2 Configuring Oracle User Messaging Service
This chapter describes the features and architecture of Oracle User Messaging Service (UMS). It also describes how to configure and secure Oracle UMS in your environment.
This chapter includes the following topics:
-
Section 2.1, "Accessing User Messaging Service Configuration Pages"
-
Section 2.4, "Configuring User Messaging Service Access to the LDAP User Profile"
-
Section 2.5, "Using Oracle User Messaging Service for Group Messaging"
-
Section 2.8, "Troubleshooting Oracle User Messaging Service"
2.1 Accessing User Messaging Service Configuration Pages
You configure Oracle User Messaging Service through Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. For more information, see Developing Applications with Oracle User Messaging Service.
2.2 Configuring User Messaging Server
User Messaging Service allows you to configure the User Messaging server and UMS drivers. In 12c, the UMS server configuration is defined at the domain level with the possibility of overriding this configuration at the cluster level. If instances of UMS in a domain need to be configured or deployed differently, UMS must then be deployed in clusters which can have different configuration. Therefore, UMS supports domain-wide and clusterwide configuration for UMS server and UMS drivers.
If a domain consists of only clusters (and no non-clustered managed servers exist in that domain), then it is recommended to have configuration at the cluster level only. UMS also supports a specific driver type (for example, email driver) to be deployed more than once under different deployment names. This makes it possible to have more than one instance of a particular driver type (in this case, the email driver) configured differently in a domain.
If the User Messaging Server configuration is defined at the cluster level, then the cluster name along with all the following properties must be specified.
Table 2-1 Properties for Configuring User Messaging Server
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
AppReceivingQueuesInfo |
The default set of queues from which the application will dequeue received messages. |
Y |
|
DuplicateMessageRetryDelay |
The delay period for deferring processing of a possible duplicate message |
Y |
|
EngineCommandQueuesInfo |
The set of queues from which the engine will dequeue command messages sent by other messaging components |
Y |
|
EnginePendingReceiveQueueInfo |
The queue from which the engine will dequeue pending messages. The format for this value is JNDIQueueConnectionFactoryName:JNDIQueueName |
Y |
|
EngineReceivingQueuesInfo |
The set of queues from which the engine will dequeue received messages |
Y |
|
EngineSendingQueuesInfo |
The set of queues from which the engine will dequeue sent messages |
Y |
|
JpsContextName |
The name of the Java Platform Security (JPS) context to use when getting an Identity Store Service instance. Empty value leads to default JPS context |
Y |
|
ReceivedmessageStatusEnabled |
Enable received message status reporting - if false, client library does not return delivery status to engine |
Y |
|
ResendDefault |
The default number of automatic resends upon delivery failure. You can override this property programmatically on a per message basis. |
Y |
|
ResendDelay |
The delay in seconds between automatic resends |
Y |
|
ResendMax |
The max number of automatic resends upon delivery failure |
Y |
|
SecurityPrincipal |
The default system user used |
Y |
|
SessionTimeout |
The duration to wait before a session timeout when the session flag is set by a Driver or Messaging Client Application |
Y |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
The set of delivery types supported by this server |
Y |
2.3 Configuring User Messaging Service Drivers
This section discusses how to configure the following Oracle User Messaging drivers by using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.
Note:
Alternatively, you can configure the UMS drivers by using the WLST command configUserMessagingDriver. For more information about this command, see WLST Command Reference for Infrastructure Components.
Note:
For the cluster environment, when you use separate messaging drivers for separate managed server nodes, all the drivers must be configured separately.
UMS Messaging Drivers are configured domain wide. If instances of UMS in a domain needs to be configured or deployed differently, UMS can then be deployed in clusters which can have different configurations. Configuring only one driver does not populate the configuration values to the drivers on the other cluster nodes.
2.3.1 Configuring a Driver
You can navigate to the driver configuration page from any one of the following:
-
Associated Drivers table on the User Messaging Service home page
-
Driver Properties menu on the User Messaging Service home page
-
Driver Properties menu for the driver target in the Target Navigation pane
To configure a driver:
-
Log in to Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control as an administrator.
-
Navigate to the User Messaging Service home page.
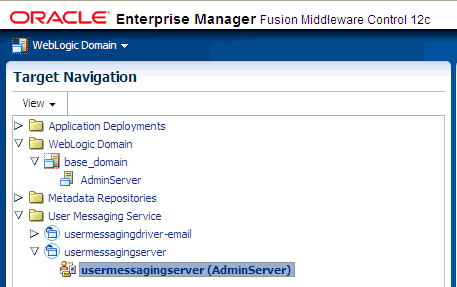
Description of the illustration ns_login.gif
-
Click usermessagingserver(AdminServer). The Associated Drivers page appears.
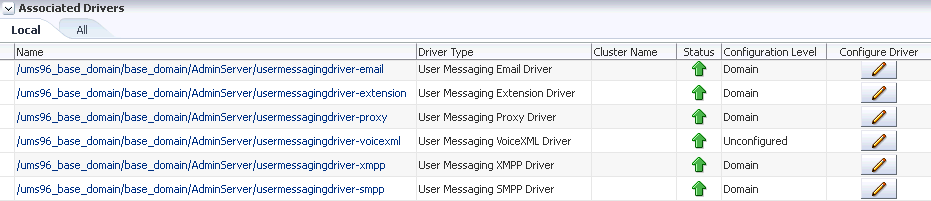
Description of the illustration ns_assoc_drv.gif
-
Select the Local tab to access the drivers collocated with the UMS server instance. These drivers may or may not be registered with the UMS server depending on whether they are properly configured. The ALL tab lists all drivers that are deployed in the domain and registered to all the UMS server instances.
-
Choose a driver from the list, for instance the email driver, and click the corresponding Configure Driver icon.
The configuration page is displayed.
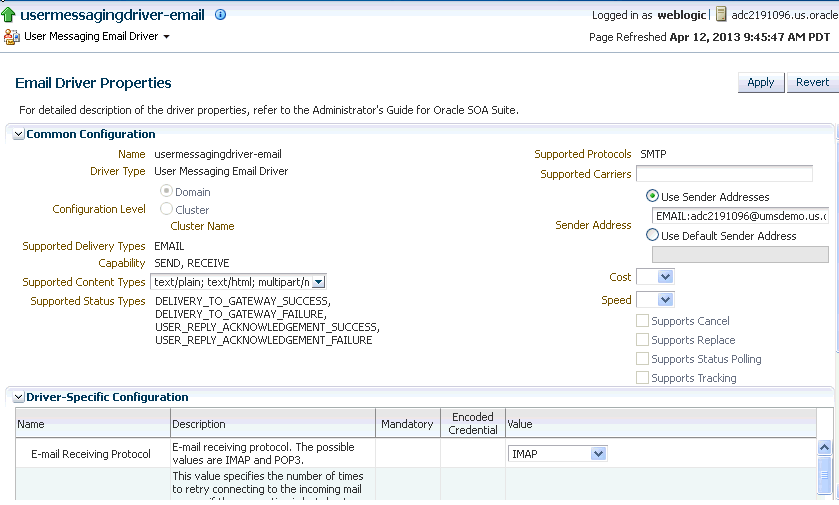
Description of the illustration ns_configdriver_latest.gif
-
If needed, expand the Driver-Specific Configuration section and configure the driver parameters. For more information, see Section 2.3.1.1, "Introduction to Driver Properties."
2.3.1.1 Introduction to Driver Properties
Oracle User Messaging Service drivers share common properties (listed in Table 2-2) that are used by the Messaging Engine when routing outbound messages. Typically, administrators set such Quality of Service (QoS) properties as driver cost (Cost) and driver speed (Speed), supported carriers (SupportedCarriers), configuration level, and supported protocols (SupportedProtocols). Driver developers configure properties that typically do not require modification by the administrator, such as supported delivery types (SupportedDeliveryTypes), and supported content types (SupportedContentTypes).
