Invoice, Credit Memo, Debit Memo, Charge Back, Deposit event. In the Parameters field of that window, enter ECX_DEBUG_LEVEL=3 and save your work.
Sending XML Invoice Documents
This overview provides general information about sending XML invoice documents to your customers.
Because the XML invoice document process varies depending on your setup, refer to Document Transfer Message Workflow to see details about how the workflow manages your XML invoice documents.
Prerequisites
-
Set up your system for XML invoice documents. See: Setting Up Your System for XML Invoice Documents.
-
Ensure that Receivables transactions exist that meet these conditions:
-
the transaction must have a status of Complete
-
the transaction must never have been transmitted
-
the bill-to customer and bill-to site for the transaction must exist as an XML Gateway trading partner setup
Important: You must process and transfer XML invoice documents before you run the concurrent programs to print invoices. The Document Transfer program does not select receivables transactions that the Print Invoice program already printed.
-
To send XML invoice documents to your customers:
For an overview of this process: see XML Invoices Process Flow.
-
Initiate the transfer of Receivables invoice documents in XML format by submitting the Document Transfer Request Set, which runs the Document Transfer Scheduling and Document Transfer concurrent programs.
Alternatively, you can submit the two programs separately in sequential order; first the Document Transfer Scheduling program, and then the Document Transfer program.
Note: Use the Document Transfer request set only for the initial XML transfer of invoice documents. If you must resend an invoice document, then you must initiate the retransmission request from the Document Transfer page. You can then submit the Document Transfer program to complete the retransmission.
Receivables selects transactions for XML transfer according to the parameters that you specify upon program submission:
-
Transaction class
-
Transaction type
-
Transaction number, low and high
-
Customer class
-
Customer
-
Transaction date, low and high
-
-
After the Document Transfer Scheduling program completes, Receivables changes the transmission status of the transaction to either Waiting or Failed. If the status is Failed, then the system administrator receives a notification via Workflow.
-
The Document Transfer program validates the transactions that have a status of Waiting. During validation, the transmission status of a transaction can change to either:
-
Started - The document has passed all validations and is ready for transfer.
-
Failed - The validation process encountered errors. Workflow notifications are sent to the appropriate Receivables user or system administrator.
The Document Transfer program then calls XML Gateway to transmit the invoice documents that pass validation. XML Gateway creates the XML invoice documents and transmits them to your customers. During this process, the transmission status of a transaction can change to either:
-
Transmitted - The invoice document was transmitted.
-
Failed - The transmission process encountered a technical error in XML Gateway. Workflow notifications are sent to the system administrator.
-
-
Your customers can now import the transmitted XML invoice documents into their payables systems. Your customers validate the incoming invoice documents and can optionally return confirmation messages back to you. For more information about confirmation messages, see: Confirming the Import Status of XML Invoice Documents.
Confirming the Import Status of XML Invoice Documents
You and your customer can optionally implement any messages and activities that meet your needs.
If you have set up the Process Invoice XML message for automatic receipt confirmation in XML Gateway, then when your customer receives the invoice message, the customer sends a Confirm BOD message back to your system.
These messages confirm the import status of an invoice document and provide reason codes for import failures. The Oracle Payables import statuses and reason codes are mapped to confirmation actions in Receivables.
Upon receipt of a confirmation message, Receivables translates the import status and reason code into the appropriate confirmation action, and updates the transmission status accordingly.
For each XML invoice, the transmission status will change to either:
-
Accepted- if you receive a confirmation message with an import status of Success.
-
Rejected - if you receive a confirmation message with an import status of Failed, with an accompanying reason code.
For information about the seeded reason codes in Receivables, refer to Troubleshooting XML Invoice Documents.
Troubleshooting XML Invoice Documents
If the Oracle Payables confirmation message indicates errors, then Workflow sends a notification to the appropriate person based on the reason code:
-
When errors are related to failed import validations, such as a missing invoice amount, the appropriate Receivables user is notified.
-
When errors are caused by technical or transmission issues, the system administrator is notified.
The following table lists the Oracle Payables import statuses and reason codes that are mapped to the confirmation actions seeded in Receivables. If your customers do not use Oracle Payables, then they need to implement these codes so that their confirmation messages map to Receivables confirmation actions.
| Status | Reason Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | NA | Invoice document import was successful. |
| 10 | DUPLICATE_INVOICE_NUMBER | Duplicate invoice document number. |
| 10 | DUPLICATE_LINE_NUMBER | Duplicate line number. |
| 10 | INCONSISTENT_CURR | Invoice document and customer's purchase order have different currencies. |
| 10 | INCONSISTENT_PO_SUPPLIER | The value you provided for supplier does not match the supplier on the purchase order. |
| 10 | INVALID_LINE_AMOUNT | Line amount not equal to Quantity x Unit Price. |
| 10 | INVALID_INVOICE_AMOUNT | You did not provide a value for Invoice Amount. |
| 10 | INVALID_PO_NUM | Invalid purchase order number. |
| 10 | INVALID_PRICE_QUANTITY | The values for Unit Price, Quantity Invoiced, and Line amount are inconsistent. (Quantity Invoiced x Unit Price = Amount) |
| 10 | INVALID_QUANTITY | The value for Quantity (QUANTITY_INVOICED) must be greater than zero for Standard type invoices. |
| 10 | INVALID_SUPPLIER | The supplier information is invalid. The Trading Partner Location code in the XML Gateway trading partner setup must match to your customer. |
| 10 | INVALID_SUPPLIER_SITE | The supplier site information is invalid. The Trading Partner Location code in the XML Gateway trading partner setup must match to your customer. |
| 10 | INVALID_UNIT_PRICE | The value for Unit Price (UNIT_PRICE) must be greater than zero. The Trading Partner Location code in the XML Gateway trading partner setup must match to your customer. |
| 10 | NO_SUPPLIER | No supplier information is provided. |
Mapping Reason Codes against Confirmation Actions
If your customer wants to use a reason code that is not listed in the table above, they can do so. However, they must communicate the reason code to you, so that you can map a Receivables confirmation action to it.
How to map a reason code to a confirmation action:
-
Navigate to the Confirmation Action page.
-
Click Add.
-
Enter the status 00 for successful processes and 10 for failed processes.
-
Enter a reason code that maps to a reason code that your customer uses.
-
Enter a start date, and optionally enter an end date.
-
Enter a handler type, usually PL/SQL, and the handler name, which is your PL/SQL program name.
If the import process fails and Receivables does not recognize the reason code, then the workflow notification indicates an unrecognizable reason code.
If the reason code indicates that a failed import was due to duplicate invoice numbers, then Receivables automatically initiates the Credit Memo Workflow to generate a credit memo for the duplicate invoice.
Reviewing and Retransmitting XML Invoice Documents
Use the Document Transfer Summary page to review the transmission statuses of your XML invoice documents. From this page, you can drill down to the Document Transfer page to see transmission details and error messages. From the Document Transfer page, you can also initiate the retransmission of failed or rejected XML invoice documents.
To review your XML transfers:
-
Navigate to the Document Transfer Summary page.
The page displays your most recently transmitted XML invoice documents. If you want to find a different invoice document transfer, then perform a query using:
-
Customer name
-
Customer number
-
Low and high transaction numbers
-
Low and high submission dates
-
Document transfer number
-
Status
-
Exception Type
-
-
In the Results region, choose the Edit button for the invoice document transfer that you want to review.
The Document Transfer page appears. This page displays the following details:
-
Document transfer number - generated after running the Document Transfer Scheduling program
-
Transaction number
-
Customer name and number
-
Last submission date - refers to the last submission dates for either the Document Transfer Scheduling program or the Document Transfer program
-
Status - indicates the transmission status of the invoice document, including Accepted, Failed, Rejected, Started, Transmitted, and Waiting
-
Event name - refers to the business event subscribed to by XML Gateway to transmit Receivables invoice documents
-
Gateway transaction name - refers to the transaction type and subtype that you defined in XML Gateway
-
Error message - includes any errors such as Setup, System, or import errors as indicated in the confirmation messages from your customer. Before submitting an XML transfer again, you must resolve the errors identified in this error message.
-
-
If this transmission has a status of Failed or Rejected, then make your corrections and save your changes.
-
Click Retransmit. The transmission status changes to Waiting.
-
Submit the Document Transfer program to complete the retransmission.
Document Transfer Message Workflow
The Document Transfer Message workflow creates an XML invoice document and sends it to your customer. This workflow consists of two item types:
-
AR Transfer Document item type
-
AR Notification item type
AR Transfer Document Item Type
The following diagram displays the workflow process in the AR Transfer Document item type:
AR Transfer Document Item Type
Retrieve Event (Node 1)
When you run the Document Transfer program, a business event is raised that starts the workflow. Workflow continues to Node 2.
XML Document Transfer (Node 2)
This function triggers outbound message creation. Oracle Transport Agent then transmits the Process Invoice message to your customer. Workflow ends successfully at Node 3.
AR Notification Item Type
The following diagram displays the workflow process in the AR Notification item type:
AR Notification Item Type
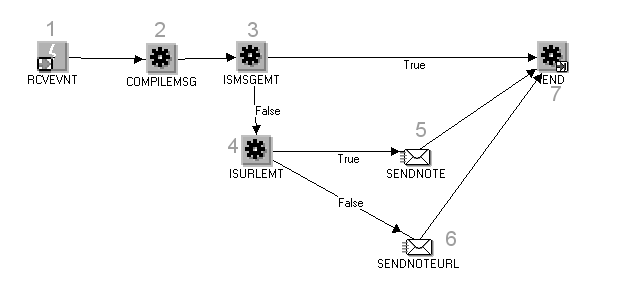
Receive Event (Node 1)
If an error occurs during the XML transfer process, a business event is raised that starts the workflow. Workflow continues to Node 2.
Compile Message (Node 2)
This node is a PL/SQL activity. The associated procedure uses the event information to construct the text of the notification. It also identifies the person who should receive the notification. Workflow continues to Node 3.
Is Message Empty (Node 3)
This function checks the message content:
-
If the message has no text, then the workflow successfully ends at Node 7.
-
If the message does have text, then the workflow continues to Node 4.
Is URL Empty (Node 4)
This function checks the message content to determine if the notification includes a hypertext link to the Document Transfer Summary page:
-
If a hypertext link exists, then the workflow continues to Node 5.
-
If a hypertext link does not exist, then the workflow continues to Node 6.
Send Notification (Node 5)
This function sends an error notification to the appropriate Receivables user. Workflow successfully ends at Node 7.
Send Notification with URL (Node 6)
This function sends an error notification, including a hypertext link to the Document Transfer Summary page, to the appropriate Receivables user. Workflow successfully ends at Node 7.
Workflow Troubleshooting
For Oracle Workflow or Oracle XML Gateway errors, review the log file for the details and use the Workflow Administrator functions to monitor and manage workflow processes. See: Monitor Workflow Processes, Oracle XML Gateway User Guide.
Related Topics
XML Transactions Mapping, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide
Oracle XML Gateway User's Guide
Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide
Oracle Workflow User's Guide
Open Applications Group (OAG) web site at http://www.openapplications.org
Maintaining Transactions
You can review and update invoice, debit memo, deposit, guarantee, credit memo, on-account credit memo, and chargeback information for transactions you enter manually or import into Receivables using AutoInvoice.
If the Allow Change to Printed Transactions system option is Yes, you can update most transaction information, even if it has been printed. However, once there is activity against it, Receivables does not let you update most transaction attributes. Activity includes actions such as payments, credit memos, adjustments, and including the transaction on a balance forward bill.
You can update debit item information such as the due date, PO number, salesperson, and remit-to address. You can also place a debit item in dispute by specifying a dispute amount, exclude a debit item from late charges, or update the bill-to information. Receivables also lets you enter or update the exchange rate of your debit item if your debit item does not have any activity against it.
You can also record other information by adding notes about your debit items in the Notes tabbed region of the Transaction window.
Prerequisites
To maintain your transactions:
-
Navigate to the Transaction window.
-
Query the transaction.
-
Update information for this transaction. For a list of fields you can update, see: Maintaining Transactions Field Reference.
Related Topics
Maintaining Transactions Field Reference
This section tells you under which conditions you can and cannot update specific attributes of your Receivables transactions. Some cells contain exception numbers, which indicate that at least one exception exists for that attribute and condition. An explanation of each exception is provided at the end of this section.
For example, the table below indicates that you can update the Bill-To Contact field when the transaction is complete. However, the number 4 indicates that there is one exception: if the transaction is a chargeback, the Bill-To Contact cannot be updated.
After your transactions have posted to your general ledger, you can still update most information. Receivables maintains a complete audit trail of all the posted changes you make to your accounting entries. Receivables does not maintain an audit trail when you change a transaction that has not been posted.
You cannot update a transaction if it has activity against it, regardless of how you set the system option Allow Change to Printed Transactions. Examples of activity include payments, credit memos, adjustments, and including the transaction on a balance forward bill.
Delete Transactions
Depending on how your administrator has set up function security on your system, there are several ways you can delete transactions in Receivables. See: Function Security in Receivables, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide. Transactions with no activity against them can be removed by one of the following methods:
-
Delete the invoice in the Transactions window by choosing Delete Record from the Edit menu. This will delete the invoice and any lines.
-
Void the invoice by changing the invoice's type in the Transaction window to a type with Open Receivables and Post to GL options set to No. This will delete the payment schedule and cancel distributions by removing the GL date.
-
Reverse the distributions by creating a Credit Memo against the invoice.
-
Delete the payment schedule by choosing the Incomplete button in the Transaction window. This makes the invoice inaccessible for payment or crediting.
Update Transactions
The following table lists changes you can make in the Transactions window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
* You cannot update a transaction's payment terms unless the Override Terms check box is checked in the Customer profile, at either the customer account or site level.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
| HEADER LEVEL | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agreement | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Bill To Address | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Bill To Contact | Yes12 | Yes 4,12 | Yes 4,12 | Yes 8,12 | No | Yes 12 |
| Bill To Customer | Yes 11,12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Class | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Comments | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Commitment | Yes | Yes 15 | Yes 15 | Yes 15 | Yes 15 | Yes 15 |
| Complete | Yes 12 | Yes 4,5,12 | Yes 12 | Yes 12 | No | No |
| Credit Reason | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Credit Reference | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Credit Reference Date | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cross Reference | Yes 2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Currency | Yes 1 | No | Yes 2 | Yes 8 | No | No |
| Default Tax | Yes | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Descriptive Flexfield [ ] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dispute Amount | NA | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Dispute Date | NA | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Document Number | No 13 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Due Date | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Late Charges | Yes 2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| GL Date | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Invoicing Rule | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Notes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Original Transaction | (read only) | No | No | No | No | No |
| Paying Customer Name and Number | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Paying Location | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Receipt Method | Yes | Yes 5 | Yes 5 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PO Date | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PO Number | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| PO Revision | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Print Date | (read only) | No | No | No | No | No |
| Print Option | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Rate | Yes 1 | Yes 4,5 | Yes 4 | Yes | No | No |
| Rate Date | Yes 2 | Yes 4,5 | Yes 4 | Yes | No | No |
| Rate Type | Yes 1 | Yes 4,5 | Yes 4 | Yes | No | No |
| Receivables Account | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Reference | Yes | Yes 7 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Remit To Address | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| Sales Territory | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Salesperson | Yes | Yes 4 | Yes 14 | Yes 8 | No | No |
| Ship To Address | Yes 1,12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Ship To Contact | Yes 1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | No | Yes |
| Ship To Customer | Yes 1,11,12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Sold To Customer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Source | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Special Instructions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| Status | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Terms* | Yes 2 | Yes 4,5 | Yes | Yes 8 | No | No |
| Transaction Date | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Transaction Flexfield | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 |
| Transaction Number | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Transaction Type | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
The following table lists changes you can make in the Lines window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
| LINE LEVEL | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounting Rule | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Amount Includes Tax flag | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Description | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No 12 | No |
| Descriptive Flexfield | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| First GL Date | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Item | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Item Flexfield | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Line Number | Yes | Yes 5 | Yes | Yes 8 | No | Yes |
| Net Extended Price | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Net Unit Selling Price | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Num of Accounting Periods | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Order Date | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Order Line | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Order Number | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | No |
| Order Revision | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Price | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Quantity | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Reason | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Reference | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Sales Channel | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Standard Memo Line | Yes 6 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Certificate | Yes | Yes 5,6 | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Code | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Handling | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Reason | Yes | Yes 5,6 | No | No | No | No |
| Transaction Code | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Transaction Flexfield | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 |
| UOM | Yes 2 | Yes 2,4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Add Lines? | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Delete Lines? | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
The following table lists changes you can make in the Tax window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
| TAX LINE | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Number | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Precedence Number | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Code | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Rate | Yes 1,12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Tax Amount | Yes 12 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Transaction Flexfield | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 |
| Descriptive Flexfield | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Add Line? | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Delete Line? | No 3 | No | No | No | No | No |
The following table lists changes you can make in the Sales Credits window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
| SALESCREDITLINE | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Revenue % | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Non-Revenue Amount | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Revenue % | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Revenue Amount | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Salesperson | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Add Line? | Yes | Yes | Yes 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Delete Line? | Yes | Yes 9 | Yes 9,14 | Yes 9 | Yes 9 | Yes |
The following tables list changes you can make in the Distributions window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
This table shows details for account distributions:
| DISTRIBU-TIONS | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent/Amount | Yes | Yes 4 | No 4 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Account* | Yes | Yes 4 | Yes 4 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Delete Line? | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Add Line? | Yes | Yes 4 | No 4 | Yes | No | No |
This table shows details for account set distributions:
| DISTRIBU-TIONS | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent/Amount | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Account* | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Transaction Flexfield | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 |
| Descriptive Flexfield | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Add Line? | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Delete Line? | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
* You can update the revenue, receivable, tax, and freight accounts, but if the transaction is posted, then you can no longer update the receivable account.
The following table lists changes you can make in the Freight window to imported, manually entered, and copied transactions.
See Legend for the legend that goes with this table.
| FREIGHT | Incomplete | Complete | Rules | Printed | Activity | Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| Ship Date | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| Shipping Reference | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| FOB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 8 | Yes | Yes |
| Amount | Yes 6 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Account | Yes 6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Transaction Flexfield | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 | Yes 6 |
| Descriptive Flexfield | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Add Line? | Yes 6 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Delete Line? | Yes 6 | No | No | No | No | No |
Legend
-
Unless the transaction is a regular credit memo (not an on-account credit memo).
-
Unless the transaction is an on-account credit memo.
-
If tax lines are added manually, they can be deleted.
-
Unless the transaction is a chargeback.
-
Unless the transaction was selected for automatic receipt but is not yet approved.
-
Unless the transaction was created by AutoInvoice or the transaction line was manually added to an imported transaction. If you must enter descriptive flexfield information for such a line, use the Invoice Line Information flexfield.
-
Unless the value was generated by a flexfield segment.
-
Unless the system option Allow Change to Printed Transactions is set to No.
-
Unless the profile option Allow Update of Existing Sales Credits is set to No.
-
Unless your accounting method is Cash Basis.
-
Unless the profile option AR: Change Customer on Transaction is set to No.
-
Unless the transaction is an on-account credit memo that has tax lines that were calculated by AutoInvoice.
-
Unless the sequence number is manual and the document number has not yet been generated.
-
Unless you have already run Revenue Recognition. (Use the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard instead. See: Revenue Accounting.)
-
Use the Apply Deposit window. (See: Using Commitments.)
NA This column is not applicable for this attribute and status.
Related Topics
Crediting Transactions
Use the Credit Transactions window to enter, update, and review credit memos against specific invoices, debit memos, or commitments. You create credit memos to reduce the balance due for a transaction. When you credit a transaction, Receivables creates the appropriate accounting entries and reverses any sales credit assigned to your salespeople.
Receivables lets you credit an entire invoice or specific invoice lines. You can also credit freight for an entire invoice or only for specific invoice lines.
You can unapply and reapply credit memos using the Applications window. When you unapply a credit memo that was created in the Credit Transactions window, Receivables retains the originally credited transaction number in the credit memo's comments, viewable from the Distributions window.
You can delete an incomplete credit memo if the system option Allow Invoice Deletion is set to Yes. See: Defining Receivables System Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
A transaction must be complete before you can create a credit memo against it.
Note: The 'Line' fields show amounts without tax, even if the transaction you are crediting is tax inclusive. These include the Amount, Original, and Balance Due fields.
If the transaction that you want to credit has already been paid, then a refund might be in order. See: Unapplying Cash when Crediting a Transaction and Automated Receipt Handling for Credits.
Prerequisites
-
Define credit memo sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define credit memo transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To create a credit memo against a transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or Credit Transactions window.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, query the transaction to credit, then choose Credit.
If you chose Credit Transactions from the Navigator, enter the number of the transaction to credit in the Find Transactions window. If you do not know the transaction number, enter selection criteria such as Class, Transaction Date, and Currency to limit your search.
-
To add this credit memo to a batch, see: Batching Credit Memos.
-
Enter the batch Source for this credit memo. The default, which you can change, is either:
-
The batch source of the transaction that you are crediting, or
-
The credit memo batch source that is entered on the batch source of the transaction that you are crediting.
-
-
Enter the Date of this credit memo. Receivables prints this date on your credit memo.
If this credit memo is part of a batch, the default is the batch date. If there is no batch information, or if the batch date is before the date of the credited transaction, the default is the current date. If the date of the invoice you are crediting is later than the credit memo date, the default is the invoice date.
-
If your batch source does not use Automatic Transaction Numbering, enter a credit memo Number; otherwise, Receivables assigns a number when you save. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
Enter a transaction type for this credit memo. The batch source provides the default transaction type. Although you can change the default transaction type, you can replace it with only those credit memo transaction types that have the same Open Receivable and Post to GL values as that of the transaction being credited.
-
Enter the GL Date for this credit memo. This date must be in an open or future enterable accounting period and must be equal to or later than the GL date of the credited transaction. If this credit memo is part of a batch, the default is the batch GL date.
-
If you are crediting a transaction that uses invoicing and accounting rules, choose one of the following Rules Methods:
Last In First Out (LIFO): Choose this option to back out revenue starting with the last general ledger period and reverse all prior periods until it has used up the credit memo.
Prorate: Choose this option to credit an equal percentage to all account assignments for this invoice.
Unit: Choose this option to reverse the revenue for the number of units you specify from an original line of the invoice.
Note: Note: If you use the Unit method, then you cannot enter a credit quantity that is greater than the quantity on the target invoice line.
-
Enter the Currency for this credit memo. If this credit memo is part of a batch, the default is the batch currency; otherwise, the default is your functional currency. If you are applying this credit memo to a transaction, the credit memo currency must be the same as the transaction currency. If you enter a currency other than your functional currency, enter exchange rate information. See: Foreign Currency Transactions.
-
If you are crediting a transaction that has multiple installments, choose one of the following Split Term Methods:
First in First Out (FIFO): This method credits the first installment first.
Last In First Out (LIFO): This method credits the last installment first.
Prorate: This method credits the installments of the credited transaction and prorates them based on the amount remaining for each installment.
-
If you are not using Automatic Sequence Numbering, open the More tabbed region, then enter a unique Document Number for this credit memo. See: Implementing Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
To credit only part of the balance due for this transaction, enter the percentage or Amount of Line, Tax, or Freight charges to credit. To credit a specific portion of the charges, enter a negative number in the Amount field (for example, enter -50 to decrease the balance due by 50 dollars). If you enter a percentage, Receivables calculates the amount, and vice versa.
Percentages are based on the original balance of the transaction you are crediting. Receivables updates the Balance Due for each type of charges that you credit and creates all of the accounting reversal entries for you. Receivables also reverses this percentage of the sales revenue and non-revenue credit assigned to your salespersons.
Note: You cannot enter an amount that would overapply the transaction unless the Allow Overapplication flag of the credited transaction's transaction type is set to Yes. To overapply a transaction, choose Credit Lines, then specify which lines to credit in the Lines window.
-
To credit the entire balance due for this transaction, choose Credit Balance. Receivables reduces the Balance Due for this transaction to zero for each type of charges.
Note: For invoices against deposits, the Balance Due is the amount available to credit, this amount includes the deposit amount used by the invoice.
-
To credit specific transaction lines, see: Crediting Transaction Lines.
-
Save your work. Receivables creates all the accounting reversal entries and reverses the amount of sales revenue and non-revenue credit assigned to your salespersons.
Receivables also copies the sales groups, if any, from the credited transaction to the new credit memo. You can change sales information, if desired, before you complete the credit memo.
If you are ready to complete this credit memo, see: Completing Transactions.
Related Topics
Unapplying Cash when Crediting a Transaction
Updating Credit Memo Installments
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
Credit Transactions Field Reference
Crediting Transaction Lines
In addition to crediting either part or the entire balance due of a transaction, Receivables lets you credit individual transaction lines. For example, if a transaction has several line items, you can partially or fully credit the amount due for each line or only a single line item.
Prerequisites
To credit specific transaction lines:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or the Credit Transactions window.
-
Query the transaction to credit.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the transaction, then choose Credit.
-
Enter general information for this credit memo. See: Crediting Transactions.
-
Choose Credit Lines.
Note: If you are viewing a credit memo in which you have already credited transaction lines, Receivables displays these credit memo lines in the Lines window. Use the list of values to select additional transaction lines to credit.
-
Select the transaction line to credit from the list of values.
-
Enter either the Quantity and Unit Price or the Amount to credit for this line. If you enter the quantity and unit price, Receivables calculates the amount. You can overapply a credit memo line if the transaction type of the transaction you are crediting has Allow Overapplication set to Yes.
You can only enter a positive amount if the Creation Sign of this credit memo's transaction type is Positive Sign. You can enter a negative amount if the Creation Sign of this credit memo's transaction type is either Negative or Any Sign. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Note: If you enter a quantity, the unit price is the unit price of the original invoice or commitment line you are crediting. If this price is not available and you are crediting a standard credit memo line, the default is the unit price of the standard line adjusted for any currency differences. If you specify an amount and a quantity for a credit memo line and Receivables cannot default a value for your unit price, the default unit price is the Amount divided by the Quantity.
-
Repeat steps 6 and 7 for each transaction line to credit.
-
To enter or review the account assignments for a credit memo or tax line, choose Distributions. See: Reviewing Accounting Information.
To enter or update sales credit information for a credit memo line, choose Sales Credits. See: Reviewing Revenue Credits.
To associate freight information with your credit memo lines, choose Freight. See: Reviewing Freight Information.
To review or update tax information for this credit memo line, choose Tax. See: Reviewing Tax Information.
Related Topics
Credit Transactions Field Reference
Updating Credit Memo Installments
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
Credit Transactions Field Reference
This section provides a brief description of some of the fields and tabbed regions in the Credit Transactions and Lines windows. It also describes how the Tax, Freight, and Distributions windows appear when you open them from the Lines window.
Credit Transactions Window
Customer Reference: A reference number for your customer. You can use this information to help keep track of your customer's credit requests.
Comments: Any comments about this credit memo that may be helpful to you or to others. This information does not appear on the printed transaction.
Special Instructions: Any specific instructions or information that may be helpful to you or to others. You can enter up to 240 characters in this field. The first 51 characters appear on the printed transaction.
Distributions Window
Amount: The amount of the credit memo line or tax line to assign to this account. When you enter an amount, Receivables calculates the percent that this amount constitutes of this line. If this credit memo is an on-account credit, the default value for this field is the credit memo line amount, if the AutoAccounting that you have defined for your revenue does not rely upon salespersons. If your AutoAccounting for Revenue does rely on salespersons to determine the segment values, multiple account assignment lines are created with one line for each salesperson equal to the amount of the salesperson line.
If you are entering this credit memo against a specific transaction, and the profile option AR: Use Invoice Accounting Rules For Credit Memos is set to No, then the default value for this credit memo is the same as an on-account credit. If this profile option is set to Yes for a credit memo that you enter against a specific transaction, the default value is an amount from the corresponding invoice distribution line using the following formula:
Amount = (Credit Memo Line Amount/Invoice Line Amount) * Invoice Account Assignment Amount
If you are reviewing the revenue account assignments for a credit memo against an invoice that uses rules, and if this transaction is a credit memo against a specific invoice or commitment, Receivables calculates this amount based on the method that you specified in the Rules Method field in the Credit Transactions window.
GL Date: The date to post this account to your general ledger. The default value for this field is the date you entered in the Credit Transactions window, unless you are crediting an invoice that uses rules. In this case, the GL date is automatically calculated using the GL dates of the invoice's account assignments and on the credit method for rules.
Percent: The percent of this credit memo line amount or tax amount to assign to this account. You can specify a negative percentage for an account assignment line. Either the sum of the percentages of your account assignment lines must be equal to 100, or the sum of the account assignment line amounts must be equal to the total line amount. However, if your credit memo uses rules, the sum of your account assignments must remain the same as when you entered this region.
-
The Sets for This Line tabbed region only appears in the Distributions window for credit memos with accounting rules and when the Use Invoice Accounting profile option is set to No.
-
The Accounts For This Line tabbed region only appears in the Distributions window for credit memos without rules. It also appears for credit memos with rules after Revenue Recognition Program has created Account Assignments for this line.
Freight Window
Use this window to associate freight information with your credit memo lines. Receivables enters the default header-level freight information for the transaction you are crediting (if any).
The Freight for Current Line tabbed region only appears in the Freight window if this is an on-account credit memo and the memo line does not have the type of tax. It also appears if this is not an on-account credit memo and the transaction line you are crediting has freight. For more information, see: Entering Freight Information.
Lines Window
For information about the Amount, Description, Reason, and Unit Price fields, refer to Lines Window Field Reference.
The Credited Transaction Line region displays information about the line you are crediting, such as unit price, original line amount and the remaining amount of this line available to credit (Uncredited field).
Note: Line amounts can either include or exclude tax for this line, depending on the tax code or tax group for this line. The Amount Includes Tax poplist indicates whether the line amount includes tax. For more information, see: Lines Window Field Reference.
Sales Order Tabbed Region
Date: The date you ordered this item. This field is for informational purposes only.
Line: The order line number to which this invoice line refers.
Number: The sales order line number for this invoice line.
Rev: The revision number for this order.
Channel: The method used to generate this sales order, such as Telemarketing or Direct Marketing. Oracle Order Management uses this information for reporting purposes.
Tax Exemptions Tabbed Region
Certificate: If you enter 'Exempt' in the Tax Handling field (see below), enter a tax exemption Certificate Number. Use the list of values to select an existing tax exemption certificate number.
Reason: If you enter 'Exempt' in the Tax Handling field, enter a Reason for creating this exemption, or select from the list of values. You can define additional exemption reasons in the Receivables Lookups window.
Tax Handling: You can enter a value for this field only if the profile option Tax: Allow Override of Customer Exemptions is Yes and the transaction is not a chargeback. Use the default value of 'Standard' if you want tax to be calculated as per the normal procedures set up in Receivables. Enter 'Exempt' if your system option Use Customer Exemptions is set to Yes and you want to force tax exemption on the invoice lines. Enter 'Require' to force tax calculation on the invoice lines. If you update this field, there will be no affect on existing invoice lines; only new invoice lines will get the new value as a default.
Sales Credits Window
Use this window to enter and update sales credit information for a specific credit memo line. If this transaction is a credit memo against a specific invoice or commitment, the default sales credit is the sales credit for the original invoice or commitment sales credit line. For more information, see: Entering Revenue Credits.
Receivables also defaults the sales group or groups that were assigned to the original invoice, but you can change the default.
Detail Tax Lines Window
The Tax for This Line selection only appears in the Detail Tax Lines window if this credit memo is on-account and the memo line does not have the type of freight. It also appears if this credit memo is not on-account and the transaction line you are crediting has tax. For more information about the fields in this window, see: Detail Tax Lines Window Field Reference.
Related Topics
Reviewing Accounting Information
Receivables lets you enter or review the account assignments for a credit memo or tax line in the Distributions window. Receivables uses AutoAccounting to create the default values for the revenue and tax accounts of your credit memo lines.
If this transaction is a credit memo against a specific invoice or commitment, and the profile option AR: Use Invoice Accounting For Credit Memo is set to Yes, Receivables does not use AutoAccounting to create the default values for these accounts. Instead, reversal entries are created using the accounts of the invoice or commitment that you are crediting.
Prerequisites
To review or update the revenue account assignments for a credit memo:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or the Transactions window.
-
Query the credit memo to view.
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, choose Open.
-
Choose Distributions.
-
To update the revenue account assignments for this credit memo line, modify the GL Account information for that account.
If you are viewing a credit memo line against an invoice with accounting rules, and the profile option AR: Use Invoice Accounting For Credit Memos is set to No, use the Account Set For Single Line tabbed region to enter or update your account set. If you are viewing a Credit Memo with accounting rules, you must run the Revenue Recognition Program before you can navigate to this window. See: Recognizing Revenue.
Note: If you update an account assignment line that has already posted, Receivables does not change the original assignment. In this case, new account assignments are created to reflect the update when you save your changes. The first assignment offsets the original account assignment you have posted and the second assignment records the new amount percent or account that you have updated. If you update an account assignment that has not posted, Receivables directly updates the account assignment you specify and does not create an offsetting account assignment entry when saving your changes.
Related Topics
Distributions Window Field Reference
Reviewing Revenue Credits
Receivables lets you enter and update sales credits for your credit memos. If you are reviewing a credit memo against a specific invoice or commitment, Receivables derives the default sales credits from the original invoice or commitment sales credit line.
Receivables also defaults the salesperson's assigned sales group, if one is available. You can change the default.
If you are viewing an on-account credit memo, all sales credits are assigned to the primary salesperson you entered in the Transactions window. See: Creating On-Account Credit Memos.
If AutoAccounting depends on sales credits and you change the Salesperson field, Receivables displays a decision window that asks if you want to rerun AutoAccounting for this credit memo line. If you choose Yes, Receivables reruns AutoAccounting and updates your revenue accounts for this credit memo line. If you rerun AutoAccounting for this sales credit line, and you have already posted the credit memo account assignments, the original accounting entries and sales credit record are not updated. In this case, new accounting entries and sales credit records are created to offset the original sales credit entries and to note the new ones. If you choose No, Receivables does not run AutoAccounting, but does save the changes to the sales credit information.
If you define your AutoAccounting for Tax, Unbilled, Unearned, and AutoInvoice Clearing Accounts to use sales credits, and you enter Yes to rerun AutoAccounting, Receivables updates these classes which are associated with this credit memo line and are currently based on salesperson.
Warning: Always use the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard, not the Transactions workbench, to adjust sales credits on a credit memo, if that credit memo's revenue was previously adjusted via the Revenue Accounting Management (RAM) wizard. See: Entering Revenue Credits.
Prerequisites
To review or update the revenue credit information for your credit memo lines:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or the Transactions window.
-
Query the credit memo to view.
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, choose Open.
-
Choose Sales Credits.
-
To update sales credits, enter a new Revenue Credit or Other Credit percentage or Amount.
To split sales credit with another salesperson, perform the following:
a. Update the sales credit Amount or percent for the primary salesperson, then choose New Record.
b. Enter the Name of the new salesperson and the percentage of sales credit they will receive.
Related Topics
Reviewing Accounting Information
Reviewing Freight Information
If the transaction you are crediting has associated freight charges, you can enter or update credit memo freight information in the Freight window. You can specify a freight amount and Accounting Flexfield for each of your credit memo lines. When you open the Freight window, Receivables defaults the header-level freight information for the credit memo you are viewing.
You cannot enter freight information for a credit memo if the credit memo's transaction type has Allow Freight set to No or if you have specified a standard memo line of type 'Tax'.
Prerequisites
-
Define freight carriers, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
To enter or review freight information for your credit memo lines:
-
Navigate to the Transactions or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the credit memo to view.
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, choose Open.
-
Choose Freight.
-
Enter the Amount of freight charges for this credit memo or credit memo line (optional). If this is a credit memo against an invoice or commitment, the default is the original freight amount and the freight balance due for the invoice line that you are crediting. For freight only lines, the default Freight Amount is the list price of the standard line you have selected, adjusted for any currency differences
-
Enter the freight GL Account for this credit memo or credit memo line (optional). If the profile option AR: Use Invoice Accounting for Credit Memos is set to No or this is an on-account credit, Receivables uses AutoAccounting to determine the default freight account for this credit memo or credit memo line. Otherwise, Receivables uses the freight account of the transaction you are crediting.
Related Topics
Reviewing Accounting Information
Freight Window Field Reference
Reviewing Tax Information
Receivables lets you review tax information for your credit memo lines in the Detail Tax Lines window.
Oracle Receivables uses Oracle E-Business Tax as its tax engine. E-Business Tax provides a single set of application features that manage tax calculations for Receivables. Additionally, E-Business Tax is the repository of all tax-related data.
E-Business Tax calculates tax according to predefined rules and a universe of data points from your transactions and transaction lines. Oracle E-Business Tax always attempts to calculate tax on credit memos, according to its predefined rules and the data existing on the credited transaction.
Prerequisites
-
Set up tax
See: Setting Up Taxes in Oracle E-Business Tax, Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
To review tax information for your credit memo lines:
-
Navigate to the Credit Transactions or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the credit memo to view.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, choose Open.
If you are in the Credit Transactions window, choose Credit Lines.
-
Choose Tax.
Related Topics
Reviewing Accounting Information
Detail Tax Lines Window Field Reference
Unapplying Cash when Crediting a Transaction
Receivables lets you unapply cash that was previously applied to a transaction and create a credit memo for that amount.
For example, your customer returns a product for which they have already paid in full. You can unapply the cash for that transaction, then create a credit memo for the full amount against the invoice.
After you unapply the cash, you can either:
-
Place the cash on account for later reallocation to a different transaction, or
-
Send the cash back to your customer
For example, to create a manual credit card refund, you could simply unapply the cash from a transaction, create the credit card refund, and then credit the transaction. See: Credit Card Refunds.
To automate this process, see Automated Receipt Handling for Credits.
Prerequisites
To unapply cash and create a credit memo:
-
Navigate to the Receipts window.
-
Query the receipt to unapply, then choose Apply.
-
Uncheck the Apply check box next to the transaction.
-
Save your work.
-
Navigate to the Credit Transactions window.
-
Query the transaction from step 3.
-
Create a credit memo for the full or partial amount.
See: Crediting Transactions.
Related Topics
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
Updating Credit Memo Installments
When you credit a transaction with multiple installments, you can use the Installments window to update the applications of your credit memo to the installments of the credited transaction. Receivables displays installment information for a transaction based on the due date of each installment. Receivables defaults line, tax, and freight information based on the Split Term Method you entered when you created this credit memo. You can accept these values or enter new ones.
You cannot update the amount of your credit memo or add tax or freight charges in the Installments window. You cannot open the Installments window if this credit memo is incomplete or if this transaction is an on-account credit.
Prerequisites
To update the installments of a credited transaction:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the credit memo to update.
-
Choose Credit Installments from the Actions menu.
-
To update the installments of this credit memo, modify the Line, Tax, or Freight Credit Amount for each installment. The sum of the line credits must equal the total line amount of this credit memo, the sum of the tax credits must equal the total tax amount of this credit memo, and the sum of the freight credits must equal the total freight amount of this credit memo.
Related Topics
Updating Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
Batching Credit Memos
If you group your credit memos into batches, you can view the difference between your control and actual batch totals as you enter credit memos. These differences alert you to data entry errors or duplicate entries. In addition, by grouping related credit memos together, they can share default attributes such as automatic or manual numbering and transaction type.
If the transaction you are crediting is part of a batch, you can add your credit memo to that batch.
Prerequisites
-
Define credit memo sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Define credit memo transaction types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
Create a batch for your credit memos (optional)
To add a credit memo to a batch:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or Credit Transactions window.
-
If you are in the Transaction or Transactions Summary window, query the transaction to credit, then choose Credit.
If you chose Credit Transactions from the Navigator, enter the number of the transaction to credit in the Find Transactions window. If you do not know the transaction number, enter selection criteria such as Class, Transaction Date, and Currency to limit your search.
-
To add this credit memo to an existing batch, choose a Batch type of 'New,' then enter the Batch Name to which you want to add this credit memo, or select from the list of values.
-
To add this credit memo to the same batch to which the credited transaction belongs, choose a Batch type of 'Credited Transaction.' When you do this, Receivables displays a decision window.
To derive the default values for this credit memo from the batch, choose Yes. To derive the default values from the transaction you are crediting, choose No. Default values include the transaction source, credit memo date, transaction type, GL date, and currency.
Note: You can update your credit memo's default values, regardless of their source.
-
Enter the credit memo. See: Crediting Transactions.
Related Topics
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
Batching Transactions for Easy Entry and Retrieval
Querying Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
You can review your credit memos and on-account credit memos in the Transactions or the Transactions Summary window.
Note: Use the Applications button to apply on-account credit memos, or to unapply and reapply credit memos that have already been applied to transactions. See: Applying On-Account Credit Memos.
Note: If you use the Transactions Summary window to query a credit memo that has been applied to an invoice, the Applications button is not available. The Applications button in the Transactions Summary window is only used to apply on-account credit memos. See: Applying On-Account Credit Memos.
Prerequisites
To query a credit memo:
-
Navigate to the Transactions or the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the credit memo or on-account credit to view.
-
If you are in the Transaction Summary window, select the transaction to view, then choose Open.
Related Topics
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
Creating On-Account Credit Memos
On-account credit memos are credits you assign to your customer's account that are not related to a specific invoice. For example, if a customer is disappointed with a product or service you sold, you can create an on-account credit memo. You can then apply this on-account credit memo to another transaction.
You can apply and reapply on-account credit memos to invoices, debit items, and chargebacks.
See: Applying On-Account Credit Memos.
You can also place amounts on account when manually applying receipts in the Applications window. This is on-account cash, which is different from on-account credit memos. See: Manually Applying Receipts.
To create an on-account credit memo:
Prerequisites
Follow the same procedure that you used when entering transactions. See: Entering Transactions.
However, when you enter the transaction amount, enter the amount of this on-account credit memo as a negative number. For example, to enter a credit for $25, enter -25.
Related Topics
Applying On-Account Credit Memos
Updating Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
Applying On-Account Credit Memos
Receivables lets you apply on-account credit memos to your customer's open debit items. For example, your customer has a $200 on-account credit memo. You can apply the on-account credit memo to one or more open debit items to either reduce or close the on-account credit memo and your customer's outstanding balance.
Note: Using the Applications button, you can also unapply and reapply credit memos that have already been applied to transactions.
Note: If you use the Transactions Summary window to query a credit memo that has been applied to an invoice, the Applications button is not available.
The Applications button in the Transactions Summary window is used only to apply completed on-account credit memos.
To apply an on-account credit memo to a transaction:
Prerequisites
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary window.
-
Query the on-account credit memo to apply.
-
Choose Applications.
-
Select the transaction to which you want to apply this on-account credit memo from the list of values.
Receivables enters the Amount Applied and updates the Unapplied Amount of the on-account credit memo and the Balance Due for this transaction.
The default Amount Applied is the balance due for this transaction, unless the balance due is greater than the amount of this on-account credit. In this case, the default Amount Applied is the unapplied amount of the on-account credit. You can accept this amount or enter a different amount (for example, if you want to apply this on-account credit to more than one transaction).
Note: Receivables uses the transaction type of the debit item to which you are applying credit to validate the application amount:
-
If the transaction type forces natural application only, then you must enter an application amount which brings the debit item's balance closer to zero.
-
If the transaction type does not allow overapplication, then you cannot enter an amount that would reverse the sign of the balance of the debit item.
-
If the transaction type allows overapplication, then you can apply this on-account credit to a closed debit item. To access closed invoices from the Transactions workbench, you must check the Show Closed Invoices check box from the Tools menu.
Note: Receivables also uses the transaction type of the debit item to determine the application rule set for this application.
-
-
To apply this on-account credit memo to another transaction, repeat step 4.
-
When you are satisfied with the application of this on-account credit, save your work. Receivables updates your customer's account balances.
Applying a Receipt with an On-Account Credit Memo
Receivables lets you apply a receipt with an existing on-account credit memo to close one or more of your customer's open debit items. For example, your customer receives goods totaling $500, but they are not satisfied with their purchase. You agree to credit their account $100. When the customer remits payment of $400, you can simultaneously apply this receipt with the on-account credit memo to close both the open invoice and their on-account credit memo.
You can also apply receipts and on-account credits to transactions in different currencies. For example, your functional currency is USD but your German customer has an open invoice in DEM. If the customer remits a partial payment for this invoice in USD, DEM, or EUR (euro), you can combine the receipt and the on-account credit and apply them to the open invoice. Receivables automatically records any gain, loss, or rounding amounts created by the application. See: Cross Currency Receipts.
To apply an on-account credit memo with a receipt:
-
Navigate to the Receipts or Receipts Summary window.
-
Query or enter the receipt to apply. See: Entering Receipts.
-
Choose Apply.
-
Select the on-account credit memo and the open transaction(s) from the list of values.
-
Apply the receipt to the on-account credit memo and the open debit item(s). See: Manually Applying Receipts.
Related Topics
Querying Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
Updating Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
Updating Credit Memos and On-Account Credit Memos
Receivables lets you update most credit memo information, depending on its status. For example, you can change the transaction type, GL date, reference number, bill-to location, salesperson, and document number of an incomplete credit memo. If the credit memo's status is Complete, you can only update the salesperson, reason, and customer reference number. For a complete listing of the rules for updating transactions, see: Maintaining Your Transactions.
If you modify the salesperson and AutoAccounting depends on salesperson, Receivables displays a decision window that asks if you want to rerun AutoAccounting to recalculate your receivable and freight accounts. If you choose Yes, Receivables reruns AutoAccounting and makes the appropriate changes to your accounts. If you choose No, Receivables saves the changes to the sales credit information, but does not rerun AutoAccounting. If there has been activity against this transaction or it has been posted to your general ledger, Receivables does not ask if you want to recalculate the accounts.
Warning: You cannot use the Credit Transactions window to update any tax related fields for on-account credits that have been passed to Receivables from AutoInvoice with tax automatically calculated based on non-ad hoc tax codes. You can identify these transaction by their tax code and transaction source.
Prerequisites
To update a credit memo:
-
Navigate to the Credit Transactions or the Transactions window.
-
Query the credit memo to update.
-
Update the credit information as necessary.
To update an on-account credit memo:
-
Navigate to the Transactions Summary or the Transactions window.
-
Query the on-account credit to update.
-
If you are in the Transactions Summary window, select the on-account credit, then choose Open.
-
Update the on-account credit information as necessary.
Related Topics
Accounting for Credit Memos
Receivables lets you fully or partially credit your invoices while it automatically creates all the accounting reversal entries for you. You can use the Credit Transactions window or AutoInvoice to create your credit memos. The accounting is always the same whether the credit memo is imported through AutoInvoice or entered manually using the Credit Transactions window.
The next several sections provide examples of how Receivables accounts for full and partial credit memos against different types of invoices.
Sample Invoice 102 - Bill in Advance
On 1/1/XX an invoice is created with these details:
-
Invoice Number = 102
-
Invoice Date = 1/1/XX
-
Invoice Amount = $100
-
Duration = 5 months
-
Invoicing Rule = Bill In Advance
-
Accounting Rule = Fixed Amount as follows:
-
Period 1 = $20
-
Period 2 = $20
-
Period 3 = $10
-
Period 4 = $30
-
Period 5 = $20
This table shows the accounting entries for invoice 102 over the five accounting periods:
ACCOUNT Debit Credit GL Date Period Status Accounts Receivable 100.00 1/1/XX Open Unearned Revenue 20.00 1/1/XX Open Unearned Revenue 100.00 1/1/XX Open Revenue 20.00 1/1/XX Open Unearned Revenue 20.00 2/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 20.00 2/1/XX Not Opened Unearned Revenue 10.00 3/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 10.00 3/1/XX Not Opened Unearned Revenue 30.00 4/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 30.00 4/1/XX Not Opened Unearned Revenue 20.00 5/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 20.00 5/1/XX Not Opened -
This example describes four separate cases:
-
Case 1 - A full credit memo entered against the invoice.
-
Case 2 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice, with credit method for rules set to Prorate.
-
Case 3 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice, with credit method for rules set to LIFO.
-
Case 4 - A partial credit memo is entered against the invoice on 6/1/XX, with credit method for rules set to UNIT.
Case 1
A full credit memo is entered on 2/15/XX against invoice 102 with these details:
-
Credit memo date = 2/15/XX
-
Credit memo amount = $100
This table shows the reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 100.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 20.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 20.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 100.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 20.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 20.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 10.00 | 3/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 10.00 | 3/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Revenue | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Revenue | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened |
Case 2
A partial credit memo for $65 is entered on 2/15/XX against invoice 102, with credit method for rules set to Prorate. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 2/15/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $65
This table shows the partial reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied, with the computations used to derive the partial amounts:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue (65/100) * ($100) | 65.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100) * ($20) | 13.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100) *($20) | 13.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 65.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 13.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 13.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100) * ($10) | 6.50 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 6.50 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100) * ($30) | 19.50 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 19.50 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Revenue (65/100) * ($20) | 13.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 13.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened |
Case 3
A partial credit memo for $65 is entered on 2/15/XX against invoice 102, with credit method for rules set to LIFO. The credit memo amount is fully applied by Period 2. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 2/15/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $65
This table shows the partial and full reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 5.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 65.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 5.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 65.00 | 2/15/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 10.00 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 10.00 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Revenue | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened | |
| Unearned Revenue | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Not Opened |
Note: Receivables derives the partial reversal amount of $5 in Period 2 by subtracting the Period 5, 4, and 3 Revenue amounts from the credit memo amount: (20 + 30 + 10 + 5 = 65). There are no accounting entries for Period 1 because the credit memo was fully applied in Periods 5, 4, 3, and 2.
Case 4
A partial credit memo for $65 is entered on 6/1/XX for 8 units against invoice 102, assuming that this invoice consists of 10 units with a value of $10 each for a total of $100. This credit memo is entered with credit method for rules set to UNIT. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 6/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $65
Receivables derives the Amount to Credit in each period by multiplying the Net Unit Price for each period by the number of units to credit (8 in this example). Receivables derives the Net Unit Price by the following formula:
Net Unit Price = (Invoice Amount in this period - any previous credit memos in this period) / Original invoice quantity
This table shows the Net Unit Price for each period:
| Period | Calculation | Net Unit Price |
|---|---|---|
| Period 5 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
| Period 4 | ($30-$0)/10units | $3 |
| Period 3 | ($10-$0)/10units | $1 |
| Period 2 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
| Period 1 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
This table shows the Amount to Credit (Net Unit Price * Units to Credit) in each period as a result of the above calculations:
| Period | Amount to Credit | Amount Credited (actual) |
|---|---|---|
| Period 5 | $2 * 8units | $16 |
| Period 4 | $3 * 8units | $24 |
| Period 3 | $1 * 8units | $8 |
| Period 2 | $2 * 8units | $16 |
| Period 1 | $2 * 8units | $1 (balance of credit memo) |
This table shows the partial reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 65.00 | 1/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 1.00 | 1/1/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 65.00 | 1/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 1.00 | 1/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 16.00 | 2/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 16.00 | 2/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 8.00 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Revenue | 8.00 | 3/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 24.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Receivable | 24.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 16.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unearned Receivable | 16.00 | 5/1/XX | Open |
Sample Invoice 103 - Bill in Arrears
On 1/1/XX the following invoice is created.
-
Invoice Number = 103
-
Invoice Date = 5/1/XX
-
Invoice Amount = $100
-
Duration = 5 months
-
Invoicing Rule = Bill In Arrears
-
Accounting Rule = Fixed Amount as follows:
-
Period 1 = $20
-
Period 2 = $20
-
Period 3 = $10
-
Period 4 = $30
-
Period 5 = $20
This table shows the accounting entries for invoice 103 over the five accounting periods:
ACCOUNT Debit Credit GL Date Period Status Unbilled Receivable 20.00 1/1/XX Open Revenue 20.00 1/1/XX Open Unbilled Receivable 20.00 2/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 20.00 2/1/XX Not Opened Unbilled Receivable 10.00 3/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 10.00 3/1/XX Not Opened Unbilled Receivable 30.00 4/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 30.00 4/1/XX Not Opened Accounts Receivable 100.00 5/1/XX Not Opened Unbilled Receivable 20.00 5/1/XX Not Opened Unbilled Receivable 100.00 5/1/XX Not Opened Revenue 20.00 5/1/XX Not Opened -
This example describes four separate cases:
-
Case 1 - A full credit memo entered against the invoice.
-
Case 2 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice on 6/1/XX, with credit method for rules set to Prorate.
-
Case 3 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice on 6/1/XX, with credit method for rules set to LIFO.
-
Case 4 - A partial credit memo is entered against the invoice on 6/1/XX, with credit method for rules set to UNIT.
Case 1
A full credit memo is entered on 6/1/XX against invoice 103 with these details:
-
Credit memo date = 6/1/XX
-
Credit memo amount = $100
This table shows the reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Entries | 1/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 2/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 3/1/XX | Closed | ||
| Revenue (reverse Period 1 entry) | 20.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (reverse Period 2 entry) | 20.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (reverse Period 3 entry) | 10.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (reverse Period 4 entry) | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 20.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 20.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 10.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (reverse Period 5 entry) | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable (reverse original receivable) | 100.00 | 6/1/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 100.00 | 6/1/XX | Open |
Case 2
A partial credit memo for $65 is entered on 6/1/XX against invoice 103, with credit method for rules set to Prorate. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 6/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $65
This table shows the partial reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied, with the computations used to derive the partial amounts:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Entries | 1/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 2/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 3/1/XX | Closed | ||
| Revenue (65/100)*($20) | 13.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100)*($20) | 13.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100)*($10) | 6.50 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100)*($30) | 19.50 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 13.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 13.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 6.50 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 19.50 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue (65/100)*($20) | 13.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 13.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 65.00 | 6/1/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 65.00 | 6/1/XX | Open |
Case 3
A partial credit memo for $65 is entered on 6/1/XX against invoice 103, with credit method for rules set to LIFO. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 6/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $65
This table shows the partial and full reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Entries | 1/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 2/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 3/1/XX | Closed | ||
| Revenue | 5.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 10.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 5.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 10.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 30.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 20.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 30.00 | 6/1/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 30.00 | 6/1/XX | Open |
Note: Receivables derives the partial reversal amount of $5 in Period 4 by subtracting the Period 3, 4, and 5 Revenue amounts from the credit memo amount.
Case 4
A partial credit memo for $40 is entered on 6/1/XX for 8 units against invoice 103, assuming that this invoice consists of 10 units with a value of $10 each for a total of $100. This credit memo is entered with credit method for rules set to UNIT and the Last Period to Credit set for the last period of the invoice. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 6/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $40
Receivables derives the Amount to Credit in each period by multiplying the Net Unit Price for each period by the number of units to credit (8 in this example). Receivables derives the Net Unit Price by the following formula:
Net Unit Price = (Invoice Amount in this period - any previous credit memos in this period) / Original invoice quantity
This table shows the Net Unit Price for each period:
| Period | Calculation | Net Unit Price |
|---|---|---|
| Period 5 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
| Period 4 | ($30-$0)/10units | $3 |
| Period 3 | ($10-$0)/10units | $1 |
| Period 2 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
| Period 1 | ($20-$0)/10units | $2 |
This table shows the Amount to Credit (Net Unit Price * Units to Credit) in each period as a result of the above calculations:
| Period | Amount to Credit | Amount Credited (actual) |
|---|---|---|
| Period 5 | $2 * 8units | $16 |
| Period 4 | $3 * 8units | $24 |
This table shows the partial reverse accounting entries after the credit memo is applied:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit | GL Date | Period Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Entries | 1/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 2/1/XX | Closed | ||
| No Entries | 3/1/XX | Closed | ||
| Revenue | 24.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 24.00 | 4/1/XX | Open | |
| Revenue | 16.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 16.00 | 5/1/XX | Open | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 40.00 | 6/1/XX | Open | |
| Accounts Receivable | 40.00 | 6/1/XX | Open |
Sample Invoice 104 - Three Payment Installments
On 1/1/XX an invoice is created with these details:
-
Invoice Number = 104
-
Invoice Date = 1/1/XX
-
Invoice Amount = $100
-
Payment Terms = 3 Installments as follows in this table:
Due Date Amount 2/1/XX $50 3/1/XX $25 4/1/XX $25
This table shows the payment schedules for these installments:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $50 | $0 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $25 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $25 | $0 |
This example describes three separate cases:
-
Case 1 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice with the credit method for split terms set to Prorate; a partial payment entered against the invoice; another partial credit memo entered against the invoice.
-
Case 2 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice with the credit method for split terms set to LIFO; a partial payment entered against the invoice; another partial credit memo entered against the invoice.
-
Case 3 - A partial credit memo entered against the invoice with the credit method for split terms set to FIFO; a partial payment entered against the invoice; another partial credit memo entered against the invoice.
Case 1
There are three transactions against invoice 104: A partial credit memo for $45 with the credit method for split terms set to Prorate; a partial payment of $20; another partial credit memo for $20.
Transaction 1
On 1/1/XX a credit memo for $45 is entered against invoice 104. The credit method for split terms is set to Prorate. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $45
To calculate the amount credited per payment schedule, Receivables uses the following formula:
Amount Credited = (Credit Memo Amount/Total Remaining Amount Due) * Amount Due Remaining on this installment
This table shows the calculations for the amount credited for each installment:
| Due Date | Calculation | Amount Credited |
|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $45/100 * $50 | $22.50 |
| 3/1/XX | $45/100 * $25 | $11.25 |
| 4/1/XX | $45/100 * $25 | $11.25 |
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $27.50 | $22.50 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $13.75 | $11.25 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $13.75 | $11.25 |
Transaction 2
On 1/15/XX a payment is received for $20. This payment affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $7.50 | $22.50 | $20 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $13.75 | $11.25 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $13.75 | $11.25 | $0 |
Transaction 3
On 1/16/XX another credit memo for $20 is entered against invoice 104. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/16/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $20
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $3.22 | $26.78 | $20 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $5.89 | $19.11 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $5.89 | $19.11 | $0 |
Note: The amounts in the Total Amount Credited column are derived from this formula:
Total Amount Credited per installment from Transaction 2 + (Credit Memo Amount/Total Remaining Amount Due from Transaction 2 * Remaining Amount Due per installment from Transaction 2).
The results are rounded to two decimal places.
Case 2
There are three transactions against invoice 104: A partial credit memo for $45 with the credit method for split terms set to LIFO; a partial payment of $20; another partial credit memo for $20.
Transaction 1
On 1/1/XX a credit memo for $45 is entered against invoice 104. The credit method for split terms is set to LIFO. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $45
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $50 | $0 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $5 | $20 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $0 | $25 |
Transaction 2
On 1/15/XX a payment is received for $20. This payment affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $30 | $0 | $20 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $5 | $20 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $0 | $25 | $0 |
Transaction 3
On 1/16/XX another credit memo for $20 is entered against invoice #104. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/16/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $20
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $15 | $15 | $20 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $0 | $25 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $0 | $25 | $0 |
Case 3
There are three transactions against invoice 104: a partial credit memo for $45 with the credit method for split terms set to FIFO; a partial payment of $20; another partial credit memo for $20.
Transaction 1
On 1/1/XX a credit memo is entered against invoice 104. The credit method for split terms is set to FIFO. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/1/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $45
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $5 | $45 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $25 | $0 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $25 | $0 |
Transaction 2
On 1/15/XX a payment is received for $20. This payment affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $0 | $45 | $5 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $10 | $0 | $15 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $25 | $0 | $0 |
| Total | $100 | $35 | $45 | $20 |
Note: When the payment applied on 1/15/XX fully covered the amount due for the first pay period, the remainder of the payment is applied to the amount due for the following period.
Transaction 3
On 1/16/XX another credit memo for $20 is entered against invoice 104. The credit memo details are:
-
Credit Memo Date = 1/16/XX
-
Credit Memo Amount = $20
This credit memo affects the payment schedules of invoice 104, as shown in this table:
| Due Date | Original Amount Due | Remaining Amount Due | Total Amount Credited | Payment Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/XX | $50 | $0 | $45 | $5 |
| 3/1/XX | $25 | $0 | $10 | $15 |
| 4/1/XX | $25 | $15 | $10 | $0 |
Credit Memos Against Invoices Against Commitments
Below are some examples that show the accounting entries that are created when you credit invoices against commitments.
Example 1 - A Full Credit Memo Against an Invoice Against a Deposit
This example includes three transactions.
Transaction 1
A deposit is entered for $1000. The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (deposit) | 1000.00 | |
| Revenue | 1000.00 |
Transaction 2
An invoice for $400 is entered against this deposit. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 400.00 |
Receivables automatically creates a receivables adjustment for the invoiced amount. This adjustment is created against the invoice resulting in an amount due in Accounts Receivable of $0. (In this example, the $400 does not include tax and freight). Therefore, there is no balance due for the $400 invoice, as it has drawn against the $1000 deposit in lieu of payment of the invoice.
Transaction 3
A credit memo for $400 is applied to the $400 invoice. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 400.00 |
The first accounting entry reverses the adjustment entered in the previous step. The second accounting entry reverses the invoice entered in the previous step, leaving a deposit balance of $600.
Example 2 - A Full Credit Memo Against an Invoice Against a Guarantee
This example includes three transactions.
Transaction 1
A guarantee is entered for $1000. The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unbilled Receivables | 1000.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 1000.00 |
Transaction 2
An invoice for $400 is entered against this guarantee. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 400.00 |
Receivables automatically creates a receivables adjustment for the invoiced amount. This adjustment is created against the guarantee. Therefore, an outstanding amount of $400 exists for this invoice and the guarantee has an outstanding balance of $600.
Transaction 3
A credit memo for $400 is applied to the $400 invoice. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unbilled Receivables | 400.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Revenue | 400.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 400.00 |
The first accounting entry reverses the adjustment entered in the previous step. The second accounting entry reverses the invoice entered in the previous step.
Example 3 - A Credit Memo Against an Invoice Against a Deposit
This case shows the accounting entries that are created when you apply an invoice to a deposit and the invoice amount is greater than the deposit. It also shows the entries that are created when you apply a partial credit memo to the invoice.
Transaction 1
A deposit is entered for $100. The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (deposit) | 100.00 | |
| Revenue | 100.00 |
Transaction 2
An invoice for $220 is entered against this deposit. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 220.00 | |
| Revenue | 220.00 | |
| Revenue | 100.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 100.00 |
The current outstanding balance for the invoice is $120.
Transaction 3
A credit memo for $150 is applied to the invoice. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 30.00 | |
| Revenue | 30.00 | |
| Revenue | 150.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 150.00 |
Receivables automatically creates a receivables adjustment for $30 against the invoice to increase the outstanding balance to $150. The second accounting entry is for the $150 credit memo, leaving a deposit balance of $30.
Example 4 - A Credit Memo Against an Invoice Against a Guarantee
This case shows the accounting entries that are created when you apply an invoice to a guarantee and the invoice amount is greater than the guarantee. It also shows the entries that are created when you apply a partial credit memo to the invoice.
Transaction 1
A guarantee is entered for $100. The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unbilled Receivable | 100.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 100.00 |
Transaction 2
An invoice for $220 is entered against this guarantee. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | 220.00 | |
| Revenue | 220.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 100.00 | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 100.00 |
The current outstanding balance for the invoice remains at $220.
Transaction 3
A credit memo for $150 is applied to the invoice. The accounting entries are described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 150.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable (invoice) | 150.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 30.00 | |
| Unbilled Receivable | 30.00 |
Receivables automatically creates a receivables adjustment for $30 against the guarantee to increase the outstanding balance to $30. The current outstanding balance for the invoice is $70.
Credit Memos Against Invoices Under Collectibility Analysis
Below is an example that shows the accounting entries that Receivables creates when you credit invoices under collectibility analysis.
For more information, see: Event-Based Revenue Management.
Example 1 - Partial Credit Memos plus Payments
An invoice is imported for $750.
The invoice has 3 lines: Line 1 is $200, Line 2 is $450, and Line 3 is $100. Line 1 is associated with a nonstandard 90-day refund policy, and Line 3 is associated with a 120-day cancellation provision.
In addition, you have granted an extended payment term to the customer, and you have set the Use Invoice Accounting for Credit Memos profile option to Yes.
Transaction 1
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Receivable | 750.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 750.00 |
Transaction 2
You apply a $300 receipt against the invoice, 45 days after the invoice date.
Based on the weighted average formula, Receivables applies $80 to Line 1, $180 to Line 2, and $40 to Line 3.
-
Receivables cannot recognize revenue for Line 1 or Line 3 due to the related contingencies. Receivables records payments to Line 1 and Line 3 as amounts that are pending revenue recognition at a later date.
-
Receivables can recognize revenue only for Line 2.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | 300.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 300.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 180.00 | |
| Earned Revenue | 180.00 |
The total amount due on this invoice is now $450. The unearned revenue amount on this invoice is $570.
Transaction 3
Then, you apply a credit memo for $200 against this invoice.
This invoice has a combination of payment-based and time-based contingencies. Therefore, the balance of the credit memo is not prorated between the Unearned Revenue and Revenue accounts. Instead, Receivables credits the Receivables account and debits the Unearned Revenue account for the full amount of the credit memo.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 200.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 200.00 |
The total amount due on this invoice is now $250. The unearned revenue amount on this invoice is $370.
Transaction 4
After 90 days pass, the Revenue Contingency Analyzer runs and identifies that the refund policy has expired. The Revenue Contingency Analyzer initiates revenue recognition for the amount of the receipt that you previously applied to Line 1.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 80.00 | |
| Earned Revenue | 80.00 |
The total amount due on this invoice is still $250. However, the unearned revenue amount on this invoice is $290.
Transaction 5
Later, you apply a credit memo for $150 against this invoice.
This invoice still has a combination of payment-based and time-based contingencies. Therefore, Receivables credits the Receivables account and debits the Unearned Revenue account for the full amount of the credit memo.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 150.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 150.00 |
The total amount due on this invoice is now $100. The unearned revenue amount on this invoice is $140.
Transaction 6
After 120 days pass, the Revenue Contingency Analyzer runs and identifies that the cancellation policy has expired. The Revenue Contingency Analyzer initiates revenue recognition for the amount of the receipt that you previously applied to Line 3.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | 40.00 | |
| Earned Revenue | 40.00 |
The total amount due on this invoice is still $100. However, the unearned revenue amount on this invoice is $100.
Transaction 7
Finally, you apply a $100 receipt against the invoice.
Based on the weighted average formula, Receivables applies $27 to Line 1, $60 to Line 2, and $13 to Line 3. At this point, all time-based contingencies have expired.
The accounting entry is described in this table:
| ACCOUNT | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | 100.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 100.00 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 100.00 | |
| Earned Revenue | 100.00 |
The invoice is now fully paid and no more unearned revenue exists on this invoice.
Related Topics
AME Credit Memo Request Workflow
The AME Credit Memo Request workflow is a predefined workflow process that routes a credit memo request for approval.
This workflow uses Oracle Approvals Management (AME), which is a web-based, self-service application that employs business rules defined by your enterprise to govern the transaction approval process in Oracle Applications.
Use this workflow instead of the workflow without AME, because the AME rules that govern the approval process more easily support operations in multiple currencies and elaborate approval chains. See: Why Use Oracle Approvals Management.
Important: To use the AME workflow, set the AR: Use Oracle Approvals Management in Credit Memo Workflow profile option to Yes, and define your AME rules. See: Setting Up the AME Credit Memo Request Workflow.
You can initiate the AME Credit Memo Request workflow from iReceivables or Oracle Collections.
-
iReceivables is a web-based, self-service application that enables registered users to access their Oracle Receivables account information using a standard web browser. When an iReceivables user chooses the Dispute a Bill function, Receivables places the specified amount in dispute and initiates the AME Credit Memo Request process to route the request for approval.
-
Oracle Collections is a Forms-based application that enables call centers, as well as credit and collections departments, to collect from their delinquent customers. The collector can place an invoice in dispute by requesting credit on behalf of a customer.
AME Credit Memo Request Workflow Process Flow
When a credit memo request is received, the AME Credit Memo Request workflow contacts the appropriate collector, who approves the request and indicates the request's approval path.
A credit memo request can follow one of two approval paths:
-
Limits Only path: uses specific approval limit rules to find the next approver
-
HR Hierarchy Limits path: uses an organization's internal management hierarchy to find the next approver
The approvers in each approval path are determined by the AME rules defined by your enterprise. Requests for approval occur via email or via notifications in the Workflow Notification Viewer window.
If the approver does not have sufficient approval authority, then the process forwards the request to the next approver based on your AME rules.
If the request is approved, then the workflow removes the amount from dispute and notifies the requestor, collector, and primary salesperson. If the request is rejected, then the workflow removes the amount from dispute and notifies only the requestor.
Use the Disputed Invoice report to view the notes that are automatically inserted on the disputed transaction as the workflow processes the credit request. See: Disputed Invoice Report.
Why Use Oracle Approvals Management?
Use the AME Credit Memo Request workflow because AME provides you with expanded flexibility.
For example, your HR department records both the departure of employees and the arrival of newly hired employees. When these kinds of organizational changes occur, you do not have to manually adjust your approval rules in AME. Instead, AME automatically reflects any organizational changes that are recorded in your HR system.
Note that AME provides a variety of other benefits. As you learn more about AME, you will discover how best to use AME to your advantage.
AME's offerings include:
-
Rules that ascend the HR supervisory hierarchy in a variety of ways
-
Exceptions that you can apply to specific approvers or specific types of transactions
-
Automatic currency conversion to your functional currency, so that you can use standardized rules with multiple business scenarios
-
The ability to easily insert SQL statements to expand your rules to fit your unique ways of doing business
Related Topics
Setting Up AME Credit Memo Request Workflow
Customizing the AME Credit Memo Request Process
Setting Up the AME Credit Memo Request Workflow
This section provides an overview of the required as well as optional steps for implementing the AME Credit Memo Request workflow.
The setup steps that follow provide you with basic credit memo request functionality. To fully leverage the capabilities of Oracle Approvals Management (AME), refer to the Oracle Approvals Management Implementation Guide.
The following setup steps span the following Oracle applications:
Oracle HRMS Setup
In Oracle HRMS:
-
Confirm that your collectors, salespeople, approvers, and Receivables user are defined as employees in Oracle HRMS.
See: Finding a Person Using the Find Person Window, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide.
The Receivables user is the employee whose approval initiates the creation of the credit memo.
-
If you want the AME Credit Memo Request workflow to behave similarly to the Credit Memo workflow without AME, then you can:
-
Create jobs for the approvers in your HR Hierarchy Limits path using approval authority levels.
See: Defining a Job, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
-
Assign a job to each employee who will be an approver in your HR Hierarchy Limits path.
See: Entering an Assignment, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide.
-
Use the approval authority levels as conditions when defining your AME rules.
-
Oracle System Administrator Setup
In Oracle System Administrator:
-
Confirm that all collectors, salespeople, approvers, and the Receivables user are defined as users with the appropriate responsibilities.
Important: When defining users in the Users window, enter the employee name in the Person field. This indicates that the user is also an employee and can receive workflow notifications.
Note: Assign the Workflow User responsibility to all users who should receive workflow notifications.
See: Defining a Responsibility, Oracle Applications System Administrator's Guide - Security.
-
Set the AR: Use Oracle Approvals Management in Credit Memo Workflow profile option to Yes.
The default value is No.
See: Overview of Receivables User Profile Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Oracle Receivables Setup
In Oracle Receivables:
-
Confirm that your collectors are set up.
See: Collectors, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
(Optional) Create additional credit memo creation reason codes, using the CREDIT_MEMO_REASON lookup type.
Set the Tag field to Yes to publish each reason code to iReceivables. When submitting a credit memo request, the requestor can select any reason code that is defined in the system.
See: Defining Receivables Lookups, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
-
(Optional) Define a credit memo batch source for use with this workflow.
Note: Define this batch source only if you want all credit memos generated by the AME workflow to use the same batch source. See: Oracle Workflow Setup.
If, however, you want credit memos generated by the AME workflow to obtain the credit memo batch source from the credited transaction's batch source, then skip this step.
See: Transaction Batch Sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Oracle Workflow Setup
To set up Oracle Workflow:
-
Map Oracle Workflow's directory service to the users and roles currently defined in your organization's directory repository by constructing views based on those database tables. The Notification System uses these views to send notifications to the approvers specified in your activities. Oracle Workflow provides example directory services views that you can modify and reload.
Your roles can be either individual users or a group of users. Users or groups of users do not need to be mapped here if they are going to be derived in real time. Perform this step only for users or groups that are constants, known in advance. For example, you do not have to map collectors, who are derived in real time.
-
In Oracle Workflow, load the following workflow roles:
-
Oracle Workflow Administrator. This role defines all workflow users and responsibilities and provides access to Oracle Workflow administration features. See: Identifying the Workflow Administration Role in the Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
-
System Administrator. Load the SYSADMIN role, if not already loaded.
By default, a seeded System Administrator responsibility exists for all notifications that inform a System Administrator about a system or setup problem.
If any of these notifications need go to a different user, then you can change it for each node having "Inform Sysadmin" in its title.
To do so, in Oracle Workflow, open the Node Properties and choose a different performer from the list (which would be available from users or groups you mapped in the previous step).
-
-
(Optional) Evaluate the role of the Receivables user at your enterprise. The Receivables user's approval of a credit request initiates the creation of the credit memo.
The AME rule that you define using the Receivables Credit Memo Receivables transaction type determines the Receivables user. If you want to change the Receivables user, then change the AME rule. See: Oracle Approvals Management Setup.
However, if you want different users to assume multiple Receivables user functions, then override the AME rule by updating the following roles:
-
Receivables Contact. Define the user to contact when Receivables fails to create a credit memo for an approved request. The Credit Memo Request process notifies the person assigned to this role to make a correction and resubmit, or to request a manual credit memo entry.
This Receivables user is used in the AME Credit Memo Creation process, in the Credit Memo Creation Problem - Inform Receivable User node.
-
Receivables Manual Entry. Define the user to contact when a request is made for a manual entry. This Receivables user is used in the AME Credit Memo Creation process, in the Request for Manual Entry - Inform Receivable User node.
To update the previous roles, open the properties for the node, update the performer type to Constant, assign the selected user, and apply your changes.
See: Roles, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide.
-
-
(Optional) Assign the credit memo batch source that you created in Receivables to the Batch Source Name item attribute.
Using the Oracle Workflow Builder, load the AR Credit Memo Using AME item type. Open the Properties sheet for the Batch Source Name item attribute and, in the Default Value field, enter the name of the credit memo workflow batch source that you previously defined.
Do this only if you want all credit memos generated by this workflow to use this batch source. Otherwise, do not enter a value here.
For more information, see: Modifying Objects in Oracle Workflow Builder, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide.
-
Create a view called WF_LANGUAGES that identifies the languages defined in your installation. Oracle Workflow uses this view to create a row in its translation tables that maps to a row found in its non-translated base table for each installed language.
-
Define the environment variable WF_RESOURCES. You only need to define this variable if you are not using the version of Oracle Workflow embedded in Oracle Applications.
-
Identify the Web Agent to be used by the Credit Memo Request process. This step identifies the Oracle Web Agent that Oracle Workflow uses to access its Web components.
-
To use Oracle Workflow web pages and the Workflow Monitor at your site, install Oracle WebServer. For more information, refer to the Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide and your Oracle WebServer documentation.
-
Secure your workflow database connection descriptor (DCD) using the Oracle WebServer authentication feature. This step ensures that only authorized users can access workflow processes.
-
If you want users to receive notifications via email, set up the Notification Mailer program. You can modify the templates for your electronic mail notifications and customize the logo and explanatory text that appears on your Workflow Notifications Web page.
-
Set up background Workflow Engines to control the load and throughput of the primary Workflow Engine on your system. You can specify the cost threshold level of your primary and background engines to determine which activities an engine processes and which activities the engine defers.
-
Modify the default workflow timeout periods for your activities. The default timeout period is three days.
See: Activities, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide.
Oracle Approvals Management Setup
The AME Credit Memo Request workflow routes a credit memo request according to the business rules that you define in AME.
To define a rule in AME, you use attributes and conditions. Receivables provides you with a selection of predefined attributes, but you can define additional attributes. See: AME Attributes for the AME Credit Memo Request Workflow.
The AME workflow consists of three phases, known as transaction types in AME. To implement the AME workflow, you must set up these three transaction types:
The following section describes the basic setup, including some example rules, that is required to implement this workflow. However, you can use AME to create as many rules as you need for each phase of this workflow.
For the Receivables Credit Memo Collector transaction type:
For the first workflow phase, define an AME rule to identify the collector who must evaluate a request before the request can proceed through the approval chain.
-
Create an approval group with an Action List of dynamic. In the Query box, include the following SQL statement exactly as shown:
SELECT ar_ame_cm_attributes_api.get_collector_id (:transactionId) FROM DUAL
This statement locates the collector who is assigned to the customer account or bill-to site.
Both the Limits Only and HR Hierarchy Limits paths use this approval group, which you set up once. This provides the same Find Collector functionality as the original workflow without AME.
Customers who do not assign their collectors by customer account or bill-to site must create a new package to find the collector. To achieve this, modify the SELECT statement for the approval group.
Your new package should point to a function that confirms that the collector exists on the AR_COLLECTORS table. If the collector exists, then the function should return the Employee ID to the AME workflow. Without this function, the new package will fail validation.
Tip: The descriptive flexfield on the AR_COLLECTORS table can store other attributes that your new function can call, such as cost center or region.
-
Create a rule for collector assignment. For example, this table illustrates the settings for one rule that uses the approval group created in the previous step:
Rule Setting Value Rule type pre-list approval-group rule Approval type group approvals before the chain of authority Approval require pre-approval from <Collector approval group that you previously defined> Ordinary-Condition Attributes ALWAYS_TRUE Ordinary Conditions ALWAYS_TRUE is TRUE
For the Receivables Credit Memo Approval Chain transaction type:
For the next workflow phase, define AME rules to identify the approvers in this credit memo request's approval chain.
After the collector approves a request, the workflow uses these rules to find the next approver in the approval chain.
An approval chain can follow either the Limits Only path, or the HR Hierarchy Limits path. Define a set of rules for each path that you intend to use.
Important: In AME, confirm that all existing rules apply to your business needs. If extraneous rules exist, then the transaction approval process might fail.
Complete the following steps for the Limits Only path:
-
Create approval groups, and assign members.
Then, add approvers to each group. When adding more than one approver to a group, assign a sequence to each approver.
For example:
-
Create one approval group that includes John Smith, who can approve all requests less than or equal to $1,000.
-
For all requests greater than $1,000, create another approval group that includes John Smith and Jane Doe. In this group, John is the first approver, and Jane is the second approver.
-
-
Create conditions. Use the seeded conditions if they meet your business needs; otherwise, create your own conditions.
Create ordinary conditions for limits for the TRANSACTION_AMOUNT attribute.
Using the example from the previous step, you might create one condition for all transactions with amounts between $0 and $1,000, and one condition for all transactions with amounts between $1,001 and $100,000.
Important: When creating the condition with the highest upper limit, use an upper limit that is greater than what you will ever need. Otherwise, if the credit memo request is for $200,000 but you set an upper limit of $100,000, then AME will incorrectly assume that the $200,000 request satisfies all conditions.
-
Create Limits Only rules that include the conditions you just defined.
The following table illustrates the settings for one rule that you might create. To cover all the conditions that your enterprise requires, you will need to create multiple rules.
Rule Setting Value Rule type pre-list approval-group rule Approval type group approvals before the chain of authority Approval require pre-approval from <Limits Only approval group that you previously defined> Ordinary-Condition Attributes APPROVAL_PATH, AR_REASON_CODE, TRANSACTION_AMOUNT Ordinary Conditions APPROVAL_PATH in {LIMITS}, AR_REASON_CODE in {DAMAGED PRODUCT}, $1,001 < TRANSACTION_AMOUNT <= $100,000 USD
Note: When evaluating transactions for approval, AME automatically converts foreign currency transaction amounts into your functional currency, unless you specify a currency in your rules.
Complete the following steps for the HR Hierarchy Limits path:
-
Create conditions. Use the seeded conditions if they meet your business needs; otherwise, create your own conditions.
-
Create HR Hierarchy Limits rules that include the conditions you just defined.
Important: Receivables seeds an example rule, HR Hierarchy Limits. Delete this rule if you do not use it.
Your rules also include approval types. For example, you can define rules that look at:
-
Supervisory or job levels
Supervisory levels refer to the number of supervisors to ascend in a hierarchy. Job levels refer to the job level to ascend to in a hierarchy. See: Oracle Approvals Management Implementation Guide.
-
Both supervisory or job levels, and approval limits
To create the latter type of rule, you might create job levels in HRMS and assign them to your approvers. You can then define rules in AME that use both job levels as well as transaction amount limits.
For example, this table illustrates the settings for one such rule:
Rule Setting Value Rule type list-creation rule Approval type chains of authority based on absolute job level Approval Require approvals up to at least level 2 Ordinary-Condition Attributes APPROVAL_PATH, AR_REASON_CODE, TRANSACTION_AMOUNT Ordinary Conditions APPROVAL_PATH in {HR}, AR_REASON_CODE in {DAMAGED PRODUCT}, 0 < TRANSACTION_AMOUNT <= $200 USD The rule illustrated in the previous table states that for requests between $0 and $200, approval is required by an employee who has a job level of at least level 2.
-
Complete the following optional steps for both paths:
-
(Optional) Set the ALLOW_REQUESTER_APPROVAL attribute to False.
Set this attribute to False only if you do not want requestors to approve their own credit memo requests.
-
(Optional) Create ordinary conditions for the AR_REASON_CODE attribute, using the lookup codes that you defined for the CREDIT_MEMO_REASON lookup type. See: Oracle Receivables Setup.
Note: Enter the lookup codes exactly as you defined them in the Code field.
Complete this step only if you plan to use reason codes as part of your AME rules.
For the Receivables Credit Memo Receivables transaction type:
For the final workflow phase, define an AME rule to identify the Receivables user whose approval initiates the creation of the credit memo.
-
Create an approval group for the Receivables user, and assign a single member.
Both the Limits Only and HR Hierarchy Limits paths use this group. This group, which you set up once, must include only one member.
-
Create a rule for the Receivables user.
For example, if you want the Receivables user to be the final approver before credit memo creation, then use the setup that the following table illustrates:
Rule Setting Value Rule type post-list approval-group rule Approval type group approvals after the chain of authority Approval require post-approval from <approval group that you previously defined> Ordinary-Condition Attributes ALWAYS_TRUE Ordinary Conditions ALWAYS_TRUE is TRUE
Related Topics
Item Types, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide
Setting Up Background Workflow Engines, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide
Conditions, Oracle Approvals Management Implementation Guide
Rules, Oracle Approvals Management Implementation Guide
AME Attributes for the AME Credit Memo Request Workflow
You can optionally use nonmandatory attributes to create conditions and rules in AME.
The following table describes the nonmandatory attributes that are available for use with the Receivables Credit Memo Collector transaction type:
| Attribute | Value | Requiring Approval Types |
|---|---|---|
| ALWAYS_TRUE | True Value | None |
| AR_COLLECTOR_ID | AR Collector ID | None |
The following table describes the nonmandatory attributes that are available for use with the Receivables Credit Memo Approval Chain transaction type:
| Attribute | Value | Requiring Approval Types |
|---|---|---|
| ALWAYS_TRUE | True Value | None |
| APPROVAL_PATH | Approval Path | None |
| APPROVER_ID | Approver ID | None |
| APPROVER_USER_NAME | Approver User Name | None |
| AR_BATCH_SOURCE_NAME | AR Batch Source Name | None |
| AR_BILL_TO_USE_ID | AR Bill To Use ID | None |
| AR_COLLECTOR_ID | AR Collector ID | None |
| AR_CUSTOMER_ID | Customer ID | None |
| AR_CUSTOMER_NAME | AR Customer Name | None |
| AR_CUSTOMER_TRX_ID | AR Customer Transaction ID | None |
| AR_ORIG_TRX_NUMBER | AR Original Transaction Number | None |
| AR_REASON_CODE | AR Reason Code | None |
| BILL_TO_CUSTOMER_NAME | Bill To Customer Name | None |
| BILL_TO_CUSTOMER_NUMBER | Bill To Customer Number | None |
| COLLECTOR_EMPLOYEE_ID | Collector Employee ID | None |
| COLLECTOR_NAME | Collector Name | None |
| COLLECTOR_USER_NAME | Collector User Name | None |
| CURRENCY_CODE | Currency Code | None |
| INCLUDE_ALL_JOB_LEVEL_APPROVERS | Whether to include all approvers at a given job level | Absolute job level, dual chains of authority, manager than final approver, relative job level |
| JOB_LEVEL_NON_DEFAULT_STARTING_POINT_PERSON_ID | Person ID of non-default first approver for job-level authority approval types | Absolute job level, final approver only, manager then final approver, relative job level |
| REQUESTOR_ID | Requestor ID | None |
| REQUESTOR_USER_NAME | Requestor User Name | None |
| SHIP_TO_CUSTOMER_NAME | Ship To Customer Name | None |
| SHIP_TO_CUSTOMER_NUMBER | Ship To Customer Number | None |
| TAX_EX_CERT_NUM | Tax Exempt Certification Number | None |
| TOP_SUPERVISOR_PERSON_ID | Person ID of the top person in the HR supervisory hierarchy | Supervisory level |
| TRANSACTION_AMOUNT | Total currency amount for the transaction | None |
The following table describes the nonmandatory attributes that are available for use with the Receivables Credit Memo Receivables transaction type:
| Attribute | Value | Requiring Approval Types |
|---|---|---|
| ALWAYS_TRUE | True Value | None |
The AME Credit Memo Request Workflow Item Type
The AME Credit Memo Request workflow consists of the AR Credit Memo Using AME item type. This item type contains all request approval workflow processes.
Currently, the AR Credit Memo Using AME item type includes six workflow processes: AR Credit Memo Request Approval; Collector Approval; Credit Memo Creation; Limits Only Approval; HR Hierarchy Approval; and Receivable Approval.
This table lists all of the attributes for the AR Credit Memo Using AME item type. Use this section if you plan to customize the workflow.
| Display Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Approval Path | The approval path. | Lookup |
| Approver Display Name | The approver display name. | Text |
| Approver ID | The approver ID number. | Number |
| Approver Notes | Approver notes. | Text |
| Approver User Name | The approver user name. | Text |
| Batch Source Name | The batch source name to assign to the credit memo. | Text |
| Bill To Customer Name | The name of the bill-to customer for this transaction. | Text |
| Bill To Customer Number | The number of the bill-to customer for this transaction. | Number |
| Bill To Site Use ID | Bill-to site use identifier | Number |
| Collector Display Name | The collector's display name. | Text |
| Collector Employee ID | Employee ID of the collector. | Number |
| Collector ID | Unique identifier of the collector. | Number |
| Collector Name | The collector name. | Text |
| Collector User Name | The collector user name. | Text |
| Comments | Any comments entered by the requestor. | Text |
| Credit Memo Creation Error | Error message to indicate that the credit memo could not be created. | Text |
| Credit Method for Accounting Rules | The credit method to use if the disputed transaction uses accounting rules (LIFO, Prorate, Unit). | Text |
| Credit Method for Installments | The credit method to use if the disputed transaction has multiple installments (LIFO, FIFO, Prorate). | Text |
| Currency Code | The currency of the disputed transaction | Text |
| Current Hub | The current hub. | Text |
| Customer ID | The number of the customer for this transaction. | Number |
| Customer Name | The name of the customer for this transaction. | Text |
| Customer Trx ID | Unique identifier for disputed transaction. | Number |
| Entered Amount Display | Amount of the transaction that is in dispute. | Number |
| Escalation Count | Number of times the request has been escalated. | Number |
| Find Approver Count | Number of approvers in the process. | Number |
| Forward From Display Name | The display name of the person who forwarded the request. | Text |
| Forward From User Name | The user name of the person who forwarded the request. | Text |
| Forward To Display Name | The display name of the person to which the request is forwarded. | Text |
| Forward To User name | User name of the person to which the request is forwarded. | Text |
| Invalid Rule Message | Error message that appears when an invalid invoicing or accounting rule is entered. | Text |
| Invalid Rule Value | The invalid rule specified. | Text |
| Manager Display Name | The display name of the approver's manager as specified in the HR tables. | Text |
| Manager ID | The ID number of the approver's manager as specified in the HR tables. | Number |
| Manager User Name | The user name of the approver's manager as specified in the HR tables. | Text |
| Notes | Any information entered by the collector, a manager, or an approver that are recorded on the disputed transaction. | Text |
| Original Freight Amount | The original freight amount for the disputed transaction. | Number |
| Original Line Amount | The original line amount for the disputed transaction. | Number |
| Original Tax Amount | The original tax amount for the disputed transaction. | Number |
| Original Total | The total amount of the disputed transaction. | Number |
| Reason | The reason for this request. | Text |
| Receivable User | User defined for the Receivable Approval subprocess. | Role |
| Request URL | The web address from which the request originated. | URL |
| Requestor Display Name | The requestor display name. | Text |
| Requestor ID | The requestor ID number. | Number |
| Requestor User Name | The requestor user name. | Text |
| Role | The role assigned to a performer in the workflow which allows access to a specific activity. | Role |
| Salesrep User Name | The salesperson user name. | Text |
| Ship To Customer Name | The name of the ship-to customer for this transaction | Text |
| Ship To Customer Number | The number of the ship-to customer for this transaction | Number |
| Starting Point for HR Hierarchy | The starting ascension point in the HR Hierarchy. | Number |
| Total Credit To Freight | The total amount of freight that is in dispute. | Number |
| Total Credit To Invoice | The total amount of the transaction that is in dispute. | Number |
| Total Credit To Lines | The amount of transaction lines that is in dispute. | Number |
| Total Credit To Tax | The amount of tax that is in dispute. | Number |
| Trx Number | The number of the credit memo (once approved and created in Receivables). | Number |
| Workflow Document ID | Unique identifier of the workflow document. | Number |
Related Topics
Item Types, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide
Notifications
The AME Credit Memo Workflow automatically sends notifications whenever a new request is created and each time an approver approves or rejects a request.
An internal approver can receive notifications in an email message or review them in the Workflow Notification Viewer window. External users can review their notifications in the Workflow Notifications Web page.
When you select a notification record in the Notifications Summary window, the Notifications window appears, listing the details of that notification. You can do the following in the Notifications window:
-
Reassign the notification to another user
-
Respond to the notification or, if it does not require a response, close the notification
-
Drill down to another Oracle Applications window associated with the notification (if icons exist in the References region)
Notification Result types list the possible results returned by an activity. Your workflow diagram may branch depending on the value returned by your completed activity. The result type of <None> should be used for notifications that do not require a response.
Note: If the request is for a line-level credit, the tax amount is not calculated until Receivables creates the credit memo. As a result, the tax amount does not appear on the notification.
Related Topics
Overview of Notification Handling, Oracle Workflow User's Guide
Setting Up an Oracle Workflow Directory Service, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
Customizing the AME Credit Memo Request Process
You can view the predefined AR Credit Memo Using AME workflow processes in a Process window using Oracle Workflow Builder.
To Display the Process in Oracle Workflow Builder
-
Choose Open from the File menu, and connect to the database.
Alternatively, you can connect to the workflow definitions file aramecm.wft, located in the product directory tree of your Oracle Applications server.
-
Expand the data source and then the item type branch within that data source.
-
Expand the Processes branch within your item type, and then double-click on a process activity to display the diagram of the process in a Process window.
Optional Customizations
Although you can use the AR Credit Memo Using AME processes as delivered, you might want to customize the processes to accommodate the specific needs of your enterprise.
For example, you can:
-
Modify the templates for your electronic mail notifications. For more information, see: Modifying Your Message Templates, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide and Adding Custom Icons to Oracle Workflow, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
-
Add icons to the standard Oracle Workflow icons to customize the appearance of your workflow process.
-
Modify the timeout value for workflow notifications. The default value for the AME Credit Memo Request timeout notifications is three days, but to suit your business needs, you might want to modify the amount of time for each notification. To do this, display the properties window for a notification and enter a new timeout value in the Node tabbed region.
Note: To help you with your customizations, refer to the sections that describe the components of this process so that you know what attributes have already been predefined and what activities are requirements in the process.
Related Topics
The AME Credit Memo Request Workflow Item Type
Summary of the AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process
Summary of the Collector Approval Subprocess
Summary of the Limits Only Subprocess
Summary of the HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess
Summary of the Receivables Approval Subprocess
Summary of the Credit Memo Creation Subprocess
Summary of the AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process
To view the properties of the AR Credit Memo Request Approval process, select the process in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu. The AR Credit Memo Request Approval process has a result type of Boolean, which indicates that when the process completes, the result type is either True or False.
To initiate this process, request a credit memo by:
-
Choosing the Dispute a Bill function in iReceivables
-
Choosing the Dispute function in Oracle Collections
-
Enabling the Credit Memo Approval and Creation API. See: Credit Memo Approval and Creation API User Notes in the Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
The Details region of the process activity properties page indicates that the Request Approval process has an error process called DEFAULT_ERROR, which is initiated only when an error is encountered that is not handled by the standard process. Most errors in the process send a notification to the system administrator to resolve (for example, if an approver is not defined as an employee in Oracle HRMS).
The DEFAULT_ERROR process simply executes the standard Default Error Notification activity to provide information associated with the error. You can customize the process further to suit your needs. For more information, see: Default Error Process, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide.
The Process window for the AR Credit Memo Request Approval process is shown below. The process consists of 16 unique activities, several of which are reused to comprise the 22 activity nodes that appear in the workflow diagram. To examine the activities of the process in more detail, we have numbered each node for easy referencing below. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process, Part 1
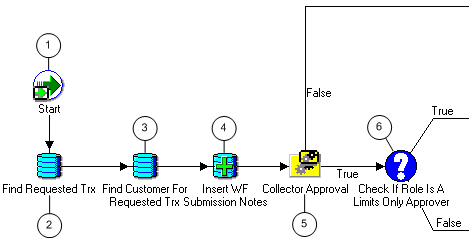
AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process, Part 2
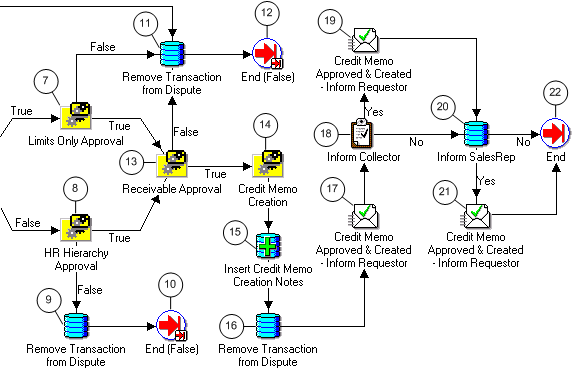
For a complete description of each activity in the AME Credit Memo Request process, see AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process Activities.
The workflow begins at Node 1 with the Start activity, which is initiated when a customer chooses the Dispute a Bill option from iReceivables, or a collector chooses the Dispute option from Oracle Collections.
At Nodes 2 and 3 the process retrieves transaction and customer information for the disputed transaction from Oracle Receivables.
At Node 4 the process places the requested amount "in dispute" and updates the notes on the disputed transaction. The process then forwards the request to the collector assigned to the transaction's bill-to site. If no collector is assigned to the bill-to site and the seeded routine is used, then the process forwards the request to the collector assigned to the customer.
Note: Instead of using the seeded routine, you can create your own SQL and replace the seeded value. For example, you might want to forward the request to the collector assigned to the customer's cost center. See: Setting Up the AME Credit Memo Request Workflow.
At Node 5 the collector either rejects the request or forwards it for approval. If the request is rejected, then the process removes the amount from dispute, updates the transaction notes, and the process ends at Node 12.
When forwarding the request for approval, the collector can either accept the default path, or select the HR Hierarchy Limits path and enter the first approver:
-
If the collector chooses the default approver, then the request follows the Limits Only Approval subprocess in Node 7.
-
If the collector forwards the request to a different approver, then the request follows the HR Hierarchy Limits subprocess in Node 8.
After the request receives the required approvals from either the Limits Only Approval or the HR Hierarchy Limits subprocess, the request follows the Receivables Approval subprocess in Node 13.
If the request receives approval from the Receivables Approval subprocess, then the Credit Memo Creation subprocess creates the credit memo in Oracle Receivables at Node 14. The process then ends at Node 22.
AR Credit Memo Request Approval Process Activities
This section provides a description of each activity in the AR Credit Memo Request Approval process, listed by the activity's display name.
The naming convention for the PL/SQL stored procedures used in the AME Credit Memo workflow is:
AR_AME_CMWF_API.<PROCEDURE>
AR_AME_CMWF_API is the name of the package that groups all of the procedures used by the AME Credit Memo Request process. <PROCEDURE> represents the name of the PL/SQL stored procedure.
Note: Oracle Workflow provides several generic activities you can use to control your process. Examples include the And/Or activities and the Start and End activities. For more information, see: Standard Activities, Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the process.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Find Requested Transaction (Node 2)
This function activity retrieves information about the disputed transaction from the RA_CM_REQUESTS table in Oracle Receivables.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindTrx |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Find Customer for Requested Transaction (Node 3)
This function activity retrieves customer information for the disputed transaction from the RA_CM_REQUESTS table in Oracle Receivables.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindCustomer |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Requested Transaction |
Insert Workflow Submission Notes (Node 4)
This function activity inserts notes on the disputed transaction.
Information associated with the disputed transaction includes the request ID, requestor name, amount, and reason for the request.
Disputed amounts appear in Receivables aging reports and can affect how Receivables calculates the customer's open balance in statements and dunning letters.
Note: Receivables users can view transaction notes in the Transactions window.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertSubmissionNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Requested Transaction |
Collector Approval (Node 5)
This activity is a subprocess that identifies the collector assigned to the bill-to site for the disputed transaction. If no collector is assigned to the bill-to site, the process uses the collector assigned to the customer.
If the collector rejects the request, this activity updates the transaction notes and notifies the requestor that it has been rejected. If the collector approves the request, then this activity checks for any credit method information (if the transaction uses invoicing or accounting rules) and updates the notes for the disputed transaction.
If the approver does not respond within a specified time, the process sends a reminder notification to the approver.
To view the subprocess, double-click on Collector Approval under the Processes branch in the navigator tree. See: Summary of the Collector Approval Sub-Process.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Customer for Requested Transaction |
Check if Role is a Limits Only Approver (Node 6)
This function activity determines the next approver for this request by checking the collector's approval action. If the collector selects Limits Only, then the request follows the Limits Only Approval subprocess.
If the collector selects HR Hierarchy Limits and the first approver, then this activity forwards the request to that person and the request follows the HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckPrimaryApprover |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval |
Limits Only Approval (Node 7)
This activity is a subprocess that notifies an approver that an action must be taken to approve or reject the request. The subprocess sends notifications to approvers, as determined by AME rules using the Limits Only path. If an approver does not respond within a specified time, then the process sends a reminder notification to the approver.
To view the subprocess, double-click on Limits Only Approval under the Processes branch in the navigator tree. See: Summary of the Primary Approval Subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval |
HR Hierarchy Approval (Node 8)
This activity is a subprocess that notifies an approver that an action must be taken to approve or reject the request. The subprocess notifies approvers defined in your organization's human resources department, as determined by AME rules using the HR Hierarchy Limits path. If an approver does not respond within a specified time, then the process sends a reminder notification to the approver.
To view the subprocess, double-click on HR Hierarchy Approval under the Processes branch in the navigator tree. See: Summary of the HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval |
Remove Transaction from Dispute (Nodes 9, 11, and 16)
This function activity updates the status of the disputed transaction in Oracle Receivables by indicating that the amount is no longer "in dispute."
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.RemoveFromDispute |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Limits Only Approval or HR Hierarchy Approval |
Receivable Approval (Node 13)
This activity is a subprocess that notifies an Oracle Receivables user that an action must be taken to approve or reject the request. If the approver does not respond within a specified time, the process sends a reminder notification to the approver.
To view the subprocess, double-click on Receivable Approval under the Processes branch in the navigator tree. See: Summary of the Receivable Approval Subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Limits Only Approval or HR Hierarchy Approval |
Credit Memo Creation (Node 14)
This activity is a subprocess that creates a credit memo in Oracle Receivables. If the API fails to create the credit memo, the process notifies a Receivables user of the problem. The Receivables user attempts to resolve the issue and resubmits the request. If the issue cannot be resolved, the process notifies the Receivables user that the credit memo must be created manually.
See: Summary of the Credit Memo Creation Subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Receivable Approval |
Insert Credit Memo Creation Notes (Node 15)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction which indicates that the credit memo received the required approvals and was forwarded for creation.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertSuccessfulApiNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Receivable Approval |
Remove Transaction from Dispute (Node 16)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction, indicating that the credit memo received the required approvals and was forwarded for creation.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.RemoveFromDispute |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Insert Credit Memo Creation Notes |
Credit Memo Approved and Created - Inform Requestor (Nodes 17, 19, and 21)
This activity notifies the requestor, salesperson, and collector, that the request was approved and the credit memo was created. The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the bill-to and ship-to customer, transaction number, and the total amount of lines, tax, and freight credited.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Credit Memo Approved & Created |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Credit Memo Creation |
Inform Collector (Node 18)
This activity informs the collector that the credit memo was approved and created in Receivables, provided that the collector is not the requestor. If the collector is the requestor, then the collector does not receive a notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InformCollector |
| Result Type | Yes/No |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Credit Memo Approved and Created - Inform Requestor |
Inform Salesrep (Node 20)
This activity informs the salesperson that the credit memo was approved and created in Receivables, provided that the salesperson is not the requestor. If the salesperson is the requestor, then the collector does not receive a notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindPrimarySalesrep |
| Result Type | Yes/No |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Inform Collector |
End (Nodes 10, 12, and 22)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Summary of the Collector Approval Subprocess
To view the properties of the Collector Approval subprocess, select its process activity in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu.
The Collector Approval subprocess has a result type of Boolean, which indicates that when the subprocess completes, it has a result of True or False.
This subprocess cannot be initiated as a top level process to run; it can only be run as a subprocess when called by another, higher level process.
When you display the Process window for the Collector Approval subprocess, you see that it consists of 22 unique activities (one of which is reused) which comprise the 23 activity nodes in the workflow diagram below.
The process activity nodes are numbered to help you reference the descriptions that follow. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
Collector Approval Subprocess
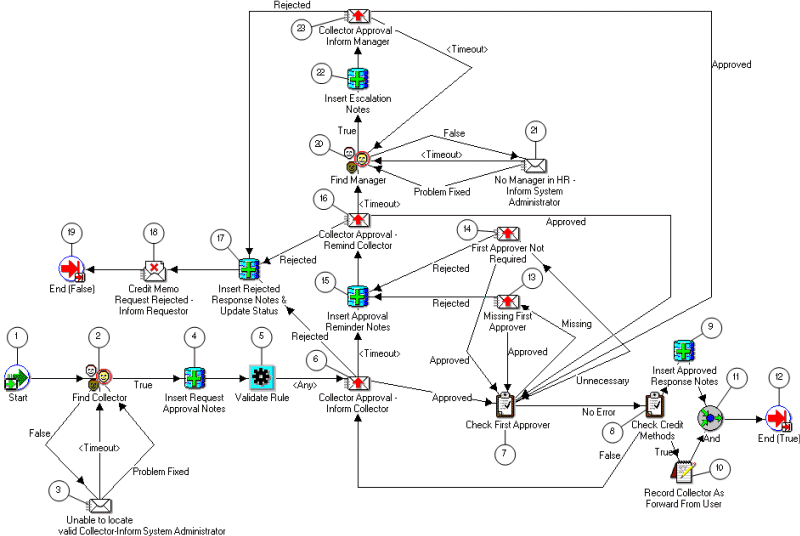
For a complete description of each activity in the Collector Approval subprocess, see Collector Approval Subprocess Activities.
The subprocess begins at Node 1 with the Start activity. At Node 6 the process notifies the collector to approve the request within a specified period of time.
If the request receives the required approvals, then the subprocess ends at Node 12 and returns a result of True to the top level Request Approval process. If the request is rejected, then the subprocess ends at Node 19 and returns a result of False.
If the collector does not respond by the due date, then the subprocess takes the <Timeout> transition to Node 16 to send a reminder to the collector to approve the request. If the collector again does not respond in the specified time, then the subprocess takes the next <Timeout> transition to escalate the issue with the collector's manager at Node 23. The collector's manager then approves or rejects the request and the workflow continues at Node 7 or 17, respectively.
Collector Approval Subprocess Activities
Following is a list of each activity in the Collector Approval subprocess, listed by the activity's display name.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Find Collector (Node 2)
This activity determines who the collector is, based on customer and bill-to site information if the seeded routine is used.
Note: Instead of using the seeded routine, you can create your own SQL and replace the seeded value. For example, you might want to assign the collector based on cost center.
If the collector is found, then this procedure returns a value of 'T' for True; otherwise, it returns a value of 'F' for False.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindCollector |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Insert Submission Notes |
Unable to Locate Valid Collector - Inform System Administrator (Node 3)
This activity notifies the system administrator that a collector could not be determined, either because no collector is assigned to the customer or customer bill-to site, or because your specific AME condition was not satisfied.
After a collector is assigned to the customer, the system administrator responds to the notification with a response of "problem fixed," and the workflow process continues.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Unable to Locate Valid Collector |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approver Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Collector |
Insert Request Approval Notes (Node 4)
This function activity inserts basic request information on the disputed transaction, including the request ID and the collector's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRequestApprovalNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Record Collector As Approver |
Validate Rule (Node 5)
This function activity checks for invoicing rules and accounting rules on the disputed transaction.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.AMECheckrule |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Insert Request Approval Notes |
Collector Approval - Inform Collector (Node 6)
This activity notifies the collector that an action needs to be taken to either approve or reject the request. This activity must be completed within the time period specified, otherwise it times out and sends a reminder notification.
The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the request number, description, amount, and the requestor name. The message also includes six 'Respond' attributes which prompt the approver for responses. These attributes include Action, Note, Installment Rule, Revenue Rule, Path, and Send To (if Path = HR Hierarchy Limits).
The Action attribute provides the approver with the values 'APPROVE' or 'REJECT' from the Approval lookup type. Action has an internal name of Result, which indicates that the value the approver selects (approve or reject) becomes the result that determines which activity branch the Workflow Engine transitions to next. The Note attribute prompts the approver for any additional comments to include in the notification response for this request.
The Installment and Revenue rules apply to invoices with rules and invoices with installments. Valid methods for invoices with rules include LIFO, Prorate, or Unit. Valid methods for invoices with installments include LIFO, FIFO, or Prorate. The only valid method for invoices without rules, or without installments, is Null (no value).
The approver can update the credit method specified on a notification. By default, the credit method is null.
If you display the property page of this activity node you see that the activity is assigned to a performer whose name is stored in an item type attribute called Forward To Username.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Request Collector Approval |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Validate Rule |
Check First Approver (Node 7)
This activity checks the first approver that the collector entered in the Send To field of the workflow notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckFirstApprover |
| Result Type | Collector Response Validation Error |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval - Inform Collector |
Check Credit Methods (Node 8)
This activity determines whether the credit method specified for invoices with rules and invoices with installments is valid.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckCreditMethods |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check First Approver |
Insert Approved Response Notes (Node 9)
This function activity inserts basic request information on the disputed transaction, including the request ID and the approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Record Collector as Forward From User (Node 10)
This function activity records the name of the collector as the person who forwarded the request for additional approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API. RecordCollectorAsForwardFrom |
| Result Type | None |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
And (Node 11)
This Standard function activity merges two or more parallel branches in the flow when the activities in all of the branches are complete.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.ANDJOIN |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Must have at least two separate activities that each transition into this activity. |
Missing First Approver (Node 13)
This notification alerts the collector that he selected the HR Hierarchy Limits path, but did not enter a first approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Missing First Approver |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check First Approver |
First Approver Not Required (Node 14)
This notification alerts the collector that he selected the Limits Only path and unnecessarily entered a first approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | First Approver Not Required |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check First Approver |
Insert Approval Reminder Notes (Node 15)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction when a reminder notification is sent to the collector to respond to the original notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovalReminderNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval-Inform Collector |
Collector Approval - Remind Collector (Node 16)
This activity occurs only if the Request Collector Approval activity times out before being completed. This activity sends a reminder notice to the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Reminder - Approval Needed - Inform Approver Request |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval-Inform Collector |
Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status (Node 17)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction when the request is rejected, and removes the transaction from dispute.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRejectedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval-Inform Collector |
Credit Memo Request Rejected - Inform Requestor (Node 18)
This activity notifies the requestor that the request was rejected. The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the request number, description, and amount.
If you display the property page of this activity you see that the activity is assigned to a performer whose name is stored in an item type attribute called Requestor Username.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Credit Memo Request Rejected |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval - Inform Collector |
Find Manager (Node 20)
This activity identifies the collector's manager and occurs only if a time-out occurs before the collector responds to the reminder notification within the time specified.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindManager |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval - Remind Collector |
No Manager in HR - Inform System Administrator (Node 21)
This activity notifies the system administrator when the Find Manager activity is unable to locate the collector's manager. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Manager in HR |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approval Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Escalation Notes (Node 22)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was forwarded to the collector's manager for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertEscalationNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Collector Approval - Inform Manager (Node 23)
This activity notifies the collector's manager indicating that the collector did not respond to the request. The collector's manager must then approve or reject the request for the process to continue.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Response Escalation |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Collector Approval - Remind Collector |
End (Nodes 12 and 19)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Summary of the Limits Only Subprocess
The Limits Only subprocess routes a credit memo request according to the rules you defined in AME for the Limits Only path.
The Limits Only subprocess has a result type of Boolean, which indicates that when the subprocess completes, it has a result of True or False.
This subprocess cannot be initiated as a top level process to run; it can be run only as a subprocess when called by another, higher level process.
To view the properties of the Limits Only subprocess, select its process activity in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu. When you do this, you see that the subprocess consists of 21 unique activities, several of which are reused to comprise the 23 activity nodes in the workflow diagram below. The process activity nodes are numbered to help you reference the descriptions that follow. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
Limits Only Subprocess, Part 1
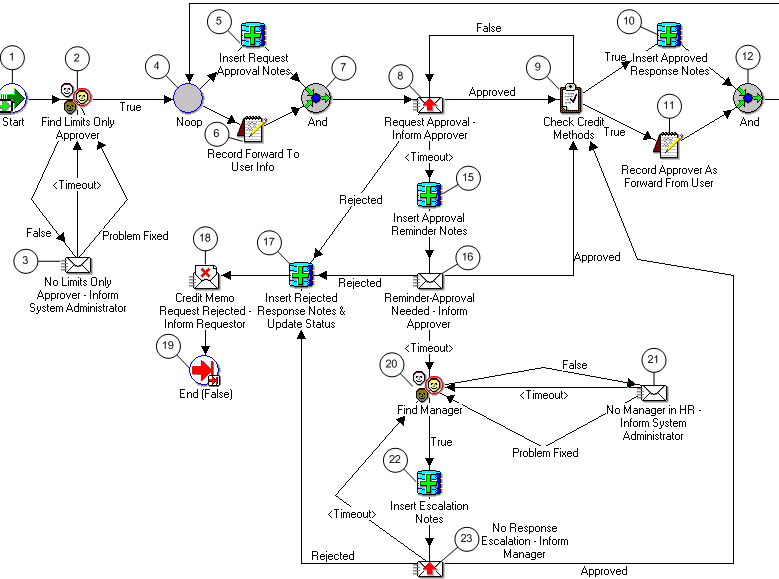
Limits Only Subprocess, Part 2
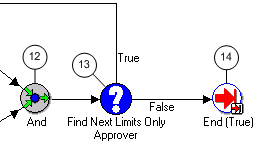
For a complete description of each activity in the Limits Only subprocess, see Limits Only Subprocess Activities.
The subprocess begins at Node 1 with the Start activity. At Node 8 the process notifies the approver to approve the request within a specified period of time.
If the approver approves the request, then the subprocess ends at Node 14 and returns a result of True to the top level Request Approval process. Similarly, if the approver rejects the request, the subprocess ends at Node 19 and returns a result of False.
If the approver does not respond to the notification, then the subprocess takes the <Timeout> transition to Node 16 to remind the approver to respond to the request. If the approver again does not respond in the specified time, then the subprocess takes the next <Timeout> transition to escalate the issue by contacting the approver's manager at Node 23.
The approver's manager then either approves or rejects the request at Node 9 or 17, respectively.
Limits Only Subprocess Activities
Following is a list of each activity in the Limits Only subprocess, listed by the activity's display name.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Find Limits Only Approver (Node 2)
This function activity identifies the first Limits Only approver for the request by checking the AME rules that were created for this path. This activity also saves the name of the requestor as well as the amount and reason for the request.
If an approver is found, then this activity returns a value of 'T' for true; otherwise it returns a value of 'F' for false.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindPrimaryApprover |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
No Limits Only Approver - Inform System Administrator (Node 3)
This activity notifies the system administrator that the first approver could not be found in Oracle Receivables. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Limits Only Approver |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approver Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Limits Only Approver |
Noop (Node 4)
This activity acts as a place holder and performs no action; it simply calls the PL/SQL procedure WF_STANDARD.NOOP.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Insert Request Approval Notes (Node 5)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a request was forwarded for approval, as well as the user ID of the next approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRequestApprovalNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Limits Only Approver |
Record Forward To User Info (Node 6)
This function activity records the name of the Limits Only approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.RecordForwardToUserInfo |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Limits Only Approver |
And (Nodes 7 and 12)
This Standard function activity merges two or more parallel branches in the flow when the activities in all of the branches are complete.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.ANDJOIN |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Must have at least two separate activities that each transition into this activity. |
Request Approval - Inform Approver (Node 8)
This activity notifies the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Request Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Request Approval |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | And |
Check Credit Methods (Node 9)
This activity determines whether the credit method specified for invoices with rules and invoices with installments is valid.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckCreditMethods |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Insert Approved Response Notes (Node 10)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was approved, as well as the user ID of the approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Record Approver as Forward From User (Node 11)
This function activity records the name of the approver for the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API. RecordApproverAsForwardFrom |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Find Next Limits Only Approver (Node 13)
This function activity determines whether this approver can provide final approval for this request.
If the request amount is within the approval limits for this approver, then the activity forwards the request to the Receivable Approval subprocess. Otherwise, it calls the Find Limits Only Approver activity again (Node 2) to identify the next approver according to the AME rules defined by your enterprise.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.AMEFindPrimaryApprover |
| Result Type | Yes/No |
| Prerequisite Activities | And |
Insert Approval Reminder Notes (Node 15)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a reminder notification was sent to the approver to respond to the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovalReminderNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Request Approval - Remind Approver (Node 16)
This activity sends a reminder notice to the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected. This activity occurs only if the Request Approval - Inform Approver activity times out before being completed.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Reminder-Approval Needed |
| Result Type | AR Collector Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status (Node 17)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction when the request is rejected, and removes the transaction from dispute.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRejectedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Credit Memo Request Rejected - Inform Requestor (Node 18)
This activity notifies the requestor that the request was rejected. The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the request number, description, and amount.
If you display the property page of this activity you see that the activity is assigned to a performer whose name is stored in an item type attribute called Requestor Username.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Credit Memo Request Rejected |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Find Manager (Node 20)
This activity identifies the last approver's manager and occurs only if a time-out occurs before the last approver responds to the notification within the time specified.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindManager |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Remind Approver |
No Manager in HR - Inform System Administrator (Node 21)
This activity notifies the system administrator when the Find Manager activity is unable to locate the approver's manager. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Manager in HR |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approval Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Escalation Notes (Node 22)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was forwarded to the approver's manager for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertEscalationNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Request Approval - Inform Manager (Node 23)
This activity notifies the last approver's manager that the approver failed to respond to a reminder notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Response Escalation |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
End (Nodes 14 and 19)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Summary of the HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess
The HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess routes the request according to the management structure defined in your Human Resources tables and the AME rules that you created that use the HR Hierarchy Limits path.
For example, a collector reports to a department manager who in turn reports to the division manager. In this example, the process forwards the request first to the collector, then to the collector's manager, and then to the division manager for final approval.
The HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess has a result type of Boolean, which indicates that when the subprocess completes, it has a result of True or False.
This subprocess cannot be initiated as a top level process to run; it can be run only as a subprocess when called by another, higher level process.
To view the properties of the HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess, select its process activity in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu. When you do this, you see that the subprocess consists of 22 unique activities, several of which are reused to comprise the 24 activity nodes in the workflow diagram below. The process activity nodes are numbered to help you reference the descriptions that follow. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess, Part 1
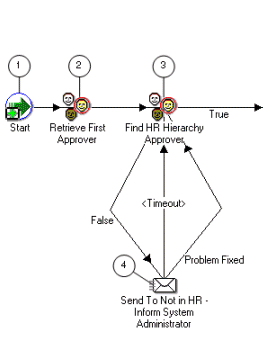
HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess, Part 2
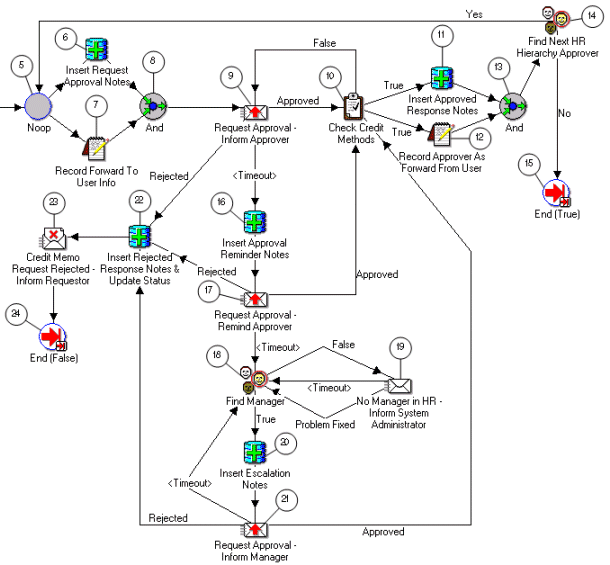
For a complete description of each activity in the HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess, see HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess Activities.
The subprocess begins at Node 1 with the Start activity. At Node 9 the process notifies the approver to approve the request within a specified period of time.
If the approver approves the request, then the subprocess ends at Node 15 and returns a result of True to the top level Request Approval process. Similarly, if the approver rejects the request, then the subprocess ends at Node 24 and returns a result of False.
If the approver does not respond, then the subprocess takes the <Timeout> transition to Node 17 to send a reminder to the approver to approve the request. If the approver again does not respond in the specified time, then the subprocess takes the next <Timeout> transition to escalate the issue by contacting the approver's manager at Node 21.
This loop continues until the approvers approve or reject the request at Node 10 or 22, respectively.
HR Hierarchy Approval Subprocess Activities
Following is a list of each activity in the HR Hierarchy Approval subprocess, listed by the activity's display name.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Retrieve First Approver (Node 2)
This function activity identifies the first approver in the HR Hierarchy Approval path that the collector selected.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.AMESetNonPrimaryApprover |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Find HR Hierarchy Approver (Node 3)
This function activity identifies the next approver for the request by checking the management hierarchy defined in your HR database. This activity also saves the name of the requestor as well as the amount and reason for the request. If an approver is found, this activity returns a value of 'T' for true; otherwise, it returns a value of 'F' for false.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.AMEFindNonPrimary Approver |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Retrieve First Approver |
Send To Not in HR - Inform System Administrator (Node 4)
This activity notifies the system administrator when the Find HR Hierarchy Approver activity is unable to identify the approver. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Send To Not in HR |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approver Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find HR Hierarchy Approver |
Noop (Node 5)
This activity acts as a place holder and performs no action; it simply calls the PL/SQL procedure WF_STANDARD.NOOP.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Insert Request Approval Notes (Node 6)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a request was forwarded for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRequestApprovalNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find HR Hierarchy Approver |
Record Forward To User Info (Node 7)
This function activity records information about the approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.RecordForwardToUserInfo |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find HR Hierarchy Approver |
And (Nodes 8 and 13)
This Standard function activity merges two or more parallel branches in the flow when the activities in all of the branches are complete.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.ANDJOIN |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Must have at least two separate activities that each transition into this activity. |
Request Approval - Inform Approver (Node 9)
This activity notifies the approver to respond to the request.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Request Approval |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | And |
Check Credit Methods (Node 10)
This activity determines whether the credit method specified for invoices with rules and invoices with installments is valid.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckCreditMethods |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval-Inform Approver |
Insert Approved Response Notes (Node 11)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was approved.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Record Approver as Forward From User (Node 12)
This function activity records the name of the approver for the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API. RecordApproverAsForwardFrom |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Find Next HR Hierarchy Approver (Node 14)
This function activity identifies the next HR Hierarchy Limits approver for the request by checking the AME rules that use the HR Hierarchy Limits path. This activity also saves the name of the requestor and the amount and reason for the request.
If an approver is found, then this activity returns a value of 'T' for true; otherwise, it returns 'F' for false.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API. AMEFindNonPrimaryApprover |
| Result Type | Yes/No |
| Prerequisite Activities | And |
Insert Approval Reminder Notes (Node 16)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a reminder notification was sent to the approver to respond to the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovalReminderNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Request Approval - Remind Approver (Node 17)
This activity sends a reminder notice to the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected. This activity occurs only if the Request Approval - Inform Approver activity times out before being completed.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Reminder-Approval Needed |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Find Manager (Node 18)
This activity identifies the last approver's manager and occurs only if a time-out occurs before the last approver responds to the notification within the time specified.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindManager |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Remind Approver |
No Manager in HR - Inform System Administrator (Nodes 19)
This activity notifies the system administrator that there is no manager defined for the approver in the human resources database. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Manager in HR |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approval Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Escalation Notes (Node 20)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was forwarded to the approver's manager for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertEscalationNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Request Approval - Inform Manager (Node 21)
This activity notifies the approver's manager that the approver failed to respond to a reminder notification within the specified time period.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Response Escalation |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status (Node 22)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction when the request is rejected, and removes the transaction from dispute.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRejectedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Inform Approver |
Credit Memo Request Rejected - Inform Requestor (Node 23)
This activity notifies the requestor that the request was rejected. The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the request number, description, and amount.
If you display the property page of this activity you see that the activity is assigned to a performer whose name is stored in an item type attribute called Requestor Username.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Credit Memo Request Rejected |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status |
End (Nodes 15 and 24)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Summary of the Receivables Approval Subprocess
The Receivables Approval subprocess routes the request for final approval to an Oracle Receivables user.
The Receivables Approval subprocess has a result type of Boolean, which indicates that when the subprocess completes, it has a result of True or False.
This subprocess cannot be initiated as a top level process to run; it can be run only as a subprocess when called by another, higher level process.
To view the properties of the Receivables Approval subprocess, select its process activity in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu. When you do this, you see that the subprocess consists of 19 unique activities (one of which is reused) which comprise the 20 activity nodes in the workflow diagram below.
The process activity nodes are numbered to help you reference the descriptions that follow. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
Receivables Approval Subprocess
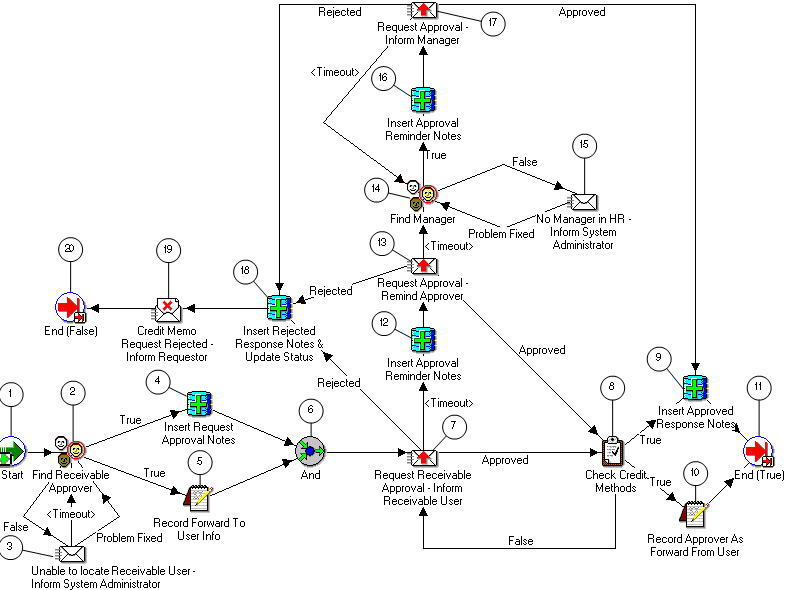
For a complete description of the Receivables Approval subprocess, see Receivables Approval Subprocess Activities.
The subprocess begins at Node 1 with the Start activity. At Node 7 the process notifies the Receivables role to approve the request within a specified period of time.
If the approver approves the request, the subprocess ends at Node 11 and returns a result of True to the top level Request Approval process. Similarly, if the approver rejects the request, the subprocess ends at Node 20 and returns a result of False.
If the approver does not respond in the time specified, the subprocess takes the <Timeout> transition to Node 13 to send a reminder to the Receivables role to approve the request. This loop continues until the approver approves or rejects the request at Node 8 or 18, respectively.
Receivables Approval Subprocess Activities
Following is a list of each activity in the Receivables Approval subprocess, listed by the activity's display name.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Find Receivable Approver (Node 2)
This function activity determines who the approver is for the request by checking the Receivables user, defined in AME rules for the Receivables Credit Memo Receivables transaction type.
This activity saves the name of the requestor as well as the amount and reason for the request.
If an approver is found, then this activity returns a value of 'T' for true; otherwise, it returns a value of 'F' for false.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindReceivableApprover |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Unable to Locate Receivable User - Inform System Administrator (Node 3)
This activity notifies the system administrator that a Receivable approver could not be found. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Unable to Locate Receivable User |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approver Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Receivable Approver |
Insert Request Approval Notes (Node 4)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a request was forwarded for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRequestApprovalNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Receivable Approver |
Record Forward To User Info (Node 5)
This function activity records information about the approver.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.RecordForwardToUserInfo |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Receivable Approver |
And (Node 6)
This Standard function activity merges two or more parallel branches in the flow when the activities in all of the branches are complete.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.ANDJOIN |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Must have at least two separate activities that each transition into this activity. |
Request Receivable Approval - Inform Receivable User (Node 7)
This activity notifies the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Request Approval |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Receivable Approver |
Check Credit Methods (Node 8)
This activity determines whether the credit method specified for invoices with rules and invoices with installments is valid.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CheckCreditMethods |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Required | Yes |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Receivable Approval-Inform Receivable User |
Insert Approved Response Notes (Node 9)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was approved.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Record Approver as Forward From User (Node 10)
This function activity records the name of the approver for the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API. RecordApproverAsForwardFrom |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Check Credit Methods |
Insert Approval Reminder Notes (Node 12)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a reminder notification was sent to the approver to respond to the request.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovalReminderNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Receivable Approval - Inform Receivable User |
Request Approval - Remind Approver (Node 13)
This activity sends a reminder notice to the approver that the request needs to be approved or rejected. This activity occurs only if the Request Approval - Inform Approver activity times out before being completed.
For a description of what this message includes, see the Collector Approval - Inform Collector node (Node 6) in the Collector Approval subprocess. This message includes an additional 'Send' attribute that displays the previous approver's name.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Reminder-Approval Needed |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Receivable Approval - Inform Receivable User |
Find Manager (Node 14)
This activity identifies the last approver's manager and occurs only if a timeout occurs before the last approver responds to the notification within the time specified.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.AMEFindManager |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Approval - Remind Approver |
No Manager in HR - Inform System Administrator (Node 15)
This activity notifies the system administrator when the Find Manager activity is unable to locate the approver's manager. After the system administrator resolves the problem, he responds to the notification with a status of "problem fixed" and the process restarts.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Manager in HR |
| Result Type | AR Fix No Approval Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Approval Reminder Notes (Node 16)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the request was forwarded to the approver's manager for approval.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertApprovalReminderNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Request Approval - Inform Manager (Node 17)
This activity notifies the last approver's manager that the approver failed to respond to a reminder notification.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | No Response Escalation |
| Result Type | AR Response to Credit Memo Request |
| Prerequisite Activities | Find Manager |
Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status (Node 18)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction when the request is rejected, and removes the transaction from dispute.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertRejectedResponseNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request Receivable Approval - Inform Receivable User |
Credit Memo Request Rejected - Inform Requestor (Node 19)
This activity notifies the requestor that the request was rejected. The message includes 'Send' attributes that display the request number, description, and amount.
If you display the property page of this activity you see that the activity is assigned to a performer whose name is stored in an item type attribute called Requestor Username.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Credit Memo Request Rejected |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Insert Rejected Response Notes & Update Status |
End (Nodes 11 and 20)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Summary of the Credit Memo Creation Subprocess
The Credit Memo Creation subprocess creates a credit memo in Oracle Receivables after the request has received all of the required approvals.
This subprocess cannot be initiated as a top level process to run; it can be run only as a subprocess when called by another, higher level process.
To view the properties of the Credit Memo Creation subprocess, select its process activity in the navigator tree, then choose Properties from the Edit menu. When you do this, you see that the subprocess consists of 7 unique activities (one of which is reused) which comprise the 8 activity nodes in the workflow diagram below. The process activity nodes are numbered to help you reference the descriptions that follow. The numbers themselves are not part of the process diagram.
Credit Memo Creation Subprocess
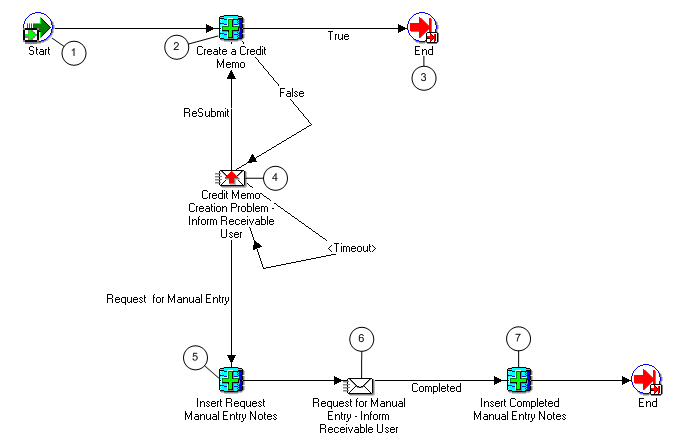
For a complete description of the Credit Memo Creation subprocess, see Credit Memo Creation Subprocess Activities.
The subprocess begins at Node 1 with the Start activity. At Node 2 the process calls an internal API and attempts to create a credit memo for the disputed amount in Oracle Receivables.
If Receivables cannot create the credit memo, then the subprocess transitions to Node 4 and notifies the Receivables user that an error occurred and the credit memo could not be created. The Receivables user can manually create the credit memo and update the notification with the credit memo number. The process ends at Node 8.
Credit Memo Creation Subprocess Activities
Following is a list of each activity in the Credit Memo Creation subprocess, listed by the activity's display name.
Start (Node 1)
This is a Standard function activity that simply marks the start of the subprocess.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | None |
Create a Credit Memo (Node 2)
This function activity creates a credit memo for the requested amount in Oracle Receivables.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.CallTrxApi |
| Result Type | Boolean |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Credit Memo Creation Problem - Inform Receivable User (Node 4)
This activity only occurs if Receivables fails to create the credit memo. The process notifies the Receivables user defined for this role with information about why the credit memo could not be created. Reasons why the API might fail include missing set up steps or the disputed transaction does not have enough balance due remaining.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Inform Receivable User - Credit Memo Creation Problem |
| Result Type | AR Credit Memo Creation Problem |
| Prerequisite Activities | Create a Credit Memo |
Insert Request Manual Entry Notes (Node 5)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that a request was forwarded to a Receivables user to create a manual credit memo.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_AP.InsertRequestManualNotes |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Credit Memo Creation Problem - Inform Receivable User |
Request for Manual Entry - Inform Receivable User (Node 6)
This activity notifies a Receivables user that the credit memo could not be created and must be entered manually.
After the user creates the credit memo, the user can enter the credit memo number into the notification and click Submit.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Message | Inform Receivable User - Request for Manual Entry |
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.FindResponder |
| Result Type | AR Request for Manual Entry |
| Prerequisite Activities | Credit Memo Creation Problem - Inform Receivable User |
Insert Completed Manual Entry Notes (Node 7)
This function activity inserts basic information on the disputed transaction indicating that the credit memo was created successfully.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | AR_AME_CMWF_API.InsertCompletedManualNotes |
| Result Type | AR Request for Manual Entry |
| Prerequisite Activities | Request for Manual Entry - Inform Receivable User |
End (Nodes 3 and 8)
This function activity marks the end of the process. Although the activity itself does not have a result type, each node of this activity in the process must have a process result assigned to it.
The process result is assigned in the property page of the activity node. Since the Credit Memo Request process activity has a result type of Boolean, each End activity node must have a process type result matching one of the lookup codes in the Boolean lookup type.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | WF_STANDARD.NOOP |
| Result Type | None |
| Prerequisite Activities | Start |
Running AutoInvoice
Run the AutoInvoice Import or Master program to transfer transactions from other systems into Receivables. You can import invoices, credit memos, debit memos, and on-account credits using AutoInvoice. Receivables ensures that the data you import is accurate and valid.
See: Importing Transaction Information Using AutoInvoice.
Note: You cannot use AutoInvoice to update existing invoices in Receivables. You can, however, create credit memos and apply them to existing invoices if the invoices are still open (or if the Allow Overapplication check box is checked for that transaction type).
You can submit the AutoInvoice Import, Master, and Purge programs from the Submit Request window. However, you can only submit the AutoInvoice Master and Purge programs from the Run AutoInvoice window. The Master program lets you run several instances of AutoInvoice to improve system performance and import transactions more quickly.
Tip: To cancel a submission of the AutoInvoice Master program, you should cancel each child program individually. Do not cancel the Master program itself.
Run the AutoInvoice Purge program to delete the interface lines that were processed and successfully transferred into Receivables by the AutoInvoice Import program. You do not have to run this program if the Purge Interface Tables option in the System Options window is set to Yes; in this case, Receivables deletes the interface lines automatically after you run AutoInvoice. See: Defining Receivables System Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Note: You can also export invoices using the Oracle e-Commerce Gateway. The e-Commerce Gateway lets you exchange information electronically with your business partners using an agreed upon, standard format. For more information, please refer to the Oracle e-Commerce Gateway User Guide.
Prerequisites
-
Define setup data, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
-
(Optional) Set the AR: AutoInvoice Gather Statistics profile option
To import transactions into Receivables using AutoInvoice:
-
Navigate to the Run AutoInvoice window.
-
Enter a request Name of AutoInvoice Master Program.
-
Enter the Number of Instances to submit.
An instance refers to how AutoInvoice groups and processes your transactions. Submitting a greater number of instances lets you import transactions into Receivables more quickly. You can submit a maximum of 15 instances.
Tip: Enter a number of instances based on how many CPUs are available. Use the following formula to determine the number of instances to enter:
(Number of Available CPUs) - 1 = Number of Instances
For example, if you have five CPUs, submit four instances of the AutoInvoice Master program.
-
Select an Organization. Receivables lets you select either any one operating unit from among the operating units to which you have access or All as the value for the Organization parameter.
Your choice of the Organization parameter affects the Invoice Source parameter. When you select a single operating unit, you can select only the batch sources for that operating unit as value for the Invoice Source parameter.
When you select All as the value for the Organization parameter, the list of values of batch sources includes all batch sources across all operating units to which you have access. If the value of the Organization parameter is All, when you submit the AutoInvoice Master program, the program runs one or more separate import processes for each organization containing batch source records. For example, assume that you have access to four organizations and you select All as the value for the Organization parameter while submitting the AutoInvoice Master program and select ORDER ENTRY batch source as the value for the Invoice Source parameter. If there are transaction records only in three of the organizations bearing the ORDER ENTRY batch source name then three separate import processes are run, one for each operating unit.
Note: When you submit the AutoInvoice Master program for All organizations, some of the other AutoInvoice Master program parameters may not work as effectively. For example, sales order numbers may not be relevant or contiguous across multiple organizations, and customers may or may not be present in each so parameters at that level of granularity may not bring the desired results if used in conjunction with All organizations.
-
Enter a Transaction Source and Default Date for this submission. These parameters are required. The Default Date must be in an open or future enterable period.
Depending on how you defined your transaction batch source and if the invoice uses rules, AutoInvoice uses the Default Date if the GL date is not provided or if the date provided is in a closed period. See: Determining Dates.
-
To limit the transactions AutoInvoice imports, enter selection criteria. For example, enter a Transaction Type, range of Bill to Customer Names, GL Dates, Ship Dates, or Transaction Numbers to import only those transactions. Leave a field blank if you do not want to limit this submission to transactions matching that criteria. Use the Transaction Flexfield parameter to specify which lines you want to import.
-
Choose whether to Base the Due Date on Transaction Date.
-
If you enter Yes, then AutoInvoice derives the due date for each transaction based on the transaction date.
-
If you enter No, then AutoInvoice looks at the setting of the Derive Date option for the transaction's batch source to derive the due date:
-
If Derive Date is No, then AutoInvoice uses either the rule start date, the transaction date, or the Default Date that you specified for this submission.
-
If Derive Date is Yes, then AutoInvoice uses the same derivation logic that it uses to determine the GL date. See: Determining Dates.
-
-
-
Enter a number of Due Date Adjustment Days (optional).
If Base Due Date on Transaction Date is Yes, then AutoInvoice ignores this parameter.
If Base Due Date on Transaction Date is No, then AutoInvoice compares the due date that was derived in the previous step against the transaction date plus the number of days that you enter here. AutoInvoice uses whichever date is later as the final due date.
If you do not enter any adjustment days, then AutoInvoice uses the due date that was derived in the previous step.
-
Choose OK.
-
To print the results of this submission, enter Print Options. Enter the number of Copies to print, a printing Style, and the Printer to use.
-
To save the output to a file, check the Save Output check box.
-
Choose Submit. Receivables displays a concurrent Request ID for this submission and creates the AutoInvoice Execution report. If you have lines that fail validation, AutoInvoice also creates the AutoInvoice Validation report. Use these reports to review the results of your AutoInvoice submission. See: AutoInvoice Reports.
You can view the status of your request in the Requests window.
To run the AutoInvoice purge program:
-
Navigate to the Run AutoInvoice window.
-
Enter a request Name of AutoInvoice Purge Program.
-
To print the results of this submission, enter Print Options. Enter the number of Copies to print, a printing Style, and the Printer to use.
-
To save the output to a file, check the Save Output check box.
-
To run this report more than once, enter Run Options. You can enter a Resubmit interval, a date and time To Start the resubmission, and an ending date on which to cease repeating.
-
Choose Submit. Receivables displays a concurrent Request ID for this submission. You can use this number to review the status of your request in the Concurrent Requests Summary window.
Related Topics
Importing Transaction Information Using AutoInvoice
Monitoring Requests, Oracle Applications User's Guide
AutoInvoice Reports
Use the AutoInvoice Execution report to review the results of your AutoInvoice request. This report lists summary information telling you how many revenue and credit transactions are selected, accepted, and rejected for each currency. The AutoInvoice Execution report also shows the total invoice amount for each transaction type for all transactions processed.
This report also includes receipts that were processed according to policy, as well as receipts that were put on account because a refund was not possible. See: Automated Receipt Handling for Credits.
AutoInvoice automatically produces this report each time you run AutoInvoice.
Use this report to match Receivables revenue and credit transaction counts to those from your other financial systems. You can also use the AutoInvoice Execution report to reconcile with other Receivables reports, such as the Transaction Register. See: Transaction Register.
Note: If AutoInvoice calculates tax, the invoice totals on the AutoInvoice Execution report and Transaction Register will not be equal. This is because the AutoInvoice Execution report only shows tax imported from RA_INTERFACE_LINES. See: Importing Tax Lines.
Use the AutoInvoice Validation report to review lines that have failed different phases of validation and the error messages associated with these lines. Receivables only generates this report when you run AutoInvoice and have lines that fail validation. To review records that were successfully imported, refer to the AutoInvoice Execution report.
Important: You can use the Interface Lines window to modify records that fail AutoInvoice validation. See: Correcting AutoInvoice Exceptions.
AutoInvoice can be divided into three major phases, pre-grouping, grouping and transfer.
-
Pre-grouping: In this phase, AutoInvoice validates all of the line-level data and any other data that is not dependent upon successful grouping. Some examples include validating that a transaction type is valid, and validating that only one freight account exist for each freight line passed.
-
Grouping: In this phase, AutoInvoice groups lines based on the grouping rules and validates header-level data that is dependent on how your lines are grouped. Some examples include validating the over application rules specified for your batch source and validating that the general ledger date of an invoice against a commitment is not before the general ledger date of the commitment. If AutoInvoice groups transactions incorrectly, check the grouping rule that you are using and confirm that your transactions properly conform to the grouping rule. For more information, see Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions.
-
Transfer: In this phase, AutoInvoice validates information that exists in Receivables tables such as tax defaulting and AutoAccounting data.
For each line, AutoInvoice can only display error messages for the phase the line is in when it fails. For example, if a line fails validation in the pre-grouping phase, AutoInvoice will display all error messages encountered in the pre-grouping phase. Additionally, if a line is already in the transfer phase when it fails, AutoInvoice will display all error messages encountered in the transfer phase. If you encounter sales credit or distribution errors, AutoInvoice prints them in a separate section below each line. AutoInvoice also prints a Summary of Transactions Rejected section at the end of the report.
You can view the AutoInvoice Execution and Validation reports online by navigating to the Requests window, selecting the report to view, and then choosing View Output.
Related Topics
Correcting AutoInvoice Exceptions
Running Standard Reports and Listings
Correcting AutoInvoice Exceptions
Use the Interface Exceptions window to view all records that failed AutoInvoice validation. Use the Interface Lines window to update these failed records.
Records that pass validation are transferred into Receivables tables. Records that fail validation are called exceptions; these records remain in the AutoInvoice interface tables. Before AutoInvoice can validate these records and create transactions in Receivables, you need to correct any invalid data, and then resubmit AutoInvoice.
Each time you run AutoInvoice, the program prints information about records that fail validation in the AutoInvoice Validation report. Use this report with the Interface Exceptions window to see which transactions failed validation and why. Then, use the Interface Exceptions window's associated drilldown windows to modify records that have errors. You can also use the Interface Lines window and its associated drilldown windows to modify records. After correcting the invalid data, resubmit AutoInvoice to import the data into Receivables tables.
Correcting AutoInvoice Exceptions
The Interface Exceptions window displays the interface ID, exception type, error message, and the invalid value associated with each error. You cannot edit data in this window, but you can edit data in the drilldown windows by selecting a record and choosing the Details button.
Note: The interface ID is the interface_line_id, interface_distribution_id, or the interface_salescredit_id for this line.
The Interface Lines window displays records of type Line or Charges that exist in the interface tables, indicates which records contain errors, and provides general information about each record. You can edit data in this window as well as drill down to view more detailed information about each record.
Note: The transaction batch source determines whether AutoInvoice will reject or partially create transactions when an error occurs in one or more of the invoice lines.
Exception Types
Records that fail validation have an associated exception type to help you identify and fix invalid data. The Interface Exceptions window displays the exception type for each record.
Valid exception types include: Charges; Freight; Freight Distribution; Line; Line Distribution; Revenue Contingency; Sales Credit; Tax; Tax Distribution.
To correct AutoInvoice exceptions:
-
Navigate to the Interface Lines window.
-
To display all of the records in the interface tables, choose Run from the Query menu. The Errors Exist check box indicates whether a record contains one or more exceptions.
To view only records in the interface tables that have errors, check the Errors Exist check box, then choose Run from the Query menu.
-
Select the record to view, then choose the Errors button.
The Line Errors window appears. In the Line Errors window, Receivables displays all of the errors associated with this record.
-
Review the error(s) for this record, then decide which error you want to fix. Note the error type, message text, and the invalid value (if any).
Note: There might be only one but there could be many errors with various error types for a single record.
-
Return to the Interface Lines window. If the error type of the error you want to fix is either Line or Charges, enter or update the appropriate information in this window, then go to step 8.
Tip: You can use the list of values to enter data for most of the fields in the Interface Lines window. You can also view additional information by placing the cursor in any folder region field, choosing Show Field from the Folder menu, and then selecting the field to view.
-
If the error type is not Line or Charges, choose the button that corresponds to the error type. For example, if the error type is Sales Credit, choose the Sales Credits button. If the error type is Line Distributions, Freight Distributions, or Tax Distributions, choose the Accounting button.
-
Update the incorrect values in the Accounting Distributions window, or choose the Errors button to view all of the errors for this distribution line.
Note: You cannot edit data in the Distribution Errors windows. You need to return to the Accounting Distributions window to modify the error for a distribution line.
-
Repeat step 3-8 for each error. After you fix all of the errors in the AutoInvoice interface tables, resubmit AutoInvoice.
Note: You might have to modify data and submit AutoInvoice several times before all of the records in the interface tables will pass validation.
To view all exceptions in the AutoInvoice interface tables:
-
Navigate to the Interface Exceptions window.
-
Choose Run from the Query menu. Receivables displays all records and their error types.
-
Select the record to edit, then choose Details.
Note: The Line Type of the record that you select determines which window appears. For example, if the Line Type is Tax, Receivables displays the Interface Tax Lines window; if the Line Type is Sales Credit, Receivables displays the Sales Credits window; if the Line Type is Line, Receivables displays the Interface Lines window, and so on.
-
Enter any missing information or update the invalid data for this record. To view all of the errors associated with this record, press the Errors button.
-
Review the error(s) for this record and return to the previous window to make your changes.
For example, if the Line Type of the record is Sales Credit, then return to the Sales Credits window to update the record.
-
Save your work.
-
To fix another error, return to the Interface Exceptions window, then repeat steps 3-5.
Related Topics
Importing Transaction Information Using AutoInvoice
AutoInvoice is a powerful, flexible tool you can use to import and validate transaction data from other financial systems and create invoices, debit memos, credit memos, and on-account credits in Oracle Receivables. You use a custom feeder program to transfer transaction data from an external system into the AutoInvoice interface tables. AutoInvoice then selects data from the interface tables and creates transactions in Receivables. Receivables rejects transactions with invalid information to ensure the integrity of your data.
AutoInvoice can also initiate receipt handling when importing credits against paid invoices.
You can run AutoInvoice together with Customer Interface or separately.
Note: The Invoicing workflow activity transfers transaction information from Oracle Order Management into the Receivables AutoInvoice tables. For more information, see: Invoice Processing, Oracle Order Management User's Guide.
Related Topics
Importing Data From Your Feeder System
Automated Receipt Handling for Credits
Overview of AutoInvoice
The following diagram shows how transaction information is imported into your Receivables tables.
Importing transaction information using AutoInvoice
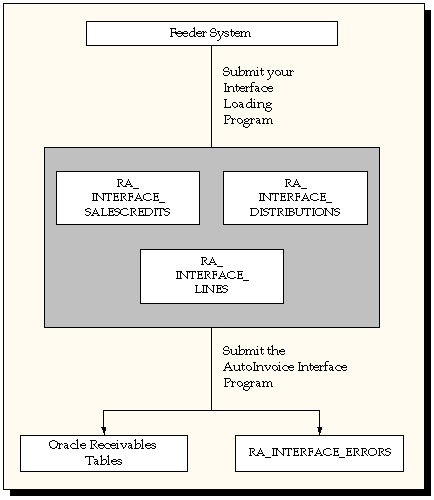
For a text description of this graphic, see: Text Description of AutoInvoice Overview Graphic.
Related Topics
Preparing Receivables for AutoInvoice
Importing Data From Your Feeder System
AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide
Preparing Receivables for AutoInvoice
To ensure that the AutoInvoice program works properly, you should prepare Receivables for any new data that you want to import. If your original system uses any setup data which is not yet defined in Receivables, you must define this data within Receivables before using AutoInvoice. Pay particular attention to the following setup data:
-
Add or import customers, if your original system contains data for customers that are not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add currencies to Receivables if your original system uses currencies not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add or update tax rates assigned to tax codes that are not defined in Receivables.
-
Add or update tax rates associated with products shipped to specific addresses.
-
Add or update full or partial customer and item tax exemptions.
-
Add Freight on Board (FOB) codes to Receivables if your original system uses FOB point codes not yet defined in Receivables. Define FOB point codes in the Receivables Lookups window with a lookup type of FOB.
-
Add freight carrier codes to Receivables if your original system uses freight carriers not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add payment terms to Receivables if your original system uses payment terms not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add transaction types to Receivables if your original system uses transaction types not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add batch sources to Receivables if your original system uses batch sources not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add salespersons to Receivables if your original system uses salespersons not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add accounting rules to Receivables if your original system uses accounting rules that are not yet defined in Receivables.
