Encumbrance Accounting
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
With General Ledger you can record pre-expenditures commonly known as encumbrances. The primary purpose of tracking encumbrances is to avoid overspending a budget. Encumbrances can also be used to predict cash outflow and as a general planning tool.
To use the full capabilities of encumbrance accounting, you must enable the budgetary control flag for a ledger. When you enable the budgetary control flag, the system automatically creates encumbrances from requisitions, purchase orders and other transactions originating in feeder systems such as Purchasing and Payables.
When you do not enable the budgetary control flag, you can still enter manual encumbrances via journal entry, but you cannot generate encumbrances from requisitions and purchase orders.
You have two options for using encumbrance data to monitor over-expenditure of a budget: After actuals and encumbrances have been posted, you can generate reports to show over-expenditures. You can also can use funds checking to prevent over-expenditures before they occur. See: Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
The following figure shows the encumbrance accounting process with the budgetary control flag enabled.
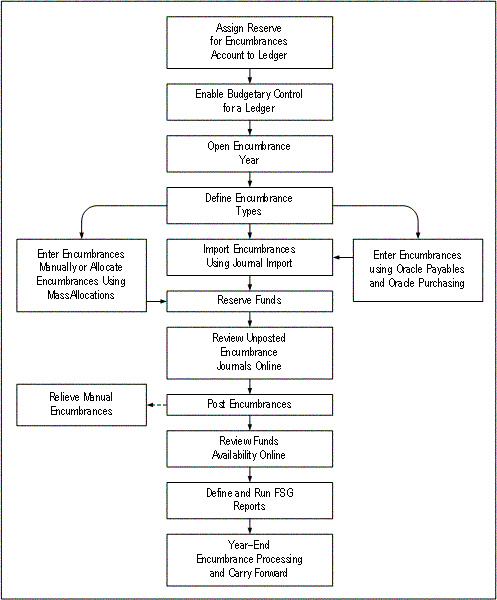
To use General Ledger encumbrance accounting:
-
Define Reserve for Encumbrance account for each ledger. See: Ledger Options.
When you post encumbrance transactions, General Ledger automatically posts offset amounts to this account.
-
Enable Budgetary Control for your ledger to automatically create encumbrance entries from Oracle Purchasing and Oracle Payables. See: Defining Ledgers, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide.
However, you need not define budgetary control options for your detail or summary accounts nor must you define budgetary control groups.
-
Open encumbrance years to enter and post encumbrance entries to future periods. Your initial encumbrance year is opened automatically when you open the first period for your ledger. See: Opening an Encumbrance Year, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
General Ledger uses the last period of your latest open encumbrance year to determine how far to calculate your project-to-date encumbrance balances.
Your data access set must provide full read and write access to your ledger, or read and write access to all balancing segment values or management segment values to open the encumbrance year for the ledger.
-
Import encumbrances using Journal Import. See: Importing Journals.
-
Enter encumbrances via Purchasing and Payables.
Purchasing automatically creates unposted encumbrance entries for General Ledger when you approve a requisition or purchase order.
Payables automatically creates unposted encumbrance entries for General Ledger to encumber funds for purchase order variances and unmatched invoices.
See: Encumbrance Entries in Payables, Oracle Payables User's Guide
General Ledger immediately updates your funds available when you reserve funds for your transactions in Purchasing and Payables. However, you must post your encumbrance entries to review funds available in Financial Statement Generator reports.
-
Reserve funds for encumbrance entries to allow posting of encumbrances. To do so, do one of the following:
-
Reserve funds online in the Enter Encumbrances window. See: Entering Encumbrances.
-
Reserve funds in batch mode by running the Mass Funds Check/Reservation program. See: Running the Mass Funds Check/Reservation Program.
-
Have the Posting program automatically reserve funds when you post your encumbrance batch. See: Posting Journals.
Note: We recommend that you let the Posting program automatically reserve funds. Since reserving funds for encumbrance entries independent of budgetary control is always successful, this method requires no user intervention.
-
-
Review unposted encumbrance journal entries online. See: Reviewing Encumbrances.
-
Define and submit encumbrance reports using the Financial Statement Generator. For example, you might define a Funds Available report to measure budgets against expenditures and encumbrances. See: Overview of the Financial Statement Generator.
You can also use standard reports to review your encumbrance balances and activity. Standard reports include the following:
Related Topics
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Defining Encumbrance Types
Encumbrance types let you classify and track expenditures according to the purchasing approval process. You can define encumbrance types in addition to the General Ledger standard encumbrance types or disable existing encumbrance types.
General Ledger has the following predefined encumbrance types:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Commitment | An encumbrance you record when you complete a purchase requisition. |
| Obligation | An encumbrance you record when you turn a requisition into a purchase order. |
You can define as many additional encumbrance types as you want or change the names of the standard encumbrance types to reflect the terminology you use within your organization. You specify an encumbrance type when you enter an encumbrance and when you perform inquiries.
