2 Getting Started with MAF Application Development
This chapter includes the following sections:
2.1 Introduction to Declarative Development for MAF Applications
The Oracle Mobile Application Framework (MAF) extension in JDeveloper provides a number of overview editors and other wizards to facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of MAF applications. Using these wizards, you can create a MAF application, define one or more application features, add content to an application feature, and deploy the MAF application to a test environment or device in a relatively short amount of time.
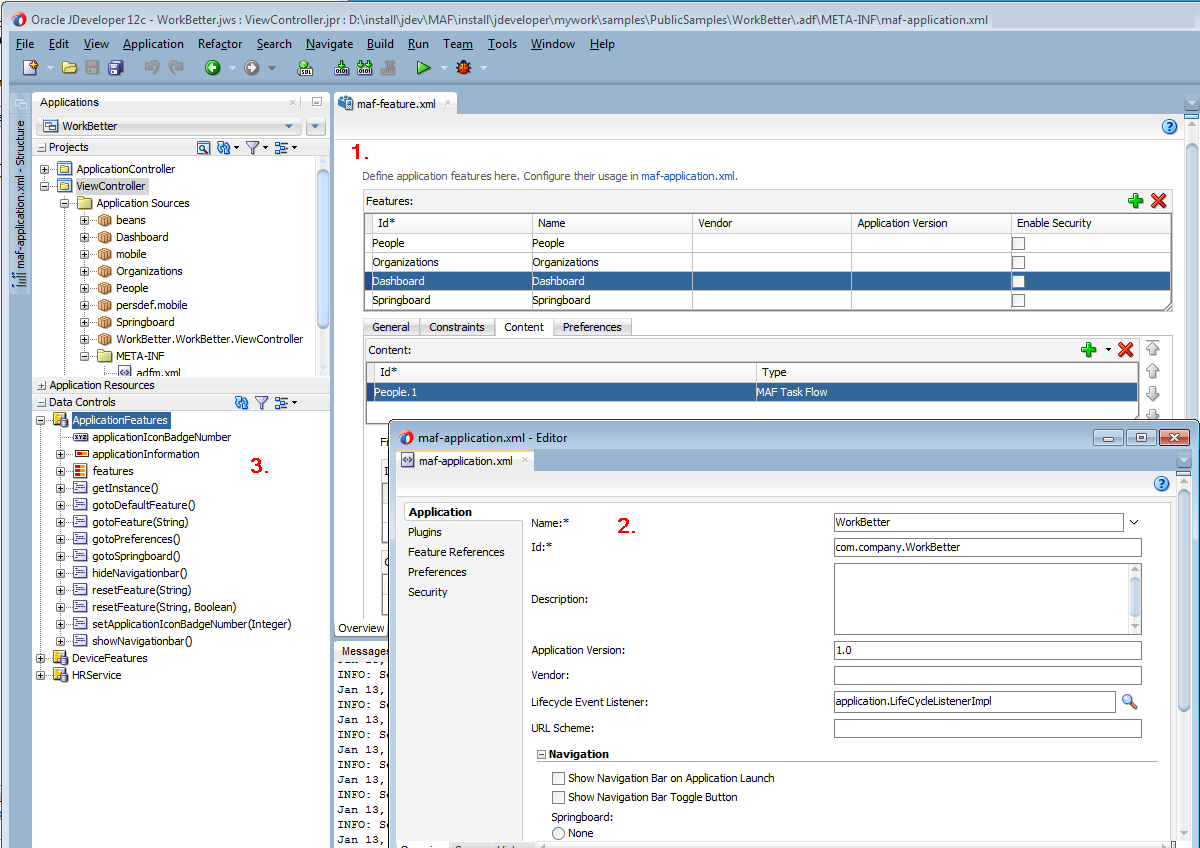
Figure 2-1 shows the WorkBetter sample application in JDeveloper's Applications window where a number of the items that you use to develop MAF applications are identified:
The overview editor for the
maf-features.xmlfile opens by default when you create a new MAF application. Use this overview editor to define the application features that your MAF application contains.Use the overview editor for the
maf-application.xmlfile used to, among other things, specify the MAF application's name, the default navigation menus (navigation bar or springboard) that the application renders, security, and device access options for the application.By default, JDeveloper creates a MAF application with two data controls (ApplicationFeatures and DeviceFeatures). These data controls expose operations that you can drag to a MAF AMX page where JDeveloper displays context menus to complete configuration of the operation when you drop it on the page. For example, dragging the
hideNavigationBar()operation to a page prompts JDeveloper to display a context menu where you configure a control for end users to hide an application's navigation bar.
The WorkBetter sample application is one of a number of sample applications that MAF provides to demonstrate how to create mobile applications using MAF. For more information, see MAF Sample Applications.
JDeveloper proposes default options in the wizards so that you can create a MAF application with one application feature displaying one MAF AMX page as follows:
Create a MAF application, as described in Creating a MAF Application.
Define an application feature for the MAF application, as described in Defining Application Features for a MAF Application.
Add content to the application feature, as described in Adding Content to an Application Feature.
Figure 2-1 Overview Editors for Application Features and Application
2.2 Creating a MAF Application
Before you can create a MAF application, download, install, and configure the MAF extension in JDeveloper. For more information, see Installing Oracle Mobile Application Framework. Once you have completed this task, create a MAF application using the creation wizards in JDeveloper.
2.2.1 How to Create a MAF Application
You create a MAF application in JDeveloper using the application creation wizard.
To create a MAF application:
- In the main menu, choose File and then Application > New.
- In the New Gallery, in the Items list, double-click Mobile Application Framework Application.
- In the Create Mobile Application Framework Application wizard, enter application and project details like name, directory, and default packages. For help with the wizard, press F1 or click Help.
- Click Finish.
2.2.2 What Happens When You Create a MAF Application
JDeveloper creates a MAF application with two projects (ApplicationController and ViewController) and two data controls (ApplicationFeatures and DeviceFeatures). It also creates files that you use to configure your MAF application and files that your MAF application needs when you deploy it to the Android and/or iOS platform(s).
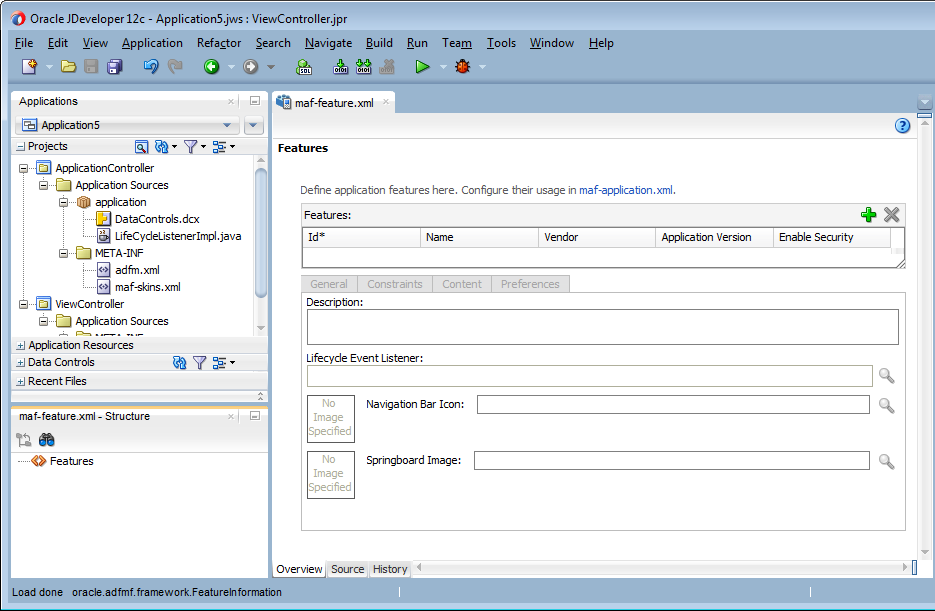
By default, JDeveloper opens the overview editor for the maf-features.xml file in the ViewController project of the newly-created MAF application, as shown in Figure 2-2 . Use this overview editor to add one or more application features to your MAF application. A MAF application must have at least one application feature. For more about adding application features to a MAF application, see Defining Application Features for a MAF Application.
For more information about the files and artifacts that JDeveloper generates when you create a MAF application, see MAF Application and Project Files.
Figure 2-2 Overview Editor for Application Features in Newly-Created MAF Application
2.3 Defining Application Features for a MAF Application
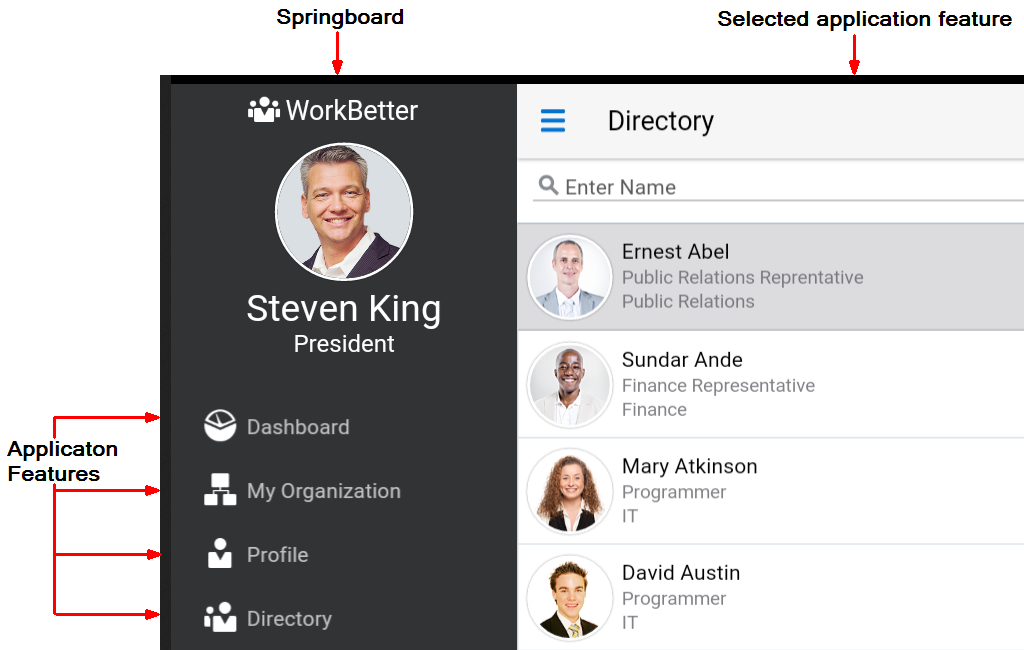
A MAF application must have at least one application feature. The WorkBetter sample application, for example, includes four application features (Dashboard, People, Organizations, and Springboard). Figure 2-3 shows three of these application features displaying in that application's custom springboard.
Figure 2-3 Application Features in the WorkBetter Application's Springboard
2.4 Adding Content to an Application Feature
One of the tasks to do after you define an application feature is to add content to the application feature. Choose among the following types to render content in your application feature:
MAF AMX Page: Choose this content type if you want the application feature to render MAF AMX pages.
MAF Task Flow: Choose this content type if you want the application feature to render a collection of activities that make up a task flow. Examples of activities that you can include in a task flow are views (to display MAF AMX pages), method calls (to invoke managed bean methods), and task flow calls (to call other task flows).
Local HTML: Choose if you want the application feature to render HTML page.
Remote URL: Choose if you want the application feature to render content from a remote URL.
The general steps to add a content type to an application feature are the same for all content types. That is, you choose the type of content to add to the application feature in the Content tab of the Features page of the maf-features.xml file's overview editor. For the specific steps for each content type, see Defining the Content Type of MAF Application Features .
2.5 Adding Application Features to a MAF Application
You can automatically add an application feature to a MAF application when you define it by selecting the Add a corresponding feature reference to maf-application.xml checkbox in the Create MAF Feature dialog, as described in How to Define an Application Feature.
Use the Feature References page of the maf-application.xml file's overview editor if you want to add an application feature that you did not add to the MAF application when you created it, you use the Feature References page of the maf-application.xml file's overview editor.
You can also add application features to your MAF application that you import from Feature Archive (FAR) files. You must import the application feature into your MAF application before you can add an application feature to the MAF application. For more information about importing from FAR files, see Reusing MAF Application Content .
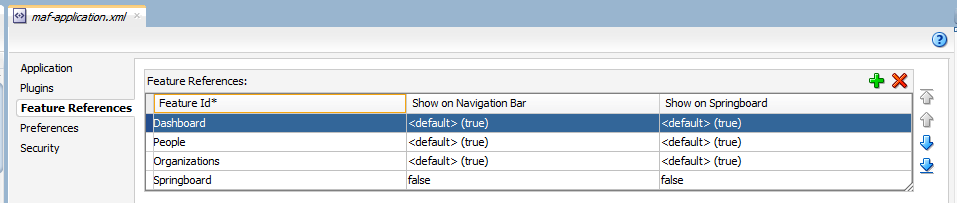
Figure 2-4 shows the Feature References page where you add application features to a MAF application.
Figure 2-4 Adding Application Features Using the Feature References Page
2.5.1 How to Add an Application Feature to a MAF Application
You use the Feature References page in the overview editor of the maf-application.xml file to add application features to a MAF application.
To add an application feature to a MAF application:
- In the Applications window, expand the Application Resources panel.
- In the Application Resources panel, expand Descriptors and then ADF META-INF.
- Double-click the maf-application.xml file and in the overview editor that appears, click the Feature References navigation tab.
- In the Feature References page, click the Add icon.
- In the Insert Feature Reference dialog, select the ID of the application feature from the dropdown list.
- Click OK.
2.5.2 What You May Need to Know About Feature Reference IDs and Feature IDs
JDeveloper writes an entry in the maf-application.xml file to reference the application feature that you add to the MAF application.
In the maf-application.xml file, the refId attribute of an <adfmf:featureReference> element identifies the corresponding application feature in the maf-feature.xml file. For this reason, the value of the refId attribute for a <adfmf:featureReference> element in the maf-application.xml file must match the value of the id attribute defined for the <adfmf:feature> element in the maf-feature.xml file.
Use a naming convention consistently to make sure that application feature IDs are unique. Application feature IDs must be unique across a MAF application.
Example 2-1 shows the entries for the People application feature in the WorkBetter sample application's maf-application.xml and maf-feature.xml files.
Example 2-1 Feature Reference and Feature ID for an Application Feature in WorkBetter Application
<!-- Feature Reference ID in maf-application.xml File --> <adfmf:featureReference id="fr2" refId="People"/> ... <!-- Feature ID in maf-feature.xml File --> <adfmf:feature id="People" name="People" icon="images/people.png" image="images/people.png"> ...
2.6 Creating MAF AMX Pages and MAF Task Flows
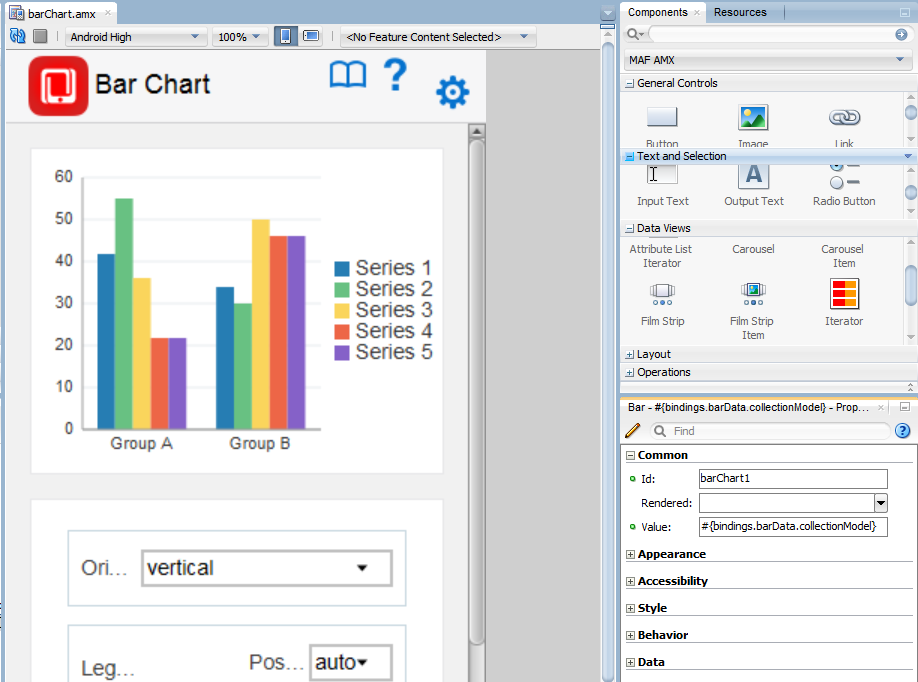
As described in Creating MAF AMX Pages , the MAF AMX components enable you to build pages that run identically to those authored in a platform-specific language. MAF AMX pages enable you to declaratively create the user interface using a rich set of components. Figure 2-5 illustrates the declarative development of a MAF AMX page.
Figure 2-5 Creating a MAF AMX Page
These pages may be created by the application assembler, who creates the MAF application and embeds application features within it, or they can be constructed by another developer and then incorporated into the MAF application either as an application feature or as a resource to a MAF application.
The project in which you create the MAF AMX page determines if the page is used to deliver the user interface content for a single application feature, or be used as a resource to the entire MAF application. For example, a page created within the application controller project, as shown in Figure 2-9 , would be used as an application-wide resource.
Tip:
To make pages easier to maintain, you can break it down in to reusable segments known as page fragments. A MAF AMX page may be comprised one or more page fragments.
MAF enables you to arrange MAF AMX view pages and other activities into an appropriate sequence through the MAF task flow. As described in Creating Task Flows, a MAF task flow is visual representation of the flow of the application. It can be comprised of MAF AMX-authored user interface pages (illustrated by such view activities, such as the WorkBetter sample application's default List page and the Detail page in Figure 2-6 ) and nonvisual activities that can call methods on managed beans. The non-visual elements of a task flow can be used to evaluate an EL expression or call another task flow. As illustrated by Figure 2-6 , MAF enables you to declaratively create the task flow by dragging task flow components onto a diagrammer. MAF provides two types of task flows: a bounded task flow, which has a single point of entry, such as the List page in the WorkBetter sample application, and an unbounded task flow, which may have multiple points of entry into the application flow. The WorkBetter sample application is located in the PublicSamples.zip file within the jdev_install/jdeveloper/jdev/extensions/oracle.maf/Samples directory on your development computer.
Figure 2-6 MAF Task Flow
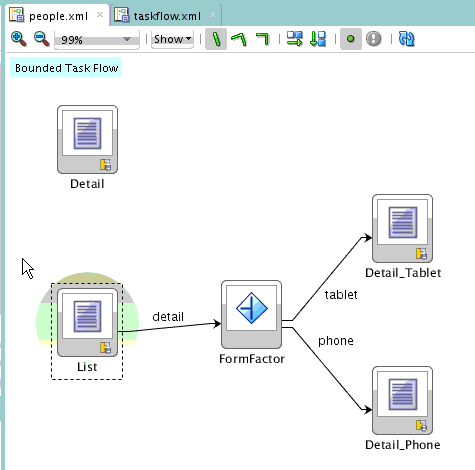
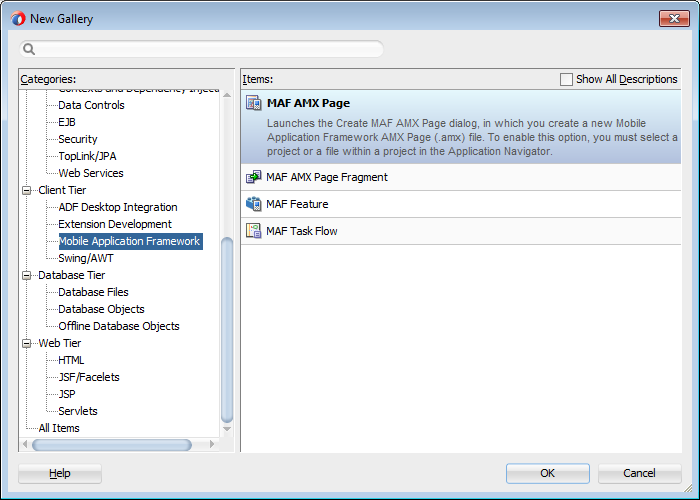
Figure 2-7 shows wizards that MAF provides to add MAF task flows, AMX pages, reusable portions of MAF AMX pages called MAF page fragments, and application features. To access these wizards, select a view controller or application controller project within the Applications window and choose File > New. Select one of the wizards after selecting Mobile Application Framework within the Client Tier.
Figure 2-7 Wizards for Creating Resources for Application Features
2.6.1 How to Create a MAF AMX Page
You can use the MAF AMX Page wizard to create AMX pages used for the user interface for an application feature, or as an application-level resource (such as a login page) that can be shared by the application features that comprise the MAF application. For more information about application feature content, see Defining the Content Type of MAF Application Features .
To create a MAF AMX page as content for an application feature:
In the Applications window, right-click the view controller project.
Choose File and then New.
From the Client Tier node in the New Gallery, choose MAF AMX Page and then click OK.
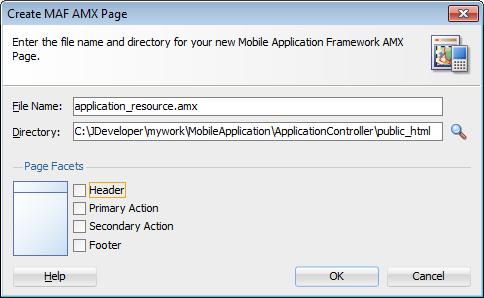
Complete the Create MAF AMX Page dialog, shown in Figure 2-8 , by entering a name in the File Name field. In the Directory field, enter the file location, which must be within the
public_htmlfolder of the view controller project.Figure 2-8 Creating a MAF AMX Page in a View Controller Project
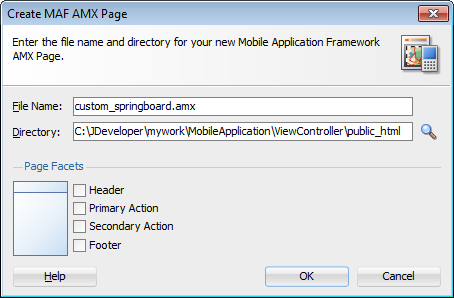
Select (or deselect) the Facets within the Panel Page that are used to create a header and footer. Click OK.
For more information, see How to Use a Panel Page Component.
Build the MAF AMX page. For more information about using the AMX components, see Creating MAF AMX Pages. See also Defining the Application Feature Content as a MAF AMX Page or Task Flow.
To create a MAF AMX page as a resource to a MAF application:
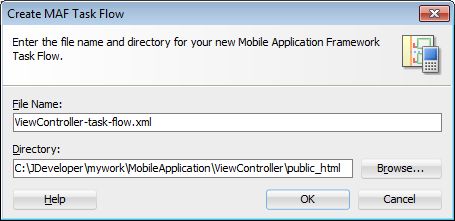
2.6.2 How to Create MAF Task Flows
You can deliver the content for an application feature as a MAF task flow.
To create a MAF Task Flow as content for an application feature:
2.6.3 What Happens When You Create MAF AMX Pages and Task Flows
JDeveloper places the MAF AMX pages and task flows in the Web Content node of the view controller project, as shown by custom_springboard.amx and ViewController-task-flow.xml (the default name for a task flow created within this project) in Figure 2-11 . These artifacts are referenced in the maf-feature.xml file. To manage the unbounded task flows, JDeveloper generates the adfc-mobile-config.xml file. Using this file, you can declaratively create or update a task flow by adding the various task flow components, such as a view (a user interface page), the control rules that define the transitions between various activities, and the managed beans to manage the rendering logic of the task flow.
Figure 2-11 MAF AMX Pages and Task Flows within Application Controller and View Controller Projects
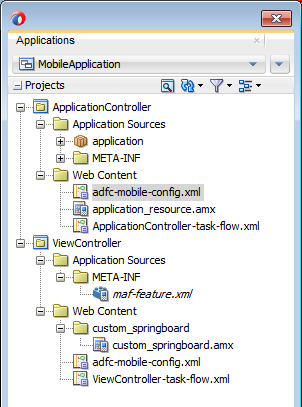
JDeveloper places the MAF AMX page and task flow as application resources to the MAF application in the Web Content node of the application controller project. As illustrated in Figure 2-11 , the file for the MAF AMX page is called application_resource.amx and the task flow file is called ApplicationController-task-flow.xml (the default name).