Table 2-2 Common Driver Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory Property? |
|---|---|---|
|
Capability |
Sets the driver's capability to send or receive messages. The values are SEND, RECEIVE, and BOTH. |
Yes |
|
Cost |
The cost level of the driver (from 0 - 10). 0 is least expensive; 10 is most expensive. If the value is not in this range, cost is considered to be 0. |
No |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
If the UMS Message has no Sender Address of the specific DeliveryType that the driver supports, then the driver may use the DefaultSenderAddress as the Sender Address. |
No |
|
SenderAddresses |
The list of sender addresses that the driver is configured to handle. A driver with specified SenderAdresses will be selected only for an outgoing message that has a matching Sender Address. A driver that has not specified any SenderAdresses is considered to be able to handle any outgoing message regardless of the Sender Address of the message. The list should consist of UMS addresses separated by comma, for example |
No |
|
Speed |
The speed level of the driver (from 0-10, with 10 being the fastest). |
No |
|
SupportedCarriers |
A comma-delimited list of supported carriers. |
No |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster. If Cluster level is selected, then the cluster name must be specified. If the domain has no clusters, then Cluster level selection is disabled. |
Yes |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
The content type supported by the driver. |
Yes |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
The delivery types supported by the driver. |
Yes |
|
SupportedProtocols |
A comma-delimited list of supported protocols. Enter an asterisk (*) for any protocol. |
No |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
The status types supported by the driver. |
No |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports a cancel operation on a message. |
No |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports a replace operation on a message. |
No |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
For certain protocols, an active polling of the remote gateway must be performed to check the status of a message previously sent. This property indicates whether the driver supports such status polling. If set to true, the messaging engine invokes the driver connection's |
No |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports a tracking operation on a message. |
No |
Note:
The following driver properties are not supported in UMS 12c:
-
SupportsCancel
-
SupportsReplace
-
SupportsStatusPolling
-
SupportsTracking
These properties appear in the driver configuration pages in EM but their configuration has been disabled.
2.3.1.2 Securing Passwords
Sensitive driver properties (namely, passwords) can be stored securely in the credential store using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. Properties are marked with the flag Encoded Credential and have a custom entry form field.
To store a sensitive driver property securely:
-
Go to the driver configuration page of the selected driver.
-
In the Driver-Specific Configuration section, locate the property with the Encoded Credential flag set.
-
Select the credential type. (Depending on the selected credential type, you are prompted to enter the username and/or password.) There are three options:
-
Indirect password, create new user (default option): specify the username and real password; the password is stored in the credential store with the username as part of the key. The key and a fixed folder (map name) are stored in the driver deployment's file.
-
Indirect password, use existing user: choose an existing username/key in the credential store (to reference the password you stored previously).
-
User a clear text password: specify the password, and it is stored directly in the driver deployment file.
-
-
Click Apply to save the changes.
-
Restart the driver application or the container for the changes to take effect.
You can check the password in the driver deployment directory's file. For an indirect password, the format is:
value="->mapName:keyName" (mapName can be any name of the user's choice, and the key is <parameter_name>.<username>)
2.3.1.3 Configuring the Messaging Extension Driver
The extension driver extends the messaging capability of the User Messaging Service by enabling support for arbitrary administrator-defined channels (protocols) and delivering the notifications for such channels to an administrator-defined web service listener endpoint.
Note:
An instance of this driver is deployed, but not targeted to any servers in the default. To enable this driver instance, it must be targeted to the appropriate servers where UMS (usermessagingserver) is running.
2.3.1.3.1 Common Properties
These are common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. See Table 2-3. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see driverconfigpropertynames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-3 Extension Driver Common Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory? | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
Extension-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
SEND |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
URI |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/plain, text/html, text/xml |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
|
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
|
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
|
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
SupportedProtocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
popup |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
|
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
2.3.1.3.2 Custom Properties
This driver supports multiple configuration groups called extension endpoint groups. An extension endpoint group holds the configuration for a remote endpoint at which to deliver extension notifications. Each endpoint must have a distinct combination of protocol and mapped domain. The properties of the extension endpoint group are listed in Table 2-4:
Table 2-4 Extension Driver Custom Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory? |
|---|---|---|
|
Group Name |
The name of this extension endpoint configuration group. |
Yes |
|
Endpoint URL |
Remote endpoint listener URL. |
Yes |
|
Mapped Domain |
The extension endpoint used to deliver messages where the domain part of the recipient URI matches this value. |
No |
|
Protocol |
The extension endpoint used to deliver messages where the protocol (scheme) part of the recipient URI matches this value. |
Yes |
|
Security Policies |
Comma-separated list of WS-Security policies to apply to this endpoint. |
No |
|
Username |
Username to propagate through WS-Security headers. |
No |
|
Keystore Alias |
Keystore alias to use for looking up WS-Security policy public keys. |
No |
|
Credential Store Key |
Key to use for looking up the WS-Security username and password from the Oracle Web Services Management credential store map. |
No |
2.3.1.3.3 Extension Driver Security
If the remote extension endpoint is secured using WS-Security, then additional configuration of the extension driver is required. There are two typical WS-Security configurations that are supported. The extension driver can either use SAML tokens or username tokens.
To use extension driver security:
-
To use SAML tokens, the Security Policies configuration property should contain value
oracle/wss11_saml_token_identity_switch_with_message_protection_client_policy, and the Keystore Alias configuration property should contain a valid alias for keystore entries that is accepted by the remote extension endpoint. -
To use username tokens, the Security Policies configuration property should contain value
oracle/wss11_username_token_with_message_protection_client_policy, and the Credential Store Key configuration property should contain a valid alias for a credential store entry that is accepted by the remote extension endpoint.
For more details about using WS-Security policies and configuring OWSM, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Web Services.
2.3.1.3.4 Client API Messageinfo Support
Table 2-5 describes whether the protocol or driver implementation honors the following message delivery-related properties that are specified through the client API.
2.3.1.3.5 Usage Instructions
Perform the following steps to use the extension driver:
To use the extension driver:
Implement and deploy a web service listener endpoint based on the
MessagingNotifyServiceWSDL (umsnotify.wsdl):<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?> <wsdl:definitions xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/ucs/messaging/extension" xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="MessagingNotifyService" targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/ucs/messaging/extension"> <wsdl:types> <xsd:schema targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/ucs/messaging/extension"> <xsd:element name="notification"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="messageId" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Unique message identifier from User Messaging Service.</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="sender" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The sender address.</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="recipient" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The recipient address (typically username).</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="subject" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The subject of the message, if available.</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="contentType" type="xsd:string" default="text/plain"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The MIME type of the message. e.g. text/plain, text/html, text/xml.</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="content" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>The main body of the message. Textual content only (no binary content).</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="parameters" type="tns:parameter" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Additional key-value pairs. This interface does not define any specific key-value pair meanings. Use of such parameters is defined on a private basis by particular implementations of this interface. </xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <xsd:complexType name="parameter"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Parameter name</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="value" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>Parameter value</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="notificationResponse"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="messageId" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation>A message identifier returned in response to successfully accepting the message. If returned, the identifier should be unique. Note: A fault is raised if the message cannot be accepted.</xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation></xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <xsd:element name="notificationFault"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="code" type="xsd:string"/> <xsd:element name="message" type="xsd:string"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema> </wsdl:types> <wsdl:message name="notifyRequest"> <wsdl:part element="tns:notification" name="parameters" /> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:message name="notifyResponse"> <wsdl:part element="tns:notificationResponse" name="parameters"/> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:message name="notifyException"> <wsdl:part element="tns:notificationFault" name="parameters"/> </wsdl:message> <wsdl:portType name="Notify"> <wsdl:operation name="invoke"> <wsdl:input message="tns:notifyRequest"/> <wsdl:output message="tns:notifyResponse"/> <wsdl:fault message="tns:notifyException" name="NotifyException"/> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:portType> <wsdl:binding name="NotifySOAPBinding" type="tns:Notify"> <soap:binding style="document" transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" /> <wsdl:operation name="invoke"> <soap:operation soapAction="http://www.oracle.com/ucs/messaging/extension/" /> <wsdl:input> <soap:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:input> <wsdl:output> <soap:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:output> <wsdl:fault name="NotifyException"> <soap:fault name="NotifyException" use="literal"/> </wsdl:fault> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> <wsdl:service name="NotifyService"> <wsdl:port binding="tns:NotifySOAPBinding" name="Notify"> <soap:address location="http://localhost:8001/NotifyService"/> </wsdl:port> </wsdl:service> </wsdl:definitions>-
Configure the extension driver.
-
Target the predeployed extension driver called
usermessagingdriver-extensionor a new deployment to the appropriate servers where UMS (usermessagingserver) is running and start the driver. -
In Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, navigate to the usermessagingserver home page.
-
Click User Messaging Service > Driver Properties.
-
Select and Edit the driver
usermessagingdriver-extensionor create a new driver with the same name as your new driver deployment. -
Under Driver-Specific Configuration, add a new extension endpoint configuration group and specify the correct properties: EndpointURL is the URL to the web service listener endpoint created in Step 1. Protocol is the value of the new messaging channel for which you want to add notification support (for example, myProtocol).
-
Under Common Configuration, update Supported Protocols with a comma-separated list of protocols defined in each Extension Endpoint group.
-
Click OK to save the configuration.
-
This completes the configuration and integration of a new messaging channel (protocol) in UMS using the extension driver.
To send notifications to this new channel (protocol), recipients must be specified for the URI delivery type using the URI addressing format:
URI:scheme:scheme-specific-address-value
where scheme is the protocol. The URI delivery type is optional. For example, if the extension driver was configured to support the protocol, myProtocol, an application can compose a message to myProtocol:john.doe@example.com.
End users can also declare their messaging preferences by creating a new messaging channel for the new channel type in the User Communication Preferences UI. Note that user preferences are only applied when applications send user-based notifications (that is, to recipients of the form USER:username).
Note:
Proper configuration of SSL/TLS in the Oracle WebLogic Server container is a prerequisite for secure connections between UMS and the email server. See "Configuring SSL" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server.
2.3.1.4 Configuring the Email Driver
The email driver both sends and receives messages (that is, its capability property is set to both by default). The email driver sends messages over SMTP and uses either IMAP or POP3 for receiving messages.
2.3.1.4.1 Email Driver Interoperability
This section details interoperability features of the email driver.
The email driver is compatible with these protocols: POP3, IMAP4, and SMTP.
Email driver features include:
-
Automatic connection retry
-
SMTP for message sending
-
IMAP4 and POP3 for message receiving (using polling)
-
scalable, highly available
-
Message loss prevention and duplication avoidance
The gateway vendors and versions in Table 2-6 have been verified.
2.3.1.4.2 Common Properties
Table 2-7 lists common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see "driverconfigpropertynames" in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-7 Common Email Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
Email-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
Both |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
|
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/plain, text/html, multipart/mixed, multipart/alternative, multipart/related |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE, USER_REPLY_ACKNOWLEDGEMENT_SUCCESS, USER_REPLY_ACKNOWLEDGEMENT_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.4.3 Email Custom Properties
Table 2-8 lists properties specific to this driver and generally associated with configuring access to the remote gateway and certain protocol or channel-specific behavior.
Table 2-8 Custom Email Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory? | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MailAccessProtocol |
Email receiving protocol. The possible values are IMAP and POP3. Required only if email receiving is supported on the driver instance. |
No |
IMAP |
|
RetryLimit |
This value specifies the number of times to retry connecting to the incoming mail server, if the connection is lost for some reason. The default value is -1, which means there is no limit to the number of tries. |
No |
-1 |
|
MailDelFreq |
The frequency to permanently remove deleted messages. The unit is in seconds and the default value is 600 seconds. A negative value indicates the messages should not be expunged. For the POP3 protocol, the message is expunged after it is processed. |
No |
600 |
|
AutoDelete |
This value indicates if the driver should mark the messages deleted after they have been processed. The default is Disabled. For the POP3 protocol, the messages are always deleted right after they are processed. |
No |
Disabled |
|
Debug |
This value indicates if the driver is running in Debug mode. When enabled, JavaMail prints out requests and responses between the email driver and the mail server to Fusion Middleware Control. The default is Disabled. |
No |
Disabled |
|
CheckMailFreq |
The frequency with which to retrieve messages from the mail server. The unit is in seconds and the default value is 30 seconds. |
No |
30 |
|
ReceiveFolder |
The name of the folder from which the driver is polling messages. The default value is INBOX. |
No |
INBOX |
|
OutgoingMailServer |
The name of the SMTP server. This is mandatory only if email sending is required. |
No |
N/A |
|
OutgoingMailServerPort |
The port number of the SMTP server; typically 25. |
No |
25 |
|
OutgoingMailServerSecurity |
The security setting used by the SMTP server. Possible values are None, TLS, and SSL. The default value is None. |
No |
None |
|
OutgoingDefaultFromAddr |
The default FROM address (if one is not provided in the outgoing message). Note: The |
No |
N/A |
|
OutgoingUsername |
The username used for SMTP authentication. Required only if SMTP authentication is supported by the SMTP server. |
No |
N/A |
|
OutgoingPassword |
The password used for SMTP authentication. This is required only if SMTP authentication is supported by the SMTP server. This includes Type of Password (choose from Indirect Password/Create New User, Indirect Password/Use Existing User, and Use Cleartext Password) and Password. |
No |
N/A |
|
IncomingMailServer |
The hostname of the incoming mail server. Required only if email receiving is supported on the driver instance. |
No |
N/A |
|
IncomingMailServerPort |
Port number of IMAP4 (that is, 143 or 993) or POP3 (that is, 110 or 995) server. |
No |
N/A |
|
IncomingMailServerSSL |
Indication to enable SSL when connecting to IMAP4 or POP3 server. The default is Disabled. |
No |
Disabled |
|
IncomingMailIDs |
The email addresses corresponding to the user names. Each email address is separated by a comma and must reside in the same position in the list as their corresponding user name appears on the usernames list. Required only if email receiving is supported on the driver instance. |
No |
N/A |
|
IncomingUserIDs |
The list of user names of the mail accounts from which the driver instance is polling. Each name must be separated by a comma, for example, foo,bar. This is required only if email receiving is supported on the driver instance. |
No |
N/A |
|
IncomingUserPasswords |
The list of passwords corresponding to the user names. Each password is separated by a comma and must reside in the same position in the list as their corresponding user name appears on the usernames list. This is required only if email receiving is supported on the driver instance. This includes Type of Password (choose from Indirect Password/Create New User, Indirect Password/Use Existing User, and Use Cleartext Password) and Password. |
No |
N/A |
|
ProcessingChunkSize |
The number of messages processed during each message polling. The default is 100. |
No |
100 |
|
ImapAuthPlainDisable |
Indication to disable or enable plain text authentication ( |
No |
Disabled. When this property is disabled, that means that plain text is allowed. |
2.3.1.4.4 Client API Messageinfo Support
These properties are message delivery-related that are specified through client API. Table 2-9 describes if the protocol or driver implementation honors such properties.
2.3.1.5 Configuring the SMPP Driver
Short Message Peer-to-Peer (SMPP) is a popular GSM SMS protocols. User Messaging Service includes a prebuilt implementation of the SMPP protocol as a driver that can send and receive short messages. If the sending feature is enabled, the SMPP driver opens one TCP connection to the Short Message Service Center (SMS-C) as a transmitter for sending. If the driver's receiving feature is enabled, it opens another connection to the SMS-C as a receiver for receiving. Only two TCP connections (both initiated by the driver) are needed for all communication between the driver and the SMS-C.
Note:
The SMPP Driver implements Version 3.4 of the SMPP protocol and only supports connections to an SMS-C or an SMS gateway that supports this version.
2.3.1.5.1 SMPP Driver Interoperability
This section details interoperability features of the SMPP Driver.
The SMPP driver is compatible with this protocol: SMPP v3.4.
SMPP driver features include:
-
Automatic connection retry
-
HTTP proxy for firewall traversal
-
Authentication configuration
-
Configurable chunk size
-
Bulk Sending
-
Encoding: UCS2, IA5, GSM_DEFAULT
-
Priority Setting
-
Configurable Window size
-
Plain text content only
The Gateway vendors in Table 2-10 have been verified.
2.3.1.5.2 Common Properties
Table 2-11 lists common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values see DriverConfigPropertyNames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-11 Common SMPP Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
SMPP-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
Both |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
SMS |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/plain |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.5.3 SMPP Custom Properties
Table 2-12 lists properties specific to this driver and generally associated with configuring access to the remote gateway and certain protocol or channel-specific behavior.
Table 2-12 Custom SMPP Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory? | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SmsAccountId |
This value indicates the addresses that the SMPP driver is requesting messages for from the server. The value is specified as a UNIX Regular Expression. For example, "555" would specify a single address, and "^123|^789" would indicate all addresses starting with 123 or 789. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
SmsServerHost |
The name (or IP address) of the SMS-C server. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
TransmitterSystemId |
The account ID that is used to send messages. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
ReceiverSystemId |
The account ID that is used to receive messages. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
TransmitterSystemType |
The type of transmitter system. The default is Logica. |
Yes |
The default value is Logica. |
|
ReceiverSystemType |
The type of receiver system. The default is Logica. |
Yes |
The default value is Logica. |
|
TransmitterSystemPassword |
The password of the transmitter system. This includes Type of Password (choose from Indirect Password/Create New User, Indirect Password/Use Existing User, and Use Cleartext Password) and Password. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
ReceiverSystemPassword |
The password for the receiver system. This includes Type of Password (choose from Indirect Password/Create New User, Indirect Password/Use Existing User, and Use Cleartext Password) and Password. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
ServerTransmitterPort |
The TCP port number of the transmitter server. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
ServerReceiverPort |
The TCP port number of the receiver server. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
DefaultEncoding |
For incoming messages, if SMS-C specifies the encoding to Choose from the drop-down list: IA5, UCS2, and GSM_DEFAULT. |
No |
IA5 |
|
EncodingAutoDetect |
If enabled, then the SMPP driver will attempt to encode outgoing messages based on the value specified in the DefaultEncoding parameter. If the encoding fails, then the driver will use the 16-bit encoding UCS2. If not enabled, then the driver will derive the encoding from the UMS Message Content-Type header. |
No |
Enabled |
|
LocalSendingPort |
The local TCP port used by the SMPP driver to send messages to the SMS-C. |
No |
N/A |
|
LocalReceivingPort |
The local TCP port used by the SMPP driver to receive messages from the SMS-C. |
No |
N/A |
|
LocalAddress |
The hostname (or IP address) of the server that hosts the SMPP driver. |
No |
N/A |
|
WindowSize |
The window size for SMS. This value must be a positive number. Default is 1. |
No |
1 |
|
EnquireInterval |
The interval, in seconds, to send an enquire message to the SMS-C. The default is 30 seconds. |
No |
30 |
|
ThrottleDelay |
The delay, in seconds, between throttles. Default is 30. |
No |
30 |
|
BindRetryDelay |
The minimum delay, in seconds, between bind entry attempts. Default is 30. |
No |
30 |
|
ResponseTimer |
Time lapse allowed between SMPP request and response, in seconds. The default is 30. |
No |
30 |
|
RegisteredDeliveryMask |
The registered delivery bit mask. The default is 0xFF, which does not change the delivery flag value. |
No |
0xFF |
|
RangeSetNull |
Set to true to set the address range field of BIND_RECEIVER to null. Set to false (the default value) to set the address range field to SmsSystemId. The default is Disabled. |
No |
Disabled |
|
PriorityAllowed |
The highest priority allowed for the SMPP driver. The range is 0 (normal) to 3 (highest). The default is 0. |
No |
0 |
|
BulkSending |
Setting this value to enabled (the default) enables sending messages in bulk to the SMS-C. |
No. |
Enabled |
|
PayloadSending |
If you enable this property, the SMPP driver always uses the |
No |
Disabled |
|
SourceTon |
The type of number (TON) for ESME address(es) served through SMPP receiver session. The default is 0. |
No |
0 |
|
SourceNpi |
The numbering plan indicator (NPI) for ESME address(es) served through the SMPP receiver session. The default is 0. |
No |
0 |
|
DestinationTon |
The TON for destination. The default is 0. |
No |
0 |
|
DestinationNpi |
The NPI for destination. The default is 0. |
No |
0 |
|
ExtraErrorCode |
A comma-separated list of error codes. |
No |
N/A |
|
MaxChunks |
The maximum SMS chunks for a message. The default is -1 (no maximum). |
No |
-1 (no maximum) |
|
ChunkSize |
The size of each SMS message chunk. Default is 160. |
No |
160 |
|
LongMessageSending |
Supports sending long messages. The default is Disabled. |
No |
Disabled |
|
DatagramMessageMode |
Supports datagram message mode. The default is Disabled. |
No |
Disabled |
2.3.1.5.4 Client API MessageInfo Support
These properties are message delivery-related that are specified through client API. Table 2-13 describes if the protocol or driver implementation honors such properties.
2.3.1.6 Configuring the XMPP Driver
The XMPP Driver provides unidirectional and bidirectional access from Oracle Fusion Middleware to end users for real-time IM through the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP). This driver enables end users to receive alert notifications or interactively chat with applications through their IM client of choice.
2.3.1.6.1 Introduction to XMPP
XMPP is an open, XML-based protocol for IM. XMPP-based software is deployed on thousands of servers across the Internet and is used by millions of people worldwide. XMPP consists of a client/server architecture, which resembles the ubiquitous email network. XMPP servers are completely decentralized, allowing anyone to set up their own server. Messaging is achieved as in the email network, where recipients are addressed by an XMPP ID (or Jabber ID or JID) with the following form: [username]@domain[/resource]. See RFC 3920 for details on the addressing scheme.
In an XMPP network, users identified by their XMPP IDs as mentioned above (which typically consist of a username and the domain of the XMPP server to which the user connects). An end user of XMPP connects to an XMPP server using an XMPP client to send instant messages to other XMPP users. XMPP, however, is not the only protocol network available for IM. XMPP has an extensible and modular architecture. It integrates with proprietary IM networks, enabling XMPP users to communicate with those on other networks.
To use the XMPP Driver in UMS, you must have access to a Jabber/XMPP server and an XMPP account for the UMS XMPP Driver instance with which to log in.
2.3.1.6.2 XMPP Driver Interoperability
This section details interoperability features of the XMPP Driver.