To define an encumbrance type:
-
Navigate to the Encumbrance Types window.
-
Enter a name and description.
-
Enable the encumbrance type.
-
Save your work.
Related Topics
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Entering Encumbrances
Enter and update encumbrance entries, as well as review and update encumbrance entries imported to General Ledger from feeder systems such as Purchasing and Payables.
Entering encumbrances is similar to entering actual journals. Before entering encumbrances manually, organize them into batches. For example, group your encumbrances by encumbrance type, date, and preparer.
You can enter encumbrances only in your ledger currency. The batch can only have journals for only one primary or secondary ledger.
Data Access Sets
You can select a ledger for your encumbrance journal if your data access set provides read and write access to the ledger, or read and write access to one or more of the balancing segment values or management segment values in the ledger. You will not be able to select a ledger if your data access set provides read access to the ledger, balancing segment values or management segment values.
You can enter encumbrance journal lines if your data access set provides read and write access to the ledger, balancing segment values or management segment values. You will not be able to enter encumbrance journal lines if you only have read access to the ledger, balancing segment values or management segment values. See Data Access Sets, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide.
Note: If you use Reporting Currencies (Journal or Subledger Transaction Level), General Ledger automatically creates and posts a converted encumbrance entry in your journal or subledger transaction level reporting currency when you post the associated encumbrance entry in your primary ledger. The reporting currencies journals are contained in the same encumbrance batch.
Note: You can modify the Enter Encumbrances folder form to customize your query capabilities on encumbrance information. Refer to the Oracle E-Business Suite User's Guide for more information on modifying and saving folder forms.
Prerequisites
-
Define your ledger using Accounting Setup Manager.
-
Define your encumbrance types.
-
Open an encumbrance year.
To enter an encumbrance batch:
-
Navigate to the Enter Encumbrances window.
-
Choose New Batch.
-
Enter a batch Name, an appropriate Accounting Period, and an optional Control Total. You can enter encumbrances up to the last period of your latest open encumbrance year.
-
Choose Journals to enter your encumbrance journals.
-
Create your encumbrance journal by entering a name, ledger, category, encumbrance type, and optional description, reference and control total.
-
Enter encumbrance lines, specifying an account and debit or credit amount for each. General Ledger automatically validates each segment value as well as the combination of segments you enter.
If the debit amounts do not equal the credit amounts in either your manual or imported encumbrance entries, General Ledger automatically enters a balancing amount to the Reserve for Encumbrances account at posting. Your encumbrance entries always balance by balancing segment value.
-
Save your work.
Related Topics
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Defining Ledgers, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
Opening and Closing Accounting Periods, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
Overview of Reporting Currencies
Reviewing Encumbrances
You can review your posted or unposted encumbrance journal batches, such as those created manually or those imported from Payables or Purchasing.
Data Access Sets
You can review your encumbrance journal batches if your data access set provides read access to the ledger, and all of the journal’s balancing segment values or management segment values. If you have partial read access to the balancing segment values or management segment values, you can only view journal lines that you have read access to. See Data Access Sets, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide.
To review your encumbrances:
-
Navigate to the Enter Encumbrances window.
-
Enter or query your encumbrance batch.
-
Choose Review Batch to review batch information or choose Review Journal to review journal information.
Related Topics
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Relieving Encumbrances
Requisition encumbrances are automatically relieved when requisitions become purchase orders.
Whether the system accrues expenses on receipt of goods or on processing of invoices, the system creates expense distribution lines from purchase order lines at the appropriate time and automatically relieves the purchase order encumbrance.
You can also relieve encumbrances manually in General Ledger. To do so, you must make an encumbrance entry.
Data Access Sets
You can relieve your encumbrance journal batches manually if your data access set provides read and write access to the ledger, or read and write access to all of the journal’s balancing segment values or management segment values. See Data Access Sets, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide.
To relieve encumbrances manually:
-
Navigate to the Enter Encumbrances window.
The Find Journals window appears.
-
Enter or query an encumbrance batch.
The Enter Encumbrances window appears.
-
Choose Reverse Batch.
The Default Reversal Period window appears.
-
Select a reversal period and choose OK.
Note: The default period is the current accounting period.
The system submits the appropriate concurrent request.
-
Post the reversal batch to relieve the encumbrances.
Related Topics
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Viewing Funds Available
You can review funds available and compare encumbrances and expenditures with budgets. You can review primary ledger currency budget, actual and encumbrance balances, and funds available for any detail or summary account. General Ledger calculates funds available by subtracting expenditures and encumbrances from budgets.
When you inquire on funds available, the amount type you specify determines how General Ledger calculates funds available.
