3 Using the Connector
After you deploy the connector, you must configure it to meet your requirements.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Note:
These sections provide both conceptual and procedural information about configuring the connector. It is recommended that you read the conceptual information before you perform the procedures.
3.1 Configuring Reconciliation
Reconciliation involves duplicating in Oracle Identity Manager the creation of and modifications to user accounts on the target system. While configuring the connector, the target system can be designated as a trusted source or target resource.
If you designate the target system as a trusted source, then during a reconciliation run:
- For each newly created user on the target system, an Oracle Identity Manager User is created.
- Updates made to each user on the target system are propagated to the corresponding Oracle Identity Manager User.
If you designate the target system as a target resource, then during a reconciliation run:
- For each account created on the target system, a resource is assigned to the corresponding Oracle Identity Manager User.
- Updates made to each account on the target system are propagated to the corresponding resource.
This section discusses the following topics related to configuring reconciliation:
- Full Reconciliation
- Limited Reconciliation
- Batched Reconciliation
- Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation
- Reconciliation Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
- Configuring the Target System As a Trusted Source
- Reconciliation Rule for Trusted Source Reconciliation
- Reconciliation Action Rule for Trusted Source Reconciliation
3.1.1 Full Reconciliation
Full reconciliation involves reconciling all existing user records from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager. After you deploy the connector, you must first perform full reconciliation.
To perform a full reconciliation run, remove (delete) any value currently assigned to the Filter attribute of the UNIX Target Resource Full User Reconciliation scheduled task. See Scheduled Tasks for Reconciliation for information about this scheduled task.
During a full reconciliation run, if you provide both batching parameters and filters, the connector processes the data in batches. Then, filters are applied to the processed data.
3.1.2 Limited Reconciliation
By default, all target system records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are reconciled during the current reconciliation run. You can customize this process by specifying the subset of added or modified target system records that must be reconciled.
The connector provides a Filter attribute that allows you to use any of the UNIX resource attributes to filter the target system records.
You can perform limited reconciliation by creating filters for the reconciliation module. This connector provides a Filter attribute (a scheduled task attribute) that allows you to use any of the UNIX resource attributes to filter the target system records.
For detailed information about ICF Filters, see ICF Filter Syntax in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager.
While deploying the connector, follow the instructions in Configuring Scheduled Tasks to specify attribute values.
3.1.3 Batched Reconciliation
During a reconciliation run, all changes in the target system records are reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. Depending on the number of records to be reconciled, this process may require a large amount of time. In addition, if the connection breaks during reconciliation, then the process would take longer to complete.
You can configure batched reconciliation to avoid these problems.
To configure batched reconciliation, you must specify values for the following user reconciliation scheduled task attributes:
-
Batch Size: Use this attribute to specify the number of records that must be included in each batch.
-
Batch Start Index: Use this attribute to specify the position from which the records will be included in each batch.
-
No. of Batches: Use this attribute to specify the total number of batches that must be reconciled.
By default, the values of all attributes is 0, indicating that all records will be included (no batched reconciliation). The following example illustrates this:
Suppose that of a total 314 records, only 200 records were processed before encountering an exception or an error. During the next reconciliation run, you can set Batch Start Index to 200 to process the records from 200 to 314.
You specify values for these attributes by following the instructions described in Configuring Scheduled Tasks.
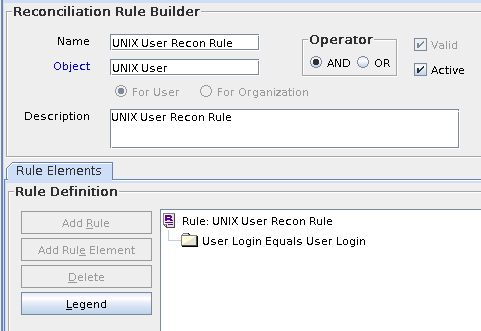
3.1.4 Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation
The following is the process-matching rule:
Rule name: UNIX User Recon Rule
Rule element: User Login equals User Login
In this rule:
-
User Login for Oracle Identity Manager:
User ID attribute on the OIM User form
-
User Login is the User Login Name attribute of the target system.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation rule for target resource reconciliation by performing the following steps:
Note:
Perform the following procedure only after the connector is deployed.
3.1.5 Reconciliation Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
This section lists the action rules for target resource reconciliation and suggests the procedure to view them.
Table 3-1 lists the action rules for target resource reconciliation.
Table 3-1 Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
None |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
Note:
No action is performed for rule conditions that are not predefined for this connector. You can define your own action rule for such rule conditions. See Setting a Reconciliation Action Rule in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for information about modifying or creating reconciliation action rules.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation action rules for target resource reconciliation by performing the following steps:
- Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Expand Resource Management.
- Double-click Resource Objects.
- Search for and open the UNIX User resource object.
- Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector.
3.1.6 Configuring the Target System As a Trusted Source
To configure trusted source reconciliation:
Note:
Skip this section if you do not want to designate the target system as a trusted source for reconciliation.
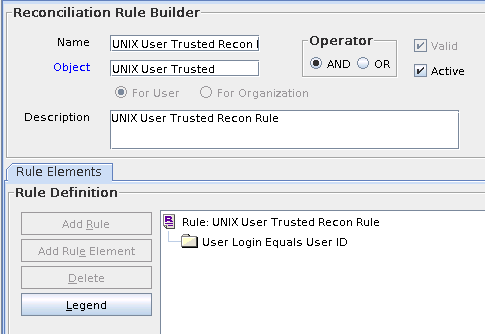
3.1.7 Reconciliation Rule for Trusted Source Reconciliation
This section describes the reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation.
Note:
Skip this section if the target system is not designated as a trusted source for reconciliation.The following is the process matching rule:
Rule name: UNIX User Trusted Recon Rule
Rule element: User Login Equals User ID
In this rule element:
-
User Login for Oracle Identity Manager:
User ID attribute on the OIM User form.
-
User ID is the User Login Name attribute of the target system.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation by performing the following steps:
Note:
Perform the following procedure only after the connector is deployed.
3.1.8 Reconciliation Action Rule for Trusted Source Reconciliation
This section lists the action rules for trusted resource reconciliation and suggests the procedure to view them.
Note:
Skip this section if the target system is not designated as a trusted source for reconciliation.
Table 3-2 lists the action rules for trusted resource reconciliation.
Table 3-2 Action Rules for Trusted Source Reconciliation
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Create User |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
Note:
No action is performed for rule conditions that are not predefined for this connector. You can define your own action rule for such rule conditions. See Setting a Reconciliation Action Rule in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for information about modifying or creating reconciliation action rules.
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation action rules for trusted source reconciliation by performing the following steps:
- Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Expand Resource Management.
- Double-click Resource Objects.
- Search for and open the UNIX User Trusted resource object.
- Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector.
3.2 Scheduled Tasks
When you run the Connector Installer or import the connector XML file, reconciliation scheduled tasks are automatically created in Oracle Identity Manager.
This section discusses the following topics related to scheduled tasks:
3.2.1 Scheduled Tasks for Lookup Field Synchronization
The following scheduled tasks are used for lookup field synchronization:
-
UNIX User Primary Group Lookup Reconciliation
This scheduled task is used to synchronize the primary group names available on the target system into the Lookup.UNIX.PrimaryGroup lookup definition.
-
UNIX User Shell Lookup Reconciliation
This scheduled task is used to synchronize the default shell on the target system into the Lookup.UNIX.UserShell lookup definition.
You must specify values for the attributes of these scheduled jobs. Table 3-3 describes the attributes of these scheduled tasks. The procedure to configure scheduled tasks is described later in the guide.
Table 3-3 Attributes of the Scheduled Tasks for Lookup Field Synchronization
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Code Key Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Code Key column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Depending on the scheduled task you are using, the default values are as follows:
Note: You must not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Decode Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Decode column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Sample value: |
|
IT Resource Name |
Enter the name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile user records. Default value: |
|
Lookup Name |
This attribute holds the name of the lookup definition that maps each lookup definition with the data source from which values must be fetched. Depending on the scheduled task you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Type |
Enter the type of object whose values must be synchronized. Depending on the scheduled task you are using, the default values are as follows:
Note: You must not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Resource Object Name |
Enter the name of the resource object that is used for reconciliation. Default value: |
3.2.2 Scheduled Tasks for Reconciliation
You can use reconciliation scheduled job to reconcile user account data from the target system.
To reconcile user data in the target resource (account management) mode of the connector:
-
UNIX Target Resource Full User Reconciliation
This scheduled task is used to reconcile all user data from the target system.
-
UNIX Target Incremental Resource User Reconciliation
This scheduled task is used to reconcile only records created, modified, or deleted after the last reconciliation run.
Note:
Full target and trusted reconciliation scheduled tasks do not support reconciliation of deleted records.
To reconcile user data in the trusted source (identity management) mode of the connector:
-
UNIX User Trusted Recon
This scheduled task is used to reconcile all user data from the target system.
-
UNIX User Trusted Incremental Recon
This scheduled task is used to reconcile only records created, modified, or deleted after the last reconciliation run.
The following is the behavior of incremental reconciliation scheduled tasks:
- Incremental reconciliation scheduled tasks do not support filtering of records.
- Incremental reconciliation scheduled tasks fetch data from the target system in alphabetical order.
- If you run an incremental reconciliation scheduled task for the first time, or if you run the task after removing the value of Sync Token parameter, then the following directories (or the directory specified in the configuration lookup definition) must be empty:
connector_mirror_files
connector_mirror_files_trusted
- After an incremental reconciliation scheduled task completes, the following files will be generated in the connector_mirror_files or connector_mirror_files_trusted directory (or in the directory specified in the configuration lookup definition). Here, SYNC_TOKEN refers to the value of the Sync Token parameter.
- SYNC_TOKEN.passwd file contains previous copy of the password file in the /etc directory, for example,
/etc/passwd. - SYNC_TOKEN.shadow file contains previous copy of the shadow file in the /etc directory, for example,
/etc/shadow. - SYNC_TOKEN.group file contains previous copy of the group file in the /etc directory, for example,
/etc/group. - passwd_difference_incr file contains differences between the
/etc/passwdand the SYNC_TOKEN.passwdfiles. - shadow_difference_incr file contains differences between the
/etc/shadowand the SYNC_TOKEN.shadowfiles. - group_difference_incr file contains differences between the
/etc/groupand the SYNC_TOKEN.groupfiles. - record file contains the actual records that will be sent back to Oracle Identity Manager in alphabetically sorted order.
- SYNC_TOKEN.passwd file contains previous copy of the password file in the /etc directory, for example,
Table 3-4 describes the attributes of the scheduled tasks.
Table 3-4 Attributes of the Scheduled Tasks for Reconciliation
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Batch Size Note: The data fetched by an incremental reconciliation scheduled task is sorted in alphabetical order. |
Specify the number of records that must be included in each batch Default value: See Batched Reconciliation for more information. |
|
Batch Start Index Note: The data fetched by an incremental reconciliation scheduled task is sorted in alphabetical order. |
Specify the position from which the records will be included in each batch Default value: |
|
No. of Batches Note: The data fetched by an incremental reconciliation scheduled task is sorted in alphabetical order. |
Specify the total number of batches that must be reconciled Default value: |
|
Filter Note: Incremental reconciliation scheduled task does not support filtering of records. |
Expression for filtering records that must be reconciled by the scheduled task By default, the value of this attribute is empty. Sample value: See Limited Reconciliation for the syntax of this expression. |
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile user records Default value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object that is used for reconciliation Default value for UNIX Target Resource Full User Reconciliation: Default value for other scheduled tasks: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Note: For the scheduled task shipped with this connector, you must not change the value of this attribute. However, if you create a copy of the task, then you can enter the unique name for that scheduled task as the value of this attribute. |
|
Sync Token |
Time stamp at which the last reconciliation run started Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value for this attribute. If you set this attribute to an empty value, then incremental reconciliation operations fetch all the records (perform full reconciliation). |
3.2.3 Configuring Scheduled Tasks
Configure scheduled jobs to perform reconciliation runs that check for new information on your target system periodically and replicates the data in Oracle Identity Manager.