2.7 Containerizing a MAF Application for Enterprise Distribution
At the time of deployment, you can choose to wrap the MAF application with the Oracle Mobile Security Suite (OMSS) to take advantage of its enterprise mobile application management capabilities. OMSS allows secure access to corporate applications and data from mobile devices while preserving a rich user experience. Its Mobile Security Container creates the enterprise Workspace on any iOS or Android device, corporate-owned or personal. Employees get seamless access to corporate data and applications with enterprise-grade security and single sign-on authentication.
With the Mobile Security App Containerization Tool, you can add a standardized security layer to native mobile applications. The containerization process is simple and injects the following security services into your application.
Secure data transport: An encrypted AppTunnel through Mobile Security Access Server to application back-end resources behind an enterprise firewall.
Authentication: Managed by the Secure Workspace application and provides single sign-on across applications in the secure workspace.
Secure data storage: Encrypted storage of application data, including files, database, application cache and user preferences.
Data leakage controls: The ability to restrict file sharing and copy paste to only other trusted applications. This enables you to control the sharing of data, including e-mail, messaging, printing and saving.
Dynamic policy engine: More than 50 detailed application controls, including authentication frequency, geo and time fencing as well as remote lock and wipe.
The OMSS single sign-on authentication and user identity propagation to MAF application services is supported only for applications configured to use the Web SSO authentication server type for login connections. Applications using HTTP Basic, OAuth, or Mobile-Social authentication will be required to log in to the MAF application after the Container authentication is successful. For details about these authentication types and the role they play in OMSS, see What You May Need to Know About Login Connections and Containerized MAF Applications.
The containerization process is simple and does not change the way you develop the MAF application. In fact, you should not change application code specifically with containerization in mind. You develop the MAF application the same way whether or not you intend to deploy with OMSS containerization enabled.
When you deploy the application with OMSS containerization enabled, JDeveloper runs the Mobile Security App Containerization Tool provided by OMSS to containerize the MAF application.
After deployment, the MAF application developer works with the OMSS system administrator to get the application added to OMSS Mobile App Catalog and to configure appropriate policies. For details, see the Managing Mobile Apps chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
When the user launches the containerized MAF application, the Secure Workspace application redirects to the Mobile Security Container, which performs SSO authentication before handing the session back to the MAF application. The containerized MAF application does not require VPN to connect to internal websites or services. Instead a secure AppTunnel is established between the application and Mobile Security Access Server (MSAS), which provides secure transport for accessing internal sites and services that have been registered for access by mobile device users.
For more information about how OMSS containerization affects MAF applications, see these sections:
For the JDeveloper procedure to containerize the MAF application for OMSS, see Deploying with Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
For details about accessing secure web services behind the corporate firewall by the containerized MAF application, see What You May Need to Know About Accessing Web Services and Containerized MAF Applications.
For details about the authentication process of containerized MAF applications, see Overview of the Authentication Process for Containerized MAF Applications.
In the OMSS documentation library, refer to the following list of resources for details about OMSS administration tasks related to mobile devices and workspace containers.
For background information about OMSS, see the Understanding Oracle Mobile Security Suite chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
For details about how system administrators use the OMSS Mobile Security Manager console to enroll the MAF application user’s mobile device and workspace, see the Enrolling Devices and Workspaces chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Suite
For details about how system administrators use the OMSS Mobile App Catalog to manage the MAF application provisioned to devices and workspaces, see the Managing Mobile Apps chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
For details about how system administrators use the OMSS Mobile Security Manager console to manage access to a corporate file shared by MAF application capabilities, see the Managing Mobile Security Policies chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
In the OMSS documentation library, refer to the following list of resources for details about MSAS administration tasks related to securing resources and authentication.
For background information about MSAS, see the Getting Started with Mobile Security Access Server chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Access Server.
For details about how system administrators create a proxy application to define forward proxy URLs for protected resources accessed by MAF applications, see the Managing Mobile Security Access Server Applications chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Access Server.
For details about how system administrators attach predefined security policies to forward proxy URLs and secure access by the MAF application to protected web services, see the Securing Mobile Security Access Server Resources chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Access Server.
For details about how system administrators configure a MSAS authentication endpoint to handle authentication on the MAF application user’s mobile device by the Secure Workspace application, see the Configuring a Mobile Security Access Server Instance chapter in Administering Oracle Mobile Security Access Server.