Amount Type How the System Calculates Funds Available
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Period-to-Date | Calculates funds available as the budgeted amount for the period, less actuals and encumbrances for the period. |
| Quarter-to-Date Extended | Calculates funds available as the budgeted amount to date for the quarter, less actuals and encumbrances to date for the quarter. For example, you budget $100 to an account for each of the three months in a quarter. The available amount for the second month of the quarter is $200. |
| Year-to-Date Extended | Calculates funds available as the budgeted amount to date for the year, less actuals and encumbrances to date for the year. For example, you budget $100 to an account for each of the 12 months. The available amount for the first half of the year is $600. |
| Project-to-Date | Calculates funds available as the budgeted amount to date, less actuals and encumbrances to date. |
You can review the cumulative funds available total only by selecting Year-to-Date Extended (or Project-to-Date) as the amount type. For example, if you budget $100 for January, spend $50 and have $10 in encumbrances, the funds available for January is $40. If you view funds available for the amount type PTD for February, the February balances will not include the $40 available at the end of January. When you choose an amount type of YTDE, you can view cumulative amounts so the February balances will include the $40 available for January.
Prerequisites
-
Enter budget amounts or journals.
-
Post actual, budget, and encumbrance journals.
To view funds available:
-
Navigate to the Funds Available Inquiry window.
-
Enter the Budget Name for the inquiry. General Ledger defaults the current budget, if you have one.
-
Enter the Period Name for the inquiry.
General Ledger defaults to the first period for the current budget. General Ledger uses the period name along with the amount type to determine funds available.
-
Select an Amount Type.
-
Enter an Encumbrance Type. You can view all encumbrances types by entering ALL.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Choose the Find button to query all accounts that meet your selection criteria.
-
Navigate to the Funds Available region and query a partial or complete account.
-
-
General Ledger displays the functional Budget, Encumbrance and Actual Amounts for each account. The displayed amounts are the posted balances plus reserved funds. General Ledger displays debit balances as positive amounts and credit balances as negative amounts.
General Ledger automatically displays Funds Available as:
-
Budget Amount for Period Interval
-
Actual Amount for Period Interval
-
Encumbrance Amount for Period Interval
If you chose the encumbrance type ALL and you have budgetary control enabled and Purchasing installed, General Ledger displays the encumbered amounts for purchase order and requisition encumbrance types and all other encumbrance types in the Encumbrance Amount region.
-
Related Topics
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking
Year-End Encumbrance Processing
Performing Year-End Encumbrance Processing
Perform year-end processing to identify outstanding purchase order and requisition encumbrances, to cancel some or all of these encumbrances, and to carry forward encumbrance, budget, and funds available balances into the new fiscal year.
You can carry forward encumbrances into the next fiscal year. If you do not carry forward encumbrances, you might want to cancel existing requisitions and purchase orders behind the encumbrances. You can easily identify purchase orders and requisitions behind encumbrances.
Prerequisites
-
Run receipt accruals in Purchasing if installed.
To perform year-end encumbrance processing:
-
Identify outstanding encumbrances in Oracle Purchasing to determine which encumbrances to cancel or to carry forward.
-
Review purchase order and requisition encumbrances by requesting the following reports:
-
Encumbrance Details Report in Oracle Purchasing
-
Open Encumbrance Balance with Transaction Detail Report
Tip: In addition to using these reports to identify outstanding encumbrances, request these reports before year-end carry-forward to create an audit trail of encumbrance balances.
Important: This report was designed specifically for government installations. You may use this report for commercial installations but you must verify its accuracy as it was not designed for this purpose.
-
-
Define the MassCancel criteria in Oracle Purchasing to select the encumbrances you want to cancel.
-
Run MassCancel in Oracle Purchasing to cancel selected outstanding purchase order and requisition encumbrances.
-
Post all encumbrance, budget, and actual journal entries. See: Posting Journal Batches.
-
Request the Encumbrance Trial Balance Report in General Ledger to review in detail encumbrance balances and activity for the general ledger accounts before year-end carry forward. See: Encumbrance Trial Balance Report
-
Close the last period of the current fiscal year. See: Opening and Closing Accounting Periods, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
-
Open the first period of the next fiscal year.
-
See: Opening an Encumbrance Year, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
-
Request the Encumbrance Trial Balance Report in General Ledger to review the year-end carry forward balances.
Note: Requesting the Encumbrance Trial Balance report before and after year-end carry-forward creates an audit trail of encumbrance balances.
Related Topics
Run MassCancel (Oracle Purchasing Reference Manual)
Define MassCancel (Oracle Purchasing Reference Manual)
Carrying Forward Year-End Encumbrance and Budget Balances
You can carry forward year-end encumbrances into the following year. You can also carry forward budget amounts equal to encumbrances and/or funds available.
When you carry forward year-end encumbrances, the Carry Forward rule you specify determines the amounts to be carried forward. Note that General Ledger carries forward balances, not as period activity, but as beginning balances.
