| C H A P T E R 2 |
|
Command-Line Interface |
The Command-Line Interface (CLI) is the recommended interface for enabling assistive technologies.
This chapter contains the following information:
Commands that can be executed from the command line are listed in TABLE 2-1, and a few of the most important commands are documented in this chapter. For further information on executing these commands, see the man page for the command in question.
To view any of the specific commands for the Sun Ray system, type:
or type:
|
The utaction program provides a way to execute commands when a Sun Ray DTU session is connected or disconnected. |
|
|
The utadm command manages the private network, shared network, and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) configuration for the Sun Ray interconnect. |
|
|
The utadminuser command is used to add, list, and delete UNIX usernames from the list of users authorized to administer Sun Ray services. The list is stored in the Sun Ray data store. |
|
|
The utamghadm command is used to configure or disable regional hotdesking, which allows users to access their sessions across multiple failover groups. |
|
|
The utcapture command connects to the Authentication Manager and monitors packets sent and packets dropped between the Sun Ray server and the Sun Ray DTUs. |
|
|
The utcard command allows configuration of different types of smart cards in the Sun Ray administration database |
|
|
The utconfig command performs the initial configuration of the Sun Ray server and supporting administration framework software. |
|
|
The utcrypto command is a utility for security configuration. |
|
|
The utdesktop command allows the user to manage Sun Ray DTUs connected to the Sun Ray server that the command is run on. |
|
|
The utdetach command disconnects the current non-smart card mobile session or authenticated smart card session from its respective Sun Ray DTU. The session is not destroyed but put into a detached state. The session can be accessed if the same user token (user name) is presented to the Sun Ray server. |
|
|
The utdevadm command is used to enable/disable Sun Ray device services. This includes USB devices connected through USB ports, embedded serial ports, and internal smartcard reader in the Sun Ray DTU. |
|
|
The utdiskadm utility is a tool for Sun Ray mass storage administration. |
|
|
The utdssync command converts the port number for the Sun Ray Data Store service to the new default port on servers in a failover group, then forces all servers in the group to restart Sun Ray services. |
|
|
The uteject command is used to eject media from a removable storage media device. |
|
|
The utfwadm command manages firmware versions on the Sun Ray DTUs. |
|
|
The utfwload command is used primarily to force the download of new firmware to a DTU running older firmware than its server. |
|
|
The utfwsync command refreshes the firmware level on the Sun Ray DTUs to what is available on the Sun Ray servers in a failover group. It then forces all the Sun Ray DTUs within the group to restart. |
|
|
The utgroupsig command sets the failover group signature for a group of Sun Ray servers. The utgroupsig command also sets the Sun Data Store rootpw used by Sun Ray to a value based on the group signature. Although utgroupsig sets the rootpw in the utdsd.conf file, it does not set the admin password, which is a separate entity, in the Admin database. |
|
|
The utgstatus command allows the user to view the failover status information for the local server or for the named server. The information that the command displays is specific to that server at the time the command is run. |
|
|
The utinstall utility installs, upgrades, and removes Sun Ray Server Software. All software required to support the Sun Ray server is installed, including the administration framework, and any patches required by the framework. |
|
|
The utmhadm command provides a way to administer Sun Ray server multihead terminal groups. The information that utmhadm displays and that is editable is stored in the Sun Ray administration database. |
|
|
The utmhconfig tool allows an administrator to list, add, or delete multiheaded groups easily. |
|
|
The utmount command is used to mount a file system on a Sun Ray mass storage device. |
|
|
The utpolicy command sets and reports the policy configuration of the Sun Ray Authentication Manager, utauthd(1M). This command's -i and -t options were deprecated as of the 2.0 release. Please continue to use the utpolicy command for policy changes, but use the utrestart command instead of utpolicy -i, and use utreader instead of utpolicy -t. |
|
|
The utpreserve command saves existing Sun Ray Server Software configuration data to the /var/tmp/SUNWut.upgrade directory. |