To configure a scheduled task:
-
Depending on the Oracle Identity Manager release you are using, perform one of the following steps:
- For Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1:
-
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
-
On the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Self Service page, click Advanced in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
- For Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration. For detailed instructions on creating and activating a sandbox, see Managing Sandboxes in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Create and activate a sandbox.
-
In the left pane, under System Management, click Scheduler.
-
- For Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1:
-
Search for and open the scheduled job as follows:
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1, then on the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Advanced Administration page, in the System Management region, click Search Scheduled Jobs.
-
In the Search field, enter the name of the scheduled job as the search criterion. Alternatively, you can click Advanced Search and specify the search criterion.
-
In the search results table on the left pane, click the scheduled job in the Job Name column.
-
-
On the Job Details tab, you can modify the following parameters:
Retries: Enter an integer value in this field. This number represents the number of times the scheduler tries to start the job before assigning the Stopped status to the job.
Schedule Type: Depending on the frequency at which you want the job to run, select the appropriate schedule type.
Note:
See Creating Jobs in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about schedule types.
In addition to modifying the job details, you can enable or disable a job.
-
On the Job Details tab, in the Parameters region, specify values for the attributes of the scheduled task.
Note:
-
Attribute values are predefined in the connector XML file that you import. Specify values only for those attributes that you want to change.
-
Attributes of the scheduled task are discussed in Scheduled Tasks for Reconciliation.
-
-
After specifying the attributes, click Apply to save the changes.
Note:
The Stop Execution option is available in the Administrative and User Console. You can use the Scheduler Status page to either start, stop, or reinitialize the scheduler.
3.3 Configuring Provisioning in Oracle Identity Manager Release 11.1.1
Provisioning a resource for an OIM User involves using Oracle Identity Manager to create a target system account for the user.
If you have configured the connector for request-based provisioning, then the process form is suppressed and the object form is displayed. In other words, direct provisioning is disabled when you configure the connector for request-based provisioning. If you want to revert to direct provisioning, then perform the steps described in Switching Between Request-Based Provisioning and Direct Provisioning.
The following are types of provisioning operations:
-
Direct provisioning
-
Request-based provisioning
-
Provisioning triggered by policy changes
See Also:
Manually Completing a Task in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Manager for information about the types of provisioning
This section discusses the following topics:
3.3.1 Guidelines on Performing Provisioning Operations
These are the guidelines that you must apply while performing provisioning operations.
Apply the following guidelines while performing provisioning operations:
-
While performing a Create User provisioning operation, before populating the Skeleton directory field, data must be populated in the Home Directory field and the Create Home Directory check box must also be selected.
-
The value in the Home Directory field must not contain spaces.
-
The maximum permitted date value for account expiry is 31-Dec-2099. It should also be a future date.
-
On HP-UX, while performing a Create User provisioning operation, the Inactive Days field must be populated only when the UNIX server is configured in trusted mode.
-
The Primary Group Name and the Secondary Group Names must have different values. The target system ignores the duplicate values.
3.3.2 Configuring Direct Provisioning
When you install the connector on Oracle Identity Manager, the direct provisioning feature is automatically enabled. This means that the process form is enabled when you install the connector.
In direct provisioning, the Oracle Identity Manager administrator uses the Administrative and User Console to create a target system account for a user.
To provision a resource by using the direct provisioning approach:
3.3.3 Configuring Request-Based Provisioning
The following sections give you a brief about request-based provisioning and how to enable them:
3.3.3.1 About Request-Based Provisioning
In request-based provisioning, an end user creates a request for a resource by using the Administrative and User Console. Administrators or other users can also create requests for a particular user. Requests for a particular resource on the resource can be viewed and approved by approvers designated in Oracle Identity Manager.
The following are features of request-based provisioning:
-
A user can be provisioned only one resource (account) on the target system.
Note:
Direct provisioning allows the provisioning of multiple target system accounts on the target system.
-
Direct provisioning cannot be used if you enable request-based provisioning.
Note:
The request dataset provided with the connector does not contain the User Login field, which is usually fed directly from Oracle Identity Manager user profile to the process form using a prepopulate adapter.