Caution: Because Carry Forward does not create journal entries, the balances brought forward cannot be reversed. Use caution in planning and executing this process.
You can choose from the following Carry Forward rules:
-
Encumbrances Only:General Ledger determines the year-to-date encumbrance balances as of the end of the fiscal year and carries forward those balances as the beginning balances of the first period of the next fiscal year.
-
Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget:General Ledger determines the year-to-date encumbrance balances as of the end of the fiscal year and carries forward those balances, plus equivalent budget amounts, as beginning balances of the first period of the next fiscal year.
-
Funds Available:General Ledger calculates funds available as year-to-date budget balances less year-to-date actual and encumbrance balances. General Ledger carries forward budget amounts equal to funds available at the end of the fiscal year as beginning balances of the first period of the next year.
Carry Forward rules 2 and 3 can be combined if you want to carry forward budget amounts equal to encumbrances plus funds available. Note that when combining these Carry Forward rules, they must be run consecutively in a specific order. First run Carry Forward rule 3, Funds Available, then rule 2, Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget. Otherwise, the budget amounts you carry forward will be understated.
The following table illustrates how balances are carried forward using the different Carry Forward rules:
| Budget | Actual | Encumbrance | Available | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balances, end of Year 1 | 1,000 | 700 | 200 | 100 |
| Balances, beginning of Year 2: | ||||
| Using Rule 1 | 0 | 0 | 200 | (200) |
| Using Rule 2 | 200 | 0 | 200 | 0 |
| Using Rule 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Using Rule 3, then rule 2 | 300 | 0 | 200 | 100 |
You can generate a preview report to see the effects of a year-end carry forward before you actually initiate the carry forward process. If you do not carry forward encumbrance balances at the end of the fiscal year, all encumbrances automatically go to zero at the beginning of the next year.
You can execute year-end carry forward a number of times for different ranges of accounts and different encumbrance types.
Note: Keep a checklist as you execute the year-end carry forward. Perform carry forward for one fund at a time, or one encumbrance type at a time, and check off each fund or encumbrance type as you process it.
Prerequisites
-
Run receipt accruals in Oracle Purchasing.
-
Post all budget, actual, and encumbrance journal entries.
-
Close the last period of the fiscal year.
-
Open the first period of the next fiscal year.
-
Open the next encumbrance year.
-
Open the next budget year.
To carry forward year-end encumbrances:
-
Navigate to the Year-End Carry Forward window.
-
Select the ledger to carry forward year-end encumbrances.
-
Enter a General Ledger Carry Forward Rule.
-
If you are using the Encumbrances Only rule or the Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget rule, enter the Encumbrance Type you want to carry forward. Select ALL to carry forward amounts for all encumbrance types.
-
If you are using the Funds Available rule, enter the From Budget to use to determine the year-to-date funds available. This budget must include the From Period.
-
If you are using the Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget or the Funds Available rule, enter the To Budget for the carry forward. This budget must include the To Period.
-
Enter the Budget Organization for which to carry forward balances or ALL for all budget organizations.
If you choose ALL, General Ledger carries forward balances for all the accounts you enter in the Carry Forward Ranges region, regardless of the budget organization.
If you specify a budget organization other than ALL, General Ledger carries forward balances only for those accounts that are included in this budget organization and in the ranges you specify in the Carry Forward Ranges region.
-
Enter the From/To Period information.
General Ledger automatically defaults the From/To Period pair when the last period of the fiscal year for which you are carrying forward balances is Closed or Permanently Closed (From Period), and the period following the closed period is Open or Future Enterable (To Period).
The period that follows the closed period must also be in one of the following:
-
An open encumbrance year if you are using the Encumbrances Only, or the Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget rule.
-
An open budget year if you are using the Encumbrances and Encumbered Budget rule, or the Funds available rule.
If the carry forward periods meet these conditions, General Ledger defaults the earliest pair meeting this criteria; you can choose a period pair from a later fiscal year if all of the same conditions are met. General Ledger then calculates year-to-date amounts based on the From Period but does not update existing From Period balances.
-
-
Enter the Carry Forward account Ranges.
The values you enter need not be valid segment values. You cannot enter overlapping ranges of accounts.
General Ledger carries forward balances for only those accounts that are included in the ranges you enter and that are assigned to the budget organization you specify.
-
Choose Preview to print a preview report that shows the effects of the year-end carry forward before you initiate it.
-
Choose Carry Forward to initiate the carry forward process and to print an audit report.
General Ledger carries forward the encumbrance and budget balances into the beginning balance of the first period of the next fiscal year. General Ledger does not roll forward encumbrance and budget balances as period activity in the next month.
Related Topics
Overview of Encumbrance Accounting
Performing Year-End Encumbrance Processing
Opening and Closing Accounting Periods, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide