Release 2.1
A76915-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle(R) Enterprise Manager Getting Started with the Oracle Diagnostics Pack Release 2.1 A76915-01 |
|
Oracle Performance Manager is an Oracle Enterprise Manager application that allows you to monitor different types of real-time performance data.
Oracle Performance Manager uses the Agent data gathering service (also called the Oracle Data Gatherer) to collect performance data. To monitor some types of data, you must install the Oracle Data Gatherer on the system (or systems) where you want to monitor data. See the Oracle Intelligent Agent User's Guide for information on managing the Agent data gathering service on a system.
If you are using Oracle Performance Manager to monitor database performance, the Agent data gathering service can be installed on another system. See "Accessing Performance Data Through an Intermediate Host" for more information on accessing data through an Agent data gathering service on another system.
The types of performance data that Oracle Performance Manager can monitor on a system depends on the products that are installed. Table 3-1 shows the types of data (or services) that Oracle Performance Manager can monitor when various Oracle products are installed.
If additional products from Oracle or other vendors are installed, Oracle Performance Manager may be able to monitor additional types of data not shown in Table 3-1.
Oracle Performance Manager relies on the Oracle Data Gatherer to monitor a service (such as a node, a database, or a concurrent manager). Usually, the collection of the data is done on the system where the service is located. However, for some types of services Oracle Performance Manager can also monitor data on a system by using the Oracle Data Gatherer on another system (an intermediate host).
This intermediate host could be the client system where the Oracle Performance Manager is running, or any other system on the network on which the Data Gatherer is available.
There are three ways to set the location of the Oracle Data Gather. The method you use depends on how you connect to the service. Consider the following three scenarios:
Performance Manager attempts to connect to the Data Gatherer on the host where the service is located. If this connection fails or cannot be attempted because no preferred credentials have been set for the database, you will be prompted with a dialog box containing logon credentials for the database. This dialog box also contains a field to specify the location of the Oracle Data Gatherer that will be used to collect performance data.

Performance Manager displays a Logon dialog box. This dialog box also contains a field to specify the location of the Data Gatherer that will be used to collect performance data.
Performance Manager displays the Database Logon dialog box for the selected service. This dialog box also contains a field to specify the location of the Data Gatherer that will be used to collect performance data.
Using Oracle Performance Manager, you can:
You can start Oracle Performance Manager from the Oracle Enterprise Manager console or from the Start menu.
You can start Oracle Performance Manager from the Oracle Enterprise Manager console in any of the following ways:
On the Start menu, follow the path: Start=>Programs=>ORACLE_HOME=>Diagnostics Pack=>Performance Manager.
When you start Performance Manager from the Start menu, you are given a choice of logging in to the Oracle Management Server or running Performance Manager in standalone mode.
To run Oracle Performance Manager in repository mode:
To select an alternate Management Server, click the Management Server button next to the Management Server drop-down list. In the resulting dialog box, you can add another node that is running Oracle Management Server software. The Oracle Management Server and its associated repository must already exist.
For information on the fields in the Management Servers dialog box, click Help.
If the repository information for the Diagnostics Pack has not been created, Oracle Performance Manager automatically updates the repository at connection time.
To run Oracle Performance Manager in standalone mode (not connected to the Oracle Enterprise Manager repository), click Standalone, no repository connection, then click OK.
The primary component of the Oracle Performance Manager user interface is the main window (see Figure 3-1), which contains two panels. The navigator or tree panel appears on the left side of the main window and the property sheet panel appears on the right side. When you select an item in the navigator panel, the property sheet panel displays the properties of the selected item.
When you first start Oracle Performance Manager, the navigator panel displays the service type folders and the property sheet panel displays the Performance Manager welcome screen.
A vertical toolbar appears on the left side of the window and a menu bar appears across the top of the window. For more information about the buttons in the toolbar and the commands available from the Performance Manager menus, choose Window from the Performance Manager Help menu.
In the navigator panel, the Network folder contains a folder for each service type. For example, when you have the Diagnostics Pack installed, the service types are Nodes, Databases, and SQL Servers.
In addition to the Network folders, the Recordings folder contains any recordings of chart data that exist. For more information about the Recordings folder, see "Recording Chart Data" .
If you are working in repository mode, expand a service type folder to view the corresponding services previously discovered through the Oracle Enterprise Manager console.

