| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
Oracle Applications GUI-based architecture aggregates several related business functions into a single form. Because all users should not have access to every business function in a form, Oracle Applications provides the ability to identify pieces of applications logic as functions. When part of an application's functionality is identified as a function, it can be secured (i.e., included or excluded from a responsibility).
Application developers register functions when they develop forms. A System Administrator administers function security by creating responsibilities that include or exclude particular functions.
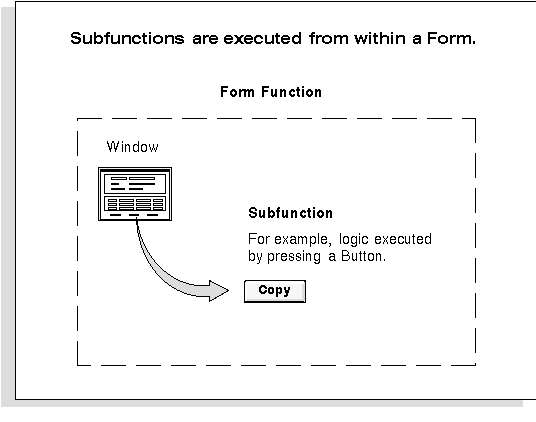
There are two types of functions: form functions, and non-form functions. For clarity, we refer to a form function as a form, and a non-form function as a subfunction, even though both are just instances of functions in the database.
A developer can write a form to test the availability of a particular subfunction, and then take some action based on whether the subfunction is available in the current responsibility.
Subfunctions are frequently associated with buttons or other graphical elements on forms. For example, when a subfunction is enabled, the corresponding button is enabled.
However, a subfunction may be tested and executed at any time during a form's operation, and it need not have an explicit user interface impact. For example, if a subfunction corresponds to a form procedure not associated with a graphical element, its availability is not obvious to the form's user.
Figure 1 - 1.
Functions, Menus, and the Navigate Window
Overview of Oracle Applications Security
Implementing Function Security
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |