| C H A P T E R 7 |
|
Server Administration |
This chapter provides an introduction to server administration tools supported on the Sun Fire V890 system. The following information is covered in this chapter:
A number of software-based administration tools are available to help you configure your system for performance and availability, monitor and manage your system, and identify hardware problems. These administration tools include:
 software
software
The following table provides a summary of each tool with a pointer to additional information.
Sun Fire V890 systems feature a variety of components that can be serviced while the machine is running.
Hot-pluggable components are components that a qualified service technician can install or remove while the system is running, without affecting the rest of the system's capabilities. However, in many cases, you must prepare the operating system prior to the hot-plug event by performing certain system administration tasks.
Components that can be serviced without such preparation are called hot-swappable components. These components can be removed or inserted at any time without preparing the operating system in advance.
Sun Fire V890 hot-pluggable components fall into three basic groups:
Each group is discussed in more detail in the sections that follow.
Sun Fire V890 fan trays and power supplies are hot-swappable--they can be removed or inserted at any time without requiring prior software preparations. Keep in mind that a power supply is not considered hot-swappable unless it is part of an N+1 redundant power configuration. Do not remove a power supply from a working system if its removal would leave the system with fewer than two working power supplies.
You can install or remove a power supply or fan tray while the system is operating at the ok prompt. However, in the case of the power supply, you must issue a reset-all command at the ok prompt in order for the change to be recognized the next time the operating system is booted.
|
Caution - When hot-swapping a redundant fan tray, do not put your hand into the empty fan tray bay. The fans in the populated bay are still spinning. |
For additional information, see:
Sun Fire V890 internal disk drives are hot-pluggable. However, certain software preparations are required. To perform Sun Fire V890 disk drive hot-plug operations, you use the Solaris luxadm utility. The luxadm utility is a command-line tool for managing intelligent storage arrays such as Sun StorEdge A5x00 series disk arrays or Sun Fire V890 internal storage arrays.
A5x00 series disk arrays or Sun Fire V890 internal storage arrays.
For more information about luxadm, see About the Solaris luxadm Utility. For complete disk hot-plug procedures, refer to Platform Notes: Using luxadm Software. This document is included on the Sun Fire V890 Documentation CD. Refer also to the Sun Fire V890 Server Product Notes for late-breaking details.
|
Caution - When hot-plugging a disk drive, after disconnecting the drive from its backplane, allow 30 seconds or so for the drive to spin down completely before removing it from its drive bay. |
On Sun Fire V890 systems, PCI cards are hot-pluggable, while the system controller card cannot be serviced when the machine is running.
Hot-plug operations for PCI cards involve Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR). DR is an operating system feature that provides the ability to reconfigure system hardware while the system is running. DR lets you logically attach or detach hardware resources within an active operating system. The main benefit of DR is that a service provider can add or replace hardware resources with little or no impact on normal system operations.
PCI hot-plug procedures may involve software commands for preparing the system prior to removing a device, and for reconfiguring the operating system after installing a new device. In addition, certain system requirements must be met in order for hot-plug operations to succeed.
For information about system requirements and limitations, and for detailed PCI hot-plug procedures, refer to the Sun Fire V890 Dynamic Reconfiguration User's Guide, which is available at http://docs.sun.com, under Solaris on Sun Hardware. Refer to the Sun Fire V890 Server Product Notes for late-breaking details.
|
Note - DR works in conjunction with (but does not require) multipathing software. You can use multipathing software to switch I/O operations from one I/O controller to another to prepare for DR operations. With a combination of DR and multipathing software, a qualified service technician can remove, replace, or deactivate a PCI controller card with little or no interruption to system operation. Note that this requires redundant hardware; that is, the system must contain an alternate I/O controller that is connected to the same device(s) as the card being removed or replaced. The alternate controller must reside on a different PCI card or be integrated into the Sun Fire V890 system motherboard or I/O board. For additional details, see About Multipathing Software. |
There are two different methods for performing PCI hot-plug operations on Sun Fire V890 systems:
The push-button method relies on push buttons and status LEDs located near each PCI slot. A qualified service technician can initiate a PCI hot-plug operation by pressing the push button for the corresponding slot. The command-line method lets a qualified service technician initiate PCI hot-plug operations via a remote login session, an RSC console, or a locally attached console. This method involves the Solaris cfgadm(1) command.