To connect to a discovered service, select the service in the navigator tree and click Connect to Service in the Performance Manager toolbar, or click the plus sign (+) next to the service in the navigator. You may be prompted with a Logon dialog box if credentials are required to connect to the service. For information on the fields in the Logon dialog box, click Help.
If you are working in standalone mode, the service type folders are empty and you must manually add each service you want to monitor to the navigator tree.
If you are working in repository mode, you can manually add additional services that have not been discovered using the Enterprise Manager console.
To add and connect to a service manually:
Performance Manager displays a Logon dialog box.
For information on the fields in the Logon dialog box, click Help.
After you connect to a service, Performance Manager displays the classes of performance information you can monitor for the selected service. Expand a class to see the individual performance data charts available for the selected class.
You can display a chart using one of the following methods:
Performance Manager displays each chart or chart group in its own window, which is separate from the main window. This window is called the Chart Display window. For more information, see "Using the Chart Display Window" .
You can view charts from multiple services concurrently by connecting to the services from the navigator tree and displaying the chart.
Some types of data include a chart group, which is two or more charts that are displayed within a single Chart Display window. You display a chart group the same way as you view any other chart (see "Viewing Performance Manager Charts").
You can display a special chart group that contains the Overview Charts for a selected service:
Performance Manager displays a chart group containing some key statistics most likely of interest to database administrators monitoring the selected service.
Charts in a chart group are displayed within a single window. You perform actions, such as setting options and displaying drill-down charts, on one chart at a time within a chart group. The currently selected chart within a chart group window is identified by a highlighted title. For example, the Memory Faults chart is the currently selected chart in Figure 3-2.
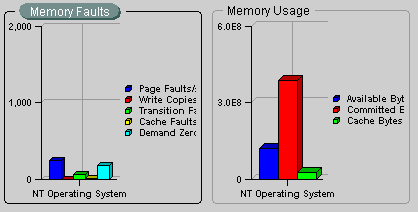
Besides viewing the Overview Charts for a selected service, you can also view a chart group provided with a data class. For example, you can select the Memory data class for a Windows NT node and display the Memory at a Glance chart group. Not all data classes provide chart groups, however.
For some charts, the chart's property sheet allows you to select the collected data to display and the data sources for which the collected data should be displayed.
The collected data are the statistics that can be monitored and displayed in the chart. The data sources are the items from which Oracle Performance Manager is able to collect the data. For example, the data source of disk statistics may be disk1 or disk2, and the data source of file statistics may be file1 or file2.
By clicking in the column next to the name of the collected data or the name of the data source in the chart property sheet, you can specify whether or not to monitor that collected data or data source and display it in the chart.

When a green check mark appears in the column, Oracle Performance Manager will display that collected data or data source in the chart. If you click in the column again, the check mark goes away, which indicates that Oracle Performance Manager will not display that collected data or data source. You can toggle back and forth between monitoring and not monitoring all the collected data or data sources by clicking in the column head. If the check mark is gray, it means Oracle Performance Manager will display the collected data or data source, and you are unable to change the selection of this data.
If the chart definition contains default data source or collected data attributes, then those items are preselected in the chart's property sheet.
When you display a chart, Oracle Performance Manager opens the Chart Display window. The window contains its own toolbar and menu bar. For information about the Chart Display window, choose Window from the Chart Display window Help menu.
To change the format of the chart, click one of the chart format buttons in the Chart Display window toolbar.
For example, suppose a chart initially displays as a bar chart. To see the data as a pie chart, click the Pie Chart button in the toolbar. You can also display a chart in one of the additional formats:
For more information about the buttons on the Chart Display window toolbar, see the Oracle Performance Manager online help.
By default, most charts are set to refresh every five seconds. That means that Performance Manager collects the data every five seconds and then immediately refreshes (or redisplays) the chart using the new data.
To change the refresh rate for the current chart:
Performance Manager displays the Set Refresh Rate dialog box.
By default, Performance Manager continues to collect performance data and update the current chart using the current refresh rate.
To pause a chart so it stops redisplaying based on the refresh rate, click the Pause Chart button in the Chart Display toolbar.
To restart the chart, click the Resume Chart button in the Chart Display toolbar.
After you display a chart in the Chart Display window, you can still modify the collected data and data sources for the chart. For more information about selecting the collected data and data sources before you display a chart, see "Selecting Collected Data and Data Sources".
To set the chart options:

Performance Manager displays the Set Options dialog box.
For more information on selecting data sources and selecting collected data, click Help.
Oracle Performance Manager also allows you to select filters to limit the data collected for a chart. However, not all charts provide filters.
For charts that allow you to filter the chart data, you can select a limit to the number of data sources that are displayed. For example, if the data sources are the processes on an operating system, you can modify the chart to display only 10 processes, rather than all the processes.
For example, to select a limit to the number of data sources that are displayed for the Pagefaults Per Session chart, do the following:
You can locate the chart by traversing the tree as follows: Network=>Nodes=><Name of Node>=>Process=>Pagefaults Per Process.
The 10 data sources will be sorted by Page Faults per second, as shown in the Sort the data by drop-down list.
Performance Manager displays the chart, but includes a maximum of 10 data sources.
You can later change this setting after the chart is displayed:
These options can be useful for finding the top resource users. In the case where processes are the data sources and the data collected is memory usage and CPU usage, you can ask the Agent data gathering service to limit the number of data sources to 10, and to sort by memory usage. Your chart would then show the 10 processes using the most memory. If you were to sort by CPU usage, you would get the 10 processes using the most CPU instead.
Some charts can also give different views of the data. If that feature is available, you will also be able to select a view of the data. An example of a data view may be the current rate per second or current rate per transaction for each piece of data collected in the chart.
Some types of charts have their own unique commands. For example, you can select the Kill Session command when you are viewing the Lock Manager charts for Oracle database services.
To see if a chart-specific command is available for a chart:
Some charts have drill-down charts associated with them. To see if any drill-down charts are available for the current chart, do one of the following:
In either case, Performance Manager displays any drill-down charts associated with that chart item as menu options on the Drilldown menu. If a list of drill-down chart names is not displayed, it means no drill-down charts are associated with that item.
|
Note: If you have trouble selecting a particular data item when you try to drill down for related data, pause the chart or reduce the refresh rate. For more information, see "Pausing and Restarting a Chart". |
From a Performance Manager real-time chart, you can drill down to see an historical view of the same data collected over a longer period of time, for example, days, months, and years. This view of historical data, provided by the Oracle Capacity Planner software, allows you to analyze long-term trends in the data.
Historical data collection must be enabled to view the historical data for a chart. If you drill down to a historical chart for which historical data collection has not been enabled, Performance Manager allows you to start historical data collection. You can also start historical data collection by starting Oracle Capacity Planner. From the Capacity Planner window, you can also control other aspects of your historical data collection, such as how often data is collected and loaded into the historical database.
To drill down to historical data:
What happens next depends on whether or not you have begun collecting historial data. Consider three possible scenarios:
Note that if you previously set up your historical database using an alternate database location, Performance Manager displays a database logon box before it displays the Analysis Chart window.
The Analysis Chart window shows you the historical information about the collected data. From here, you can modify the format of the chart or perform a trend analysis on the historical data. For more information, select an option from the Help menu in the Analysis Chart window or see the chapter about Capacity Planner in this manual.
The historical chart cannot be displayed because there is no history available for the data sources or data items. Would you like to begin collecting the history of these data sources and data items now so that you can view the chart in the future?
Click Yes to begin collecting historical data automatically or click Help to learn how to collect historical data using the Oracle Capacity Planner software.
When you click Yes, Performance Manager displays another message explaining that historical data is now being gathered, but is not yet available. Click Continue to return to the Display Chart window.
Error connecting to the historical database.
The specified schema is not a Capacity Planner database.
Click Continue. Performance Manager displays the message described in the previous bullet item.
Click Yes to begin collecting historical data or click Help for more information about how historical data is collected. When you click Yes, Performance Manager displays another message explaining that historical data is now being gathered, but is not yet available.
Click Continue to return to the Display Chart window.
You can display bar charts with either a horizontal or vertical orientation.

To change the orientation of the bar chart, click the button associated with the orientation that you want.
When a chart is displaying data in table format, the sort order of the column data can be changed by clicking the column headers in the table. The first click on a column header sorts the data in ascending order, and a second click sorts the data in descending order.
Changing the sort order in the chart table does not affect the data's sort order on the server. To change the sort order of the data on the server, use the Options page. For more information, see "Selecting Chart Options".
If you are working in repository mode and you make modifications to a chart (for example, if you change the format, orientation, or sorting order of a chart), you can save your changes in one of two ways:
Performance Manager saves your changes using the same name as the original chart. When you display the chart again, your changes will appear in the Chart Display window.
To later remove your changes and display the predefined chart using its original settings, click Remove Chart on the Chart menu.
Performance Manager displays the Save Custom Chart dialog box. Use this dialog box to enter a name for the custom chart and to indicate whether you want to create a similar chart for other services of the same type. For information about the fields on the Save Custom Chart dialog box, click Help.
Click OK in the Save Custom Chart dialog box to save the custom chart using the name you provided. Performance Manager saves the chart in the Custom Charts folder for the selected service.
To delete a custom chart from the Custom Charts folder, select the chart and click Remove Chart on the Chart menu.
To get help on a class or chart:
If help is available for the selected chart, Performance Manager displays a message box or a help topic window describing the chart data.
To get help on a data item:
If help is available for the selected item, Performance Manager displays a pop-up balloon or a message box describing the data item.
To print a chart, click the Print Screen button on the Display Chart window toolbar.
The size of the chart on the screen determines the size of the chart in the chart printout. For example, when you print a chart that is 5 inches high and 7 inches wide on your screen, the chart will be 5 inches high and 7 inches wide in the printout.

To generate an HTML report for a chart:
Performance Manager displays a dialog box that tells you the name of the HTML file used to display the report and where the file will be saved.
You can view the report later using a Web browser, or--if you have experience with Web publishing tools and techniques--you can share the report with your co-workers by publishing the HTML file and its associated graphic files on a Web server.
Oracle Performance Manager allows you to record the data being monitored in a chart. After a recording is complete, you can play it back. During playback, you can pause and fast forward the recording, if you wish.
Chart recordings are saved under the Recordings folder and on the Recordings tab of the right pane of the Performance Manager main window when a recorded chart is selected. The Recordings tab is added to a chart's property sheet after you record the chart.
You can manage chart recordings in the Recordings folder without connecting to the service from which a chart was recorded. If you are already connected to a service, you can see a chart's recordings by selecting the Recordings tab in that chart's Detail property sheet.
You start a recording by performing one of the following steps:
Oracle Performance Manager displays the Recording Parameters dialog box. For more information on the fields in the Recording Parameters dialog box, click Help.
To stop recording a chart, do one of the following:
|
Note: Before you can play a recording, you must stop the recording. For more information, see "Stopping a Recording". |
To play a recording, do the following in the Performance Manager main window:
The Stop Playback, Pause Playback, and Fast Forward buttons become available in the playback window (Figure 3-3). When the playback is complete, the Reset Playback button becomes available.
To remove a recording:
In addition to predefined charts, you can define your own charts for database services based on user-defined scripts. By defining your own charts, you can take a snapshot of data at any given interval. After successful evaluation of the script, you can define the operations to be performed on the data.
To define a new chart:
The resulting New Chart property sheet includes the SQL Script Command page and the Data Items page.
Performance Manager evaluates the SQL script. If the script is valid, Performance Manager displays the Data Items page.
You can remove columns and change the names of the columns. You can also define new columns with data calculated from existing columns. For more information, see "Modifying the Data Items for a User-Defined Chart".
To modify an existing chart you perform the same steps as outlined in "Creating a User-Defined Chart". The only exception is that the chart label is already defined.
To modify an existing chart:
On the SQL Script Command page, you can modify the script used to gather statistics for the chart. On the Data Items page, you can remove, add, or modify the data items associated with the chart. For more information, see "Modifying the Data Items for a User-Defined Chart".
When you select a user-defined chart and then display the Data Items page, you can modify the data items for the chart as follows:

A key icon appears next to the data item you designate as the data source. The data source is the object about which Performance Manager is able to collect the data. You must designate one of the data items as the source for the user-defined chart. To designate a data item as the data source, highlight the data item you want as the data source and click this button. By default, the first data item is set as the data source.
Performance Manager removes the data item from the Data Items page.
Performance Manager displays the Add/Modify Chart Columns dialog box. For more information about this dialog, click Help. The Oracle Performance Manager Help provides details on the functions and operations available. The Help also provides an example of creating a user-defined chart.
You can copy user-defined charts from one service to another or within the same serve by using the Create Like option. To copy a user-defined chart:
Performance Manager displays the Create Like User-Defined Chart dialog box.
Note that chart labels must be unique within a service.
In the Create Like User-Defined Chart dialog box, you can choose the SQL Script Command or Data Items page to view the attributes of the chart you are copying. However, you cannot change the values of the attributes. Once the chart has been copied, you can select the new chart in the navigator tree and make any desired adjustments.
If you created user-defined charts using Oracle Performance release 1.5.0 or earlier (the Windows versions of Oracle Performance Manager), you can convert these user-defined charts so that they can be used with Oracle Performance Manager release 2.1. See "Converting User-Defined Charts From Previous Releases of Performance Manager" for information on how to perform the conversion.