Oracle® Enterprise Manager Ops Center
Manage the Configuration of a Logical Domain
12c Release 3 (12.3.0.0.0)
E60037-01
June 2015
This guide provides an end-to-end example for how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center.
Introduction
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center provides operations for managing logical domains. A logical domain is created in a virtualization host, that can either be stand-alone or placed in a server pool.
When you create a logical domain, you define the required resources for it. After you create the logical domain, you can manage the resources and add new resources.
This guide shows you how to manage the configuration of a logical domain, including modifying the allocated CPU threads and memory units, adding storage, adding network resources, and moving its metadata.
In this example, a guest domain in a running state is used and the modifications in the CPU, memory, network, and storage of the domain are applied dynamically.
See Related Articles and Resources for links to related information and articles.
What You Will Need
In this example, you need the following to manage a logical domain configuration:
-
A user with Virtualization Admin role to manage the logical domain.
-
A logical domain with guest domain role, running on Oracle VM Server for SPARC 3.1 version which is associated with a server pool.
-
A SAN storage library to be associated with the guest domain.
-
At least one available network to be assigned to the guest domain.
-
At least six CPU threads, and 9 GB of memory to assign to the logical domain.
Managing Logical Domain Configuration Actions
The following actions are available to manage the configuration of a logical domain in Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center:
Adding Storage
Storage libraries provide the storage resources required for a logical domain. When you associate a storage library with an Oracle VM Server, the library becomes available for the logical domains running in that host. A logical domain in a server pool can access and share storage associated with a server pool. You can add storage from the libraries that are available to the logical domain.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center provides storage redundant access for logical domains. You can enable virtual disk multipathing to access the backend storage of the domain by more than one path. You can select to enter the name of the multipathing group or a group is created automatically in a default naming pattern. When the virtual disk has only one path to access the backend storage, multipathing group is not created automatically unless you enter the name of the group.
In this example, a virtual disk is added to a logical domain from a SAN storage library for a static block storage. The multipathing configuration for the virtual disk is also defined for the logical domain.
The existing storage details of the guest domain is displayed in the UI as follows:
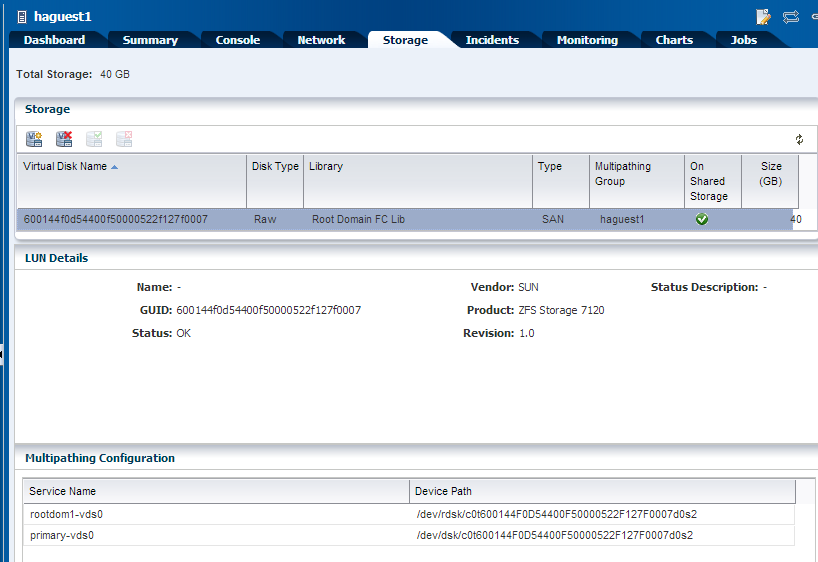
Description of the illustration existing_storage.png
The following procedure details the steps required to add storage to a logical domain:
-
Select the logical domain from the Assets section in the Navigation pane.
-
Click Add Storage in the Actions pane.
The Add Storage window is displayed.
-
Select the Add icon to add a virtual disk to the logical domain.
The storage libraries associated with the server pool are listed. The library can be a NAS or a SAN library.
-
Select a SAN storage library from the list and provide the following details for the library:
-
Select a LUN from the list. The size is of the LUN is fixed and cannot be changed.
-
Enter the name of the multipathing group to be created as mp_group1 in this example.
-
Select the virtual disk service provided by primary and root domain.
-
Select the primary virtual disk service as the Active path.
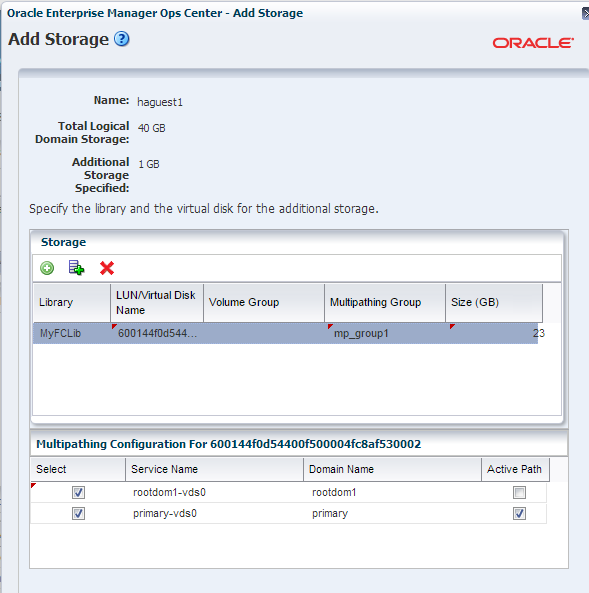
Description of the illustration add_storage.png
-
-
Click Finish to add the specified storage to the guest domain.
The specified storage is added to the logical domain and displayed in the UI as follows:
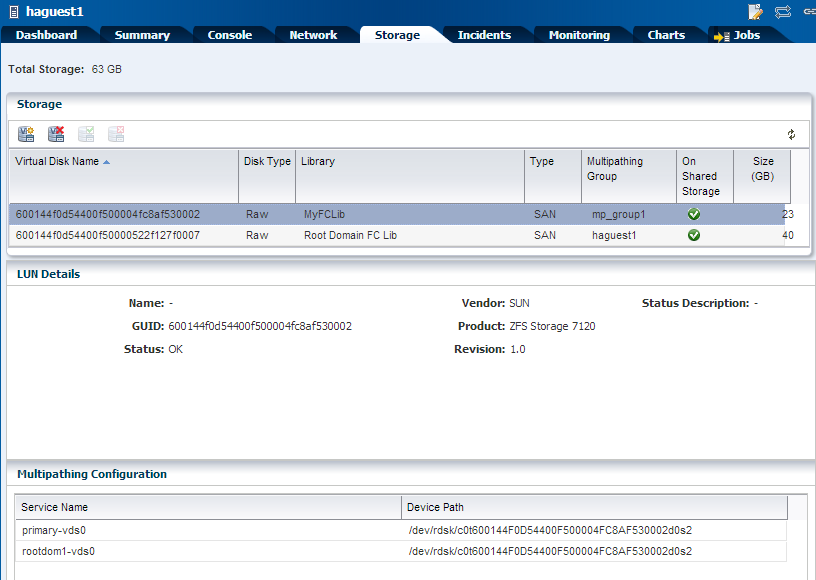
Description of the illustration after_storage.png
Connecting a Logical Domain to a Network
A network enables logical domains to communicate with each other (depending on the virtual switch settings) or with other physical or virtual machines. When a network is assigned to a server pool, the network is accessible from each virtualization host in the pool. You can connect a logical domain to an accessible network assigned to a server pool.
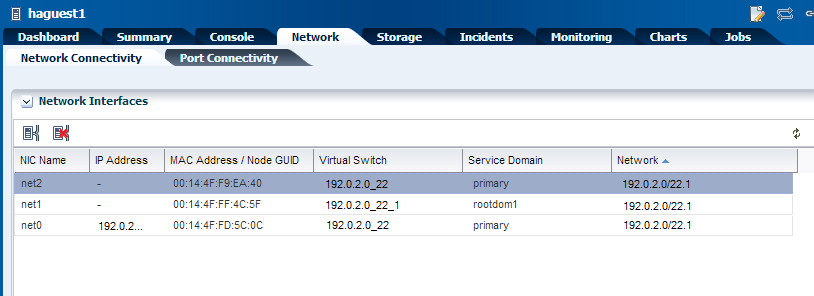
The network connection for a guest domain is displayed as follows:
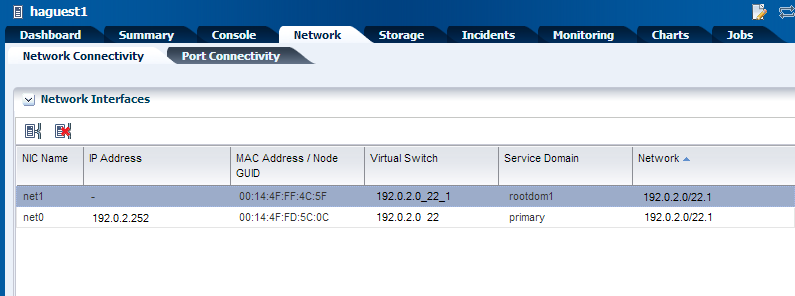
Description of the illustration guest_network.png
The following procedure describes the steps to connect a logical domain to a network:
-
Select the guest domain in the Assets section.
-
Click Connect Network in the Actions pane.
-
Select the networks to which you want to connect the guest and select the following details for each network connection:
-
The selected network is not configure with a VLAN ID. Therefore, the Mode automatically displays as No VLAN.
-
Select the service domain that provide the network services. Select the control domain in this example.
-
Select the virtual switch in the Map Connection column through which you connect the network to the guest domain. The virtual switches or the physical functions available in the selected service domain are listed.
-
Do not select SR-IOV option for this network connection.
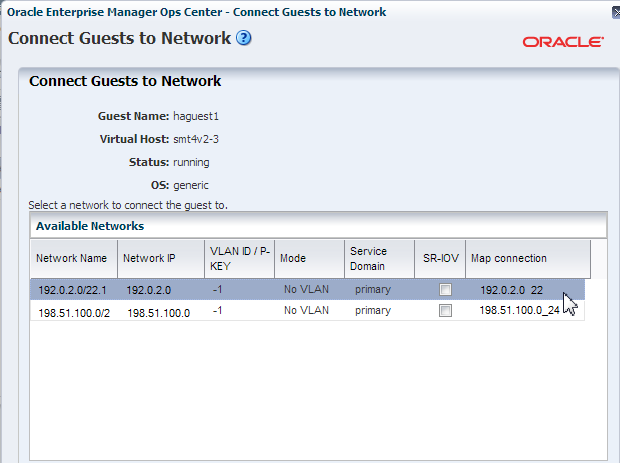
Description of the illustration guest_attach_network.png
-
The specified network is connected to the logical domain and displayed in the UI as follows:
Description of the illustration after_connect_network.png
You can use the networks connected to the logical domain to create IPMP groups or link aggregations in the guest domain operating system.
Editing CPU and Memory Utilization
The CPU allocation and memory are defined when you create a logical domain. You can modify the configuration of a logical domain to change the CPU or memory resources.
In this example, a guest domain's CPU threads and memory allocation are modified. The CPU Model used for the logical domain is Virtual CPU. The guest domain is created on Oracle VM Server for SPARC 3.1 version and hence does not require to be rebooted for modifying the memory configuration.
If you have any physical bindings constraint for the memory, CPU cores, or both, then you cannot edit CPU and memory configuration of the logical domain in the UI.
The following procedure takes you through the steps to edit the CPU and memory utilization of a guest domain:
-
Select the guest domain in the Assets section.
-
Select the Summary tab to view the guest domain configuration.
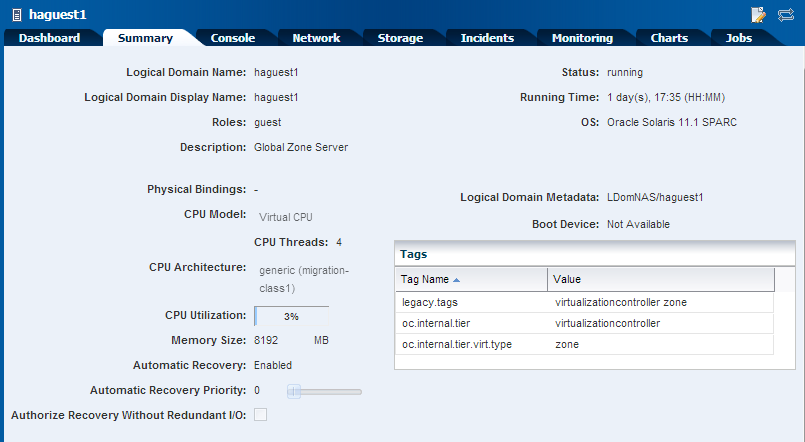
Description of the illustration view_guest_summary.png
-
Click Edit Attributes in the Actions pane.
Some of the information displayed in the Summary tab is now editable.
-
In this example, change the number of CPU threads from 4 to 6, and modify the amount of memory that you want to assign to the logical domain to 9000 MB. Click the Save icon to save changes.
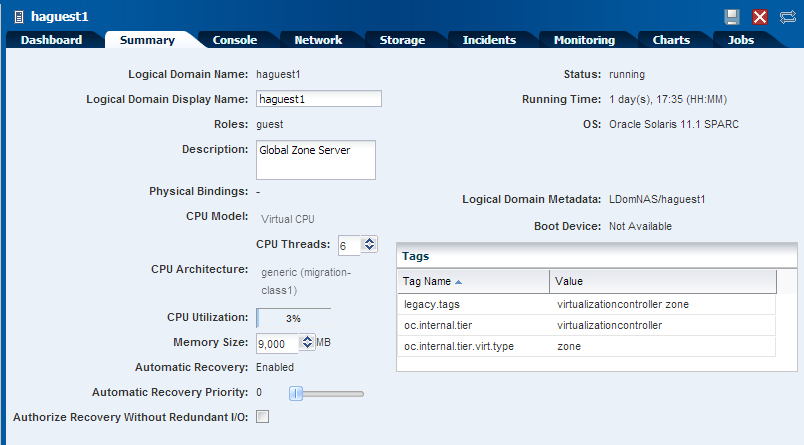
Description of the illustration editing_summary.png
The specified CPU and memory utilization information is applied to the logical domain. When supported, the change in the configuration is applied dynamically on a logical domain that is in a running state. If the logical domain is running on an Oracle VM Server for SPARC version earlier than 2.0, you cannot dynamically modify the memory size of a logical domain. The logical domain is rebooted, and the change in the configuration is applied. The following warning message is displayed irrespective of the Oracle VM Server for SPARC version:
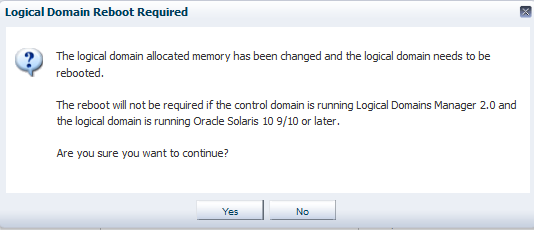
Description of the illustration edit_warning.png
Click Yes to continue the modification of the CPU and memory parameters.
The job is executed and the guest domain Summary tab displays as follows:
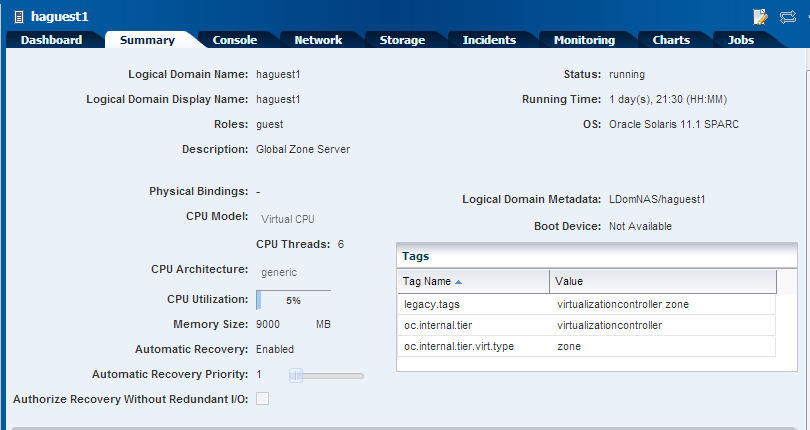
Description of the illustration after_edit.png
What's Next?
Starting with the 12.2.2.0.0 release, you can add multiple SAN LUNs to a logical domain from different libraries using the Add Multiple SAN LUNs option of the Add Storage wizard. Refer to Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Adding SAN Volumes to a Guest Libraries for more details about using this option.
After managing your logical domains configuration, you can continue managing their life cycle with operations such as shut down, shut down and detach, start, or reboot. You can also migrate your logical domains from one virtualization host to another virtualization host.
Related Articles and Resources
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center 12c Release 3 documentation is available at http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/index.htm.
See the following for more information:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Virtualization Reference
-
For information about Oracle VM Server for SPARC, see its documentation at
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/vm-sparc-194287.html.
See the Deploy How To library at http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/nav/deploy.htm and the Operate How To library at http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E59957_01/nav/operate.htm for deployment and operational examples.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Oracle customers that have purchased support have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Manage the Configuration of a Logical Domain, 12c Release 3 (12.3.0.0.0)
E60037-01
Copyright © 2007, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.