Oracle® Enterprise Manager Ops Center
Configuring and Installing Logical Domains
12c Release 1 (12.1.2.0.0)
E27355-02
November 2012
This guide provides an end-to-end example for how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center.
Introduction
Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center, you can configure and install logical domains on Oracle VM Server for SPARC systems.
A logical domain is a virtual machine with resources, such as a boot environment, CPU threads, memory, I/O devices, and its own operating system that runs independently on Oracle VM Server for SPARC Control Domain.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center provides a complex plan that includes the steps to create logical domains and to provision an operating system on them.
This guide describes how to create two logical domains on an Oracle VM Server for SPARC system. The logical domains will have the following characteristics:
-
Resource configuration of 8 CPU threads, 4 GB of memory, and 50 GB of disk space.
-
NAS Storage library to store the metadata and for the storage disk space.
-
Oracle Solaris 10 9/10 operating system to provision the logical domains.
-
Operating system installed with Agent Controller.
-
Operating systems are not placed in a server pool.
See Related Articles and Resources for more information about Oracle VM Server for SPARC and creating logical domains.
What You Will Need
You will need the following to configure and deploy logical domains:
-
Oracle VM Server for SPARC system
A server installed and configured with Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 using Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. Refer to the guide Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Deploying and Configuring Oracle VM Server for SPARC.
-
Network Connection
A network connected to the Control Domain. The logical domains and the Control Domain must be in the same subnet. When you want to use a particular network to the logical domains, you must first attach it to the Control Domain. Refer to Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for more information about attaching networks to the Control Domain.
-
Storage Libraries
A NAS storage library associated with Oracle VM Server for SPARC. The library is used to store the logical domain metadata and to provide disk space.
You must allocate appropriate virtual disk to the logical domains. The minimum size of the virtual disk for the logical domain to contain the Oracle Solaris OS is 8 GB. The maximum size of the virtual disk is 100 GB. In this example, allocate 50 GB to each logical domain.
-
OS Image
An Oracle Solaris 10 9/10 OS image to provision OS on the logical domains. Upload the OS image into Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. Refer to Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for more information about uploading or importing OS images.
-
Roles and Permissions
A user with Virtualization Admin and Profile and Plan Admin roles to create and install logical domains, and to create profiles and plans.
Hardware and Software Configuration
In this example, the logical domains are installed on Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 version. The Control Domain is configured and deployed in stand-alone mode and it is not placed in a server pool.
A sample Oracle VM Server for SPARC configuration is summarized as follows:
-
UltraSPARC T2 server – Sun SPARC Enterprise T5240 Server
Eight core with eight threads per each core. Total 64 CPU threads.
32 GB memory
-
Installed with Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 version
-
The Control Domain is configured with the following parameters:
-
Eight CPU threads
-
One complete core and one Crypto Unit
-
Four GB of memory
-
Configuring and Installing Logical Domains
The steps to configure and install logical domains are as follows:
Create a Logical Domain Profile
Create a logical domain with the resource requirements as described in the previous section.
-
Click the Plan Management section.
-
Expand Profiles and Policies and select Logical Domain.
-
Click Create Profile from the Actions pane.
The Create Logical Domain Profile wizard is displayed.
-
Enter a name and description to identify the profile.
Deselect the option Create a deployment plan for this profile.
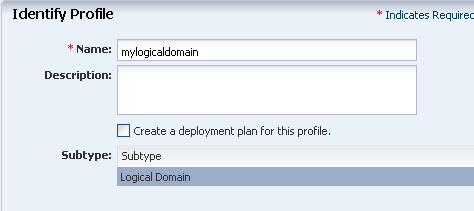
Description of the illustration identify_profile.gif
Click Next.
-
Enter the name of the logical domain as TestDomain and the starting number as 10. The two logical domains will be created with the names TestDomain10 and TestDomain11.
Provide description and add new tags for the logical domain. All the logical domains created using this profile uses the same description and tags.
Click Next to configure the CPU Threads and memory.
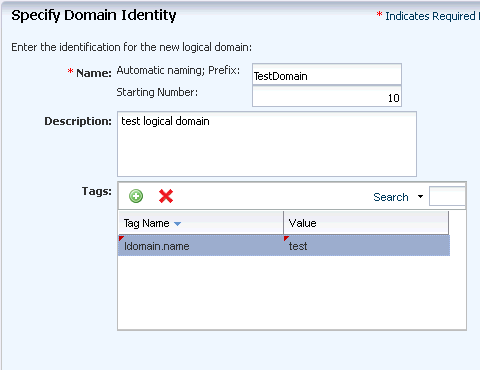
Description of the illustration domain_identity.gif
-
The physical CPUs of the Oracle VM Server are shared among the CPU threads of all the logical domains. Enter the values for CPU Threads and memory to be allocated for a logical domain:
-
CPU Threads – 8
-
Memory – 4 GB
-
Do not specify a value for Crypto Units. Depending on the number of CPU threads, the Crypto units are assigned automatically.
-
Select Automatic Recovery and provide the value of Priority of Recovery as 10.
Click Next to specify the storage for the logical domains.
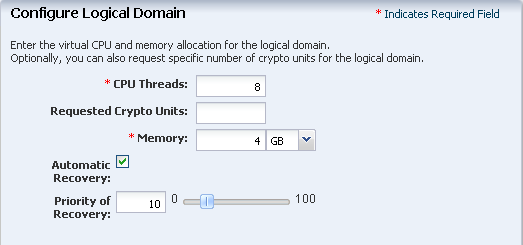
Description of the illustration cpu_memory_configure.gif
-
-
Select a NAS storage library to store the logical domain's metadata and for the storage virtual disks. Enter the disk size as 50 GB.
Click Next to specify the networks for the domains.
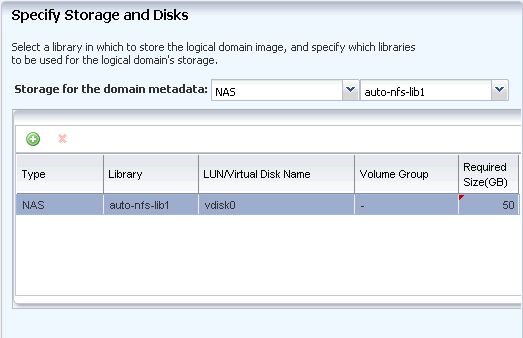
Description of the illustration domain_storage.gif
-
Select the network from the list of networks that are in the same subnet as that of the Control Domain. Enter the number of connections for the network.
Click Next to view the summary of the logical domain details.
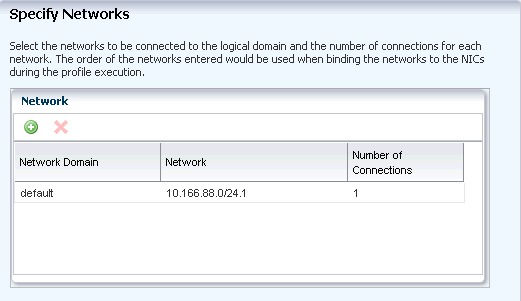
Description of the illustration third_netw_assign.gif
-
Review the information and click Finish to save the profile.
Create an OS Provisioning Profile and Plan
Upload or import an Oracle Solaris 10 9/10 OS image into Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. Do not use the default profile and plan created while importing the image. Instead, create a new OS provisioning profile and plan.
-
Click the Plan Management section in the Navigation pane.
-
Expand Profiles and Policies and choose OS Provisioning profile.
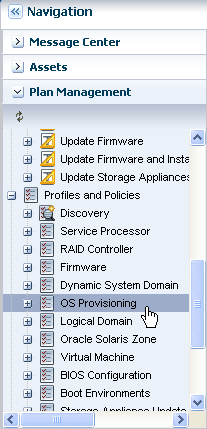
Description of the illustration select_os_prov.png
-
Click Create Profile in the Actions pane.
The Create Profile - OS Provisioning wizard is displayed.
-
Provide the following details for the profile identification:
-
Enter the name of the profile as ldom_os_profile.