The XMPP driver is compatible with these protocols: XMPP (RFC 3920, 3921).
XMPP Driver features include:
-
Automatic connection retry
-
HTTP proxy for firewall traversal
-
Plain text content only
The gateway vendors and versions in Table 2-14 have been verified.
2.3.1.6.3 Third-Party Software
The XMPP Driver uses or requires the following third-party software (you may optionally choose to install and configure your own XMPP server):
Table 2-15 Required Third-Party Software
| Name | Instructions | Version(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
Apache Smack |
This driver uses the Apache Smack XMPP Java library to connect to a Jabber/XMPP IM Server. This driver includes a licensed copy of Smack. |
3.2.2 |
Note:
You are not required to install your own XMPP Server if you have access to an existing server. For a list of public servers, see http://www.jabber.org.
2.3.1.6.4 Driver Application Archive (EAR)
The EAR file is $ORACLE_HOME/communications/applications/usermessagingdriver-xmpp-ear-12.1.2.ear.
2.3.1.6.5 Common Properties
Table 2-16 lists common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see DriverConfigPropertyNames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-16 Common XMPP Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
XMPP-IM-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
Both |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
IM |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/plain |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports a cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports a replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports a tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports a status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.6.6 XMPP Custom Properties
The XMPP Driver includes the custom properties shown in Table 2-17.
Table 2-17 Custom XMPP Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IMServerHost |
Jabber/XMPP server hostname. |
No |
N/A |
|
IMServerPort |
Corresponding Jabber/XMPP server port. The default is 5222. |
Yes |
5222 |
|
IMServerUsername |
Jabber/XMPP username with which you log in. You may also enter a complete Jabber ID if its domain name is different from the Jabber/XMPP server hostname (for example: myUserName or myUserName@xmpp-domain). Note: An attempt is made to register this user account if it does not exist and the server supports account registration. |
No |
N/A |
|
IMServerPassword |
Corresponding password for the username listed above. Includes Type of Password (choose from Indirect Password/Create New User, Indirect Password/Use Existing User, Use Cleartext Password) and Password. |
No |
N/A |
|
SecurityMode |
Security mode to use when making a connection to the server. Available options are: None (Security is disabled and only unencrypted connections are used), TLS (Security through TLS encryption is used whenever it is available), and SSL (Security through SSL encryption is used). The default is TLS. |
No |
TLS |
|
SASLAuthenticationEnabled |
Whether to use SASL authentication when logging into the server. If SASL authentication fails, then the driver tries to use non-SASL authentication. By default, SASL is enabled. |
No |
Enabled |
2.3.1.6.7 Client API MessageInfo Support
These properties are message delivery-related that are specified through the client API. Table 2-18 describes if the protocol or driver implementation honors such properties.
2.3.1.7 Configuring the VoiceXML Driver
Note:
The VocieXML driver (described in this section) is deprecated.
The VoiceXML Driver supports the Genesys VoiceGenie gateway's outbound call protocol to send messages authored in VoiceXML. The gateway delivers the message using text-to-speech synthesis.
2.3.1.7.1 VoiceXML Driver Interoperability
This section details interoperability features of the VoiceXML Driver.
The VoiceXML driver is compatible with this protocol: VoiceXML over HTTP (VoiceGenie gateway protocol).
The VoiceXML driver features include:
-
VoiceXML content only
The gateway vendor and version in Table 2-19 has been verified.
2.3.1.7.2 Common Properties
Table 2-20 lists common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see DriverConfigPropertyNames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-20 Common VoiceXML Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
VoiceXML-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
SEND |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
VOICE |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/vxml, text/x-vxml |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender Addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default Sender Address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.7.3 VoiceXML Custom Properties
The VoiceXML Driver includes the custom properties shown in Table 2-21.
Table 2-21 Custom VoiceXML Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VoiceXMLOutboundServletURI |
The URL of the VoiceXML gateway. |
Yes |
N/A |
|
VoiceXMLOutboundServletUserName |
The user name of the VoiceXML gateway. |
No |
N/A |
|
VoiceXMLOutboundServletPassword |
The password of the user of the VoiceXML gateway. |
No |
N/A |
|
VoiceXMLOutboundServletDNIS |
The number that should appear in the recipient's caller ID display. |
No |
N/A |
|
VoiceXMLReceiveURL |
The URL of this driver's servlet that handles incoming requests from the VoiceXML Gateway. The format is |
No |
N/A |
Note:
In a clustered (high-availability) environment with Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) configured, do not use the OHS port to configure the VoiceXML driver receive URLs. Using the OHS port to configure the VoiceXML driver receive URLs causes a conflict with the drivers.
Each VoiceXML driver must be configured with its own WLS server's port.
2.3.1.7.4 Client API MessageInfo Support
These properties are message delivery related which are specified through client API. Table 2-22 describes if the protocol or driver implementation honors such properties.
2.3.1.8 Configuring the Proxy Driver
The Proxy Driver acts as a Messaging Web Service client to a Fusion Middleware Messaging server hosted elsewhere in the intranet or Internet. It uses SOAP over HTTP to send messages and receive messages and return message delivery status. The ParlayX Web Service relays messages from one UMS instance to another. It can relay traffic from multiple instances in an Intranet to a terminating instance that has all of the protocol-specific drivers configured to an external gateway such as an SMSC, or to an SMTP or IMAP mail server.
2.3.1.8.1 Common Properties
Table 2-23 shows common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see DriverConfigPropertyNames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-23 Common Proxy Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
Proxy-Driver |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
SEND |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
EMAIL, SMS, VOICE, IM, WORKLIST |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
* |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported status types |
No |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.8.2 Proxy Custom Properties
The Proxy Driver includes the custom properties shown in Table 2-24.
Table 2-24 Custom Proxy Properties
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
GatewayURL |
The URL to the hosted 11g UMS Web Service gateway. The URL is in the following format: http://<host>:<port>/sdpmessaging/parlayx/SendMessageService |
Yes |
N/A |
|
Username |
Username of the messaging gateway. |
No |
N/A |
|
Password |
The password of the username |
No |
N/A |
|
Policies |
Comma-delimited list of Oracle Web Services Manager WS-Security policies to be attached to proxy driver requests |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.8.3 Client API MessageInfo Support
These properties are message delivery related which are specified through client API. Table 2-25 describes if the protocol or driver implementation honors such properties.
2.3.1.9 Configuring the Twitter Driver
The Twitter driver is a User Messaging Services (UMS) driver that communicates with the Twitter API server. It provides a bi-directional messaging service to/from the Twitter server. Thus, the Twitter driver enables the application users to publish their Twitter feed and receive response for the same.
2.3.1.9.1 Twitter Driver Interoperability and features
The Twitter driver is compatible with UMS server 12.1.x. The Twitter driver is not deployed by default. It can be independently deployed and undeployed.
The following are the features of the Twitter driver:
-
Multiple Authentication Modes: The Twitter REST API allows the following two forms of authentication mode:
-
OAuth: This is a Single Sign-On type of authentication mode. You can enable this authentication mode from the Fusion Middleware Control (EM) page. On the driver specific EM page, you must set the Authentication Mode parameter to
Oauth, and configure two pairs of keys, namely, Customer key, Customer Secret, Access Token, and Access Token Secret. For more information about these keys, see Table 2-27, "Custom Properties of the Twitter Driver".xAuth: This authentication mode is based on OAuth. The Twitter driver grants xAuth to only those applications that do not meet the requirements of OAuth. The user must provide the username and password at each request in order to enable this authentication mode.
-
-
Mutiple Options for Messaging: The following are the two categories of messages that a user comes across when using the Twitter driver:
-
Outbound Message: The messages sent from a UMS client application to the Twitter server are called Outbound messages. These messages could be treated as Tweets or Direct Messages.
