| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.0 Administration Guide |
1. Overview of the Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software
2. Installing and Enabling Software
4. Setting Up Services and the Control Domain
Introduction to a Virtual Network
Set Options for an Existing Virtual Switch
Managing a Virtual Network Device
Set Options for an Existing Virtual Network Device
Remove a Virtual Network Device
Virtual Device Identifier and Network Interface Name
Find Oracle Solaris OS Network Interface Name
Assigning MAC Addresses Automatically or Manually
Range of MAC Addresses Assigned to Logical Domains
Automatic Assignment Algorithm
Duplicate MAC Address Detection
Using Network Adapters With Logical Domains
Determine If a Network Adapter Is GLDv3-Compliant
Configuring Virtual Switch and Service Domain for NAT and Routing
Set Up the Virtual Switch to Provide External Connectivity to Domains
Configuring IPMP in a Logical Domains Environment
Configuring Virtual Network Devices Into an IPMP Group in a Domain
Configuring and Using IPMP in the Service Domain
Using Link-Based IPMP in Logical Domains Virtual Networking
Configure Physical Link Status Updates
Configuring and Using IPMP in Releases Prior to Logical Domains 1.3
Configuring IPMP in the Guest Domain
Configuring IPMP in the Service Domain
Assign VLANs to a Virtual Switch and Virtual Network Device
Install a Guest Domain When the Install Server Is in a VLAN
Using Link Aggregation With a Virtual Switch
Configure Virtual Network and Virtual Switch Devices to Use Jumbo Frames
Compatibility With Older (Jumbo-Unaware) Versions of the vnet and vsw Drivers
12. Performing Other Administration Tasks
A. Oracle VM Server for SPARC Physical-to-Virtual Conversion Tool
B. Oracle VM Server for SPARC Configuration Assistant
C. Logical Domains Manager Discovery
D. Using the XML Interface With the Logical Domains Manager
The virtual I/O framework implements a hybrid I/O model for improved functionality and performance. The hybrid I/O model combines direct and virtualized I/O to allow flexible deployment of I/O resources to virtual machines. It is particularly useful when direct I/O does not provide full capability for the virtual machine, or direct I/O is not persistently or consistently available to the virtual machine. This could be because of resource availability or virtual machine migration. The hybrid I/O architecture is well-suited for the Network Interface Unit (NIU) on Sun UltraSPARC T2 and SPARC T3 platforms. An NIU is a network I/O interface that is integrated on chip. This architecture enables the dynamic assignment of Direct Memory Access (DMA) resources to virtual networking devices and, thereby, provides consistent performance to applications in the domain.
NIU hybrid I/O is available for Sun UltraSPARC T2 and SPARC T3 platforms. This feature is enabled by an optional hybrid mode that provides for a virtual network (vnet) device where the DMA hardware resources are loaned to a vnet device in a guest domain for improved performance. In the hybrid mode, a vnet device in a guest domain can send and receive unicast traffic from an external network directly into the guest domain using the DMA hardware resources. The broadcast or multicast traffic and unicast traffic to the other guest domains in the same system continue to be sent using the virtual I/O communication mechanism.
Note - NIU hybrid I/O is not available on UltraSPARC T2 Plus platforms.
Figure 8-7 Hybrid Virtual Networking
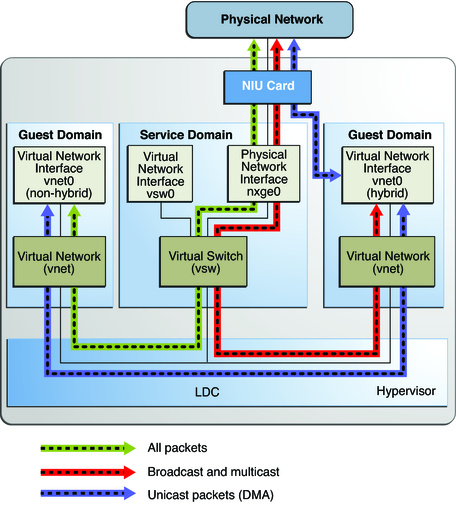
The hybrid mode applies only for the vnet devices that are associated with a virtual switch (vsw) configured to use an NIU network device. As the shareable DMA hardware resources are limited, up to only three vnet devices per vsw can have DMA hardware resources assigned at a given time. If more than three vnet devices have the hybrid mode enabled, the assignment is done on a first-come, first-served basis. As there are two NIU network devices in a system, there can be a total of six vnet devices on two different virtual switches with DMA hardware resources assigned.
Following are points you need to be aware of when using this feature:
Hybrid mode option for a vnet device is treated as a suggestion only. That means the DMA resources are assigned only when they are available and the device is capable of using them.
Logical Domains Manager CLI commands do not validate the hybrid mode option; that is, it is possible to set the hybrid mode on any vnet or any number of vnet devices.
Guest domains and the service domain need to run Oracle Solaris 10 10/08 OS at a minimum.
Up to a maximum of only three vnet devices per vsw can have DMA hardware resources loaned at a given time. As there are two NIU network devices, there can be a total of six vnet devices with DMA hardware resources loaned.
Note - Set the hybrid mode only for three vnet devices per vsw so that they are guaranteed to have DMA hardware resources assigned.
Hybrid mode is disabled by default for a vnet device. It needs to be explicitly enabled with Logical Domains Manager CLI commands. See Enable Hybrid Mode.
(Refer to the ldm(1M) man page for more details.)
The hybrid mode option cannot be changed dynamically while the guest domain is active.
The DMA hardware resources are assigned only when a vnet device is active that is plumbed in the guest domain.
The NIU 10-gigabit Ethernet driver (nxge) is used for the NIU card. The same driver is also used for other 10-gigabit network cards. However, the NIU hybrid I/O feature is available for NIU network devices only.
The following example shows the output on an UltraSPARC T2 server:
# grep nxge /etc/path_to_inst "/niu@80/network@0" 0 "nxge" "/niu@80/network@1" 1 "nxge"
The following example shows the output on a SPARC T3-1 server:
# grep nxge /etc/path_to_inst "/niu@480/network@0" 0 "nxge" "/niu@480/network@1" 1 "nxge"
# ldm add-vsw net-dev=nxge0 primary-vsw0 primary
# ldm add-vnet mode=hybrid vnet01 primary-vsw0 ldom01
# ldm set-vnet mode= vnet01 ldom01