-
Enter a suitable description for the profile.
-
Deselect the option Create a deployment plan for this profile.
-
Select Solaris SPARC as the Subtype.
Click Next to specify the provisioning parameters.
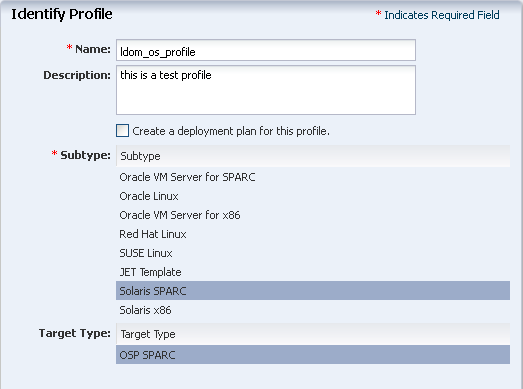
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_1.png
-
-
Select the following OSP parameters:
-
Select the image from the list.
All the images for Oracle Solaris OS on SPARC platform are listed.
-
Select Entire Distribution Plus OEM Support as the Software Group.
Click Next to specify the OS Setup.
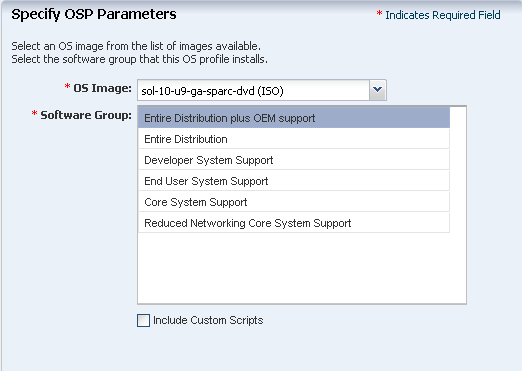
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_2.png
-
-
Specify the OS setup parameters:
-
Enter the time zone, language, terminal type, console serial port, and console baud rate.
-
Enter the password.
-
The NFS4 domain is set to dynamic in this example. If a naming service is configured in your environment, enter the NFS4 domain value.
-
Select Deploy Agent Controller to manage the OS by Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center.
Click Next.
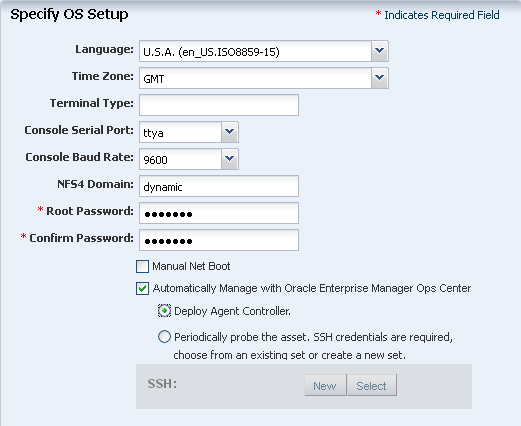
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_3.png
-
-
It is optional to install any Jumpstart Enterprise Toolkit (JET) modules. Skip this step and click Next.
-
Specify the file system layout for the OS. Retain the default partition that is displayed.
Click Next to specify the naming service.
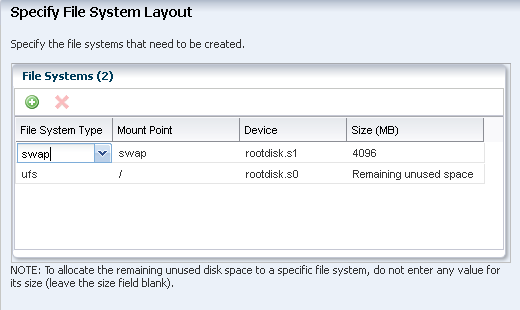
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_4.png
-
Select None as there are no name services configured in the environment.
If you have naming services configured in your environment, select the appropriate service and provide the details of the name service.
Click Next.
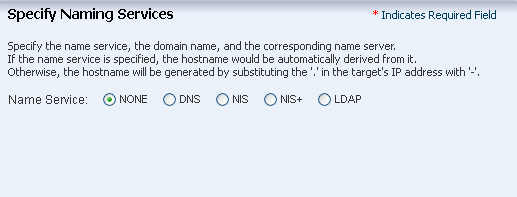
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_5.png
-
In this example, we will not specify any networking options for the operating system. Select None and click Next to continue.

Description of the illustration os_profile_step_6.png
-
Select the networks that you want to attach to the operating system. You can attach multiple networks to the operating system.
Click Next to continue.
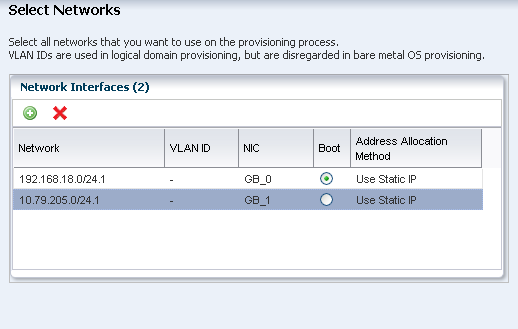
Description of the illustration os_profile_step_7.png
-
Click Finish to create the OS provisioning profile.
The OS provisioning profile is created and listed under the OS provisioning profiles. Use this profile to create an Install Server plan.
Create Install Server Plan
In this example, create an Install Server Plan using the OS provisioning profile created in the previous section. The Install Server plan provides the steps to provision OS, install software, updates and scripts, and add monitoring thresholds.
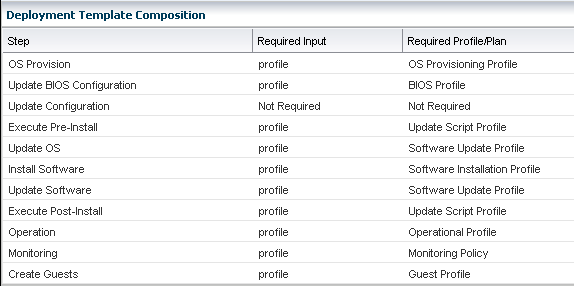
Description of the illustration install_server_compo.png
In this example to configure and install logical domains, limit the Install Server Plan to only provision the OS and skip the other steps.
-
Click the Plan Management section in the Navigation pane.
-
Expand Deployment Plans and select Install Server.
Description of the illustration show_install_server.png
-
Click Create Plan from Template in the Actions pane.
The Create a Deployment Plan window is displayed.
-
Enter the following details for the plan:
-
Enter the name and description for the plan.
-
Select Stop at Failure option for the failure policy.
-
In the OS Provision step, select the OS provisioning profile from the list.
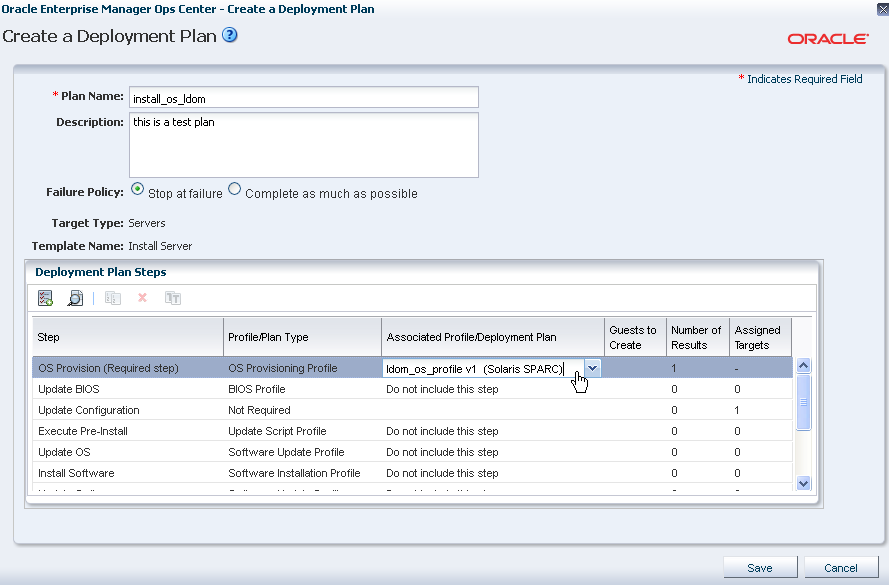
Description of the illustration install_server_plan_create.png
-
-
Click Save to create the deployment plan.
The new Install Server deployment plan appears under the list of Install Server plans.
At this point, you must have created a logical domain profile and an OS provisioning plan to provision OS on a logical domain. Use these profile and plan in the complex plan to configure and install logical domains.
Create Configure and Install Logical Domain Plan
The configure and install logical domain plan is a complex plan that includes the following steps:
-
Create Logical Domains – Requires the logical domain profile.
-
Install and Update OS – Requires the Install Server plan that includes the OS provisioning profile and other updates.
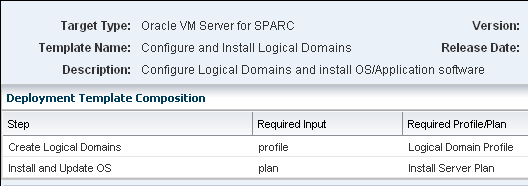
Description of the illustration config_instl_plan.gif
Provide the logical domain profile and OS provisioning plan created in the previous steps and create the plan.
-
Click the Plan Management section.
-
Expand Deployment Plans and choose Configure and Install Logical Domains plan.
-
Click Create Plan from Template in the Actions pane.
Create a Deployment Plan window displays.
-
Enter the name and description for the new plan.
-
Select Stop at Failure for the failure policy.
-
In the Deployment Plan Steps, select the logical domain profile and the OS provisioning plan created in the previous sections.
-
Enter the number of guests to create as 2. This is the number of logical domains to create.
The number of assigned targets for the Install and Update OS step automatically changes to 2. The logical domains created using this plan will have the same OS provisioning plan applied on them.
If you want to assign a different OS provisioning plans to the logical domains, refer to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide for more information.
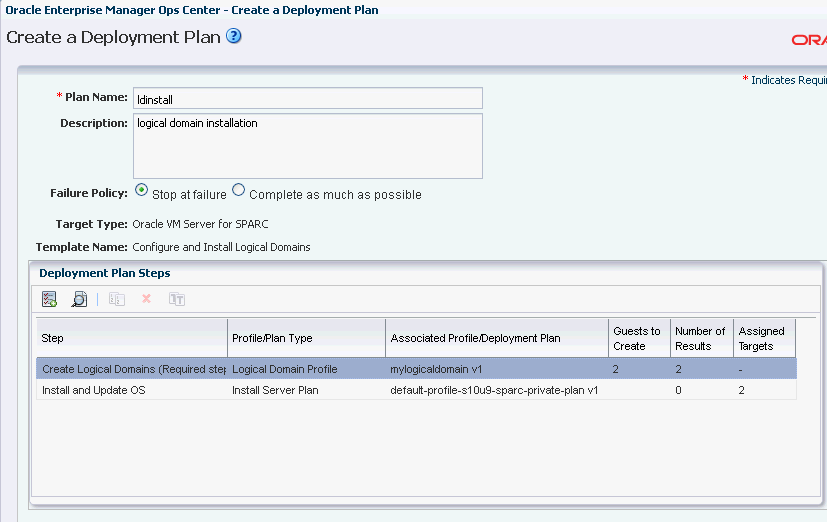
Description of the illustration ld_deploy_plan.gif
-
Click Save to save the deployment plan.
Deploy the Complex Plan
Apply the Configure and Install Logical Domain plan, and provide the required resource assignments.
-
Click Plan Management section in the Navigation pane.
-
Expand Deployment Plans and select Configure and Install Logical Domains.
-
Select the plan that was created in the previous section.
-
Right-click the plan and click Apply Deployment Plan.