Both hot-plug methods make use of the status LEDs located near each PCI slot. These LEDs indicate where and when it is safe to insert or remove a card, and also show whether the operation has succeeded or failed. For additional details on hot-plug status LEDs, see About PCI Slot LEDs.
For detailed PCI hot-plug procedures, refer to the Sun Fire V890 Dynamic Reconfiguration User's Guide, which is available at http://docs.sun.com, under Solaris on Sun Hardware. Refer to the Sun Fire V890 Server Product Notes for late-breaking details.
Multipathing software lets you define and control redundant physical paths to I/O devices such as storage devices and networks. If the active path to a device becomes unavailable, the software can automatically switch to an alternate path to maintain availability. This capability is known as automatic failover. To take advantage of multipathing capabilities, your server must be configured with redundant hardware, such as redundant network interfaces or two FC-AL host bus adapters connected to the same dual-ported storage array.
Multipathing software is often used in conjunction with Solaris Dynamic Reconfiguration (DR) software (see About Hot-Pluggable and Hot-Swappable Components). In response to a component failure in an active path, the multipathing software automatically switches to an alternate path, while the DR feature lets you remove and replace the faulty component without impacting normal system operations.
For Sun Fire V890 systems, two different types of multipathing software are available:
For information about setting up redundant hardware interfaces for storage devices or networks, see:
For instructions on how to configure and administer Solaris IP Network Multipathing, consult the IP Network Multipathing Administration Guide provided with your specific Solaris release.
Sun Management Center software provides a single solution for managing multiple Sun systems, devices, and network resources. With its intuitive Java technology-based graphical interface, Sun Management Center offers powerful management capabilities that let you:
Sun Management Center software is provided on the Software Supplement CD supplied in the Solaris Media Kit for your release. For information about installing and using Sun Management Center software, see the following documents provided with the Sun Management Center software:
Sun Remote System Control (RSC) software is a remote server management tool that lets you monitor and control supported Sun servers over serial lines or over a network. RSC provides remote system administration for geographically distributed or physically inaccessible systems and complements existing Sun monitoring and diagnostics tools such as Sun Management Center, SunVTS, OpenBoot PROM, and OpenBoot Diagnostics.
RSC software works with the system controller card included in all Sun Fire V890 servers. The system controller card runs independently of the host server, and operates off of 5-volt standby power from the system's power supplies. Together the hardware and software allow RSC to serve as a "lights-out" management tool that continues to function even when the server operating system goes offline or the system is powered off.
The system controller card plugs in to a dedicated slot on the system I/O board and provides the following ports through an opening in the system rear panel:
RSC offers the following user interfaces:
The Java technology-based GUI client application runs on workstations running the Solaris, Microsoft Windows 98, or Windows NT operating systems.
Sun RSC software is included on the Software Supplement CD for your specific Solaris release. For installation instructions, see the Solaris Sun Hardware Platform Guide provided in the Solaris Media Kit. For information about configuring and using RSC, see the Sun Remote System Control (RSC) 2.2 User's Guide, which is included on the Sun Fire V890 Documentation CD.
Sun Microsystems offers two different volume management applications for use on Sun Fire V890 systems:
Volume management software lets you create disk volumes. Volumes are logical disk devices comprising one or more physical disks or partitions from several different disks. Once a volume is created, the operating system uses and maintains the volume as if it were a single disk. By providing this logical volume management layer, the software overcomes the restrictions imposed by physical disk devices.
Sun's volume management products also provide RAID data redundancy and performance features. RAID, which stands for redundant array of independent disks, is a technology that helps protect against disk and hardware failures. Through RAID technology, volume management software is able to provide high data availability, excellent I/O performance, and simplified administration.
Sun's volume management applications offer the following features:
Sun StorEdge Traffic Manager software for Solaris OS, which is part of the Sun SAN Foundation Suite, automates multipath I/O failover, failback, and SAN-wide load balancing. For more information about this product, see the Sun Fire V890 Server Product Notes.
Solstice DiskSuite software supports RAID technology to optimize performance, availability, and user cost. RAID technology improves performance, reduces recovery time in the event of file system errors, and increases data availability even in the event of a disk failure. There are several levels of RAID configurations that provide varying degrees of data availability with corresponding trade-offs in performance and cost.
This section describes some of the most popular and useful of those configurations, including:
Disk concatenation is a method for increasing logical volume size beyond the capacity of one disk drive by creating one large volume from two or more smaller drives. This lets you create arbitrarily large partitions.