-
Tweets: The messages sent to the username, that is configured with the Twitter driver, are posted as tweets. For instance, if the Twitter driver is configured with the credentials of user TW, then all messages sent to
URI.twitter:TWwill be posted as tweets from user TW. -
Direct Message: The messages sent from the username of the configured user to another Twitter user can be treated as Direct messages. Twitter allows a configured user to send direct messages to his direct followers only. If the recipient of a direct message is not a registered user of Twitter and is not a direct follower of the sender, then the delivery of the message will fail and an error message will be displayed.
-
-
Inbound Message: The messages received by the Twitter driver from the Twitter server are called Inbound messages. Inbound messages can be of the following types:
-
Timeline Message: This is a list of tweets posted by the configured user or a Twitter user who is followed by the configured user.
-
Direct Message: This is a private message sent to the configured user by a Twitter user, who is followed by the configured user.
-
-
-
Limited Size of the Tweet: Twitter limits the length of each tweet to 140 bytes. Any tweet exceeding this limit is rejected by the Twitter server. The Twitter driver truncates long tweets before sending them to the Twitter server.
-
Limited Rate of Tweets: Twitter limits the usage of tweets per user. For information about all Twitter limits, see the About Twitter Limits page. If the rate limit of a user exceeds the rate limit of that Twitter user, then the delivery of outbound messages fail and the reception of inbound messages are ceased.
If you are using UMS behind a firewall, then you must configure proxy settings for WebLogic Server. For information about configuring proxy settings for WebLogic Server, see "Using System Properties to Specify the Proxy Server" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Getting Started With JAX-RPC Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
2.3.1.9.2 Common Properties
Table 2-26 shows common driver properties that are indicative of the capabilities of this driver for use by the messaging engine when routing outbound messages. Some properties are set by the driver developer and do not normally require modification, while others can be modified by the administrator to change the routing behavior. For a complete description of these properties and available values, see DriverConfigPropertyNames in User Messaging Service Java API Reference.
Table 2-26 Common Properties of the Twitter Driver
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
InstanceName |
Instance name (for internal use only) |
Yes |
usermessagingdriver-twitter |
|
Capability |
Message sending and receiving capability |
Yes |
SEND, RECEIVE |
|
SupportedDeliveryTypes |
Supported delivery types |
Yes |
URI |
|
SupportedContentTypes |
Supported content types |
Yes |
text/plain, text/html, text/xml |
|
SupportedStatusTypes |
Supported Status types |
Yes |
DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_SUCCESS, DELIVERY_TO_GATEWAY_FAILURE |
|
Cost |
Cost |
No |
N/A |
|
Speed |
Speed |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportedCarriers |
Supported carriers |
No |
N/A |
|
Configuration Level |
Enables driver configuration at the domain level or at the cluster level for the selected cluster |
Yes |
Domain |
|
Supported Protocols |
Supported protocols |
No |
N/A |
|
SupportsCancel |
Supports a cancel operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsReplace |
Supports a replace operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsTracking |
Supports a tracking operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SupportsStatusPolling |
Supports a status polling operation on the message |
No |
False |
|
SenderAddresses |
Sender addresses |
No |
N/A |
|
DefaultSenderAddress |
Default sender address |
No |
N/A |
2.3.1.9.3 Twitter Custom Properties
Table 2-27 lists configurable properties specific to the Twitter driver.
Table 2-27 Custom Properties of the Twitter Driver
| Name | Description | Mandatory | Default Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Authentication Mode |
This property specifies the authentication mode that the Twitter driver must use. Valid values are OAuth and xAuth. |
Yes |
xAuth |
|
Username |
The user name of the Twitter user. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is xAuth. |
|
|
Password |
The password of the Twitter user. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is xAuth. |
|
|
Consumer Key |
The public key of the Twitter user. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is OAuth. |
|
|
Consumer Secret |
The private key of the Twitter user. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is OAuth. |
|
|
Access Token |
The public key of a registered Twitter application. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is OAuth. |
|
|
Access Token Secret |
The private key of a registered Twitter application. |
This field is mandatory if the selected authentication mode is OAuth. |
2.4 Configuring User Messaging Service Access to the LDAP User Profile
As part of the LDAP provider setup in a SOA deployment, you configure the "User Name Attribute" through the WebLogic Server Administration Console. If you configure that attribute with a value other than the default "cn" or if the user's email address is stored in an LDAP attribute which is different from "mail", you must make an additional configuration change in Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) for UMS to successfully access the user profile to obtain the list of communication channels provisioned in LDAP, such as business email.
For more information about Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS), see Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services.
To configure access to the LDAP user profile:
-
Modify the
jps-config.xmlfile in the$DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfigdirectory by adding a<property>element in theidstore.ldap serviceInstancesection.-
To use the value of the User Name Attribute while searching the back-end LDAP server for user profile, add the following element:
<property name="username.attr" value="username_attribute_value"/>where
username_attribute_valueis the value of the User Name Attribute property in the LDAP provider configuration. For instance, if the value of the User Name Attribute ismail, add the following line:<property name="username.attr" value="mail"/>
The following sample code shows the above line inserted in the
jps-config.xmlfile:<!-- JPS WLS LDAP Identity Store Service Instance --> <serviceInstance name="idstore.ldap" provider="idstore.ldap.provider"> <property name="idstore.config.provider" value="oracle.security.jps.wls.internal.idstore.WlsLdapIdStoreConfigProvide r"/> <property name="CONNECTION_POOL_CLASS" value="oracle.security.idm.providers.stdldap.JNDIPool"/> <property name="username.attr" value="mail"/> </serviceInstance>
-
If the LDAP attribute containing the user's business email addresses is something other the
mailattribute, add the following element:<property name="PROPERTY_ATTRIBUTE_MAPPING" value="BUSINESS_EMAIL=attr_containing_email"/>where
attr_containing_emailis the attribute name in the LDAP provider that contains the user's email address. For instance, if the user attribute containing the email address isexternalEmail, add the following line:<property name="PROPERTY_ATTRIBUTE_MAPPING" value="BUSINESS_EMAIL=externalEmail"/>
The following sample code shows the above line inserted in the
jps-config.xmlfile:<!-- JPS WLS LDAP Identity Store Service Instance --> <serviceInstance name="idstore.ldap" provider="idstore.ldap.provider"> <property name="idstore.config.provider" value="oracle.security.jps.wls.internal.idstore.WlsLdapIdStoreConfigProvide r"/> <property name="CONNECTION_POOL_CLASS" value="oracle.security.idm.providers.stdldap.JNDIPool"/> <property name="PROPERTY_ATTRIBUTE_MAPPING" value="BUSINESS_ EMAIL=externalEmail"/> </serviceInstance>
Note:
You may have other properties defined in the same section.
-
-
Restart your domain.
2.5 Using Oracle User Messaging Service for Group Messaging
In addition to supporting bi-directional mutli-channel messaging through a variety of channels, UMS supports group messaging. This feature includes sending a message to a group of users by sending it to a group URI, or sending a message to LDAP groups (or enterprise roles) and application roles.
The group messaging feature enhances the capability of UMS by providing support for the following:
-
Sending messages to a group
-
Sending messages to a group through a specific channel
-
Sending messages to an application role
-
Sending messages to an application role through a specific channel
For more information about sending messages to groups and application roles, see "Sending Group Messages" in Developing Applications with Oracle User Messaging Service.
The group messaging feature does not require any new configuration of UMS. It reuses the UMS utility to access the User Role API. Since the User Role API configuration is not possible in UMS, any such configuration is done outside UMS. The User Role API is automatically configured to use the first Oracle Weblogic Server authenticator and does not require any special configuration.