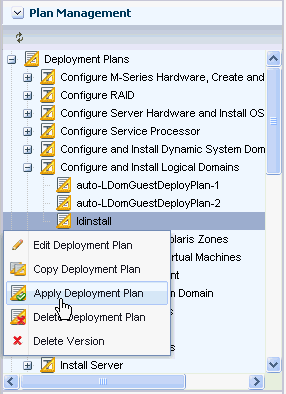
Description of the illustration plan_apply.gif
-
Select the target on which you want to apply the plan.
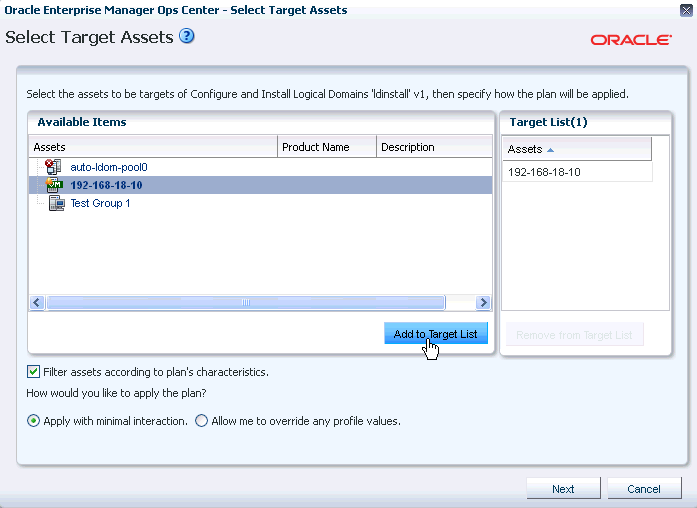
Description of the illustration select_target.gif
-
In the Introduction step, select the option to Do not review steps that are not included in the plan. This will skip the profiles and plans that were not selected in the plan.
Click Next.

Description of the illustration ldinstall_intro.png
-
The wizard first collects the information for creating logical domains.
Click Next.

Description of the illustration first_step_install.gif
-
In the Specify Domain Identity, check the naming of the logical domains. If the name defined in the profile is already allocated, then the name is marked in red. You must provide a unique name to the logical domains.
Click Next.
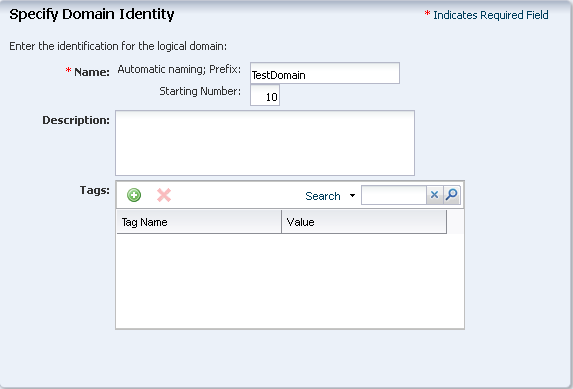
Description of the illustration specify_domain_ident.png
-
Check whether the storage assignments are correct. You can modify if you want to change the disk size.
Click Next.
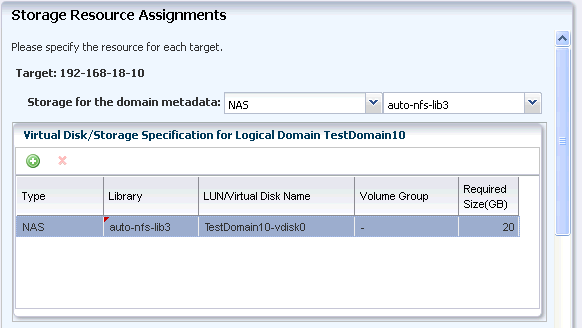
Description of the illustration second_stor_res_assign.gif
-
Check for network resource assignment and click Next.

Description of the illustration third_netw_assign.gif
-
Review the summary of information for creating logical domains.
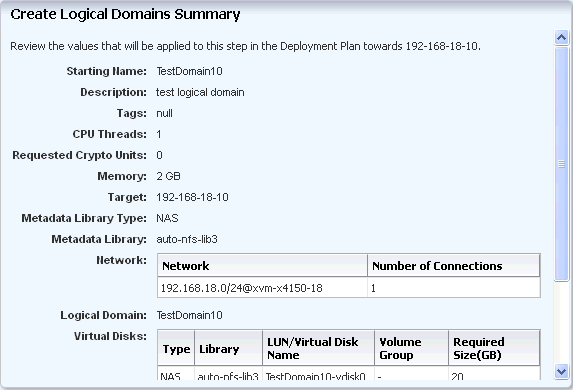
Description of the illustration fourth_create_ld_sum.gif
The next step indicates that the following steps in the wizard collects the data for provisioning OS in the logical domains. Click Next to continue.
-
Specify the IP address for each of the logical domains to be installed with the OS.
Provide the IP address in the range to be applied to the logical domains. You can also enter the IP addresses separated by comma.
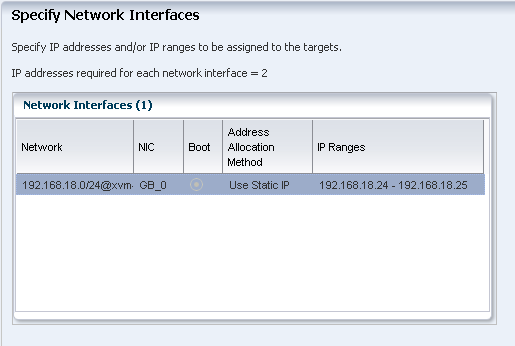
Description of the illustration sixth_netw_inter_assign.gif
-
Review the network resource assignments. Make any modifications in the network assignment, if required.
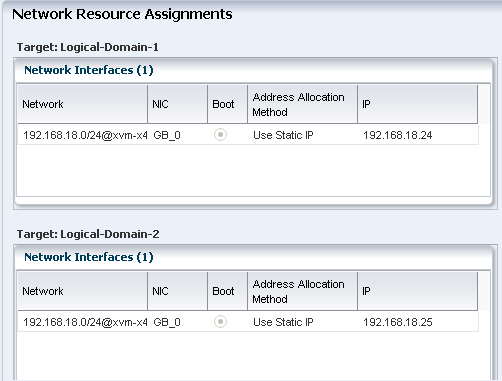
Description of the illustration seventh_netw_res_assign.gif
-
Do not pool the operating systems of the logical domain into a Oracle Solaris Zones server pool. Select the option Do not assign to a server pool.

Description of the illustration eight_serv_pool_assign.gif
-
Review the summary of the information for provisioning the OS.
-
Schedule the job to run now.
-
Click Apply to run the configure and install logical domains plan.
At the end of the execution of the job, you will have two logical domains TestDomain10 and TestDomain11 provisioned with the Oracle Solaris 10 9/10 OS.
Logical Domain Network Connection
When you create a logical domain, the following network connection is set up:
-
For each network connection, a virtual network device is created and the virtual NIC is named as vnet0.
-
A MAC address is allocated to the vnet.
-
The virtual network device is connected to the virtual switch in the Control Domain. In the Control Domain, for each network connection, a virtual switch is created and the switches are named accordingly. For example, a network 192.168.0.1/24, the virtual switches are created as 192.168.0.1_24, 192.168.0.1_24_1 and 192.168.0.1_24_2. The virtual switches are incremented according to the number of connections made to the network. The logical domains are allocated to the first available virtual switch when configured and installed. You can also select the virtual switch when you shut down and start the logical domain.
What's Next?
You can perform the following operations on the logical domains:
-
Migrate
-
Shut down and start
-
Reboot
-
Add storage
-
Connect to network
Related Articles and Resources
Refer to the following resources for more information:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Feature Reference Guide
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Configuring and Deploying Oracle VM Server for SPARC
-
See
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/vm-sparc-194287.htmlfor Oracle VM Server for SPARC documentation. -
See
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E27363_01/index.htmfor Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center documentation.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Configuring and Installing Logical Domains Guide, 12c Release 1 (12.1.2.0.0)
E27355-02
Copyright © 2007, 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.