| C H A P T E R 3 |
|
Environmental and Electrical Specifications |
This chapter describes the environmental and electrical requirements for Sun Fire V1280/Netra 1280 systems. It contains the following sections:
The system can be installed in an environment with the specific operating ranges shown in TABLE 3-1.
The design of your environmental control system--such as computer room air-conditioning units--must ensure that intake air to the server system complies with the limits specified in this section.
TABLE 3-1 lists the environmental limits for Sun Fire V1280/Netra 1280 systems.
|
Ambient temperature[1] |
41° to 95°F (5° to 35°C)
|
||
|
Relative humidity[3] |
|||
|
For UltraSPARC IV+ 1.8 GHz CPU/Memory boards only, maximum 7000 feet (2134 meters) All other CPU/Memory boards, maximum 10000 feet
|
|||
|
In addition to the above environmental conditions, the Netra 1280 complies with the requirements of Telcordia SR-3580 (NEBS) Level 3. |
|||
The operating environmental limits in TABLE 3-1 reflect systems testing. The optimum condition is the suggested operating environment. Operating computer equipment for extended periods at or near the temperature or humidity extremes is known to significantly increase the failure rate of hardware components. It is strongly suggested that customers plan and use the optimal temperature and humidity ranges in order to minimize any chance of downtime due to component failure.
The ambient temperature range of 69.8° to 73.4°F (21°C to 23°C) is optimal for system reliability and operator comfort levels. Most computer equipment can operate within a wide temperature range, but a level near 71.6°F (22°C) is desirable because it is easier to maintain safe associated relative humidity levels at this temperature. Operating in this temperature range provides a safety buffer in the event the environmental support systems go down for a period of time. Though individual standards vary slightly, 69.8° to 73.4°F (21°C to 23°C) should be used as an optimal setting.
The ambient relative humidity levels between 45 percent and 50 percent are the most suitable for safe data processing operations. Under certain circumstances, most data processing equipment can operate within a fairly wide environmental range (20 percent to 80 percent), but the optimal goal should be between 45 percent to 50 percent for the following reasons:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is easily generated and less easily dissipated in areas where the relative humidity is below 35 percent. ESD becomes critical when levels drop below 30 percent. The 5 percent relative humidity range might seem unreasonably tight when compared to the guidelines used in typical office environments or other loosely controlled areas; where as, it is not as difficult to maintain in a data center because of the high efficiency vapor barrier and low rate of air changes normally present.
The maximum rate of heat release from a Sun Fire V1280/Netra 1280 system with all slots occupied and active is 3300 W (11300 British Thermal Units (BTU) per hour). TABLE 3-2 shows detailed figures.
The Sun Fire V1280/Netra 1280 system has been designed to function while mounted in a natural convection airflow. The following rules must be followed to meet the environmental specification.
The Sun Fire V1280 system is supplied ready for installation in an equipment rack.
|
Note - The voltage must be in the range 200-240 VAC for the system to power up. |
The Sun Fire V1280 system is supplied with four detachable power cords fitted with wall plugs to mate with the local electrical socket outlets. TABLE 3-3 shows the power cord ratings.
|
Note - The plug at the end of each power cord is the primary means of disconnection for this product. |
TABLE 3-4 shows the on-site AC power requirements.
TABLE 3-5 shows the current and power consumption of the Sun Fire V1280 system at 200 VAC.
The Sun Fire V1280 system enclosure has an additional safety earth bonding point.
This bonding point must meet the central office requirements for enclosure or shelf grounding in GR1089-CORE. This is for a path between the unit system and enclosure metal or nearby point on the central office ground system.
The use of this bonding point connection is optional and is generally dependent on the equipment practice of the installer.
This bonding point is independent of the safety ground connection for the power system grounding, which is provided by the earth wire present in each of the power cords. This connection must be present.
|
Caution - For optimum redundancy, the power cords should be connected to two independent power sources (two power cords for each power source). |
Most commonly, two independent power sources means an outside power line as one source and an uninterrupted power supply backup system (UPS) as the second source. That way, if a single power source should fail, the system will continue to function.
Each power cable should have its own circuit breaker.
The system will not enter standby unless two system power supplies have in range AC inputs.
The Netra 1280 system is supplied ready for installation in an equipment rack.
|
Caution - This system has multiple power connections. You must open all associated circuit breakers in order to completely remove power from the system. |
|
Note - The voltage must be in the range -40 to -72 VDC for the system to power on. |
The power switch of the Netra 1280 system is a rocker style momentary action switch. This switch controls only low voltage signals. No high voltage circuits pass through this switch.
At least two dedicated power sources should be provided with positive-ground circuit breakers, see Section 3.4.2, Connecting DC Power for Redundancy for details. Connector lugs are provided for crimping on to customer-supplied cables.
The Netra 1280 system is supplied with connections for four feed pairs. TABLE 3-6 shows the feed-pair current ratings.
|
Note - In North America, 90 degrees C 6 AWG copper conductors must be used. Where other codes apply, 10 mm2 copper conductors must be used. |
TABLE 3-7 shows the current and power consumption of the Netra 1280 system at -48 VDC.
|
Note - The circuit breakers are the primary means of disconnection for this product. |
|
38A per feed pair, if only two feed pairs are powered[4] |
|
|
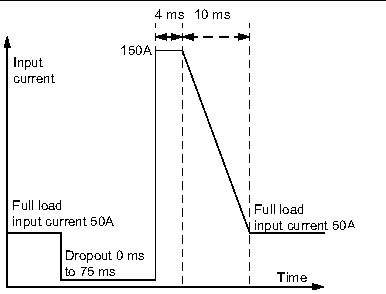
After a brown-out of up to 75 ms, short term surge is < 150A for a maximum of 4 ms, linearly decaying to the normal running current in less than 10 ms (FIGURE 3-1). |
|
|
3530W maximum total split across two or more power feed pairs. |
The Netra 1280 system enclosure has an additional safety earth bonding point. This bonding point must meet the central office requirements for enclosure or shelf grounding in GR1089-CORE. This is for a path between the unit system and enclosure metal or nearby point on the central office ground system. The use of this bonding point connection is optional and is generally dependent on the equipment practice of the installer.
This is independent of the safety ground connection for the power system grounding, which is provided by the two-hole connection on the DC inlet module.
Overcurrent protection devices must be provided as part of each host equipment rack.
|
Note - Overcurrent devices must meet applicable national and local electrical safety codes and must be approved for the intended application. |
The disconnect devices for servicing are defined as the circuit breakers in all negative supply conductors.
|
Caution - For optimum redundancy, the feed pairs should be connected to two independent power sources (two feed pairs to each power source). |
Most commonly, two independent power sources means an outside power line as one source and an uninterrupted power supply backup system (UPS) as the second source. That way if a single power source should fail, the system will continue to function.
Each power cable should have its own circuit breaker.
Copyright © 2006, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.