About OS Configuration Profiles
OS Configuration profiles define the operating system, network configuration details, host name, and server pool configuration.
The OS Configuration profile enables you to specify and assign the following network resources:
-
Controller
-
Interface
-
Address Allocation Method
-
Network
-
IP address
A server pool is a group of one or more virtualization hosts with the same processor architecture that have access to the same virtual and physical networks, and storage resources. Server pools provide load balancing, high availability capabilities, and sharing of some resources for all members of the pool. Once created, you can edit the server pool settings.
You can create server pools for Oracle VM Server (for SPARC and x86) and for Oracle Solaris Zones. When you want the server to be added to a server pool, you can configure the OS Configuration profile to assign the newly provisioned server to a compatible server pool or you can create a new server pool based on the attributes of the newly provisioned server and assign default server pool settings.
Two advanced network interface options are available for Oracle Solaris and Oracle VM Server for SPARC systems:
-
Link Aggregation: Provides high availability and higher throughput by aggregating multiple interfaces at the MAC layer.
-
IP Multipathing (IPMP): Provides features such as higher availability at the IP layer.
You can implement both methods on the same network because they work at different layers of the network stack.
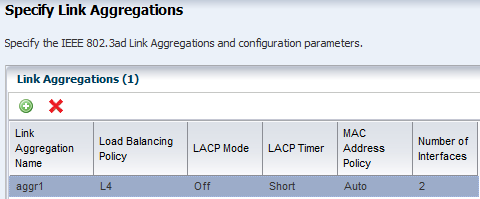
Defining Link Aggregation in an OS Configuration Profile
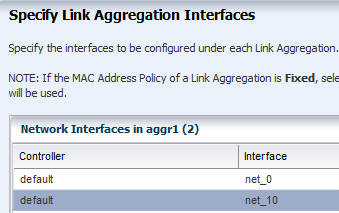
Link aggregation groups two or more NICs. All members of the link aggregation provide network access at the same time and are treated as a single network interface. The link aggregation appears in the list of available NICs in the UI as an individual interface.
Link aggregation is a networking option when you create an Oracle Solaris or Oracle VM Server for SPARC OS Configuration profile. You define the link aggregation load balancing policy and a MAC address policy.
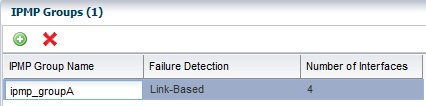
Defining IPMP in an OS Configuration Profile
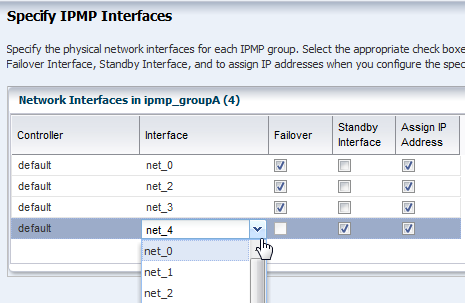
IP multipathing (IPMP) groups provide network failover for your Oracle Solaris operating system, Oracle VM Server for SPARC system, and guests.
You can configure one or more physical interfaces into an IPMP group. After configuring the IPMP group, the system monitors the interfaces in the IPMP group for failure. If an interface in the group fails or is removed for maintenance, IPMP migrates, or fails over, the failed interface's IP addresses. The failover feature of IPMP preserves connectivity and prevents disruption of any existing connections. The network access changes from the failed interface to the standby interface in the IPMP group and the data address of the failed interface migrates to the standby interface. See IP Multipathing Groups and Creating IPMP Groups for more information about IPMP groups.