Configuration Tables
This section contains tables that you can use when performing the tasks described in Chapter 2, Initial Host Configuration." It is recommended that you make a copy of these pages and fill out the tables before starting the procedures in Chapter 2, Initial Host Configuration."
Initial Host Configuration
Initial host configuration divides into the following sequence:
-
Network interface configuration
-
Completing initial host configuration (time zone, root password, and so on)
You can perform network interface configuration by either of two ways, the TTY method or the diskette method. These methods, as well as the entire initial host configuration process, are illustrated in Figure 1-4.
Figure 1-4 Initial Host Configuration
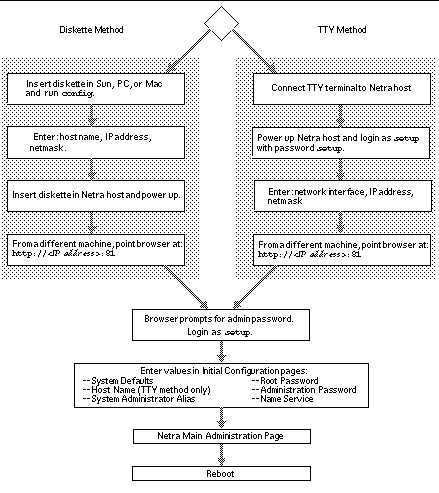
In terms of what you need to know, there is no difference between the TTY and diskette methods. In the diskette method, you enter the Netra Proxy Cache Server's host name during network interface configuration. In the TTY method, you specify a host name following network interface configuration.
Table 1-2 lists the data required for network interface configuration. You perform this configuration on each host in a Netra Proxy Cache Array. Among the data in the table, only the host name and IP address are unique to a single host. The remaining items apply to all hosts in the array.
Table 1-2 Data Required for Network Interface Configuration|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Enter Value Here: |
|---|---|---|
|
network interface (TTY method only) |
This is the network interface (hme0) with which your host name is associated. Your server's other interface (hme1) is used for the control network. Example: hme0 |
hme0 |
|
host name of Netra Proxy Cache Server (diskette method only) |
For convenience, this should be registered in your NIS and/or DNS maps. Example: host1 |
|
|
host IP address of Netra Proxy Cache Server |
Use dotted decimal notation. Make a note of this address. You will use it when configuring the Netra Proxy Cache software. Example: 129.144.118.2 |
|
|
netmask |
Netmask used in service network, in dotted decimal notation. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
|
After you perform network interface configuration, you point a browser at your Netra Proxy Cache Server and complete initial host configuration using the product's administration web pages. Table 1-3 lists the data required to complete initial host configuration.
Table 1-3 Data Required to Complete Initial Host Configuration|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Enter Value Here: |
|---|---|---|
|
time zone |
Time zone in which host resides. Example: US/Pacific |
|
|
locale |
Locale in which host resides. Example: English (Only choice in the current release) |
|
|
host name of Netra Proxy Cache Server (only if you performed TTY method for network interface configuration) |
For convenience, this should be registered in your NIS and/or DNS maps. Example: host1 |
|
|
System administrator alias |
Email addresses that will receive mail addressed to root@<netra host name> or Postmaster@<netra host name>. |
|
|
root password |
There is no default. That is, you start with no root password. |
|
|
administration account name |
The administration account name is setup. |
|
|
administration password |
The default password is setup. You need this password to access the Netra Proxy Cache administration web pages and the setup system account. |
|
|
DNS domain name (if DNS is used) |
Domain in which your Netra Proxy Cache host resides. Examples: acme.com or sales.acme.com |
|
|
IP address of DNS server (if DNS is used) |
Use dotted decimal notation. This is the DNS server outside of the Netra Proxy Cache Array that will resolve the name of the subdomain formed by the array. Example: 129.144.91.24
|
|
|
NIS domain name (if NIS is used) |
NIS domain in which your Netra Proxy Cache host resides. Examples: acme.com or eng.acme.com |
|
Choosing an Administrative Host
Following initial configuration on each host in the Netra Proxy Cache Array, you configure the Netra Proxy Cache software. You perform this configuration on one host in the array. The choice of which machine is arbitrary. We refer to the machine on which you perform configuration as the administrative host.
Proxy Cache Service Configuration
Use your entries in the following tables to respond to prompts in the administrative web pages. In these pages, configuration is broken down as follows:
-
Proxy cache configuration
-
Array configuration
-
Array member configuration
The tables correspond to pages you find in the administrative web pages.
Use the values you enter in Table 1-4 and Table 1-5 to configure the proxy cache service.
Table 1-4 Data for Basic Proxy Cache Configuration|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Enter Value Here: |
|---|---|---|
|
HTTP port |
Port number used by the Netra Proxy Cache Server for receiving web requests. Most users can accept the default of 8080. Example: 8080 |
|
|
Inside firewall? |
In a corporate setting, most proxy cache servers are inside a firewall. |
|
|
Domains inside firewall |
For domains not on this list, if the server cannot find a requested object in its local cache, it always tries to fetch the URL from a parent or sibling. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Parent proxies |
If you are inside a firewall, you probably have a parent proxy. You can have multiple parents. See following table. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
The Netra Proxy Cache Server supports multiple parent and sibling proxies. For each parent of your server, find out the following information:
-
The port it uses for HTTP
-
The port it uses for the Inter Cache Protocol (ICP)
-
Whether it supports tunneling of the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol
-
Whether it supports persistent connections (as supported by popular browsers such as Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer)
(Netscape and Netscape Navigator are trademarks of Netscape Communications Corporation. Microsoft and Internet Explorer are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.)
If your parent is a Netra Proxy Cache Server, keep in mind that the server uses default port numbers of 8080 and 3130, for HTTP and ICP, respectively. Also the Netra Proxy Cache Server supports SSL tunneling and persistent connections.
If your Netra Proxy Cache Server is part of an array, sibling configuration is automatic: there is no need to specify other machines in the array as your siblings. You can specify machines not in the array as siblings.
If your parent is not a Netra Proxy Cache Server, consult the documentation for that server to determine whether it supports ICP, SSL tunneling, and persistent connections.
Table 1-5 Parent Proxies (Enter Names and Values)|
Parent Name |
HTTP Port |
ICP Port (Enter 0 if ICP not supported) |
Support SSL tunneling? (y/n) |
Support persistent connections (y/n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use the values in Table 1-6 to complete basic array configuration.
Table 1-6 Data for Basic Array Configuration|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Enter Value Here: |
|---|---|---|
|
control network |
Subnet number of the control network, expressed as, for example, x.x.x.0 for a Class C netmask. It is recommended that you use 10.0.0.0 or 192.168.0.0. Example: 192.168.89.0 |
|
|
control network netmask |
You can probably accept the default of 255.255.255.0. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
service network |
Subnet number of the service network, expressed as, for example, x.x.x.0 for a Class C netmask. This value must be different from the subnet number used for the control network. Example: 129.144.118.0 (Note that this is the subnet portion of the host IP address and of the proxy cache and DNS service addresses) |
|
|
service network netmask |
The default is 255.255.255.0. Example: 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
Proxy cache domain name |
Name of the DNS domain formed by the hosts in the array. Example: cache.acme.com |
|
|
Array DNS service address |
An IP address associated with the DNS on the array DNS server. As a service address, this address is subject to moving to a different host upon host failure. Example: 129.144.118.200 |
|
|
Array DNS host name |
Host name of the host within the array that will act as the DNS server for the domain formed by the array. You can choose any machine in the array. It is strongly recommended that you use your administrative host. Example: host1 |
|
Use the data in Table 1-7 to complete basic array member configuration.
Table 1-7 Data for Basic Array Member Configuration|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Enter Value Here: |
|---|---|---|
|
For each host in the array: |
||
|
host name |
Just as you entered it during initial configuration. See Table 1-1. Example: host1 |
|
|
host address |
IP address associated with hme0 interface. This is the address you specified as the IP address of the Netra Proxy Cache Server during initial configuration. See Table 1-1. Unlike a service address, this address is not subject to moving to a different host. This address must have the same subnet number that you specified for the service network. Example: 129.144.118.2 |
|
|
control address |
IP address associated with the hme1 interface, used to connect to the control network. This address must have the same subnet number that you specified for control network. See Table 1-5. Example: 192.168.89.1 |
|
|
service address |
An IP address associated with the proxy cache service on a host. As a service address, this address is subject to moving to a different host upon host failure. This address must have the same subnet number as the host address, above. This is also the same subnet number you specified for the service network. See Table 1-5. Example: 129.144.118.100 |
|
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
