| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers Topic Set |
Documentation, Support, and Training
Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers Site Planning Guide
Minimum Clearance for Service Access
Agency Compliance Specifications
Operating Environment Requirements
Input Power Information and Precautions
Optional Component Installation
Configuring the Service Processor
Cabling Notes for Both Servers
Port, Connector, and LED Locations for Both Servers
Slide Rail Assembly Notes for Both Servers
Cable Management Notes for Both Servers
Installing the SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers
Installing the Servers in a Rack
Installing the Cable Management Arm for Both Servers
Connecting the Server Cables for Both Servers
Powering On the System for the First Time
Enabling the Service Processor Network Management Port
Logging Into the Service Processor
Log Into the Service Processor Using the Serial Management Port
Configure the Service Processor Network Management Port
Log Into the Service Processor Using the Network Management Port
Using the Service Processor for Common Operations
Perform a Normal System Initialization
Devices in the OpenBoot Device Tree
Boot the Solaris Operating System
Avoid Booting the Solaris Operating System at Startup
Verifying System Functionality
Installing the Servers With the Express Rail Rackmounting Kit
Slide Rail Assembly Notes for the Express Rail Rackmounting Kit
Installing the Servers in a Rack With Express Rails
Installing the Cable Management Arm
Assembling and Installing DC Power Cables for the Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 Server
Requirements for Servers With DC Input Power
DC Supply and Ground Conductor Requirements
Overcurrent Protection Requirements
Assembling and Installing the DC Input Power Cables
Connecting the DC Input Power Cords to the Server
Assembling and Installing DC Power Cables for the Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Server
Requirements for Servers With DC Input Power
Assembling and Installing the DC Input Power Cables
Creating Hardware RAID Volumes
Devices and Device Identifiers
Sun SPARC Enterprise T5x20 Device Tree
Managing Logical Domains Software
Logical Domains Software Overview
View OpenBoot Configuration Variables
OpenBoot Configuration Variables on the SCC
Understanding ILOM 3.0 for the Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers
Platform-Specific ILOM Features
Viewing and Configuring Host Control Information
Managing System User Interactions
Managing the Service Processor
Change Console Escape Characters (CLI)
Changing Configuration Policy Settings
ILOM Information Stored on the SCC
Managing Virtual Keyswitch Settings
Discover IPMI Sensors and Indicators
Sensors on Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers
Indicators on Oracle's Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers
Discover ALOM Compatibility Information
Event Messages Available Through the ALOM Compatibility Shell
SPARC: Infrastructure Boards in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
SPARC: Infrastructure Boards in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Internal System Cables for Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Internal System Cables for Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Front Panel Controls and Indicators on Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Rear Panel Components and Indicators on Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Front Panel Controls and Indicators on Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Rear Panel Components and Indicators on Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Status LEDs for Ethernet Ports and Network Management Port
Diagnostics Tools Quick Reference
Managing Faults Using the PSH Feature
Managing Components With Automatic System Recovery Commands
Detecting Faults Using SunVTS Software
Preparing to Service the System
Find the Chassis Serial Number
Removing Power From the System
Positioning the System for Servicing
Four-Drive Capable Backplane Configuration Reference
Eight-Drive Capable Backplane Configuration Reference
Sixteen-Drive Capable Backplane Configuration Reference
Servicing Motherboard Components
Servicing the Motherboard Assembly
Power Supply Configuration Reference
Servicing Boards and Components
Servicing the Hard Drive Backplane
Servicing Front Control Panel Light Pipe Assemblies
Servicing Power Distribution Boards
Servicing Power Supply Backplanes (Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers)
Returning the Server to Operation
Reinstall the Server in the Rack
Return the Server to the Normal Rack Position
Connect Power Cords to the Server
Power On the Server Using the poweron Command
Power On the Server Using the Front Panel Power Button
Identifying FRUs in SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Motherboard Components in T5120 Servers
I/O Components in SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Power Distribution/Fan Module Components in SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Internal Cables for Onboard SAS Controller Cards in SPARC Enterprise T5120 Servers
Identifying FRUs in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Motherboard Components in T5220 Servers
I/O Components in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Power Distribution/Fan Module Components in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
Internal Cables for Onboard SAS Controller Cards in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
HDD Data Cable Routing for SAS RAID Controller Cards in Sun SPARC Enterprise T5220 Servers
See the instructions in Preparing for Installation.
See the instructions in Installing the SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers.
Configure the terminal or terminal emulator with these settings:
A null modem configuration is needed, meaning the transmit and receive signals are reversed (crossed over) for DTE to DTE communications. You can use the supplied RJ-45 crossover adapters with a standard RJ-45 cable to achieve the null modem configuration.
Note - When you power on the server for the first time and you do not have a terminal or terminal emulator (PC or workstation) connected to the service processor serial management port, you will not see system messages.
(Optional) Connect an Ethernet cable between the server’s NET MGT port and the network to which future connections to the SP and host will be made.
Connect an Ethernet cable between one of the server’s NET ports and the network to which the server will communicate.
Figure 28 Server Connections
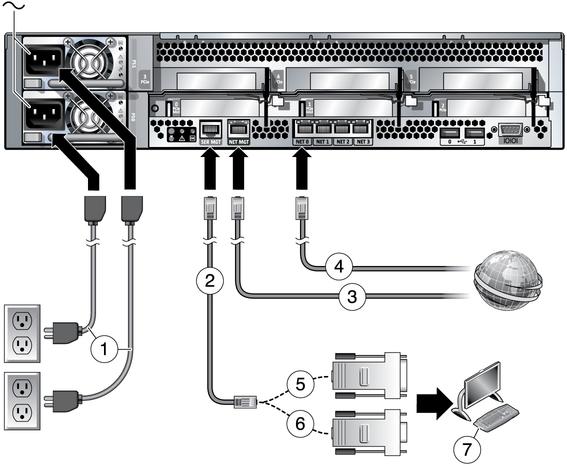
Figure Legend
1 Power Cables
2 Ethernet cables
3 Service processor to ethernet
4 NET MGT to network (optional)
5 RJ-45 to DB-25 crossover adapter
6 RJ-45 to DB-9 crossover adapter
7 Terminal device
To provide redundancy, plug both power supplies into separate power sources.
The system can operate with only one power connection, but there is no redundancy in this case.
The service processor runs on the 3.3V standby voltage. As soon as AC power is connected to the system, the service processor powers on, runs diagnostics, and initializes the ILOM firmware.
After a few minutes, the SP login prompt appears on the terminal device. The host is not initialized or powered on yet.
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX login: root Password: changeme . . . ->
After a brief delay, the SP prompt is displayed (->). At this point, there are many commands you can perform using the Integrated Lights Out Manager interface.
Additional SP information, such as how to change the password and how to set up the SP network parameters is available in the online documentation set.
-> start /SYS Are you sure you want to start /SYS (y/n)? y -> start /SP/console Are you sure you want to start /SP/CONSOLE (y/n)? y Serial console started. To stop, type #. . . .
After you start the SP console, the server initialization takes approximately 20 minutes to complete.
You will be prompted to confirm the configuration several times, enabling confirmation and changes. If you are not sure how to respond to a particular value, you can accept the default, and make future changes when the Solaris OS is running.
|
There are many commands you can use to verify the functionality of the system. The following list describes a few of them:
Review the Solaris OS man pages and documentation for more details.
Sun SPARC Enterprise T5120 and T5220 Servers Administration Guide.