Note:
For UMS to be able to resolve an application role, specific security grants are required. The application deployer must configure these security grants using WLST commands as in the following example:
connect('weblogic','welcome1','t3://host.example.com:7601')
createApplicationPolicy(appStripe="myapp")
grantPermission(appStripe="myapp", principalClass="oracle.security.jps.service.policystore.PolicyStoreAccessPermission",codeBaseURL="file:MW_HOME/oracle_common/communications/applications/myapp.ear/-",principalName="orcladmin",permClass="java.security.AllPermission")
grantPermission(appStripe="myapp", principalClass="oracle.security.jps.service.credstore.CredentialAccessPermission",codeBaseURL="file:MW_HOME/oracle_common/communications/applications/myapp.ear/-",principalName="GMgroup1",permClass="java.security.AllPermission"
grantPermission(appStripe="myapp", principalClass="oracle.security.jps.service.credstore.CredentialAccessPermission",codeBaseURL="file:MW_HOME/oracle_common/communications/applications/myapp.ear/-",principalName="GMrole2",permClass="java.security.AllPermission")
For more information about the security commands, see Infrastructure Security WLST Command Reference.
2.6 Configuring Automatic Message Resend
In 11g, the UMS API supports specifying fail-over addresses that are used if the message could not be delivered to the original recipient. If there are no fail-over addresses or all fail-over addresses have been tried and failed, then the message send is a complete failure. However, an administrator can select a failed message and resend it using the Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.In 12c, the automatic resend feature can be configured to automate the administrator's resend. This means that when a message send attempt is classified as a complete failure, then the message is automatically scheduled for resend. This is repeated until the message is successfully sent or the configured number of resends is achieved. The delay time and the maximum number of resends can be configured. Functionally, this is the same as an administrator manually resending the messages when the delay time has expired. The purpose of the automatic resend is to resolve temporary network problems or temporary unavailability of backend services.
The UMS server configuration parameters, ResendDefault, ResendDelay, and ResendMax have been introduced for configuring this feature. For more information about these parameters, see Table 2-1.
The number of resend attempts is configured for the server, but may be overridden programmatically per message by the client. The client can specify the number of resends to be used per message to override the ResendDefault server configuration parameter. Note that although overridden, it is limited by the ResendMax configuration parameter.
For more information about setting the number of resend attempts programmatically, see sections "Using UMS Java API to Specify Message Resends" and "Using UMS Web Service API to Specify Message Resends" in Developing Applications with Oracle User Messaging Service.
The status of the failover addresses can be received by calling getTotalFailovers() and getFailoverOrder(). For more information about these methods, see User Messaging Service Java API Reference. When failover order equals total failovers, the API user knows that the failover chain is exhausted. However, the resend functionality works as a loop over the failover chain. You can call getMaxResend() and getCurrentResend() to know when the resend and failover chain is completely exhausted.
Note:
If message resend fails even after automatically trying to resend the message the maximum number of times, then the administrator can send it manually from the Enterprise Manager. The resend counter will be reset. If the maximum number of resends is configured to 0, then the behaviour will be identical to that in 11g, that is an administrator will have to manually select the failed message and resend it using the Enterprise Manager.
2.7 Securing the Oracle User Messaging Service
The User Communications Preferences User Interface can be secured at the transport-level using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). By default, all deployed web services are unsecured. Web Service Security should be enabled for any services that are deployed in a production environment.
-
To enable SSL in the Oracle WebLogic Server, see "Configure SSL for Oracle WebLogic Server" in the Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. This step is sufficient to secure the User Communication Preferences User Interface.
UMS supports the use of Oracle Web Services Manager WS-Security policies to protect UMS web services. For more information about Oracle Web Services Manager, see "Using Oracle Web Services Manager Security Policies", in Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
The recommended security configuration for web services uses Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) tokens to pass identities between web service clients and UMS. With SAML tokens, instead of the web service client passing a username and password to UMS, a trust relationship is established between the client and UMS because of exchanging certificates. Once this keystore configuration is in place, the web service client passes only the user identity, and vouches for the fact that it has authenticated the user appropriately.
The recommended policies to use for UMS web services are:
-
oracle/wss11_saml_token_with_message_protection_service_policy (server-side) -
oracle/wss11_saml_token_with_message_protection_client_policy (client-side) -
oracle/wss11_saml_token_identity_switch_with_message_protection_client_policy (client-side)Note:
The choice of client-side policy depends on the security context in which your application is executing.
-
If the thread that is making the web service call has the intended Subject associated with it (for example, from a web application that performs user authentication, or a Java EE module with a run-as identity defined), then use the policy
oracle/wss11_saml_token_with_message_protection_client_policy.The current thread Subject is passed through using the SAML Policy WS-Security headers. In this case you should not specify the parameter
javax.xml.ws.BindingProvider.USERNAME_PROPERTYwhen creating your web service client instance. -
If the thread that is making the web service call has an undefined Subject associated with it, or if you must programmatically supply a different identity, then use the policy
oracle/wss11_saml_token_identity_switch_with_message_protection_client_policy, and specify the parameterjavax.xml.ws.BindingProvider.USERNAME_PROPERTYwhen creating your web service client instance. If you want to perform dynamic identity switching, you must grant additional code permissions to your application. For more information, see Administering Web Services.
-
2.7.1 Web Service Security on Notification
The different web services include corresponding notification web services (MessageNotification) that run on the client side and receive notifications (message delivery status, message receipt, presence status change) when the appropriate event occurs.
2.7.2 Enabling UMS Web Service Security
To enable a policy for a UMS web service, follow the steps in "Attaching OWSM Security Policies Using the Administration Console" in Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server, selecting policy oracle/wss11_saml_token_with_message_protection_service_policy. This configuration must be repeated for each service that you want to secure.
2.7.3 Enabling Client Security
Web service client security must be enabled programmatically. When using the client libraries described in Developing Applications with Oracle User Messaging Service, WS-Security policy configuration is provided when a client object is constructed. The client constructors take an argument of type Map<String, Object>. In general when using SAML authentication, the key/value pairs (Table 2-28) should be added to the configuration map in addition to other required properties such as the endpoint address.
Table 2-28 Client Security Keys
| Key | Typical Value |
|---|---|
oracle.ucs.messaging.ws.ClientConstants.POLICIES |
oracle/wss11_saml_token_ with_message_protection_ client_policy |
|
|
Endpoint URL for the remote UMS WS. This is typically "http://<host>:<port>/ucs/messaging/webservice". |
javax.xml.ws.BindingProvider.USERNAME_PROPERTY |
(Optional) Note: Do not specify this key while using |
oracle.wsm.security.util.SecurityConstants.Conf ig.KEYSTORE_RECIPIENT_ALIAS_PROPERTY |
(optional) keystore alias for target service. See Client Aliases. |
|
|
Used for OWSM policy attachment. Specifies a credential store key to use for looking up remote username/password information from the Oracle Web Services Management credential store map. |
Example 2-1 Web Service Client Security
HashMap<String, Object> config = new HashMap<String, Object>();
config.put(BindingProvider.ENDPOINT_ADDRESS_PROPERTY,
"http://example.com:8001/ucs/messaging/webservice");
config.put(oracle.ucs.messaging.ws.ClientConstants.POLICIES, new String[]
{"oracle/wss11_saml_token_with_message_protection_client_policy"});
mClient = new MessagingClient(config);
2.7.4 Keystore Configuration
To use the recommended WS-Security policy, you must configure a keystore containing the public and private key information required by OWSM. Refer to "Configuring the Credential Store Using WLST" in Securing Web Services and Managing Policies with Oracle Web Services Manager for information on how to configure the keystore and corresponding credential store entries.