To include the User Login field in request dataset, perform the following procedure:
- Export the current dataset using the MDS export utility.
- Update the dataset to include the User Login field.
- Import the updated dataset using the MDS import utility.
- Purge the cache, as described in Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache.
3.3.3.2 Enabling Request-Based Provisioning
The following sections discuss the steps to be performed to enable request-based provisioning:
Note:
The procedures described in these sections are built on an example in which the end user raises or creates a request for provisioning a target system account. This request is then approved by the approver.
3.3.3.2.1 End User's Role in Request-Based Provisioning
The following steps are performed by the end user in a request-based provisioning operation:
3.3.3.2.2 Approver's Role in Request-Based Provisioning
The following are steps performed by the approver in a request-based provisioning operation:
3.3.3.2.3 Importing Request Datasets Using Deployment Manager
A request dataset is an XML file that specifies the information to be submitted by the requester during a provisioning operation. These request datasets specify information about the default set of attributes for which the requester must submit information during a request-based provisioning operation.
To import a request dataset XML file by using the Deployment Manager:
3.3.3.2.4 Enabling the Auto Save Form Feature
To enable the Auto Save Form feature:
- Log in to the Design Console.
- Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
- Search for and open the SSH User process definition.
- Select the Auto Save Form check box.
- Click Save.
3.3.3.2.5 Running the PurgeCache Utility
Run the PurgeCache utility to clear content belonging to the Metadata category from the server cache. See Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache for instructions.
The procedure to configure request-based provisioning ends with this step.
3.3.4 Switching Between Request-Based Provisioning and Direct Provisioning
During the provisioning operation, you can switch between request request-based provisioning to direct provisioning.
Note:
It is assumed that you have performed the procedure described in Configuring Request-Based Provisioning.To switch from request-based provisioning to direct provisioning:
-
Log in to the Design Console.
-
Disable the Auto Save Form feature as follows:
-
Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
-
Search for and open the UNIX User process definition.
-
Deselect the Auto Save Form check box.
-
Click the save icon.
-
-
If the Self Request Allowed feature is enabled, then:
-
Expand Resource Management, and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the UNIX User resource object.
-
Deselect the Self Request Allowed check box.
-
Click the save icon.
-
To switch from direct provisioning back to request-based provisioning:
-
Log in to the Design Console.
-
Enable the Auto Save Form feature as follows:
-
Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
-
Search for and open the UNIX User process definition.
-
Select the Auto Save Form check box.
-
Click the save icon.
-
-
If you want to enable end users to raise requests for themselves, then:
-
Expand Resource Management, and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the UNIX User resource object.
-
Select the Self Request Allowed check box.
-
Click the save icon.
-
3.4 Configuring Provisioning in Oracle Identity Manager Release 11.1.2
Provisioning involves creating and updating users on UNIX through Oracle Identity Manager.
To configure provisioning operations in Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x:
Note:
The time required to complete a provisioning operation that you perform the first time by using this connector takes longer than usual.
-
Log in to Oracle Identity Administrative and User console.
-
Create a user. See Managing Users in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Manager for more information about creating a user.
-
On the Account tab, click Request Accounts.
-
In the Catalog page, search for and add to cart the application instance, and then click Checkout.
-
Specify values for fields in the application form and then click Ready to Submit.
-
Click Submit.
-
If you want to provision a UNIX User, then:
-
On the Users page, search for the required user.
-
On the user details page, click Accounts.
-
Click the Request Accounts button.
-
Search for the UNIX application instance in the catalog search box and select it.
-
Click Add to Cart.
-
Click Checkout.
-
Specify values for fields in the application form and then click Ready to Submit.
-
Click Submit.
-
3.5 Configuring Action Scripts
Actions are scripts that you can configure to run before or after the create, update, or delete an account provisioning operations. For example, you could configure a script to run before every user creation.
Every connector should specify which scripting language and which target it supports. The UNIX connector supports the following script:
- shell: shell script
- target: Resource
The target refers to the location where the script is executed. In this case, the script is executed on the computer where the target resource is running (and is typically interpreted by the target computer).
To configure the action:
Now, this action will be executed every time you create a user. You must configure these three values for each action you want to execute.