|
|
The utpw command changes the Sun Ray administrator password (also known as the UT admin password) used by the Web-based and command-line administration applications. |
|
|
The utquery command collects DHCP information from the Sun Ray DTUs. |
|
|
The utreader command is used to add, remove, and configure token readers. |
|
|
The utreplica command configures the Sun Ray Data Store server to enable replication of administered data from a designated primary server to each secondary server in a failover group. The data stores of the secondary servers remain synchronized automatically unless there is a power outage. The -z option is useful for updating the port number. |
|
|
The utresadm command allows an administrator to control the resolution and refresh rate of the video monitor signal (persistent monitor settings) produced by the Sun Ray unit. |
|
|
The utresdef command lists the monitor resolutions and refresh rates that can be applied to Sun Ray units through the utresadm command. |
|
|
The utselect command presents the output of utswitch -l in a window and allows mouse-based selection of a Sun Ray server to which the Sun Ray DTU in use is reconnected. |
|
|
The utsession command lists and manages Sun Ray sessions on the local Sun Ray server. |
|
|
The utsettings command opens a Sun Ray Settings dialog box that allows the user to view or change audio, visual, and tactile settings for the Sun Ray DTU. |
|
|
The utswitch command allows switching a Sun Ray DTU among Sun Ray servers in a failover group. It can also list the existing sessions for the current token. |
|
|
The utumount command is used to unmount a file system from a Sun Ray mass storage device. |
|
|
The utuser command allows the administrator to manage Sun Ray users registered on the Sun Ray server that this command is run on. It also provides information on the currently inserted token (smart card) for a specified DTU that is configured as a token reader. |
|
|
The utwall utility sends a message or an audio file to users having an Xnewt (X server unique to Sun Ray) process. The messages can be sent in email and displayed in a pop-up window. |
|
|
The utwho script assembles information about display number, token, logged-in user, etc., in a compact format. |
|
|
The utxconfig program provides X server configuration parameters for users of Sun Ray DTU sessions. |
|
|
This procedure starts Sun Ray services without clearing existing sessions.
This procedure starts Sun Ray services and clears existing sessions.
In addition to automatic redirection after a user's token has been authenticated, whether via smart card token or direct login, the utselect graphical user interface (GUI) or the utswitch command can be used to redirect the session to a different server.
|
 From a shell window on the DTU, type:
From a shell window on the DTU, type:
The selections in the window are sorted in order of the most current to least current active sessions for the token ID.
In FIGURE 2-1, the Server column lists the servers accessible from the DTU. The Session column reports the DISPLAY variable X session number on the server if one exists. In the Status column, Up indicates that the server is available. The first server in the list is highlighted by default. Select a server from the list or enter the name of a server in the Enter server: field. If a server without an existing session is selected, a new session is created on that server.
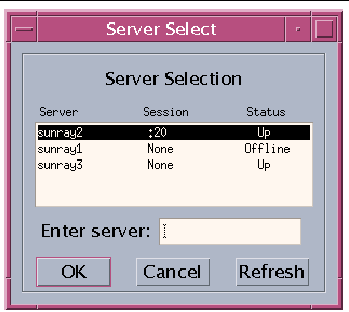
The OK button commits the selection of the highlighted or manually entered server. The Cancel button dismisses the GUI without making any changes to the session. The Refresh button reloads the window with the most current information.
|
 From a shell window on the DTU, type:
From a shell window on the DTU, type:
where host is the host name or IP address of the Sun Ray server to which the selected DTU is redirected, and token is the user's token ID.
|
Hosts available from the Sun Ray DTU are listed.
|
The DTU is redirected to the server with the latest session connect time.
When a policy is set with utpolicy, the group policy is set automatically, so all that is needed at that point is to reset or restart services.
In previous releases, the Sun Ray Admin GUI supported authentication for only one user account, called admin, against the Sun Ray Data Store. Beginning with SRSS 3.1, the Sun Ray Admin GUI allows UNIX usernames other than admin to administer Sun Ray services, and it provides an audit trail of their activity. Any valid UNIX user in the authorized user list can now administer Sun Ray services. See the man page for utadminuser(1M).
Sun Ray Admin GUI authentication is now based on the PAM authentication framework.