-
If both your web service client and UMS server are in the same domain, then they share a keystore and credential store.
-
If your web service client and UMS server are in different domains, then you must import the UMS public key into your client domain's keystore, and must import your client domain's public key into the UMS keystore.
2.7.5 Client Aliases
When using certain WS-Security policies such as the SAML policy recommended here, the client must use the server's public key to encrypt the web service request. However, there is generally only one keystore configured per domain. Therefore, if you have a domain in which there are web service clients that communicate with web services in multiple other domains, then you may be required to override the default keystore entry used by OWSM.
For example, if you have a domain in which application "A" is a web service client to a UMS web service, and application "B" is a web service client to a web service in another domain, then A's requests must be encrypted using the public key of the UMS domain, and B's requests must be encrypted using the public key of the other domain. You can accomplish this goal by overriding the keystore alias used by OWSM for each request:
-
Import (for example) the UMS public key with alias "ums_public_key", and the other public key with alias "other_public_key".
-
When creating an UMS Web Service client, specify the recipient keystore alias parameter, setting the key to
oracle.wsm.security.util.SecurityConstants.Config.KEYSTORE_RECIPIENT_ALIAS_PROPERTYand the value to "ums_public_key" as shown in Example 2-2.HashMap<String, Object> config = new HashMap<String, Object>(); config.put(BindingProvider.ENDPOINT_ADDRESS_PROPERTY, "http://example.com:8001/ucs/messaging/webservice"); config.put(ClientConstants.POLICIES, new String[] {"oracle/wss11_saml_token_ identity_switch_with_message_protection_client_policy"}); config.put(BindingProvider.USERNAME_PROPERTY, "user1"); config.put(oracle.wsm.security.util.SecurityConstants.Config.CLIENT_CREDS_ LOCATION, oracle.wsm.security.util.SecurityConstants.Config.CLIENT_CREDS_LOC_ SUBJECT); config.put(oracle.wsm.security.util.SecurityConstants.Config.KEYSTORE_RECIPIENT_ ALIAS_PROPERTY, "ums_public_key"); config.put(MessagingConstants.APPLICATION_NAME, "MyUMSWSApp"); mClient = new MessagingClient(config); -
The other web service client similarly must override the keystore alias, but the exact mechanism may differ. For example if using a JAX-WS client stub directly, then you can add the override property to the JAX-WS request context. See "Overriding the Policy Configuration for the Web Service Client" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server for more details.
2.7.6 Securing JMS Resources
This (optional) procedure enables administrators to restrict access to the Oracle User Messaging Service's JMS resources (such as queues) for enhanced security.
To secure the JMS system resources, lock all JMS sub-deployments that start with the name UMSJMSSystemResource (there may be multiple automatically-created resources for UMS in a multi-server or cluster deployment) with the role OracleSystemRole. Do this using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, or you may run a WLST script (available at MIDDLEWARE_HOME/oracle_common/communications/bin/secure_jms_system_resource.py) as follows:
MIDDLEWARE_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin/wlst.sh
./secure_jms_system_resource.py
-userConfigFile=<UserConfigFile>, -userKeyFile=<UserKeyFile>
-url=<AdminServer_t3_url> -jmsSystemResource=<JMSSystemResourceName> -role=<SecurityRoleToUse>
The UserConfigFile shall contain encrypted username and password for the AdminUser. The key for the encrypted data shall be in UserKeyFile.
By default, the UMS system runs as the user OracleSystemUser for accessing JMS resources. If the user OracleSystemUser does not exist, or you secure the UMS JMS resources with any other role that some other user has been granted, you must override the default user identity used by the UMS system by specifying an alternate username.
2.8 Troubleshooting Oracle User Messaging Service
To debug User Messaging Service, first check the server diagnostic logs. The logs may contain exception, error, or warning messages that provide details about incorrect behavior along with actions to remedy the problem. Table 2-29 describes additional methods for debugging common User Messaging Service problems.
Table 2-29 Troubleshooting UMS
| Symptom | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
|
SSL handshake error. |
The default keystore ( |
Change the default keystore for WebLogic Server. Configure the Custom Identity and Java Standard Trust keystore for the WebLogic Server. For more information about configuring the keystore using WebLogic Server Administration Console, see the "Configuring Keystores" topic in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. |
|
Notifications are not being sent from BPEL or Human Workflow components in SOA. |
Notification Mode is set to NONE in SOA Workflow Notification configuration. |
Change the Notification Mode setting to EMAIL or ALL using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control. |
|
Email notification is not being sent. |
The Outgoing (SMTP) Mail Server settings in the UMS Email Driver are incorrect. |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
Note: Validate the values by using them in any email client for connecting to the SMTP server. |
|
The SMTP server requires authentication or a secure connection (TLS or SSL). |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
|
|
|
Notifications are not being sent because of error message: |
The UMS Driver for the appropriate channel is configured with a specific list of SenderAddresses, and the message sent by the application has set a non-matching Sender Address. Note: UMS Server matches the outbound message's sender address, if set, against the available drivers' SenderAddresses to find a matching driver to use for delivering the message. If a driver has set one or more SenderAddresses, then the UMS Server only sends messages with the matching sender address to it. |
|
|
The email client inconsistently receives notifications. |
The Incoming Mail Server settings in the UMS Email Driver are configured with the same email account to which notifications are being sent. If the notification is sent to the same account, the UMS Email Driver may download and process the email before the email client can display it. |
Use an exclusive email account for Incoming Mail Server settings. Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
|
|
SOA Human Workflow notifications are sent, but are not actionable. |
The Actionable Email Address is not configured in SOA Workflow Notification Properties. |
Set the Actionable Email Address in SOA Workflow Notification Properties with the address of the email account configured in the UMS Email Driver. |
|
The Human Workflow task is not set to send actionable notifications. |
Set the actionable attribute for the Human Workflow task in JDeveloper and redeploy the SOA composite application. |
|
|
SOA Human Workflow actionable notifications are sent, but no action is taken after responding. |
The Incoming Mail Server settings in the UMS Email Driver are incorrect. |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
Note: Validate the values by using them in any email client for connecting to an IMAP or POP3 server. |
|
The mail access protocol is incorrect. |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
|
|
|
The email server is SSL-enabled. |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
|
|
|
The receive folder name is incorrect. |
Check the following settings in the UMS Email Driver using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control:
Note: Some email servers may expect the value INBOX to be inbox or Inbox (that is, case-sensitive). Based on your email server, use an appropriate value. |
|
|
A nondefault email client is configured for receiving notifications. When the user clicks the approval link, the default mail client page opens, which may send emails to a different email server. |
Configure the default email client to receive actionable notifications. |
|
|
SOA BPEL User Notification or Human Workflow notifications are sent to the correct delivery type (email, sms, and so on) but to the wrong address. |
A self-provisioned messaging channel was created by the user in User Messaging Preferences for use in BPEL User Notification or Human Workflow use cases. Note: The User Messaging Preferences UI allows the end user to create his or her own messaging channel for various use cases, but these are not to be used for BPEL User Notification and Human Workflow. |
Do not use a self-provisioned messaging channel for BPEL User Notification or Human Workflow use cases (that is, do not set as Default channel, and do not use in a messaging filter for such use cases). BPEL User Notification and Human Workflow use User Messaging Preferences only for the delivery type preference, and the actual address is retrieved from the user profile in the identity management system. Note: Addresses from the user profile in the identity management system are available through User Messaging Preferences using predefined channel names, such as Business Email, Business Mobile, Business Phone, Instant Messaging. Use these predefined messaging channels instead for BPEL User Notification and Human Workflow use cases. |