-
Add units of measure to Receivables if your original system uses units of measure not yet defined in Receivables.
Accounting Flex Tuning Segment
If you want to increase the performance of AutoInvoice and indices already exist for the GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS table, use the value that you specified for your index as your Accounting Flexfield tuning segment. If you defined a concatenated index use the first column of your concatenated index.
If no indices exist for the GL_CODE_COMBINATIONS table, enter the segment with the most distinct values for your Accounting Flexfield tuning segment. Use the System Options window to define your Accounting Flexfield tuning segment.
System Items Tuning Segment
If you want to increase the performance of AutoInvoice and indices already exist for the MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS table, use the value that you specified for your index as your System Items Flexfield tuning segment. If you defined a concatenated index, use the first column of your concatenated index.
If no indices exist for the MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS table, enter the segment with the most distinct values for your System Items Flexfield tuning segment. Use the System Options window to define your System Items Flexfield tuning segment.
Territory Tuning Segment
If you want to increase the performance of AutoInvoice and indices already exist for the RA_TERRITORIES table, use the value that you specified for your index as your Territory Flexfield tuning segment. If you defined a concatenated index use the first column of your concatenated index.
If no indices exist for the RA_TERRITORIES table, enter the segment with the most distinct values for your Territory Flexfield tuning segment. Use the System Options window to define your Territory Flexfield tuning segment.
SQL Trace
In the System Options window, specify whether you want to activate SQL trace for AutoInvoice. You might want to use SQL trace for troubleshooting if AutoInvoice is running slowly.
Purge Interface Tables
In the System Options window, specify whether you want Receivables to automatically run the AutoInvoice Purge program after AutoInvoice has completed. The purge program only deletes records from the temporary interface tables that were successfully transferred into Receivables tables. If the Purge Interface Tables system option is set to No, you need to submit the AutoInvoice Purge program from the Run AutoInvoice window to delete the records.
Max Memory (in bytes)
In the System Options window, you can enter the maximum amount of memory that you want to allocate AutoInvoice for validation. The default is 65535 bytes. Enter a lower number if AutoInvoice displays the message 'Failed to allocate memory for scratch_memory.' Enter a higher number if AutoInvoice displays the message 'The given piece of memory is not large enough to hold a single row.'
Log File Message Level
In the System Options window, enter a number from 0 to 3 that represents the amount of detail that you want displayed in the AutoInvoice log file. For day-to-day business needs and to improve performance, set the level to 0. If you experience errors while running AutoInvoice, set the message level to 3 to see detailed information in the log about the error. Enter a number of 10 to display information specific to AutoAccounting.
Message Level 0 gives the following entries in the log file:
-
Product Version
-
Program Name
-
AutoInvoice Start Time
-
AutoInvoice Concurrent Request Arguments
-
Error and Warning Messages
-
AutoInvoice End Time
-
AutoInvoice Logical Steps
Message Level 1 gives you all of the above entries plus:
-
Time-Stamped function labels
Message Level 2 gives you all of the above entries plus:
-
Sizes of Allocated Arrays
-
Dynamic SQL Statements
-
Number of Rows Updated, Inserted and Deleted
Message Level 3 gives you all of the above entries plus:
-
Method IV SQL Array Values
Message Level 10 gives you all of the above entries plus:
-
AutoAccounting debugging information
Accounting Flexfield Segment Values
Add Accounting Flexfield segment values to Receivables if your original system uses values not yet defined in Receivables. Enter the name of the Accounting Flexfield segment for which you want to add a value, and the segment value itself. Be sure to enable the segment value.
Transaction Flexfield
Receivables uses the Transaction Flexfield to uniquely identify each transaction and transaction line you import through AutoInvoice. Transaction Flexfields are also used to refer to and link transaction lines.
To define the line-level Transaction Flexfield, query 'Line Transaction Flexfield' in the Title field of the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window and enter the context and segments associated with this Transaction Flexfield. To define the Transaction Flexfield at the header-level, query 'Invoice Transaction Flexfield' and enter the context and segments associated with this Transaction Flexfield. All segments in the line level transaction flexfield that refer to header information must also exist in the header level transaction flexfield. For example if you define a line-level Transaction Flexfield with 4 segments and only the last 2 segments refer to line-level information, define the header Transaction Flexfield using the first two segments. You must define both the line-level and header-level Transaction Flexfield.
If you do not create Reference and Link-to transaction flexfields, then Receivables will use your Line Transaction Flexfield structure to link and reference different lines. You do not have to define separate Reference and Link-to transactions in this case.
However, if you are planning to create a customized form to enter interface data which will display the Reference and Link-to Transaction Flexfields, then you must define Transaction Flexfields in the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window. These flexfields must have the same flexfield structures as the line-level Transaction Flexfield. See: Transaction Flexfields.
Territory Flexfield
If you use territories, you should create your territory flexfield structure before using AutoInvoice. See: Territory Flexfield, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Line Ordering Rules
Define ordering rules used by AutoInvoice to determine how to order your transaction lines. AutoInvoice randomly orders lines on your transaction if you do not define line ordering rules. See: AutoInvoice Line Ordering Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Grouping Rules
Define additional grouping rules or update the default grouping rule provided by Receivables. AutoInvoice uses grouping rules to determine how to create your transactions. Grouping rules are required if you use AutoInvoice.
AutoInvoice uses the following hierarchy when determining the grouping rule to use:
-
Transaction batch source
-
Customer site level
-
Customer profile level
-
System Options window
See: Grouping Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide and Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions.
Important: To be able to use the information that you pass in your header Transaction Flexfield, you must group by the segments that make up your header Transaction Flexfield.
AutoAccounting
You must set up Receivables' AutoAccounting feature before you run AutoInvoice. AutoAccounting determines default revenue, receivable, freight, tax, unbilled, unearned, and suspense accounts for your invoices. See: AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Salesperson
Add salespersons to Receivables if your original system uses salespersons that are not yet defined in Receivables. See: Salespersons, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
AR: AutoInvoice Gather Statistics Profile Option
When you submit the AutoInvoice Master program, AutoInvoice can first analyze the interface tables (RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL, RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL, and RA_INTERFACE SALESCREDITS_ALL) and automatically gather statistics to determine how best to execute the transaction import.
If you want AutoInvoice to automatically gather statistics, then set this profile option to Yes.
Note: If the number of records to be imported and the number of worker processes are approximately the same as the previous submission of AutoInvoice, then you may set the profile option to No and skip this analysis.
Automatic Receipt Handling Batch Source Setting
If you want AutoInvoice to automatically evaluate imported credits for receipt handling, then set the Receipt Handling for Credits option on the AutoInvoice transaction batch source according to your enterprise's credit policies.
See: Transaction Batch Sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Related Topics
Importing Data From Your Feeder System
Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions
Importing Data From Your Feeder System
Your on-site personnel or Oracle consultant must first write a custom feeder program that transfers transaction data from your original system into Receivables AutoInvoice Interface tables. Your feeder program must convert data from your original system into a standard data format that AutoInvoice can read. AutoInvoice can then convert your imported data into Receivables invoices, credit memos, on-account credits, and debit memos.
Writing a Feeder Program
The type of environment from which you want to transfer your data determines the type of feeder program you need to write. For example, you can use SQL*Loader, SQL*Report, PL/SQL, or Pro*C to write a feeder program to transfer transaction data from a non-Oracle system. Or, you can write a conversion program to transfer historical data from your previous accounting system.
Selecting an Import Utility
SQL*Loader and SQL*Report are powerful and easy-to-use tools that should be able to accommodate all of your import needs. However, depending on the complexity of your import program, you may also want to use Oracle's Pro* language products such as Pro*C, Pro*Cobol, and Pro*Fortran to write the program.
Understanding the Interface Tables
Receivables uses the following tables to temporarily store the data you transfer from other systems:
-
AR_INTERFACE_CONTS_ALL
-
RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL
-
RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL
-
RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL
AutoInvoice uses a fifth table, RA_INTERFACE_ERRORS_ALL, to store information about interface data that failed validation. For a detailed description of these tables, see: AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
Related Topics
Passing Receipt Methods and Customer Bank Accounts
AutoInvoice Validation
AutoInvoice validates your data for compatibility with Receivables. It ensures that the columns in Receivables' Interface tables reference the appropriate values and columns in Receivables. To learn more about the validation AutoInvoice performs for each column in the AutoInvoice tables, see: AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
Existence
For some columns, AutoInvoice ensures that the values are already defined in Receivables or in other Oracle applications.
Batch Sources
You use transaction batch sources that have a type of 'Imported' when importing transactions into Receivables. See: Transaction Batch Sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
You do not have to pass values for all of the fields that are referenced in the Transaction Sources window into Receivables. If you do not want AutoInvoice to pass certain data into Receivables for a specific batch source, then you can set the related field to 'None' in the Transaction Sources window.
Note: Even if you set a field on a batch source to 'None' because you do not want to import this information into Receivables tables, AutoInvoice might still validate the data and could reject the containing line(s) if that data is invalid.
Uniqueness
AutoInvoice ensures that the invoice number you supply is unique within a given batch source and the document number you supply is unique within the associated sequence type.
AutoInvoice also ensures that the Transaction Flexfield you supply is unique. For more information, refer to Transaction Flexfields.
Precision
Precision is the number of digits to the right of the decimal point that are used in regular currency transactions. AutoInvoice ensures that the amount and the accounted amount you supply have the correct precision for a given currency.
Cross Validation
AutoInvoice ensures that certain column values agree with each other. These values can be within an interface table or multiple interface tables.
For example, if you specify in your batch source that you do not want to use accounting rules, AutoInvoice ignores any values you supply for invoicing rule, accounting rule, and accounting rule duration. However, if you do import transactions that use accounting rules, AutoInvoice requires that these transactions also include an invoicing rule.
Validation for Lines With Rules
Besides validating dates, AutoInvoice also validates and rejects lines if:
-
The accounting rule has overlapping periods
-
All of the accounting periods do not exist for the duration of your accounting rule
For more information, see: Importing Invoices with Rules.
Create Transactions with Invalid or Incorrect Data
You can specify whether AutoInvoice will reject or partially create transactions that have an invalid line, invalid tax rate, or a GL date in a closed period. For example, you import an invoice with three invoice lines and one of the lines is invalid. If the value of the Invalid Line option for this batch source is set to 'Create Invoice,' AutoInvoice will create the invoice with only the two valid lines. You can then use the Transaction window to add the line that was rejected. If Invalid Line is set to 'Reject Invoice,' AutoInvoice will not import this transaction or any of its lines into the interface tables. Transactions that fail validation appear in the AutoInvoice Validation report.
The values you enter in the AutoInvoice Processing Options tabbed region of the Transaction Sources window determine how AutoInvoice will process transactions with invalid data. See: Transaction Batch Sources, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Validations for Lines with Receipt Distributions
AutoInvoice validates lines with receipt distributions and performs the following actions:
-
Merges lines with separate receipt distributions into a transaction with a single receipt distribution, provided the lines share the same account (CODE_COMBINATION_ID).
-
Rejects a transaction, if the receipt distributions of its lines have different accounts.
-
Separates a transaction into two or more transactions when the receipt distributions of its lines have different accounts, if you added Receivables account (CODE_COMBINATION_ID) as an optional grouping column for the grouping rule for the batch source.
Credit Memos Against Paid Invoices
AutoInvoice validates credit memos by reviewing the automatic receipt handling setting on the submission's transaction batch source.
If you enabled automatic receipt handling, then AutoInvoice automatically reviews each credit memo and associated invoice to determine its eligibility for receipt handling. See: Automatic Receipt Handling for Credits.
If you did not enable automatic receipt handling, then AutoInvoice evaluates credit memos using standard invoice validation:
-
If the invoice's transaction type allows natural application only, then AutoInvoice rejects the credit memo.
You must unapply the receipt from the credited invoice and rerun AutoInvoice to successfully import the credit memo.
-
If the invoice's transaction type allows overapplication, then AutoInvoice imports the credit memo and the invoice is overapplied until you unapply the receipt from the credited invoice.
See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Related Topics
Using AutoInvoice
AutoInvoice Purge Program
You can choose whether to delete data from the AutoInvoice Interface tables once it has been validated and transferred into Receivables. If you want AutoInvoice to automatically delete the data, check the Purge Interface Tables box in the System Options window. If you want to delete data from the AutoInvoice Interface tables later, do not check this box. You can choose to run the AutoInvoice Purge program at any time from the Run AutoInvoice window.
The AutoInvoice Purge program and the Purge Interface Tables system option only delete data from the interface tables that has been validated and successfully transferred into Receivables.
Calculating Tax
AutoInvoice provides the functionality you need to meet your sales tax and other taxing requirements, such as Value Added Tax (VAT). You can either pass tax code lines, tax exempt lines or have AutoInvoice automatically determine your tax rates using the hierarchy determined by the tax calculation flow charts. If AutoInvoice determines your tax rates, it will take into account any customer or item tax exemptions or item tax exceptions.
Transactions in Closed Accounting Periods
Use AutoInvoice to pass transactions in closed accounting periods. Receivables automatically uses the first day of the next open accounting period as your default date to determine your accounting distributions. See: Adjusting General Ledger Dates.
Creating Transactions
AutoInvoice creates invoices, debit memos, credit memos and on-account credits using the grouping and invoice line ordering rules you specify. AutoInvoice verifies that your data is valid before it creates transactions in Receivables.
Deriving Invoice and Accounting Dates
AutoInvoice lets you choose how you want to determine invoice and accounting dates for your transactions. Your feeder program can either load these dates directly into the interface tables or, if you leave the date fields empty, Receivables will determine your invoice and accounting dates using a straightforward algorithm. See: Determining Dates.
Invoices Against Commitments
AutoInvoice lets you create invoices against commitments in the same way you would with a manually entered invoice.
Note: Note: An invoice can be attached to only one commitment. Upon import, if an invoice has multiple lines where different commitment line values are provided in the REFERENCE_LINE_ID column, then Receivables creates one or more invoices, accordingly.
Tip: If an invoice has multiple lines but a commitment's balance covers only a partial invoice amount, then Receivables can still create a single invoice upon import. To accomplish this, all lines must have the same commitment line value but, using the PROMISED_COMMITMENT_AMOUNT column, some invoice lines will deplete the commitment's remaining balance while other invoice lines will have an allocated commitment value of zero. See:
-
AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
Running AutoInvoice
You submit AutoInvoice using the Run AutoInvoice window. If AutoInvoice converts your transaction data into the required data format, and all of the data passes validation in Receivables, then you can run AutoInvoice in one step.
However, if your feeder program loads the interface tables with invalid data, AutoInvoice informs you of the validation errors in both the AutoInvoice Execution and AutoInvoice Validation reports. In this case, you must correct any errors by modifying data in the interface tables and then rerun AutoInvoice on the corrected data.
See: Running AutoInvoice.
Execution Phases
AutoInvoice can be divided into three major phases: pre-grouping, grouping, and transfer.
In the pre-grouping phase, AutoInvoice validates all of the line-level data as well as any other data that is not dependent upon successful grouping. Some examples include validating that a transaction type is valid and validating that only one freight account exists for each freight line passed.
In the grouping phase, AutoInvoice groups lines based on the grouping rules and validates header-level data that is dependent on how your lines are grouped. Some examples include validating the overapplication rules specified for your batch source and validating that the general ledger date of an invoice against a commitment is not before the general ledger date of the commitment. If AutoInvoice incorrectly groups transactions, check the grouping rule that you are using, paying particular attention to the mandatory and optional attributes that are included in this rule. For more information, see Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions.
In the transfer phase, AutoInvoice validates information that exists in Receivables tables, such as tax defaulting and AutoAccounting data.
Reviewing the AutoInvoice Execution and Validation Reports
Use the AutoInvoice Execution Report to review summary information about your transactions. AutoInvoice automatically creates this report each time you run AutoInvoice. The AutoInvoice Execution report lists the total number of transaction, sales credit, and distribution lines that were successfully imported, as well as those that failed. See: AutoInvoice Validation.
The AutoInvoice Execution report also includes a detailed list of the receipts that were automatically processed. This list includes receipts that were processed according to policy, as well as receipts that were put on account because a refund was not possible. See: Automated Receipt Handling for Credits.
Note: It is possible to have the number of Successfully Processed lines be less than the number Selected and have no lines that Failed Validation. This will occur when a credit memo for an invoice and the invoice itself are submitted in the same batch and the credit memo is selected first. Since the invoice has not been processed yet, the credit memo will go unprocessed during this import, but will not fail. The unprocessed credit memo remains in the interface table and will be processed the next time you submit AutoInvoice. In this example, the Interface Lines section of the execution report would appear as follows:
-
Selected: 9
-
Successfully Processed: 8
-
Failed Validation: 0
AutoInvoice also automatically generates the AutoInvoice Validation Report if you have records that failed validation. This report displays all error messages associated with each transaction, sales credit, and distribution line that failed validation. The report also includes the invoices that Receivables could not select for receipt handling, and why.
You can use this information to identify which records need to be modified. Refer to the next section, Correcting Errors.
For each line, AutoInvoice can only display error messages for the phase the line is in when it fails. For example, if a line fails validation in the pre-grouping phase, AutoInvoice will display all error messages encountered in the pre-grouping phase. Likewise, if a line is already in the transfer phase when it fails, AutoInvoice will display all error messages encountered in the transfer phase.
If you encounter sales credit or distribution errors, AutoInvoice prints a separate section for these errors. These sections will display below each line.
Note that transaction lines that fail with invalid sales group IDs are also reported in this section.
Lastly, a Summary of Transactions Rejected section is printed at the end of the report. See: AutoInvoice Reports.
Correcting Errors
Use the AutoInvoice Validation Report and the Interface Exceptions window to review records that failed AutoInvoice validation. Depending on the error, you may need to make changes in Receivables, your feeder program, or the imported records in the interface tables. For example, if you receive an error message stating that the salesperson specified for an invoice does not exist in Receivables, you can either add the salesperson to Receivables or modify your feeder program to only transfer salespersons that Receivables recognizes. Use the Interface Lines window to modify invalid records in the interface tables. See: Correcting AutoInvoice Exceptions.
Transaction Flexfields
AutoInvoice provides you with a way to uniquely identify each transaction you import into Receivables. Use Transaction Flexfields to capture information that will help you trace transactions from Receivables back to the systems from which they originated.
AutoInvoice ensures that each Transaction Flexfield is unique so you can refer to previously processed transactions. For example, if you are importing a credit memo, you would use the Transaction Flexfield of the credit memo to refer to the transaction being credited. You can also use Transaction Flexfields to link transaction lines to other transaction lines and to tax and freight lines. See: Transaction Flexfields.
Related Topics
Passing Receipt Methods and Customer Bank Accounts
Importing Transaction Information Using AutoInvoice
Passing Receipt Methods and Customer Bank Accounts
All references to parent customer information in this section are only applicable if the bill-to customer has only one parent and the relationship is not reciprocal. For example, if the bill-to customer for the line has more than one parent, lines 1 & 2 below will not apply.
Receipt Methods
Regardless if you are passing manual or automatic receipt methods, AutoInvoice validates that the receipt method belongs to the bill-to customer/site or the parent of the bill-to customer/site, if it has one. Additionally, the receipt method must have at least one bank account in the currency of the transaction or its Receipts Multi-Currency flag must be set to Yes.
If you do not pass a receipt method, AutoInvoice defaults one using the following hierarchy:
-
Primary receipt method assigned to the primary site for the parent
-
Primary receipt method assigned to the parent customer
-
Primary receipt method assigned to the bill-to site for the line
-
Primary receipt method assigned to the bill-to customer for the line
Customer Bank Accounts
If you are passing a customer bank account and the receipt method associated with the transaction is automatic, AutoInvoice validates that the customer bank account belongs to one of the following, otherwise the line is rejected:
-
Bank account assigned to the primary site for the parent
-
Bank account assigned to the parent customer
-
Bank account assigned to the bill-to site for the line
-
Bank account assigned to the bill-to customer for the line
If you do not pass a customer bank account and the receipt method associated with the transaction is automatic, AutoInvoice defaults one using the following hierarchy:
-
Primary bank account assigned to the primary site for the parent
-
Primary bank account assigned to the parent customer
-
Primary bank account assigned to the bill-to site for the line
-
Primary bank account assigned to the bill-to customer for the line
If AutoInvoice is unable to default a customer bank account, the line is rejected.
AutoInvoice uses the customer bank account to determine whether the paying customer is the parent or the bill-to customer. If the paying customer is the bill-to customer, the paying site is the bill-to site. If the paying customer is the parent, the paying site is the primary bill-to site of the parent. Customer bank accounts are not used for manual receipt methods.
Related Topics
Receipt Methods, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Importing Freight Lines
AutoInvoice lets you pass freight lines as individual transactions or as references to other transactions. The columns LINK_TO_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and LINK_TO_LINE_CONTEXT in RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL determine whether a freight line will become an individual freight-only transaction or part of another transaction.
To pass a freight line that refers to another transaction line, enter the Line Transaction Flexfield of the transaction to which you want this freight line to refer. To pass freight lines, RA_INTERFACE_LINES.LINE_TYPE must be set to 'FREIGHT'.
To pass a freight-only line, enter a Line Transaction Flexfield that refers to a 'dummy' line. This 'dummy' line must have a value in RA_INTERFACE_LINES.MEMO_LINE_ID or RA_INTERFACE_LINES.MEMO_LINE_NAME, and the memo line must have AR_MEMO_LINES.LINE_TYPE = 'FREIGHT'. In addition, the Quantity, Unit Price, and Amount fields for this line must be null or zero.
Using AutoAccounting for Freight
If AutoAccounting for Freight is based on Standard Lines, you will not be able to import invoices with header level freight. All freight lines in this case must be associated with a standard line for AutoAccounting to determine the account. If the transaction has a line type of "LINE" with an inventory item of freight ("FRT"), AutoAccounting will use the accounting rules for the freight type account rather than the revenue type account.
Importing Multiple Header Freight Lines
AutoInvoice ensures that there is at most one freight line for an imported invoice, or at most one freight line per transaction line, but not both. If multiple header freight lines applied to one invoice have been imported, AutoInvoice will validate that all of the freight lines apply to the same freight account and consolidate them to one line. This consolidated freight line will be the only freight line for this invoice that is passed to the core receivables tables. If all of the freight lines do not apply to the same freight account, AutoInvoice will reject the invoice.
Audit Trail for Consolidated Freight Lines
The log file generated by AutoInvoice will list the following freight attributes for auditing purposes:
-
customer_trx_id
-
interface_line_id of the freight line chosen for consolidation
-
sum of the freight amounts
Calculating Tax on Freight
If you want to calculate tax on freight for orders created in Oracle Order Management, set the profile option Tax: Inventory Item for Freight to Yes. If you do this, Order Management creates a line item of type 'Line' on the invoice for the freight amount (in the Ship Confirm window) so that it can be taxed. When you print the invoice from Receivables, the tax amount appears as the last invoice line with the description 'Freight.'
If Tax: Inventory Item for Freight is set to Yes, also set the profile option Tax: Invoice Freight as Revenue to Yes. This profile option enables you to control the rate of tax applied to freight. To do this, define an inventory item of User Type "Freight" and set this option to your new inventory item. When Oracle Order Management identifies this inventory item, it uses the tax code assigned to it or any item exceptions to control the applicable tax rates and accounting for the freight service. On the printed invoice, Receivables derives the description of the freight line from the inventory item that you defined, rather than the default description 'Freight'.
Related Topics
AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Freight Carriers, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Importing Tax Lines
AutoInvoice gives you flexibility to handle all of your taxing needs. If your tax method is VAT, you can either pass tax lines through the AutoInvoice interface tables or have Receivables automatically calculate your tax lines for you. If your tax method is Sales Tax, Receivables will always calculate tax for you. However, you can choose to pass additional tax lines with tax codes of type VAT, Sales Tax, or Location.
Passing Tax Lines Through AutoInvoice
AutoInvoice lets you pass tax lines as individual transactions or as references to other transactions. If you are passing tax lines, you can only pass tax lines associated with tax codes of type VAT, Sales Tax, or Location. The RA_INTERFACE_LINES.LINK_TO_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and RA_INTERFACE_LINES.LINK_TO_LINE_CONTEXT columns will determine whether a tax line will become an individual tax only transaction or part of another transaction.
To pass a tax line that refers to another transaction line, enter the Line Transaction Flexfield of the transaction to which you want this tax line to refer. To pass tax lines, RA_INTERFACE_LINES.LINE_TYPE must be set to 'TAX.'
If you want to pass a tax-only line, enter a Line Transaction Flexfield that refers to a 'dummy' line. This 'dummy' line must have a value in RA_INTERFACE_LINES.MEMO_LINE_ID or RA_INTERFACE_LINES.MEMO_LINE_NAME and the memo line must have AR_MEMO_LINES.LINE_TYPE = 'TAX'. In addition, the Quantity, Unit Price, and Amount fields for this line must be null or zero.
Calculating Tax
Certain criteria must be met before AutoInvoice will calculate tax.
The table below shows, for each desired result, what tax information needs to be passed to the interface tables.
| Desired Result | Line Type | Tax Code | Tax Rate/Tax Amount | Tax Exempt Flag | Tax Exempt Number | Tax Exempt Reason Code or Meaning | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receivables should calculate the tax based on the standard tax logic. | Line - No Tax line associated with this line | NULL | NULL | NULL or 'S' | NULL | NULL or 'S' | If you have not passed any tax lines with the invoice lines, and the tax exempt flag is NULL or 'S', Receivables will calculate tax for you. |
| You want Receivables to calculate Sales tax, but want to pass additional tax codes. | Tax | Of type VAT or Sales Tax and must be ad hoc. Or, of type Location, but such tax lines are only allowed when importing invoices from Oracle Lease Management. | Must pass either the tax rate or amount | NULL or 'S' | NULL | NULL | The invoice line will have 2 tax lines. The first will be a location-based tax calculated by Receivables. The second will be the tax line passed through AutoInvoice. |
| You want to exempt the invoice line from any taxes and your system option 'Use Customer Exemptions' is set to Yes. | Line | NULL | NULL | 'E' | Pass tax exemption number | Pass reason forexemption | If the tax exemption number does not exist on file, Receivables will create an unapproved exemption. There will be no tax calculated on this invoice line. |
| You want to enforce tax on an invoice line, even if any exemptions exist on the file. | Line | NULL | NULL | 'R' | NULL | NULL | Receivables calculates tax as per its standard logic, ignoring any exemptions. |
Sales Tax
Sales tax is calculated by AutoInvoice using the tax rates associated with your shipping address. Sales tax will only be calculated for shipping addresses which are in the country defined in the Default Country field of the System Options window. Receivables lets you pass exception rates and exemptions for customers or items. Sales Tax lines cannot be passed into AutoInvoice tables.
AutoInvoice uses the following hierarchy when deriving the tax rate:
-
Tax code assigned to ship-to/bill-to address
-
Tax code defined at the customer level
-
Tax code defined at the item level
-
Tax code defined in the System Options window (if your tax method is 'VAT')
Other Tax Codes
If you do not want AutoInvoice to calculate tax based on location, you can pass tax codes through lines with line_type = 'Tax'. Tax codes can be of type VAT or Sales Tax and must be ad hoc. Additionally, tax codes can be of type Location, but such tax lines are only allowed when importing invoices from Oracle Lease Management.
If the tax code is not ad hoc, you must set the Invalid Tax Rate field in the AutoInvoice Options tabbed region of the Transaction Sources window to Correct. You must also pass either a tax rate or amount with the code. Any exemptions must be calculated into the rate or amount.
Related Topics
Importing Transaction Information Using AutoInvoice
Importing Invoices with Rules
Use AutoInvoice to import invoices with accounting and invoicing rules if your accounting method is 'Accrual'. AutoInvoice rejects all invoices with rules if your accounting method is 'Cash Basis' because with Cash Basis Accounting, you only recognize revenue when payment is received. Invoices with rules are therefore not applicable for the Cash Basis method, as they are designed to distribute revenue over several periods before receipt of payment.
Accounting rules determine the accounting period(s) in which the revenue distributions for an invoice line are recorded. Invoicing rules determine the accounting period in which the receivable amount is recorded.
Receivables provides two invoicing rules: Bill in Advance and Bill in Arrears. You supply AutoInvoice with the model account which contains the accounting distributions and the percent allocated to each account. You must run the Revenue Recognition Program before Receivables can create your accounting entries. See the example below for the effects of using accounting and invoicing rules through AutoInvoice. Assume that you have already run the Revenue Recognition Program for each accounting period.
Example
Invoice #101
Transaction Amount: $300
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.QUANTITY (3)*
RA_INTERFACE_LINES.UNIT_SELLING_PRICE ($100))
Accounting Rule: Monthly
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID)
Invoicing Rule: Bill in Advance
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.INVOICING_RULE_ID)
Duration (Number of Periods): 3
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION)
Rule Start Date: 1/1/XX
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.RULE_START_DATE)
Payment Term: Net 30
(RA_INTERFACE_LINES.TERM_ID)
Receivables creates the following accounting entries as illustrated in this table:
| Period | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1/XX | Accounts Receivable | 300 | |
| 1/1/XX | Unearned Revenue | 200 | |
| 1/1/XX | Revenue | 100 | |
| 2/1/XX | Unearned Revenue | 100 | |
| 2/1/XX | Revenue | 100 | |
| 3/1/XX | Unearned Revenue | 100 | |
| 3/1/XX | Revenue | 100 |
In the above example, the transaction date for this invoice is 1/1/XX, with a payment due date of 1/31/XX. If we had chosen an invoicing rule of 'Bill in Arrears', the transaction date in the above example would have been 3/1/XX with a payment due date of 3/31/XX.
For a description of how Receivables determines GL dates when importing invoices with rules, see Determining Dates.
Validation for Lines With Rules
Besides validating dates, AutoInvoice also validates and rejects lines if:
-
The accounting rule has overlapping periods
-
All of the accounting periods do not exist for the duration of your accounting rule
Related Topics
Importing Credit Memos
You can use AutoInvoice to import and validate transaction data from a legacy system to create credit memos in Receivables. Receivables lets you import:
-
On-account credit memos (credit memos that are not linked to an invoice)
-
Credit memos against invoices with rules
-
Credit memos against invoices without rules
Note: You cannot apply a credit memo to a chargeback using AutoInvoice.
You can import credit memos against invoices that were already paid. When importing credit memos against paid transactions, AutoInvoice can evaluate these credits for automatic receipt handling. See: Automated Receipt Handling for Credits.
However, if an invoice's transaction type does not allow overapplication and the Receipt Handling for Credits feature is not enabled, then AutoInvoice will leave the related credit memo in the interface tables until you unapply the invoice from the receipt. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide and AutoInvoice Validation.
Use the AutoInvoice table and column descriptions to determine the fields that are mandatory or optional when importing transaction data into Receivables. Pay particular attention to those columns in the interface tables that require values. See: AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
For more information, see: Transaction Flexfields.
On-Account Credit Memos
To create an on-account credit memo (i.e. not linked to an invoice), do not populate the REFERENCE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15, REFERENCE_LINE_CONTEXT, or REFERENCE_LINE_ID columns on the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL table.
Credit Memos against Transactions
You can link a credit memo to an invoice in one of two ways:
-
Populate the REFERENCE_LINE_ID column on the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL table with the CUSTOMER_TRX_LINE_ID of the invoice, or
-
On the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL table, populate the REFERENCE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 columns with the INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 columns of the invoice. The INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 columns are stored on the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL table.
In addition, you must populate the REFERENCE_LINE_CONTEXT column with the INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT column of the invoice. The INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT column is stored on the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL table.
When you import credit memos against transactions, AutoInvoice ensures that the Open Receivables flag of the credit memo being imported matches the Open Receivables flag of the transaction it is crediting.
Credit Memos Against Invoices With Rules
When you import credit memos against invoices with rules, AutoInvoice uses the method you entered in RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL.CREDIT_METHOD_FOR_ACCT_RULE to determine how to reverse the accounting entries created for the original invoice. You can either enter 'LIFO', 'PRORATE', or 'UNIT'. If you choose 'LIFO', AutoInvoice reverses the accounting entries beginning with the last period. If you choose 'PRORATE', AutoInvoice prorates the credit amount across all accounting periods. If you choose 'UNIT', AutoInvoice lets you credit specific quantities, starting with the period specified in the column RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL.LAST_PERIOD_TO_CREDIT and working backwards.
Note: Note: If you choose 'UNIT', then AutoInvoice rejects the credit memo if the credit quantity exceeds the quantity on the target invoice line.
Credit Memos Against Invoices Without Rules
When you import credit memos against invoices without rules, AutoInvoice first uses the general ledger date in the interface table as the general ledger date of the credit memo. If you do not pass a general ledger date, AutoInvoice uses the default date you specified in the Run AutoInvoice window. The credit memo lines must always have the same general ledger date as the credit memo.
The credit memo general ledger date must be equal to or greater than the general ledger date of the invoice you are crediting. Also, the credit memo general ledger date must be in an 'Open' or 'Future' period.
Credit memos against invoices without rules that are imported through AutoInvoice behave the same as those entered manually through the Credit Memos window. For example, you pass the amount you want to credit and Receivables automatically creates all the accounting reversal entries. Receivables also automatically reverses the sales and non-revenue credit assigned to your salespeople.
Credit Memos Against Tax and Freight Lines
When you import credit memos, AutoInvoice ensures that you do not overapply your tax and freight lines.
Related Topics
Late Charges
AutoInvoice processes debit memos with late charge lines and credit memos that are against debit memos with late charge lines.
If LINE_TYPE = 'CHARGES', AutoInvoice does not calculate tax, freight, or sales credits on this line. Also, if you are passing your late charges distribution in RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL, ACCOUNT_CLASS must be 'CHARGES.'
In order for AutoInvoice to pass a late charge line, do not enter a value for the following columns in RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL:
-
INVOICING_RULE_ID
-
INVOICING_RULE_NAME
-
ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID
-
ACCOUNTING_RULE_NAME
-
ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION
-
RULE_START_DATE
-
UOM_CODE
-
UOM_NAME
-
AMOUNT
If you are passing a debit memo late charges line RA_INTERFACE_LINES.QUANTITY must = 1. If you are passing a credit memo against a debit memo with a late charges line RA_INTERFACE_LINES.QUANTITY must = -1 or 1.
Related Topics
Account Assignments
AutoInvoice lets you determine how to assign general ledger accounts to transactions you import through AutoInvoice. You can either pass your accounts through the AutoInvoice Interface tables or have AutoAccounting determine them. You can even pass some of your accounts and have AutoAccounting determine the rest.
Passing Account Information
If you choose to pass your accounts, AutoInvoice looks at the batch source to determine whether to expect Accounting Flexfield segment values or IDs. (You specify this information in the Transaction Sources window, Accounting Information tabbed region.)
If you pass segment values, you must assign values to RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS.SEGMENT1-30. Only assign values to enabled segments. For example, if you enable six Accounting Flexfield segments, you must assign values in SEGMENT1-6.
If you pass IDs, you must enter the code combination ID of the Accounting Flexfield in RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL. CODE_COMBINATION_ID.
Important: If you want the option of AutoInvoice dynamically inserting code combinations, you must pass segments.
If using Event-Based Revenue Management to automatically defer or recognize revenue for imported transactions, and you want to pass IDs to Receivables for those transaction lines, then ensure the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL.OVERRIDE_AUTO_ACCOUNTING_FLAG is Y.
Using AutoAccounting
If you want AutoAccounting to determine your general ledger accounts you must not enter values in RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL. AutoInvoice will determine all of your accounts using information you pass for each line. Use the Automatic Accounting window to define your revenue, receivables, tax, freight, clearing, unbilled receivable, and unearned revenue accounts.
Note: If AutoAccounting for Freight is based on Standard Lines, you will not be able to import invoices with header level freight. If the transaction has a line type of "LINE" with an inventory item of freight "FRT," AutoAccounting will use the accounting rules for the freight type account rather than the revenue type account.
Note: If AutoAccounting is set up to derive its segments from Salesreps, then you must pass rows in RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL for each invoice line in RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL. This is true even if your system option Require Salesreps is set to No.
Related Topics
AutoAccounting, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Transaction Flexfields
Transaction flexfields are descriptive flexfields that AutoInvoice uses to identify transactions and transaction lines. Receivables lets you determine how you want to build your transaction flexfield structure and what information you want to capture.
There are four types of transaction flexfields:
-
Line Transaction Flexfield
-
Reference Transaction Flexfield
-
Link-To Transaction Flexfield
-
Invoice Transaction Flexfield
You must define the Line Transaction Flexfield if you use AutoInvoice. You can use the Line Transaction Flexfield to reference and link to other lines because the Line Transaction Flexfield is unique for each transaction line. AutoInvoice always uses the Line Transaction Flexfield structure for both the Link-to and Reference information when importing invoices. You must explicitly define the Link-to, Reference, and Invoice Transaction Flexfield structures only if this information is to be displayed on a custom window.
Receivables gives you the option of displaying Invoice Transaction Flexfield information in the Reference column of invoice lists of values. Use the Reference Field Default Value field in the Transaction Sources window to select the Invoice Transaction Flexfield segment that you want to display. For example, if you want to be able to reference the order number for imported invoices when using an invoice list of values, you must assign the transaction flexfield segment that holds the order number in the Reference Field Default Value field in the Transaction Sources window. The order number will now display in the Reference column of invoice lists of values.
Line Transaction Flexfield
Use columns INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT to define the Line Transaction Flexfield. Line Transaction Flexfields are unique for each record in the interface table and therefore can be used as record identifiers.
The context that you specify in the INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT column of the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL table determines what information AutoInvoice places in the INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 columns. Oracle Receivables provides contexts for other Oracle applications that you use with AutoInvoice, for example Order Management. If you import transactions with AutoInvoice from a legacy system, you can define a new context for the Line Transaction Flexfield to distinguish these transactions from transactions that originated in Oracle applications.
Reference Transaction Flexfield
Reference Transaction Flexfields have the same structure as the Line Transaction Flexfields.
Reference Transaction Flexfields are used to apply a credit memo to an invoice or associate an invoice to a specific commitment. For example, to refer a credit memo to a specific invoice, use the REFERENCE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and REFERENCE_LINE_CONTEXT columns of the credit memo to enter the Line Transaction Flexfield of the invoice. To refer an invoice to a specific commitment, use the REFERENCE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and REFERENCE_LINE_CONTEXT columns of the invoice to enter the Line Transaction Flexfield of the commitment.
Link-To Transaction Flexfield
Link-To Transaction Flexfields also have the same structure as the Line Transaction Flexfield.
Use Link-To Transaction Flexfields to link transaction lines together in the interface table. For example, you might want to import tax and freight charges that are associated with specific transaction lines. If you want to associate a specific tax line with a specific transaction line, use the LINK_TO_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15 and LINK_TO_LINE_CONTEXT columns of the tax line to enter the Line Transaction Flexfield of the invoice.
Invoice Transaction Flexfields
Create a new flexfield with a similar structure as the Line Transaction Flexfield, but only include header level segments. For example, if the Line Transaction Flexfield structure has four segments and the last two segments contain line level information, define your Invoice Transaction Flexfield using the first two segments only. Segments included in the Invoice Transaction Flexfield should be included in the AutoInvoice grouping rules.
Transaction Flexfields: An example
This example illustrates how records described in the Line Transaction Flexfield are linked in the interface table using the Link-To or the Reference Transaction Flexfield columns.
Consider an invoice against a commitment with four records: two Line records, one header Freight record, and one Tax record. The transaction type for records of an invoice is INV.
The table below shows how the four invoice records are represented in the interface table. There are two segments enabled for the Line Transaction Flexfield OM (Order Management) context. The combination of context plus the two segments is unique for each record. Because the invoice is against an existing commitment, the Reference_line_id (Reference ID) column of the two Line records is populated with the unique identifier (customer_trx_line_id) of the commitment:
In this table, Line TF means Line Transaction Flexfield, Link-To TF means Link-To Transaction Flexfield, and Ref TF means Reference Transaction Flexfield. Also, Cont. means Context, Seg. means Segment, and Ref means Reference.
| Line Type | Line TF Cont. | Line TF Seg. 1 | Line TF Seg. 2 | Link-To TF Cont. | Link-To TF Seg. 1 | Link-To TF Seg. 2 | Ref TF Cont. | Ref TF Seg. 1 | Ref TF Seg. 2 | Ref ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | OM | A | 1 | C1 | ||||||
| Line | OM | A | 2 | C1 | ||||||
| Freight | OM | A | T1 | |||||||
| Tax | OM | A | 3 | OM | A | 1 |
Note: You can also link the invoice to the commitment using the Reference Transaction Flexfield.
Note: Records with different contexts can be grouped together into one invoice. See Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions.
The Tax record is linked to the first line record by the Link-To Transaction Flexfield. Since the Freight record is at the header level, it is not linked to any line record.
Now consider a credit memo that credits the Freight and the first Line of the previous invoice. The transaction type for credit memos is CM. The table below shows how the Reference Transaction Flexfield is used to link the credit memo to the invoice.
In this table, Line TF means Line Transaction Flexfield, Link-To TF means Link-To Transaction Flexfield, and Ref TF means Reference Transaction Flexfield. Also, Cont. means Context, Seg. means Segment, and Ref means Reference.
| Line Type | Line TF Cont. | Line TF Seg. 1 | Line TF Seg. 2 | Link-To TF Cont. | Link-To TF Seg. 1 | Link-To TF Seg. 2 | Ref TF Cont. | Ref TF Seg. 1 | Ref TF Seg. 2 | Ref ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freight | OM | A | T2 | OM | A | T1 | ||||
| Line | OM | A | T3 | OM | A | 1 |
Note: You can also link the credit memo to the invoice using the reference_line_id (Reference ID column).
AutoInvoice assumes that all records with the transaction type CM are on-account credits, as long as there are no values in the Reference Transaction Flexfield or the reference_line_id (Reference ID column). The table below shows how an on-account credit is represented in the Line Transaction Flexfield:
In this table, Line TF means Line Transaction Flexfield, Link-To TF means Link-To Transaction Flexfield, and Ref TF means Reference Transaction Flexfield. Also, Cont. means Context, Seg. means Segment, and Ref means Reference.
| Line Type | Line TF Cont. | Line TF Seg. 1 | Line TF Seg. 2 | Link-To TF Cont. | Link-To TF Seg. 1 | Link-To TF Seg. 2 | Ref TF Cont. | Ref TF Seg. 1 | Ref TF Seg. 2 | Ref ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | OM | B | 1 |
Indexing Transaction Flexfields
We suggest that you create indexes on your Transaction Flexfield columns if you want to query transaction flexfield information in your invoice headers and lines. Additionally, without the indexes the validation portions of the AutoInvoice program could be slow. You should define non-unique, concatenated indexes on the tables and columns that you use for your Transaction Flexfield header and line information. The tables and columns are described in this table:
| Table | Columns |
|---|---|
| RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL | interface_line_attribute1-15 |
| RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL | interface_header_ attribute1-15 |
| RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL | interface_line_attribute1-15 |
| RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL | interface_line_attribute1-15 |
| RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL | interface_line_attribute1-15 |
To determine which indexes you might need to create, navigate to the Descriptive Flexfield Segments window, then query your Line Transaction Flexfield. Note each context of this Flexfield and, for each context, note which segments are enabled using interface line attribute columns from the RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL table.
You should then create non-unique, concatenated indexes for the same interface line attribute columns in the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL and RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL tables and for the same interface header attribute columns in the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL table.
Next, if you are importing sales credit and accounting information, then create indexes for the same interface line attribute columns in the the RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL and RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL tables. Create these indexes only if you are using these tables to import sales credit and accounting information.
Indexing Transaction Flexfields: An example
For example, you have set up a Transaction Flexfield context that uses INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-3. In addition, you are populating sales credits in the RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL table.
For best performance, you should create indexes for these tables:
-
RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL
-
RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL
-
RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL
-
RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL
The indexes that you create should reference the three enabled segments. For example, an index that you create for the RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL table might look like this:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL (INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT, INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1, INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE2, INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE3);
Tip: Including the context column in your indexes is optional. However, if you use multiple active contexts (three or more), then you should include the context column as the first column in your indexes to improve performance.
Sharing Indexes
If you just have one context defined, then you only need to create one index for each table mentioned above. However, if you have multiple contexts defined, you may want to create multiple indexes per table. Use the example below to help you decide how to set up your indexes.
The table below shows a Line Transaction Flexfield with three contexts. Context1 has two attribute columns, Context2 has three attribute columns, and Context3 has two attribute columns. Context1 and Context2 share two attribute columns:
| Flexfield Context | Attribute Columns assigned to Enabled Segments |
|---|---|
| Context1 | Interface_line_attribute1 |
| Context1 | Interface_line_attribute2 |
| Context2 | Interface_line_attribute1 |
| Context2 | Interface_line_attribute2 |
| Context2 | Interface_line_attribute3 |
| Context3 | Interface_line_attribute3 |
| Context3 | Interface_line_attribute9 |
Define the combination of indexes that best meets your needs. In the example above, you can create three indexes per table, one for each context, or create just two indexes: one for Context3 and another for Context1. In the latter case, Context2 would use the same index as Context1, because Context1 and Context2 have the same first two attribute columns.
In other words, if you are using the same, or similar, attribute columns for two or more contexts, then you can optionally create a single index instead of creating an index for each context.
Use the following syntax for your Create Index Statement:
$ sqlplus <AR username>/<AR password>
SQL> CREATE [UNIQUE] INDEX index ON
{Table (column1, column2, ...)
|CLUSTER cluster}
|INITRANS n] [MAXTRANS n]
[TABLESPACE tablespace]
[STORAGE storage]
[PCTFREE n]
[NOSORT];
Related Topics
Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions
Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions
AutoInvoice uses grouping rules to determine what items to include on invoices, debit memos and credit memos. Grouping rules contain transaction attributes that must be identical for all items on the same transaction. For example, transaction number (TRX_NUMBER) is a mandatory attribute of all grouping rules. If you have two records in the interface tables with different transaction numbers, AutoInvoice will create separate transactions for each record.
Receivables provides two different types of transaction attributes: mandatory and optional. You cannot delete a mandatory attribute from any grouping rule, but you can add optional attributes to the mandatory attributes to create a new grouping rule.
Following is a list of mandatory and optional grouping rule columns:
Mandatory Attributes
AGREEMENT_ID
APPLICATION_ID
BILLING_DATE
COMMENTS
CONS_BILLING_NUMBER
CONTRACT_ID
CONVERSION_DATE
CONVERSION_RATE
CONVERSION_TYPE
CREDIT_METHOD_FOR_ACCT_RULE
CREDIT_METHOD_FOR_INSTALLMENTS
CURRENCY_CODE
CUSTOMER_BANK_ACCOUNT_ID
CUST_TRX_TYPE_ID
DEFAULT_TAXATION_COUNTRY
DOCUMENT_NUMBER
DOCUMENT_NUMBER_SEQUENCE_ID
DOCUMENT_SUB_TYPE
GL_DATE
HEADER_ATTRIBUTE1-15
HEADER_ATTRIBUTE_CATEGORY
HEADER_GDF_ATTRIBUTE1-30
HEADER_GDF_ATTR_CATEGORY
INITIAL_CUSTOMER_TRX_ID
INTERNAL_NOTES
INVOICING_RULE_ID
LEGAL_ENTITY_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_BILL_ADDRESS_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_BILL_CONTACT_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_BILL_CUSTOMER_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_SOLD_CUSTOMER_ID
PAYMENT_ATTRIBUTES
ORIG_SYSTEM_BATCH_NAME
PAYMENT_SET_ID
PREVIOUS_CUSTOMER_TRX_ID
PRIMARY_SALESREP_ID
PRINTING_OPTION
PURCHASE_ORDER
PURCHASE_ORDER_DATE
PURCHASE_ORDER_REVISION
REASON_CODE
RECEIPT_METHOD_ID
RELATED_CUSTOMER_TRX_ID
SET_OF_BOOKS_ID
TAXED_UPSTREAM_FLAG
TERM_ID
TERRITORY_ID
TRX_DATE
TRX_NUMBER
Optional Attributes
ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION
ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID
ATTRIBUTE1-15
ATTRIBUTE_CATEGORY
CODE_COMBINATION_ID
INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15
INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT
INVENTORY_ITEM_ID
LINE_GDF_ATTRIBUTE1-20
LINE_GDF_ATTR_CATEGORY
ORIG_SYSTEM_SHIP_ADDRESS_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_SHIP_CONTACT_ID
ORIG_SYSTEM_SHIP_CUSTOMER_ID
REFERENCE_LINE_ID
RULE_START_DATE
SALES_ORDER
SALES_ORDER_DATE
SALES_ORDER_LINE
SALES_ORDER_REVISION
SALES_ORDER_SOURCE
TAX_CODE
TAX_RATE
If you have transactions that fail validation, Receivables looks at the value you entered in the Invalid Line field for your transaction batch source to determine the grouping of your transactions. (This field is located in the Transaction Sources window, AutoInvoice Processing Options tabbed region.) If you entered 'Reject Invoice', AutoInvoice rejects all of the transactions that make up one invoice if any of the transactions are invalid. For example, if your grouping rule specifies that three transactions should be created as one invoice and one of the transactions has an error, AutoInvoice rejects all three transactions and does not create an invoice.
However, if you entered 'Create Invoice', AutoInvoice rejects the one invalid transaction and creates an invoice from the two remaining valid transactions.
Transaction Number Validation
Receivables validates that transaction and document numbers are unique within a batch after grouping has completed. In certain cases, AutoInvoice will create multiple invoices in the same group with the same transaction or document number. Once grouping is completed, AutoInvoice checks for duplicate transaction and document numbers and reports any lines that fail validation.
For example, two lines are imported with the same transaction number, but they have different currency codes. These lines will be split into two separate invoices during grouping due to the different currency codes. Once grouping has completed, both of the invoices will fail validation due to identical transaction numbers.
Related Topics
Grouping Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Using Line Ordering Rules
AutoInvoice uses line ordering rules to determine how to order and number each line after your transactions have been grouped into invoices, debit memos and credit memos. You can specify a line ordering rule for each grouping rule. You might want to use line ordering rules to ensure that the highest invoice line amounts are listed first. In this case, define a line ordering rule where amount is your transaction attribute and descending is your order by type.
Receivables provides the following transaction attributes that you can use in your line ordering rules (from the table RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL):
ACCOUNTING_RULE_DURATION
ACCOUNTING_RULE_ID
ACCOUNTING_RULE_NAME
AMOUNT
ATTRIBUTE_CATEGORY
ATTRIBUTE1-15
FOB_POINT
INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15
INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT
ORIG_SYSTEM_SHIP_ADDRESS_ID
QUANTITY
QUANTITY_ORDERED
REASON_CODE
REASON_CODE_MEANING
REFERENCE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1-15
REFERENCE_LINE_CONTEXT
REFERENCE_LINE_ID
SALES_ORDER
SALES_ORDER_DATE
SALES_ORDER_LINE
SALES_ORDER_SOURCE
SHIP_DATE_ACTUAL
SHIP_VIA
TAX_CODE
UNIT_SELLING_PRICE
UNIT_STANDARD_PRICE
UOM_CODE
UOM_NAME
WAYBILL_NUMBER
Related Topics
AutoInvoice Line Ordering Rules, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Using Grouping Rules to Create Transactions
Determining Dates
AutoInvoice determines the General Ledger date for invoices using the following criteria:
-
Does a GL date exist for this invoice in the interface table?
-
Does the invoice use rules?
-
What is the setting of the Derive Date option for this Transaction Batch Source (Yes or No)?
-
What is the setting of the GL Date in a Closed Period option for this Transaction Batch Source (Adjust or Reject)? See: Adjusting General Ledger Dates.
Determining General Ledger Dates for Invoices Without Rules
If your invoice does not use rules, AutoInvoice uses the following process to determine the general ledger date:
-
AutoInvoice uses the general ledger date in the interface table, if one exists and it is in an open or future enterable period.
-
If you did not pass a general ledger date and Derive Date is set to No, AutoInvoice uses the value of the Default Date parameter for this AutoInvoice submission.
If you did not pass a general ledger date and Derive Date is set to Yes, then AutoInvoice uses the ship date in the interface table. If the ship date does not exist, then AutoInvoice uses the sales order date. If the sales order date does not exist, then AutoInvoice uses the value of the Default Date parameter for this AutoInvoice submission.
Note: If the derived general ledger date for a transaction line exists but is in a closed period, and the GL Date in the Closed Period field in the Transaction Sources window is set to Adjust, then AutoInvoice automatically adjusts the GL date to the first GL date of the next open or future enterable period.
The following diagram illustrates this process.
General Ledger Date Derivation for Invoices without Rules
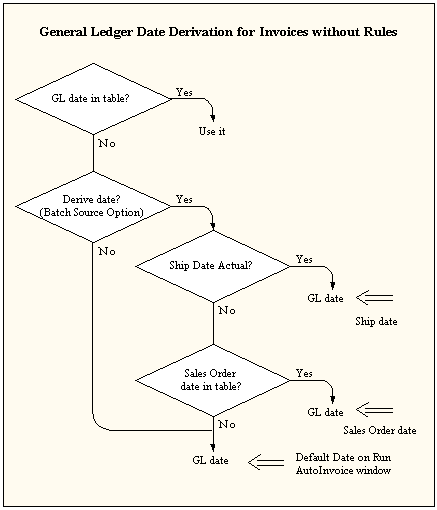
Determining General Ledger Dates for Invoices With Rules
If your invoice uses Bill in Advance as the invoicing rule, then AutoInvoice uses the GL date provided in the interface table as the invoice GL date. If no GL date is provided in the interface table, then AutoInvoice uses the earliest accounting rule start date as the invoice GL date.
If your invoice uses Bill in Arrears as the invoicing rule, the invoice line has an accounting rule of type Fixed Schedule and a period of Specific Date, AutoInvoice computes an ending date using the latest accounting rule date.
For all other accounting rules, AutoInvoice computes an ending date for each invoice line based on the accounting rule, accounting rule start date, and duration. Once AutoInvoice computes the ending date for each line of your transaction, it takes the latest date and uses it as the invoice GL date.
Rule Start Date
If your invoice does not use an accounting rule with a type of Fixed Schedule and a period of Specific Date, or if you have not elected to derive the rule start date, Receivables uses the date specified in the Run AutoInvoice window.
If your invoice has an accounting rule with a type of Fixed Schedule and a period of Specific Date, AutoInvoice uses the earliest accounting rule date as your rule start date. For example, if your accounting rule dates are 10-JUN-93, 10-JUL-93 and 10-AUG-93, AutoInvoice uses 10-JUN-93 as your rule start date.
If you elected to derive the rule start date, AutoInvoice first uses the ship date in the interface table. If the ship date does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the sales order date. If the sales order date does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the date you entered in the Run AutoInvoice window.
The following diagram illustrates this process.
Rule Start Derivation
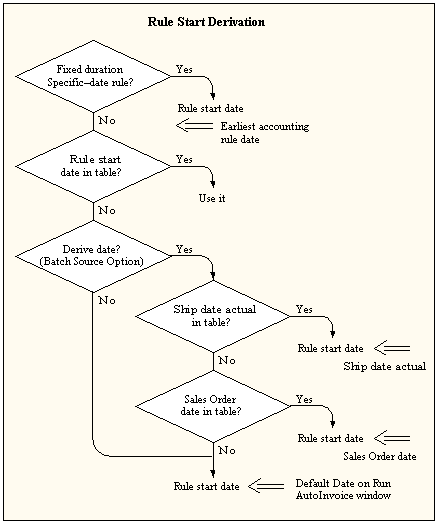
Determining Credit Memo Dates
If a transaction date is passed for your credit memo, AutoInvoice uses the following hierarchy to determine the credit memo date:
-
The credit memo general ledger date.
-
The general ledger date for the invoice's receivable distribution, or the Default Date in the Run AutoInvoice window, whichever is later.
If a general ledger date is not passed, AutoInvoice uses the general ledger date for the invoice's receivable distribution or the Default Date in the Run AutoInvoice window, whichever is later.
Determining the Transaction Dates
If a transaction date is not passed for your invoice or debit memo, AutoInvoice uses the general ledger date.
Tip: If you use Oracle Inventory and Oracle Order Management for sales order shipments, you should elect to derive your dates and use the shipment date for your invoice general ledger date. In this way you can ensure that you have booked your revenue and cost to the same accounting period.
If you do not match revenue and cost in the same period, you violate basic GAAP principles, and may distort your profit. In addition, you cannot run a meaningful Margin Analysis report. This report summarizes your revenue and cost of goods sold transactions by item and customer order, and specifies a transaction date range. If your transactions are booked in the wrong period, the Margin Analysis report reflects those incorrect transactions.
Related Topics
Adjusting General Ledger Dates
Validating Dates
AutoInvoice uses the following logic when validating general ledger and rule start dates that you either pass or are determined by AutoInvoice. If you use time stamps when you enter dates (e.g. 31-Jul-92 23:59:00), AutoInvoice will remove the time stamp prior to validation.
General Ledger Dates
AutoInvoice rejects lines if:
-
The accounting period for the general ledger date is not defined.
-
The general ledger date is in a 'Closed,' 'Closed Pending,' or 'Not Opened' period and the GL Date in a Closed Period field for your batch source is set to 'Reject.' (For invoices that use Bill in Arrears rules, AutoInvoice only rejects lines that have a general ledger date in a Closed period.)
-
The general ledger date of the credit memo is before the invoice general ledger date and/or the credit memo date is before the invoice date.
Rule Start Dates
AutoInvoice rejects lines if:
-
The rule start date for lines that used Bill in Advance rules are in 'Closed' or 'Not Opened' periods and the GL Date in a Closed Period field for your batch source is set to Reject, or if the accounting period for the rule start date is not defined.
-
The rule start date for lines that used Bill in Arrears rules results in a general ledger date in a Closed period and the GL Date in a Closed Period field for your batch source is set to Reject, or if the accounting period for the general ledger date is not defined.
-
The rule start date is not the earliest date specified for your accounting rule and you are passing an accounting rule with a type of Fixed Schedule and a period of Specific Date.
Related Topics
Adjusting General Ledger Dates
Adjusting General Ledger Dates
If the GL Date in a Closed Period field for your batch source is set to 'Reject' and you pass a general ledger date that is in a Closed or Not Opened period, AutoInvoice will reject the line.
If the GL Date in a Closed Period field for your batch source is set to 'Adjust' and you pass a general ledger date that is in a Closed or Not Opened period, AutoInvoice will change the date to an open or future enterable period. If the invoice does not use rules, AutoInvoice enters a GL date using the logic described in Determining Dates.
If the invoice uses either the Bill in Advance or Bill in Arrears rule, AutoInvoice adjusts the GL date using the following rules in the order listed:
-
AutoInvoice uses the last day of the prior period, if this period has a status of Open.
-
If a prior period with a status of Open does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the first day of the first subsequent period that has a status of Open.
-
If an Open period does not exist, AutoInvoice uses the first day of the first subsequent period that has a status of Future. If there is more than one subsequent period with a status of Future, or if it cannot find a future period, AutoInvoice cannot adjust the general ledger date, and the line is rejected.
Related Topics
Determining Exchange Rates
Exchange Rates
If your transaction uses exchange rates, AutoInvoice uses the exchange rate on the conversion date, if one is provided. Otherwise, AutoInvoice determines the exchange rate using the transaction date. If the conversion type is 'User,' AutoInvoice will use the rate that you specified (you must provide a rate in this case).
Receivables Tables
AutoInvoice transfers transaction data from the interface tables AR_INTERFACE_CONTS_ALL, RA_INTERFACE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL, RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL, and RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL into the following Receivables tables:
-
RA_BATCHES_ALL
-
RA_CUSTOMER_TRX _ALL
-
RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES _ALL
-
RA_CUST_TRX_LINE_GL_DIST_ALL
-
RA_CUST_TRX_LINE_SALESREPS_ALL
-
AR_PAYMENT_SCHEDULES_ALL
-
AR_RECEIVABLE_APPLICATIONS_ALL
-
AR_ADJUSTMENTS_ALL
Related Topics
AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide
Oracle Exchange Invoice Import Request Set
Use the Oracle Exchange Invoice Import request set to import Exchange fee data from Oracle Exchange into Receivables as new invoices and credit memos.
The Oracle Exchange Invoice Import request set populates the Receivables interface tables with information about the fees that the Exchange operator charged to the registered parties. Once the import data is loaded into the interface tables, the request set automatically submits AutoInvoice to create invoices and credit memos in Receivables.
The Oracle Exchange Invoice Import request set includes these programs:
-
Oracle Exchange Invoice Data Feeder program (AREXINVP) - The feeder program that extracts data from Oracle Exchange and stores it in the interface tables in Receivables
-
Oracle Receivables AutoInvoice program
Prerequisites
Prior to running this request set, submit the Oracle Exchange Customer Import request set to ensure that all customers in Exchange have been imported into Receivables. See: Oracle Exchange Customer Import Request Set.
For complete information on the Oracle Exchange Billing integration with Receivables, see the Oracle Exchange and Oracle Sourcing System Operator Implementation Guide, Release 6.2.2 and above.
Using Commitments
You can enter invoices against your deposits and guarantees by using the Transaction window or by importing your invoices using AutoInvoice. You can enter an invoice against an existing or related customer deposit or guarantee by navigating to the Commitment field in the Transactions window. Enter the commitment number that you want to reference and Receivables automatically creates the adjusting accounting entries for you. You can review commitment activity for your customers using the Commitment Balance Report.
See: Entering Transactions.
You can choose to enter orders or invoices for more than your customer's remaining commitment balance. For example, if your customer has a deposit with a remaining balance of $500 and has placed an order with you for $600, you can still reference that deposit. Receivables automatically creates a receivables adjustment in Receivables for $500, bringing the commitment balance to $0, leaving an amount due on the invoice of $100.
Note that you can never use more than the original deposit amount. Additionally, you can never increase the deposit amount.
You can also add a deposit to an invoice that is already completed, and partially paid or credited. From the Transactions workbench, choose Apply Deposit from the Actions menu.
Important: If you set the Sequential Numbering profile option to Always Used, then you must assign a document sequence to the Commitment Adjustment document category in order to successfully enter an invoice against a commitment. See Setting Up Document Sequences, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Review the following sections to learn more about:
Additionally, see: Setup and Accounting for Commitments.
Calculate Your Commitment Balance
Your customer's commitment balance is available to you in several places within Receivables and is also available if you are using Oracle Order Management. You can see the balance for a particular commitment when entering an order (if you are using Order Management), a manual invoice, or a credit memo against a commitment, or by running the Commitment Balance Report. All transactions that reference a commitment or reference an invoice that references a commitment affect the balance of that commitment. The general formula for calculating the balance of a commitment at any given time is as follows:
-
Original Amount of Commitment: $10,000
-
minus: Invoices against commitment: $500
-
minus: credit memos that reference invoices that reference commitments: <$250>
-
plus: credit memos against the commitment itself: <$100>
-
Resulting Commitment Balance: $9,650
Note: The commitment balance also reflects reservations created in Order Management, if the OM: Commitment Sequencing profile option is set to Yes. See: Profile Options in Oracle Order Management, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Reserve Commitment Balances
At the time of order entry, a customer can reserve some portion of an existing deposit towards payment for the order. In Order Management, you can also enter a promised amount for the freight on the order.
When the order is invoiced via AutoInvoice, Order Management or another feeder system passes the promised amount to Receivables. For a description of the AutoInvoice column that holds the promised amount, see:
-
AutoInvoice Table and Column Descriptions, Oracle Receivables Reference Guide.
Receivables then adjusts the invoice and reduces the commitment balance by the lesser of the promised amount, the commitment balance, or the remaining amount due on the invoice. Depending on the deposit's transaction type, you can choose to include tax and freight when applying a deposit to a transaction. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Setup and Accounting for Commitments
Commitment Transaction Types
Receivables creates adjusting accounting entries to reflect invoicing activity against your customer commitments based on transaction type. Receivables provides the following commitment transaction types:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Deposits | The accounting reversal is made by creating a receivables adjustment in Accounts Receivable to the invoice for the total of the invoice lines. This adjustment has the effect of reducing the invoice's payment schedule by the amount of the invoiced items (tax and freight amounts may be deducted from the deposit balance) and creating the reversing accounting entries. If, however, the amount of the invoice exceeds the remaining commitment balance, Receivables only creates a receivables adjustment for the remaining commitment balance. |
| Guarantees | The accounting reversal is made by creating a receivables adjustment in Accounts Receivable to the guarantee for the total of the invoice lines. This adjustment has the effect of reducing the guarantee's payment schedule by the amount of the invoiced items (tax and freight are not deducted from the commitment balance) and creating the reversing accounting entries. If however, the amount of the invoice exceeds the remaining commitment balance, Receivables only creates a receivables adjustment for the remaining commitment balance. |
Define Your Commitment Transaction Types
You can define multiple transaction types with a class of either Deposit or Guarantee to classify or group your commitments for reporting purposes. Transaction types for commitments also provide additional control features, such as accounting controls, printing controls, and other defaults. You can define transaction types in the Transaction Types window. See: Transaction Types, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
When you define transaction types for commitments, you can define them for both deposits and guarantees. The transaction type class determines whether it is of type deposit or guarantee.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Class | The class is used to distinguish transaction types. When defining commitment types, use a class of either Deposit or Guarantee. |
| Open Receivable and Post to GL | These fields control posting to your general ledger and the updating of customer balances. Receivables sets these fields to Yes when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Allow Freight | This field is used to control freight charges. Receivables sets this field to No when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Tax Calculation | This field controls tax charges. Receivables sets this field to No when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Creation Sign | This field is used to specify the creation sign of your transaction. This field is set to Positive Sign when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Natural Application Only | Use this field to determine whether you want to restrict the direction of your transaction balances when applying payments. For example, if you invoke Natural Application and have an invoice with an amount due remaining of $300, you can only make applications that will reduce this amount towards zero. This field is set to Yes when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Allow Overapplication | This field determines whether you want to allow over applications against items with this transaction type. This field is set to No when you define transaction types for commitments. |
| Receivable Account and Revenue Account | These are default accounts used by the Transactions window. You can accept these defaults or enter other accounts when you enter your commitments. For guarantees, enter the Unbilled Receivable account in the Receivable Account field, and the Unearned Revenue account in the Revenue Account field. For deposits, use the Offset Account field in the Deposits tabbed region to record the offset account for this deposit. |
| Invoice Type | This is the transaction type used for invoices that reference a commitment. If you create a deposit, then all invoices that reference this deposit would be assigned to this invoice type. You should choose an invoice type that has Post to GL and Open Receivable set to Yes. Receivables displays a warning message if the invoice type you choose has Post to GL or Open Receivable set to No. |
| Credit Memo Type | This is the transaction type used for credit memos that reference a commitment. If you create a deposit, then all credit memos that reference this deposit must be assigned to this credit memo type. You should choose a credit memo type that has Post to GL and Open Receivable set to Yes. Receivables displays a warning message if the credit memo type you choose has Post to GL or Open Receivable set to No. |
Deposit Accounting
Below is an example of the accounting transactions that Receivables creates when you record a deposit and an invoice against this deposit.
Enter a deposit for ABC Company of $10,000. When you record this deposit you can enter AR Trade as the debit account and Unearned Revenue (or Offset Account) as the credit account. Receivables automatically creates the following accounting entry as described in the table below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| AR Trade (Deposit) | $10,000 | |
| Unearned Revenue (or Offset Account) | $10,000 |
You can print the deposit invoice and mail it to your customer for payment. ABC Company receives the invoice and pays you the amount of the deposit.
ABC Company places an order for $500 and would like to draw against their commitment for this order. You enter an invoice for ABC Company for $500 and reference their $10,000 deposit. Receivables automatically creates the following accounting entry as described in the table below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| AR Trade (Invoice) | $500 | |
| Revenue | $500 |
Receivables then automatically creates a receivables adjustment for the invoiced amount against the invoice. The result is an amount due in Accounts Receivable of $0 (Note: In our example the $500 invoice does not include tax and freight.) You can print and send this invoice to your customer to provide them with a record of the activity against their commitment. Receivables creates the following accounting entry, as described in the table below, to reflect this adjustment:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | $500 | |
| AR Trade (Invoice) | $500 |
Therefore, ABC Company has no balance due for this $500 invoice, and an available commitment balance of $9,500.
Guarantee Accounting
Below is an example of the accounting transactions that Receivables creates when you record a guarantee and invoice against this guarantee.
Enter a guarantee for ABC Company. ABC Company agrees to purchase a specified amount of product from you, and you would like to track progress against this guarantee, and record it in your general ledger. The amount of this guarantee is $10,000. When you record this guarantee you can enter Unbilled Receivable as the debit account, and Unearned Revenue as the credit account. Receivables creates the following accounting entry as described in the table below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unbilled Receivable | $10,000 | |
| Unearned Revenue | $10,000 |
You can print this guarantee in the form of an invoice if you wish.
ABC Company places an order for $500 and would like to draw against their commitment for this order. You enter an invoice for ABC Company for $500 and reference their $10,000 guarantee. Receivables automatically creates the following accounting entry as described in the table below:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| AR Trade | $500 | |
| Revenue | $500 |
Receivables then automatically creates a receivables adjustment for the invoiced amount against the guarantee. Therefore, ABC Company owes $500 for this invoice, and has an outstanding commitment balance of $9500. Receivables creates the following accounting entry, as described in the table below, to reflect this adjustment.
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Unearned Revenue | $500 | |
| Unbilled Receivable | $500 |
Related Topics
Printing Transactions
The Print Invoices window lets you generate invoices, debit memos, commitments, chargebacks, credit memos, and adjustments to send to your customers.
You can preview the transactions that will print by selecting the Invoice Print Preview program.
Note: You can also use Balance Forward Billing to create a single document that summarizes all of a customer's activity for a specific period. For more information, see: Balance Forward Billing.
The system option Allow Change to Printed Transactions determines whether you can update a transaction after it has been printed. However, you cannot update a transaction if it has activity against it, regardless of how you set this option. Examples of activity include payments, credit memos, adjustments, and including the transaction on a balance forward bill.
The Print Date field in the Transactions window shows you the last time a transaction was printed.
Previewing Transactions Online
If you use Bill Presentment Architecture (BPA), then you can use the BPA icon to preview completed transactions online. See: Viewing Online Bills, Oracle Bill Presentment Architecture User Guide.
To print your transactions:
Prerequisites
-
Navigate to the Print Invoices window.
-
Enter the Name of the print program, or select from the list of values. Choose from the following:
Invoice Print New Invoices: Print all transactions that have not been printed previously and have a print status of 'Print'. For a description of the print parameters for this and other print program listed here, see: Print Invoice Reports.
Invoice Print Selected Invoices: Print specific transactions, regardless of whether you have already printed them. You can limit your printout by entering a range of dates, transaction numbers, a specific transaction type, transaction class, customer class, installment number, and a specific customer. You can also select to print only open invoices. Receivables does not include any transactions with a print status of 'Do Not Print'.
Invoice Print Batch of Invoices: Print a single batch of transactions, regardless of whether you have already printed it. You specify the batch to print in the Parameters window. Receivables does not include transactions with a print status of 'Do Not Print'.
Print Adjustments: Print specific adjustments to transactions which have not been printed previously and have a print status of 'Print.' Receivables does not include transactions with a print status of 'Do Not Print'.
Invoice Print Preview Report: Preview transactions that would be printed if you chose to print a batch of invoices, new invoices, or specific invoices. This report will list the transactions that would be printed in each case.
-
Enter print Parameters. For example, choose to Order By transaction number, customer, or postal code, enter a Transaction Class or Type, choose to print only Open Invoices, or enter a range of Transaction Numbers to print only transactions matching that criteria. Leave a field blank if you do not want to limit your printout to transactions matching that criteria. For a description of the print parameters, see: Print Invoice Reports.
Tip: To print credit memos, set Open Invoices Only to No.
-
Choose OK.
-
To change the default Print Options, enter the number of Copies to print, a printing Style, and the Printer to use.
-
To save the output of this submission to a file, check the Save Output check box.
-
To submit this print program more than once, enter Run Options. You can enter a Resubmit interval, a date and time To Start the resubmission, and an ending date on which to cease repeating.
-
Choose Submit. Receivables displays the request ID for this submission. You can use this number to view the status of your request in the View Concurrent Requests window.
Related Topics
Understanding Your Printed Transactions
Receivables Invoice Print Reports
Understanding Your Printed Transactions
The Receivables Print Invoices program lets you generate invoices, debit memos, commitments, chargebacks, credit memos and adjustments to send to your customers. By specifying values for your report parameters you can control the type of transactions you want Receivables to generate. For example, if you only want to generate transactions for a specific customer, you can specify the customer's name as one of your report parameters.
When printing invoices, format pages are printed for each new group of documents. These pages are provided to help with printer alignment. To prevent the invoice print programs from printing format pages you must reset the Default Value field for each program. The Invoice print programs have a parameter 'Number of alignment pages' that determines how many header pages to print out. To change the default, use the Application Developer responsibility, navigate to the Define Concurrent Program window, then query the following programs:
-
RAXINV_SEL
-
RAXINV_NEW
-
RAXINV_BATCH
-
RAXINV_ADJ
For each program, choose Parameters. Change the Default Value to '0,' then save the change. You must change the Default Value for each program.
Printing Invoices
Consider the following when determining the range of invoice dates to print:
If the invoice you are printing has a payment term where Print Lead Days is 0, Receivables uses the transaction date to determine if this transaction falls into the Start and End Date range you specify.
If the invoice you are printing has a payment term where Print Lead Days is greater than 0, Receivables uses the formula Due Date - Print Lead Days to determine if this transaction falls into the Start and End Date range you specify.
Invoices & Debit Memos
For each invoice Receivables displays the quantity ordered, shipped, unit price, and extended amount.
Receivables prints the entire description for each invoice line. Text wraps to the next line.
Receivables displays the total amount of the lines, tax, and shipping in the body of the printed invoice.
For installments, Receivables displays the total amount due for each installment as well as the line, tax, and freight amount in the subtotal fields.
Credit Memos
For each credit memo, Receivables displays a row for every invoice line, tax, or freight amount you are crediting.
Credit memo amounts display as negative numbers.
Receivables displays the percent of the credit memo applied to the transaction you are crediting.
Deposits
For each deposit, Receivables prints unit price, extended amount, and '1' in the quantity ordered and quantity shipped columns. Unit price and extended amount will always be the same.
Receivables prints 'N' in the Tax column and does not print tax and shipping amounts since these amounts are not part of the deposit.
Receivables prints the effective start date and the effective end date if you enter one.
Guarantees
For each guarantee, Receivables prints unit price, extended amount, and '1' in the quantity ordered and quantity shipped columns. Unit price and extended amount will always be the same.
Receivables prints 'N' in the Tax column and does not print tax and shipping amounts since these amounts are not part of the guarantee.
Receivables prints the effective start date and the effective end date if you enter one.
Receivables prints a message in the body of the guarantee explaining that this is not a request for payment.
Invoices Against Deposits
Receivables prints a row for each invoice line. If your line includes tax charges, Receivables displays 'Y' in the tax column. Receivables also prints the amount deducted from the deposit. This amount displays as a negative number.
Receivables displays the original balance of your deposit, less any activity. Activity includes any previous transactions as well as the current invoice. Receivables calculates and displays the current deposit balance. The deposit balance does not include any tax or shipping charges. Tax and shipping charges are printed at the bottom of the invoice in their respective columns and must be collected.
Invoices Against Guarantees
Receivables prints a row for each invoice line. If your line includes tax charges, Receivables displays 'Y' in the tax column.
Receivables displays the original balance of your guarantee, less any activity. Activity includes any previous transactions as well as the current invoice. Receivables calculates and displays the current guarantee balance. The guarantee balance does not include any tax or shipping charges. Tax and shipping charges are printed at the bottom of the invoice in their respective columns and must be collected in addition to the line amount(s).
Printing Tax
Receivables prints tax on your invoices and debit memos depending upon the value you entered for the Tax Printing option assigned to your customer's profile class. See: Defining Customer Profile Classes, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide. If you do not enter a Tax Printing option in your customer's profile class, Receivables uses the value you entered in the System Options window.
For a description of the tax printing options in Receivables, see: Transactions and Customers System Options, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Related Topics
Receivables Invoice Print Reports
Balance Forward Billing
Use balance forward billing to print a single bill that includes all of a customer’s transactions for the billing period and any balance carried forward from the previous billing period. This lets you send one consolidated bill to a customer, instead of a separate invoice for each transaction.
A balance forward bill includes the following items:
-
A beginning balance or the balance carried over from the last billing period.
-
An itemized list of current charges and activities (such as invoices, credit memos, debit memos, adjustments) in either summary or detail format.
Important: You cannot update transactions that are included on a balance forward bill, regardless of how you set the system option Allow Change to Printed Transactions or the AR: Update Due Date profile option. Receivables considers inclusion on a balance forward bill to be an activity and you cannot update a transaction once it has activity against it.
-
Payment received for the last billing period.
-
Current total outstanding balance.
You can generate balance forward bills on a weekly, monthly, bimonthly, quarterly, yearly, or even daily basis. To indicate billing frequency, define billing cycles. Or, use external billing cycles that you maintain outside Receivables. See: Balance Forward Billing Cycles, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
You can generate bills consolidated at either the customer account or site level:
-
Account-level balance forward billing lets you generate one bill for each operating unit of the account, addressed to the primary bill-to site of the account.
-
Site-level balance forward billing lets you generate a balance forward bill for each bill-to site of a customer with multiple bill-to sites.
You can exclude one or more sites, and even one or more transactions, from a balance forward bill.
See: Setting Up Balance Forward Billing, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Statements and balance forward bills are similar, but they have different purposes. The table below lists the differences between a statement and a balance forward bill.
| Statements | Balance Forward Bill |
|---|---|
| Generated at customer account level. | Generated at account or site level. |
| Customer uses for informational purposes. | Customer pays from the bill. |
| Customers selected by statement cycle. | Customers selected by billing cycle and currency. |
Important: Alternatively, consolidate imported invoices using the Imported Billing Number feature, instead of balance forward billing. See: Imported Billing Number.
Balance Forward Bill Number
When you print a draft or final balance forward bill, Receivables generates a unique balance forward bill number, which is assigned to each transaction on the bill.
Note: The balance forward bill number is automatically generated by a database sequence; you cannot create one manually.
Use the bill number to:
-
Query transactions that were included in a balance forward bill.
-
Accept a final balance forward bill.
-
Optionally reprint a draft or final balance forward bill.
-
Apply payment against a balance forward bill.
Important: The balance forward bill number field always appears to the left of the transaction number field.
The balance forward bill number is displayed in these Receivables reports and windows:
Windows
-
Credit Transactions
-
Receipts
-
Transactions
-
Transaction Overview
Reports
-
Account Status
-
Aging Reports
-
Billing and Receipt History
-
Disputed Invoice
-
Past Due Invoice
-
Sales Journal by GL Account
-
Transaction Detail
Online Balance Forward Bill Presentment
Receivables uses Bill Presentment Architecture (BPA) to present the balance forward bill in an online view.
Use the BPA icon on the Transactions window to preview balance forward bills. These balance forward bills are the same as those seen by your customers using Oracle iReceivables.
BPA presents the balance forward bill in either summary or detail format, based on how Receivables originally generated the bill. You can drill down to individual invoices from the Balance Forward Bill window. See: Viewing Online Bills, Oracle Bill Presentment Architecture User Guide.
You can optionally modify the bill template or information as required and reprint the bill. See: Template Management, Oracle Bill Presentment Architecture User Guide.
Related Topics
Setting Up Balance Forward Billing, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
How Receivables Selects Transactions for Balance Forward Billing
Creating Balance Forward Bills
Working with Bill Presentment Architecture, Oracle Bill Presentment Architecture User Guide
How Receivables Selects Transactions for Balance Forward Billing
To generate balance forward bills, submit the Generate Balance Forward Bill program. See: Creating Balance Forward Bills.
The following diagram illustrates how the Generate Balance Forward Bill program selects transactions for balance forward billing.
Balance Forward Bill Generation and Printing Process Flow
The Generate Balance Forward Bill program selects transactions for inclusion on a balance forward bill by following these steps:
-
When submitting the Generate Balance Forward Bill program, you enter parameters, such as billing cycle and billing date.
-
Next, the program gathers all balance forward billing customers whose balance forward billing payment terms have a matching billing cycle.
Note: Transactions that have non-balance forward billing payment terms or whose bill type is Imported are not included in a balance forward bill.
Receivables checks payment terms at the account profile for customers enabled for account-level balance forward billing, and at the site profile (or account profile if no payment term is specified at a site) for customers enabled for site-level balance forward billing.
Important: The balance forward billing program does not select transactions from customers who are related either by customer or account relationships.
-
The program selects all transactions for the balance forward billing customers that:
-
Have a balance forward billing payment term.
-
Have not been included in a previous balance forward bill.
Important: The Generate Balance Forward Billing program does not include the transactions for which you select the Do Not Print option on the More tab of the Transactions window.
-
-
The program captures the ending balance of the previous billing period to be used as the opening balance of the new bill. For first-time balance forward billing runs, the opening balance is zero.
-
The program calculates the ending balance of the new bill, accounting for previous balance, new transactions, and any activity occurring during the billing cycle.
-
Depending on the entered parameters, the program assigns the bill the print status of Draft or Final and assigns a unique balance forward bill number.
-
Finally, depending on the entered parameters, the program prints the bill by calling the BPA Balance Forward Print program.
Note: The Generate Balance Forward Bill program generates a bill even if there is no activity in a billing cycle. Such a balance forward bill displays the previous balance, zero current charges, and ending balance.
Changing Payment Terms on Transactions
You can change the billing cycle for a customer by changing the payment term assigned to the customer's profile.
Future transactions will inherit the new payment term. Receivables includes existing transactions that have the old payment term in the next submission of the Generate Balance Forward Bill program.
-
Transactions with no activity inherit the new payment term, billing date, and due date.
-
Transactions with activity retain their existing payment terms, billing dates, and due dates.
Note: This might cause an aging discrepancy, because these transactions could have due dates that are different from the other transactions on the bill.
Selection of Transactions with the External Cycle
You can assign the predefined external billing cycle, Oracle Receivables, to transactions. Use this external billing cycle for billing cycles that are maintained outside Receivables.
Transactions with external billing cycles that are imported into Receivables must have an existing billing date, so that AutoInvoice can calculate the transaction due date. Transactions without billing dates will not be successfully imported into Receivables. However, you can import these transactions before their billing dates, to ensure timely revenue recognition.
Related Topics
Creating Balance Forward Bills
Setting Up Balance Forward Billing, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide
Creating Balance Forward Bills
Creating balance forward bills involves the following steps:
You can optionally reprint balance forward bills, if required. See: Reprinting Balance Forward Bills.
Generating and Printing Draft and Final Balance Forward Bills
Use the Generate Balance Forward Bill program to generate and print balance forward bills. The Generate Balance Forward Bill program includes on balance forward bills the transactions that meet its entered parameters, and calls the BPA Balance Forward Print Program to print the bills.
You can also launch this program from an external system.
Prerequisites
-
Generating Style Sheet for BPA Templates
Selected Program Parameters
Required Parameters:
-
Print Option: Select Print draft balance forward bills or Print final balance forward bills.
Receivables assigns the Draft print status to draft balance forward bills and lets you accept or reject them. Receivables assigns the Final print status to final balance forward bills.
-
Billing Cycle: Specify the billing cycle for which you want to generate balance forward bills. If you submit the Generate Balance Forward Bill program from Receivables, then the Billing Cycle list of values displays all defined billing cycles. If you launch the program from an external system, then only the External billing cycle is available.
-
Print Output: Select Yes to obtain a viewable output of the bills. If you select No, then Receivables creates the bills, but you cannot view the bills from the concurrent request. To view the bills, you must query them in the Transactions workbench and select the BPA icon.
-
Currency Code: Receivables generates balance forward bills for customers matching the selected currency code.
Optional Parameters:
-
Operating Unit: To generate balance forward bills for a specific operating unit, select that operating unit from the list of values. Leave this field blank to generate balance forward bills for each eligible operating unit.
-
Billing Date (required for External billing cycles): Specify the billing date for the bill run.
The Generate Balance Forward Bill program includes on a bill only those transactions that share the same billing date or an earlier date.
-
Customer Name and Number Low/High: Select from the list of values to generate balance forward bills for a specific customer or a range of customers. The list of values contains only customers that have balance forward billing enabled.
Leave this field blank to generate balance forward bills for all eligible customers.
-
Bill-to-Site Low/High: If you have selected a customer from the Customer Name or Number list of values, and this customer is enabled for site-level billing, then you can select a specific bill-to site. Leave this field blank to print balance forward bills for all sites that are enabled to receive them.
-
Payment Term: The list of values includes all balance forward billing payment terms with the specified cycle. If you have specified a customer or bill-to site, then the list of values includes only the payment terms specific to the customer and bill-to site.
Leave this field blank to include all eligible transactions with balance forward billing payment terms which have the specified cycle.
Related Topics
Creating Balance Forward Bills
Accepting or Rejecting Draft Balance Forward Bills
Reprinting Balance Forward Bills
Accepting or Rejecting Draft Balance Forward Bills
Use the Confirm Balance Forward Bill program to accept or reject draft bills. The Confirm Balance Forward Bill program does not reprint the bill. To reprint a bill, submit the BPA Balance Forward Print Program.
You can also launch the Confirm Balance Forward Bill program from an external system.
Selected Program Parameters
Required Parameters:
-
Confirm Option: Select Accept draft balance forward bills or Reject draft balance forward bills.
Accepting a draft balance forward bill changes the bill print status from Draft to Accepted. Rejecting a draft balance forward bill changes the bill print status from Draft to Rejected.
Optional Parameters:
-
Operating Unit: To generate balance forward bills for a specific operating unit, select that operating unit. Leave this field blank to generate balance forward bills for each eligible operating unit.
-
Customer Number Low/High (required if bill number or concurrent Request ID is not specified): Confirm one or more account-level balance forward bills. The list of values includes all balance forward billing customers.
-
Bill-to Site Low/High: Confirm one or more site-level balance forward bills. The list of values includes only bill-to locations for the selected customer.
-
Billing Date Low/High: Enter a billing date range. Or, to print all bills for the specified account or site, do not specify a range.
-
Bill Number Low/High (required if customer number or concurrent request ID is not specified): Confirm one or more balance forward bills.
-
Concurrent Request ID (required if no other parameters are specified): Select the concurrent request ID for the Generate Balance Forward Bill program to accept or reject a batch of balance forward bills.
Related Topics
Generating and Printing Draft and Final Balance Forward Bills
Reprinting Balance Forward Bills
Reprinting Balance Forward Bills
Use the Bill Presentment Architecture (BPA) Balance Forward Print program to reprint draft or final balance forward bills.
You can also launch this program from an external system.
Prerequisites
-
Generating Style Sheet for BPA Templates
Selected Program Parameters
-
Operating Unit: To reprint balance forward bills for a specific operating unit, select that operating unit. To reprint balance forward bills for each eligible operating unit, do not select an operating unit.
-
Customer Number Low/High (required if bill number or concurrent Request ID is not specified): Reprint one or more account-level balance forward bills. The list of values includes all balance forward billing customers.
-
Bill to Site Low/High: Enter a bill-to site range to reprint one or more site-level balance forward bills. The list of values includes only bill-to locations for the selected customer.
-
Billing Date Low/High: Enter a billing date range. Or, to print all bills for the specified account or site, do not specify a range.
-
Bill Number Low/High (required if customer number or concurrent request ID is not specified): Enter a bill number range to reprint one or more specific balance forward bills.
-
Concurrent Request ID (required if no other parameter is specified): Select the concurrent request ID for the Generate Balance Forward Bill program to reprint a batch of balance forward bills.
-
Print Template: To reprint bills using the originally selected format assigned by the BPA rules engine, do not specify a print template. Or, select a template to override the originally assigned print format.
Tip: Selecting a template overrides the originally assigned template for the reprint only. If you view the bill online, then BPA derives the template according to the BPA rules engine. To permanently change the print format, update the BPA rules engine.
Related Topics
Creating Balance Forward Bills
Generating and Printing Draft and Final Balance Forward Bills
Accepting or Rejecting Draft Balance Forward Bills
Imported Billing Number
The Imported Billing Number feature provides you with an alternative way to group your imported invoices at the site level for consolidated presentation of billing. You supply the value for the billing number and then create your own custom consolidated bill formats.
AutoInvoice has been enhanced to accept the billing number when you use this alternative method. You can use existing receipt application functionality which allows you to match your customer to their payments using this billing number.
When the Imported Billing Number feature is activated, AutoInvoice validates all of the invoices imported under a single bill. For all invoices grouped under one bill, AutoInvoice checks each invoice to ensure that:
-
all invoices have the same customer bill-to address. (If any single invoice from the group fails the validation, then all of the invoices belonging to this bill will be rejected.)
-
the Imported Billing Number is unique for the given operating unit.
To use the Imported Billing Number feature:
-
Set up the customer profile to enable Balance Forward Billing. Select Imported as the format.
Important: The Imported format is available only if you select site as the Bill Level.
-
Run AutoInvoice to populate the CONS_BILLING_NUMBER column in the RA_INTERFACE_LINES table.
Note: This lets you group invoices under one bill even if the invoices have different payment terms, receipt methods, payment details, PO numbers, or invoicing rules, as long as they are all addressed to the same customer bill-to address.
-
Generate custom invoices.
Related Topics