In order to support the old Data Store authentication, a new PAM module, /opt/SUNWut/lib/pam_sunray_admingui.so.1, is included in the Sun Ray product.
utconfig(1M) adds the following new PAM entry for Sun Ray Admin GUI configuration:
|
To configure the Sun Ray Admin GUI to use UNIX usernames instead of the default admin account:
 Copy the auth entries from /etc/pam.d/login file into /etc/pam.d/utadmingui:
Copy the auth entries from /etc/pam.d/login file into /etc/pam.d/utadmingui:
|
Note - Make sure to include the comment line, which is needed for the cleanup to work properly. |
|
To return to the old Sun Ray Admin GUI authentication scheme:
 Replace the PAM entries in the /etc/pam.d/utadmingui file with the pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 module:
Replace the PAM entries in the /etc/pam.d/utadmingui file with the pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 module:
# added to utadmingui by Sun Ray Server Software -- utadmingui auth sufficient /opt/SUNWut/lib/pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 |
|
Note - Make sure to include the comment line, which is needed for the cleanup to work properly. |
The administration framework now provides an audit trail of the Administration GUI. The audit trail is an audit log of the activities performed by multiple administration accounts. All events that modify system settings are logged in the audit trail.
SRSS 3.1.1 uses the syslog implementation. Events are logged into /var/opt/SUNWut/log/messages file, where audit events are prefixed with the keyword utadt:: so that administrator can filter events from the messages file.
For example, session termination from the Admin GUI generates the following audit event:
Sun Ray device services can be enabled/disabled with the utdevadm command line tool or with the Admin GUI. Sun Ray device services include USB devices connected through USB ports, internal serial ports, and internal smart card readers on the Sun Ray DTU.
When internal serial service is disabled, users cannot access embedded serial ports on the Sun Ray DTU. The Sun Ray 170 has two embedded serial ports.
When internal smart card reader service is disabled, users cannot access the internal smart card reader through the PC/SC or SCF interfaces for reading or writing; however, this does not affect session access or hotdesking with unauthenticated smart cards.
When USB service is disabled, users cannot access any devices connected to USB ports. This does not, however, affect HID devices such as the keyboard, mouse, or barcode reader.
After installation of Sun Ray Server Software, all device services are enabled by default. You can use the utdevadm command to enable or disable device services only in the configured mode, that is, after the Sun Ray Data store is activated.
This configuration affects all the servers in a group and all the DTUs connected to that group.
The following example shows how to enable/disable USB service. The other device services can be enabled or disabled with the same syntax.
|
This displays enabled or disabled state of the devices.
|
 Use the utdevadm command as below:
Use the utdevadm command as below:
|
 Use the utdevadm command as below:
Use the utdevadm command as below:
|
 Use the utrestart command as below:
Use the utrestart command as below:
Use the utadm command to manage the Sun Ray interconnect fabric.
|
Note - If you make manual changes to your DHCP configuration, you will have to make them again whenever you run utadm or utfwadm. |
|
This command configures the network interface interface_name as a Sun Ray interconnect. Specify a subnet address or use the default address, which is selected from reserved private subnet numbers between 192.168.128.0 and 192.168.254.0.
|
Note - If you choose to specify your own subnet, make sure it is not already in use. |
After an interconnect is selected, appropriate entries are made in the hosts, networks, and netmasks files. (These files are created if they do not exist.) The interface is activated.
Any valid network interface can be used. For example:
|
This command deletes the entries that were made in the hosts, networks, and netmasks files and deactivates the interface as a Sun Ray interconnect.
|
For each interface, this command displays the hostname, network, netmask, and number of IP addresses assigned to Sun Ray DTUs by DHCP.
|
Note - Sun Ray servers require static IP addresses; therefore, they cannot be DHCP clients. |
|
|
|
|
Use the utadm -r command to prepare for removal of the Sun Ray Server Software.
This command removes all of the entries and structures relating to all of the Sun Ray interfaces and subnets.
