40 Update A/R Information for Customer Analysis
This chapter includes the following topics:
40.1 Updating A/R Information for Customer Analysis
From Accounts Receivable (G03), choose Credit/Collection Management
From Credit & Collection Management (G0315), choose Credit Analysis Refresh
To effectively analyze and manage account activity for a customer, you should update the customer's A/R information. To do so, run Credit Analysis Refresh (P03525) at the beginning or end of each business day. This ensures that the credit and collections information for the customer is current.
When you run Credit Analysis Refresh, the system includes all the customers with an open balance (regardless of whether the balance is past due) in the A/R Cash Management worktable.
After you run Credit Analysis Refresh, you can determine which customers:
-
Are over their credit limit
-
Are due for a credit review
-
Have overdue balances on their account
-
Are due for a collection review
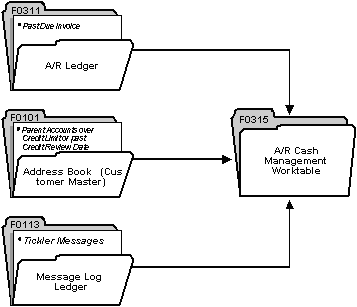
When you run Credit Analysis Refresh, the system gathers information from the following tables and then updates the A/R Cash Management worktable (F0315):
-
A/R Ledger (F0311)
-
Customer Master (F0301)
-
Electronic Mail (F0113)
If you update parent information and do not run Update A/R from Address Book (P03802) before running Credit Analysis Refresh, you might have customers who are associated with two or more parent records. This can result in duplicate records for the same customer.
40.1.1 Temporary Credit Messages
The Credit Analysis program also updates the temporary credit messages on Customer Master Information based on the settings of the Temporary Credit Messages processing options for the program.
The following graphic illustrates the types of information that the system updates in the A/R Cash Management worktable.
Figure 40-1 A/R Cash Management Worktable
Description of ''Figure 40-1 A/R Cash Management Worktable''
40.1.2 Example: Updating Credit Messages
The following example shows a customer record before and after it is updated by the Credit Analysis Refresh program.
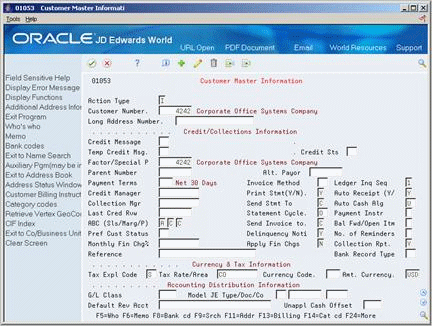
40.1.2.1 Before
On Customer Master Information, both the credit message and temporary credit message information is blank for customer 3333.
Figure 40-2 Customer Master Information (Before) screen
Description of ''Figure 40-2 Customer Master Information (Before) screen''
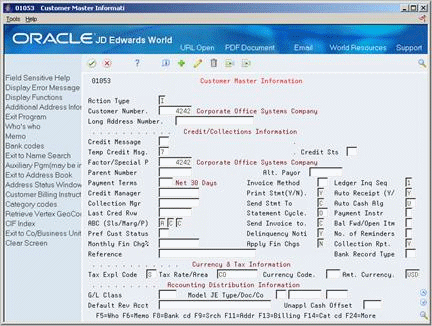
40.1.2.2 After
Notice that the temporary credit message code is now set to 7, On Credit Hold per Accounting. Customer 3333 has an invoice that is past due within the 91-to-120-day aging category. The permanent credit message remains unchanged.
Figure 40-3 Customer Master Information (After) screen
Description of ''Figure 40-3 Customer Master Information (After) screen''
40.1.3 Technical Considerations
When you run Credit Analysis Refresh, the system creates a minimum of four records in the A/R Cash Management table (F0315) for each customer. For example, if you enter one invoice for customer 1234 for company 00001, the system creates the following records in the table:
-
One record for the child information (RTPART = C) for the company that the invoice was entered against (RTCO = 00001).
-
One record for the child information (RTPART = C) for company 00000. The system uses the record for company 00000 to total the information for all company records.
-
One record for the parent information (RTPART = P) for the company that the invoice was entered against (RTCO = 00001). Even if you do not use parent/child relationships, the system still generates a parent record.
-
One record for the parent information (RTPART = P) for company 00000 (RTCO = 00000). The system uses the record for company 00000 to total the information for all company records.
If you had invoices entered for multiple companies, the system would generate additional records, one record for each company for both the child and the parent.
40.1.4 Before You Begin
-
Run the Update A/R from Address Book program to ensure that the A/R Ledger table contains current information.
-
Use processing options for this program to define the aging criteria. You may either use Accounts Receivable Constants to specify how the system ages your customer's invoice information or set up the aging criteria in the specific aging processing options. For example, you define the following information that the system uses to determine whether an account is delinquent and if it is, the number of days it is delinquent:
-
The aging method
-
The date that the aging is based on
-
The beginning and ending aging categories
-
See Chapter 70, "Set Up A/R Constants" for information about setting up A/R aging information.
40.1.5 Processing Options
See Section 106.1, "Credit Analysis Refresh (P03525)" for more information.
40.2 Import Mass Data into A/R
You can run the Address Book Credit Management/Granting Z File (P0305Z) program which accepts data from the Address Book - Credit Management/Granting Z File (F0305Z) and allows you to process mass amounts of data easily and efficiently. This Z File program accepts data from an outside source and uses the Credit Granting/Management (P0305) program to validate the data.
You can process any number of records to add, change, or delete. You also have the advantage of:
-
Data selection to limit the records you want to process.
-
Processing options that allow you to choose the version of the interactive program to process the records.
-
Error report printing.
See:
From Customer Master Z File Processes (G0301Z), choose Credit Granting and Management
40.2.1 Processing Options
See Section 106.3, "Credit Granting and Management (P0305)" and Section 106.4, "Address Book Credit Management/Granting Z File (P0305Z)" for more information.