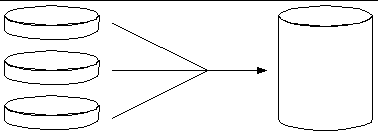
Using this method, the concatenated disks are filled with data sequentially, with the second disk being written to when no space remains on the first, the third when no room remains on the second, and so on.
Disk mirroring (RAID 1) is a technique that uses data redundancy--two complete copies of all data stored on two separate disks--to protect against loss of data due to disk failure. One logical volume is duplicated on two separate disks.
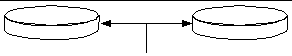
Whenever the operating system needs to write to a mirrored volume, both disks are updated. The disks are maintained at all times with exactly the same information. When the operating system needs to read from the mirrored volume, it reads from whichever disk is more readily accessible at the moment, which can result in enhanced performance for read operations.
RAID 1 offers the highest level of data protection, but storage costs are high, and write performance is reduced since all data must be stored twice.
Disk striping (RAID 0) is a technique for increasing system throughput by using several disk drives in parallel. Whereas in non-striped disks the operating system writes a single block to a single disk, in a striped arrangement, each block is divided and portions of the data are written to different disks simultaneously.
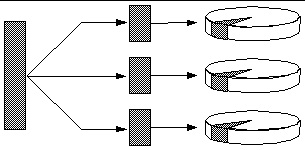
System performance using RAID 0 will be better than using RAID 1 or 5, but the possibility of data loss is greater because there is no way to retrieve or reconstruct data stored on a failed disk drive.
RAID 5 is an implementation of disk striping in which parity information is included with each disk write. The advantage of this technique is that if any one disk in a RAID 5 array fails, all the information on the failed drive can be reconstructed from the data and parity on the remaining disks.
System performance using RAID 5 will fall between that of RAID 0 and RAID 1; however, RAID 5 provides limited data redundancy. If more than one disk fails, all data is lost.
In a hot spares arrangement, one or more disk drives are installed in the system but are unused during normal operation. Should one of the active drives fail, the data on the failed disk is automatically reconstructed and generated on a hot spare disk, enabling the entire data set to maintain its availability.
For more information, see the documentation supplied with Solstice DiskSuite software.
The luxadm program is a command-line management utility for administering the Sun Fire V890 internal Fibre Channel-Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) storage subsystem and supported external storage arrays. You use luxadm to perform physical disk management tasks, including disk hot-plug operations. The luxadm utility is installed automatically when you install the Solaris OS.
The luxadm utility performs a variety of control and query tasks through a number of subcommands and command-line options. Using luxadm, you can:
|
Note - Setting the front panel keyswitch to the Locked position prevents reprogramming of system firmware. If the keyswitch is turned to the Locked position after a firmware update operation has started, the operation is allowed to proceed to completion. For more information about the front panel keyswitch, see About the Status and Control Panel. |
Platform Notes: Using luxadm Software provides information about the luxadm utility, including descriptions of hot-plug procedures for Sun Fire V890 internal disk drives. This document is available on the Sun Fire V890 Documentation CD. Refer also to the luxadm(1M) man page, and for late-breaking information, to the Sun Fire V890 Server Product Notes.
Sun Cluster software lets you connect multiple Sun servers in a cluster configuration. A cluster is a group of nodes that are interconnected to work as a single, highly available and scalable system. A node is a single instance of Solaris software--it may be running on a standalone server or on a domain within a standalone server. With Sun Cluster software, you can add or remove nodes while online, and mix and match servers to meet your specific needs.
Sun Cluster software delivers high availability through automatic fault detection and recovery, and scalability, ensuring that mission-critical applications and services are always available when needed.
With Sun Cluster software installed, other nodes in the cluster will automatically take over and assume the workload when a node goes down. It delivers predictability and fast recovery capabilities through features such as local application restart, individual application failover, and local network adapter failover. Sun Cluster software significantly reduces downtime and increases productivity by helping ensure continuous service to all users.
The software lets you run both standard and parallel applications on the same cluster. It supports the dynamic addition or removal of nodes, and enables Sun servers and storage products to be clustered together in a variety of configurations. Existing resources are used more efficiently, resulting in additional cost savings.
Sun Cluster software allows nodes to be separated by up to 10 kilometers. This way, in the event of a disaster in one location, all mission-critical data and services remain available from the other unaffected locations.
For more information, see the documentation supplied with the Sun Cluster software.
Copyright © 2005, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.