Use the utfwadm command to keep the firmware version in the PROM on Sun Ray DTUs synchronized with that on the server. See also Enhancements to Firmware Download and Configuration Support.
|
Note - If the DHCP version variable is defined, then when a new DTU is plugged in, its firmware is changed to the firmware version on the server. |
|
Note - If you make manual changes to your DHCP configuration, you will have to make them again whenever you run utadm or utfwadm. |
|
|
If you restart the Sun Ray Data Store daemon (utdsd), you must also restart the Sun Ray Authentication Manager. The Sun Ray Data Store daemon may need to be restarted if you change one of its configuration parameters. The following procedure shows the correct order of the steps to take if you need to restart SRDS.
|
2. Stop the Sun Ray Data Store daemon:
3. Restart the Sun Ray services:
|
Tip - Use the Administration Tool or the utcard command to add additional smart card vendor configuration files. |
Smart card configuration files are available from a variety of sources, including Sun. For more ample information on smart cards, see the latest version of the Solaris Smart Card Administration Guide.
|
 Copy the vendor configuration file containing the vendor tags to the following location:
Copy the vendor configuration file containing the vendor tags to the following location:
The additional vendor cards are displayed under the Available column in the Add page in the Administration Tool.
Some manufacturers print the smart card ID on the card itself, but many do not. Since all the administrative functions refer to this token ID, Sun Ray Server Software provides a way to designate one or more specific DTUs as dedicated token readers. Site administrators can use these dedicated DTUs to administer Sun Ray users. When you enable an authentication policy with registered users, be sure to specify smart card IDs.
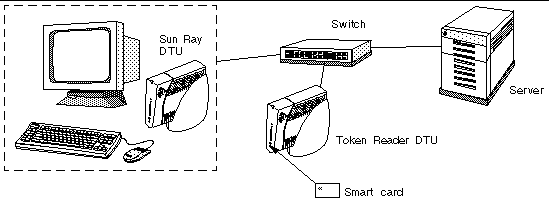
In the example configuration in FIGURE 2-2, the second DTU acts as a token reader.
|
Note - The token reader is not used for normal Sun Ray services, so it does not need a keyboard, mouse, or monitor. |
|
The utreader command specifies a DTU for registering smart cards. When a DTU is configured as a token reader, inserting or removing a smart card does not cause session mobility to occur; instead, any session connected to the DTU remains connected to that DTU over a card movement event.
Token reader mode is useful when you want to determine the raw token ID of a smart card.For example, to configure the DTU with MAC address 0800204c121c as a token reader, issue the following utreader command:
To re-enable the DTU with MAC address 0800204c121c to recognize card movement events and perform session mobility based on the smart card inserted into the DTU:
To unconfigure all token readers on this server:
|
In releases prior to SRSS 3, access to the token card reader was limited to the server to which it was connected. In other words, the utuser command had to be invoked from that server. Beginning with SRSS 3.1, however, you can access the token card reader by invoking utuser -r from any server in the relevant failover group. The procedure otherwise remains as it was in earlier releases.
where Token Reader is the MAC address of the DTU containing the token (smart card) whose ID you want to read. Insert the token into the DTU and run the utuser command. This command queries the DTU for the token's ID and, if successful, displays it. For example:
# /opt/SUNWut/sbin/utuser -r 08002086e18f Insert token into token reader '08002086e18f' and press return. Read token ID 'mondex.9998007668077709' |
The utcapture tool connects to the Authentication Manager and collects data about the packets sent and packets dropped between the Sun Ray server and the DTU. The data in TABLE 2-3 is then displayed on the screen in the following format:
The following utcapture options are supported:
|
From a command line, enter one of the following commands
This command lists the help commands for the utcapture tool
This command captures data every 15 seconds from the Authentication Manager running on the local host and then writes it to stdout if there is any change in packet loss for a DTU
This command captures data every 15 seconds from the Authentication Manager that is running on the local host and then writes it to stdout.
This command captures data every 15 seconds from the Authentication Manager running on server5118.eng and then writes the output to stdout if there is any change in packet loss for the DTU with ID 080020a893cb or 080020b34231.
This command processes the raw data from the input file raw-out.txt and then writes to stdout only the data for those DTUs that had packet loss.
Copyright © 2006, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.