20
Using Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
This chapter describes how an enterprise database administrator uses Oracle Enterprise Security Manager to administer database security in an enterprise domain of Oracle8i databases.
This information is organized into the following sections:
Introduction
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager is an administration tool that provides a graphical user interface to manage enterprise users, enterprise domains, databases, and enterprise roles that are held in a directory server.
Table 20-1 explains the terminology used when describing this tool and its features.
Table 20-1 Oracle Enterprise Security Manager Terms and Definitions
Installing and Configuring Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
The following instructions outline how to install Oracle Management Server and Oracle Enterprise Manager with the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager.
These installation steps are discussed in the following sections:
Task 1: Install Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
You do this when you install Oracle Enterprise Manager. See the platform-specific installation documentation for Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Task 2: Configure Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager must be able to connect to databases published in the directory. Therefore, there should be a TNS alias for each database, and that alias should match the global name of the database and its common name in the directory.
Use the Net8 Configuration Assistant to create a tnsnames.ora file in ORACLE_HOME/network/admin, and create service names for the databases you want to manage. This is not necessary if all databases to be managed are set up to listen for incoming TCP connections on port 1521 (part of the default setup) and their global database names are exactly hostname.domain.
Use the Net8 Configuration Assistant to set up directory access. This creates an ldap.ora file on ORACLE_HOME/network/admin.
Note:
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager allows you to specify the Net8 service to connect to a database published in the directory.
|
Task 3: Start Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
To start Oracle Enterprise Security Manager, in the command line, enter
oemapp esm
If the ldap.ora file is not configured, you receive the following alert:
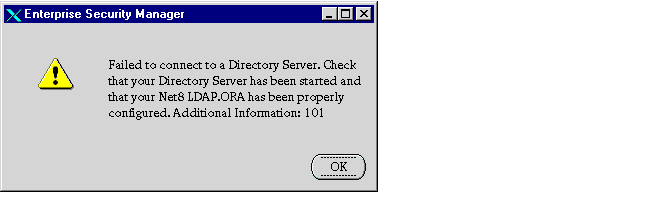
In this case, you can exit Oracle Enterprise Security Manager and run Net8 Configuration Assistant to set up directory access, then restart Oracle Enterprise Security Manager. Alternatively, you can:
If the ldap.ora file is properly configured, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager starts and automatically connects to the directory server.
- Windows NT: If you are using Microsoft's Active Directory, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager logs in to the directory using native authentication.
- UNIX: Oracle Enterprise Security Manager attempts to connect to the directory server by using SSL. If this fails, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager attempts to connect by using anonymous authentication.
On startup, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager looks something like this:
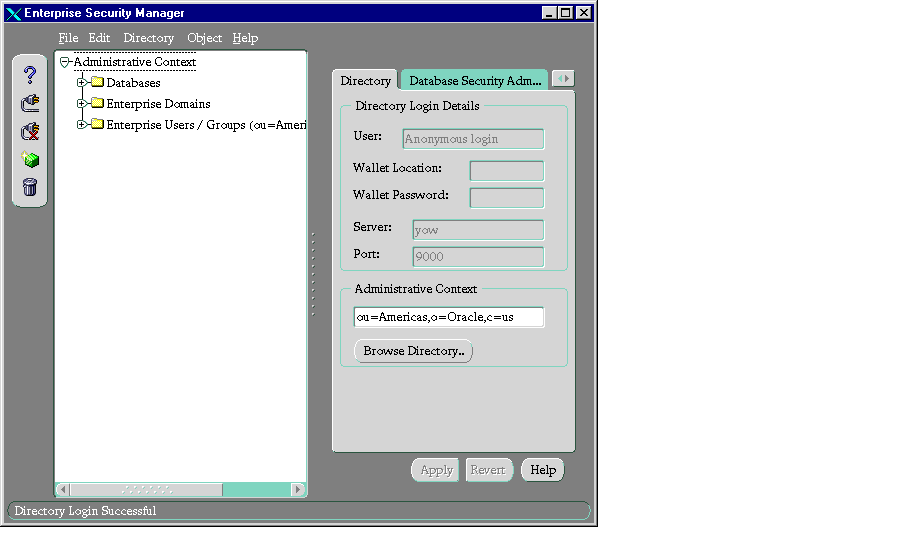
If the result of automatic login is not what you want, log out, then log back in again with the user name you want to use. To do this:
- From the menu bar, choose Directory > Logout.
- From the menu bar, choose Directory > Login. This displays the Directory Server Login dialog box.
- Proceed to "Task 4: Log Into the Directory" for instructions on filling in the fields in this dialog box.
Task 4: Log Into the Directory
To log into the directory:
- From the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager menu bar, choose Directory > Login.
- Choose the authentication type. Options are:
- Password Authentication: Uses simple authentication requiring a user DN and password.
- SSL Client Authentication: Uses two-way SSL authentication in which both client and server use Oracle wallets containing digital certificates.
- Native Authentication (Windows NT or Windows 2000 only): Relies on the operating system to determine how you log in.
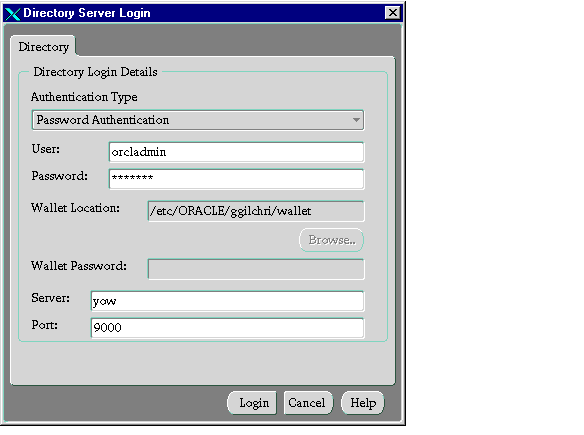
- If you are using SSL, enter the wallet location and the wallet password.
- Enter the server and port number. If you are using SSL, be sure to enter the directory's SSL port number.
- Click OK.
Navigating Oracle Enterprise Security Manager
This section introduces some basic features of Oracle Enterprise Security Manager. It does so in the following sections:
Changing a Search Base
By default, when Oracle Enterprise Security Manager performs a search, it uses as its search base the administrative context you have already set. If you want to use a search base other than the configured administrative context, do the following:
- On the menu bar, click Edit > Preferences. The Edit LDAP Preferences dialog box appears.
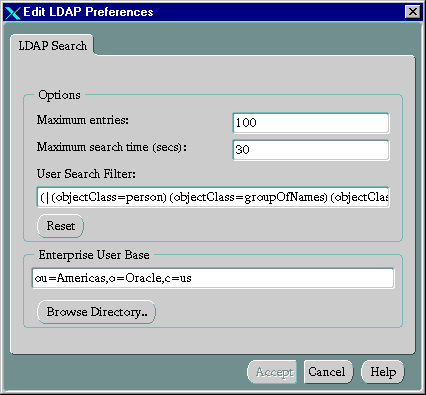
- In the Enterprise Users Base field, enter the DN you want to use as the base of the search.
You can also click Browse Directory to navigate to a directory object to use as the base of the search.
- Click Accept.
Browsing the Directory
A Browse Directory button appears frequently as you use Oracle Enterprise Security Manager. Whenever you click a Browse Directory button, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager displays a dialog box that allows you to focus your search by specifying a naming context and directory search criteria. In each context, you use this dialog box in the same way.
For example, suppose you want to change the administrative context to c=acme,c=us. To do this, you would:
- Navigate to the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager initial screen (Task 3), and click Browse Directory. The corresponding dialog box appears.
- In the Naming Context field, you would enter
c=us.
- In the Directory Search Attributes field, in the Searchable Attribute Value column, in the object class row, you would enter
organization. The entries for organizations in the U.S. would appear in the Directory Search Results: Directory Entry field.
- In the Directory Search Results: Directory Entry field, you would select the directory entry that you want to use as the new administrative context, and click OK. This would return you to the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager initial screen. The administrative context you just specified would appear in the Administrative Context field.
Use the same steps when browsing for directory objects in other contexts, for example, when using the Edit LDAP Preferences dialog box to change the base of a search.
Administering Enterprise Databases, Domains, and Users
The following instructions assume you are running Oracle Enterprise Manager and have invoked the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager.
Managing enterprise users involves working in the three top level nodes in the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager navigator pane. These three nodes are discussed in the following sections:
Administering Databases
This section tells you how to manage user/schema separation for a database.
Managing User/Schema Separation
To map an enterprise user to a database schema:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Database.
- Select the server on which you want to support user/schema separation. The corresponding tab pages appear in the right pane.
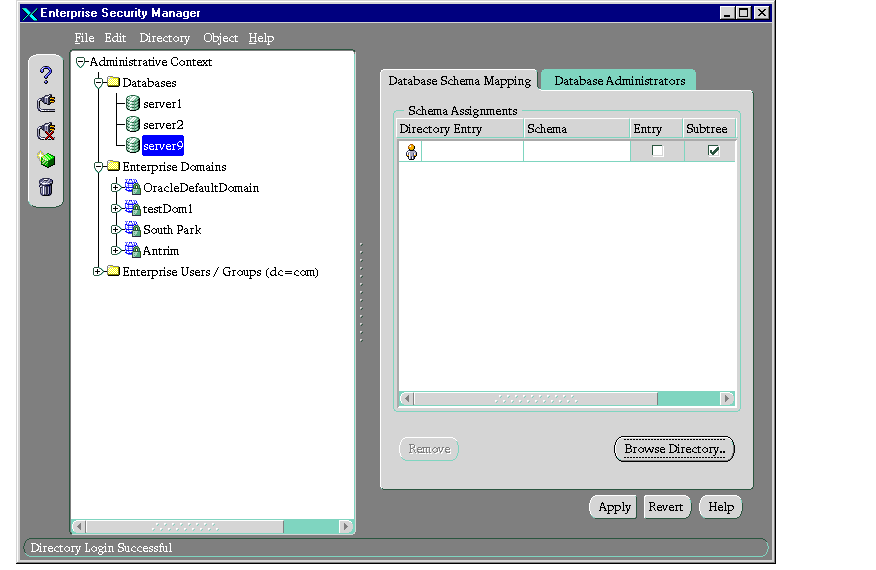
- In the Database Schema Mapping tab page, in the Schema Assignments window, in the Directory Entry column, enter either the full or partial DN of the entry that you want to map to a shared schema. You can also click the Browse Directory button to navigate to that DN.
- In the same row, in the Schema column, enter the name of an existing schema on that database.
- If this is a full DN, in the Entry column, select the check box. If this is a partial DN, in the Subtree column, select the check box.
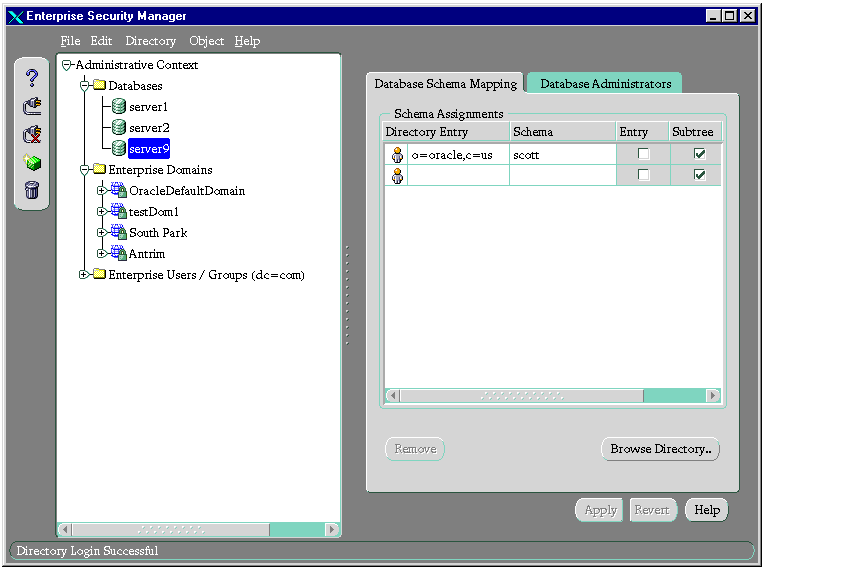
- Click Apply. The database object is updated in the directory, and an empty row is added in the Schema Assignments window should you want to add more mappings.
Administering Enterprise Domains
There is initially one enterprise domain listed under the Enterprise Domains node in the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager navigator: Oracle Default Domain. Each enterprise domain you define in the LDAP directory is added under the Enterprise Domains node.
This section discusses topics in the following subsections:
Managing User/Schema Separation
The section "Administering Databases" discussed how you manage user/schema separation on an individual database. This section tells you how to manage user/schema separation on all the databases in a given domain.
To map an enterprise user to a database schema:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains.
- Select the enterprise domain on which you want to support user/schema separation. The corresponding tab pages appear in the right pane.
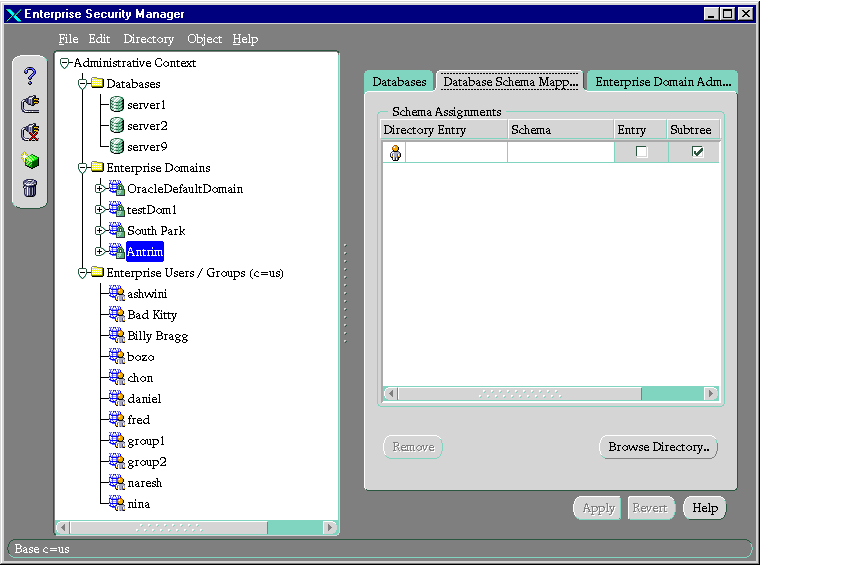
- Select the Database Schema Mapping tab.
- In the Schema Assignments window, in the Directory Entry column, enter either the full or partial DN that you want to map to a shared schema. You can also click the Browse Directory button to navigate to the DN.
- In the same row, in the Schema column, enter the name of an existing schema supported by all the databases in the domain.
- If this is a full DN, in the Entry column, select the check box. If this is a partial DN, in the Subtree column, select the check box.
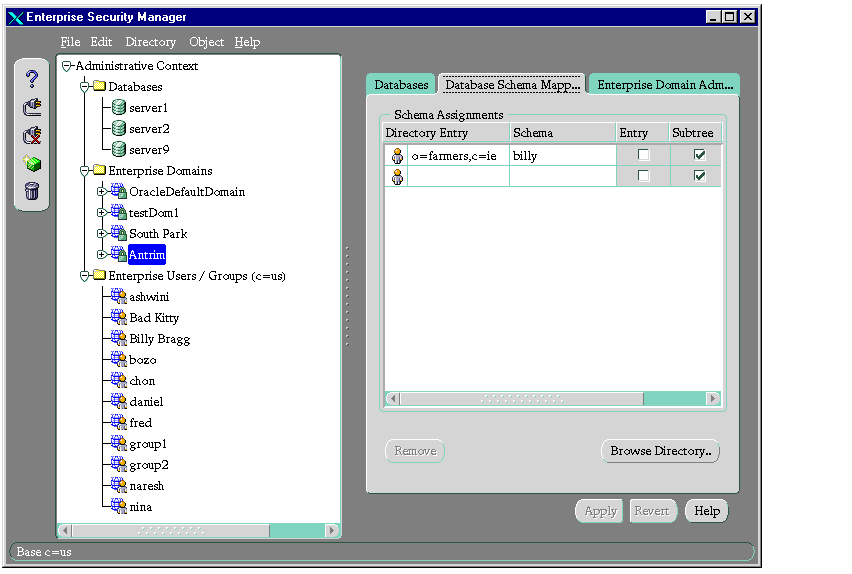
- Click Apply. The database object is updated in the directory, and an empty row is added in the Schema Assignments window should you want to add more mappings.
Creating an Enterprise Domain
An enterprise domain contains databases and enterprise roles. You create a new enterprise domain by giving a name to the new enterprise domain and defining where the enterprise domain is to be located in the directory.
To create an enterprise domain:
- Click Object > Create on the menu bar. The Create Directory Object dialog appears.
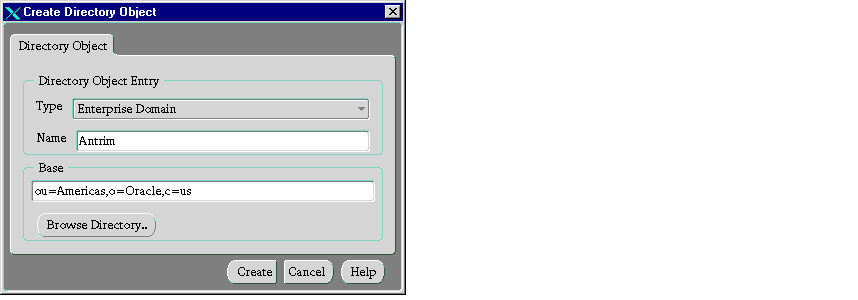
- In the Type menu, select Enterprise Domain.
- In the Name field, enter the name of the enterprise domain you want to create.
- In the Base field, Oracle Enterprise Security Manager fills in the name of the administrative context. If you want to use a different administrative context, you may change the values in this field. However, be careful to enter the name of a valid administrative context, that is, one that contains and Oracle Context.
- Click Create.The enterprise domain you just created appears at the bottom of the Enterprise Domains node.
- In the navigator pane, click the name of the enterprise domain you just created. The corresponding group of tab pages appear in the right pane.
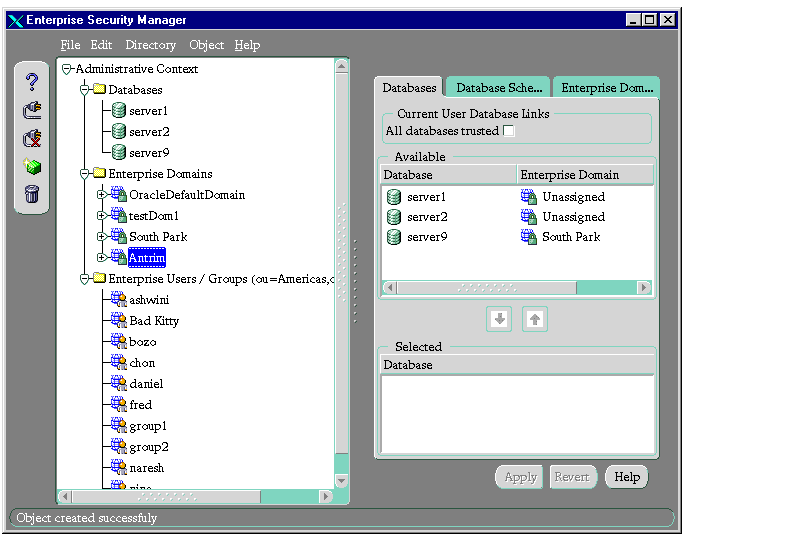
- Select the All Databases trusted check box, if desired. This allows databases within the enterprise domain to have current user database links between each other.
Note:
Individual database administrators still have the capability to configure their databases to not trust other databases.
|
You have now created an enterprise domain and can proceed to add databases to the enterprise domain you just created.
Adding a Database to an Enterprise Domain
At the completion of database installation, you directed Oracle Database Configuration Assistant to publish the database in the directory. Once you have created an enterprise domain, you can view a list of all databases registered in the directory, select a database from that list, and assign it to the enterprise domain you created.
A database should exist in only one enterprise domain at a time. Therefore, you should assign a database to an enterprise domain only if the database has a value of "Unassigned" on the Databases property page.
To assign a database to the enterprise domain:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains.
- In the navigator pane, select the enterprise domain to which you want to add a database.
- In the right pane, in the Available window, select a database name.
- Click the down arrow to move the selected database to the Selected list.
- Click Apply.
You have added a database to an enterprise domain and can proceed to create an enterprise role in that enterprise domain.
Creating an Enterprise Role within an Enterprise Domain
Once you have created an enterprise domain and added a database to it, you can create an enterprise role within the enterprise domain.
An enterprise role is a set of global roles that operate on multiple databases within an enterprise domain. An enterprise role is assigned to one or more enterprise users. The Enterprise Database Administrator uses these enterprise roles to assign sets of global roles on multiple databases to a selected user all at once.
You cannot create two enterprise roles with the same name within a single enterprise domain.You can, however, create enterprise roles with the same name in separate enterprise domains. Enterprise roles with the same name that exist in separate enterprise domains have no implied relationships.
Note:
The database obtains a user's global roles when the user logs in. If you change a user's global roles, those changes do not take effect until the next time the user logs in.
|
To create an enterprise role in an enterprise domain:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains and select the enterprise domain name. The corresponding group of tab pages appear in the right pane.
- On the menu bar, click Object > Create. The Create Directory Objects dialog box appears.
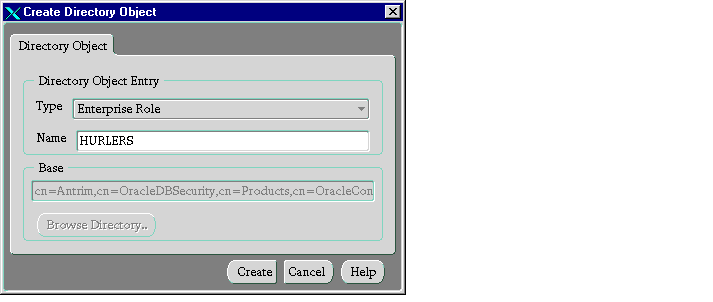
- In the Type menu, select Enterprise Role.
- In the Name field, enter the name of the enterprise role you want to create.
Note that the directory base chosen for the new enterprise role derives from the currently selected enterprise domain. You cannot edit this value.
- Click Create.
- In the navigator pane, expand Enterprise Domains > enterprise_domain_name > Enterprise Roles.
- In the navigator pane, in the Enterprise Domains subtree, select the name of the enterprise role you just created. The corresponding group of tab pages appear in the right pane.
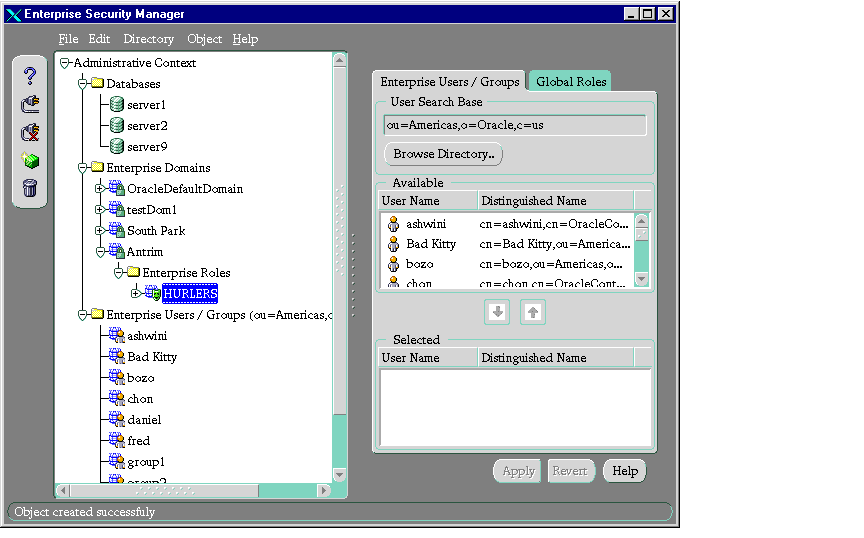
- Select the Global Roles tab.
- Select a database. The Database Login dialog box appears.
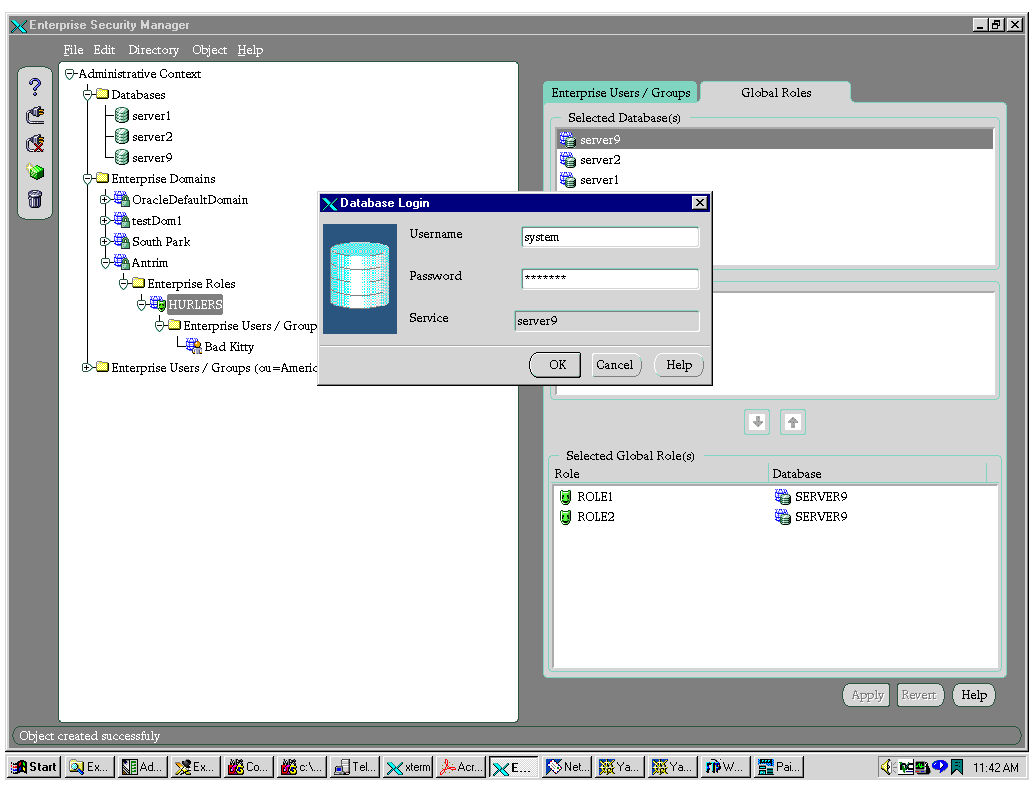
- Supply the correct information about the selected database. Click OK. The selected database roles appear in the Available Global Role(s) area.
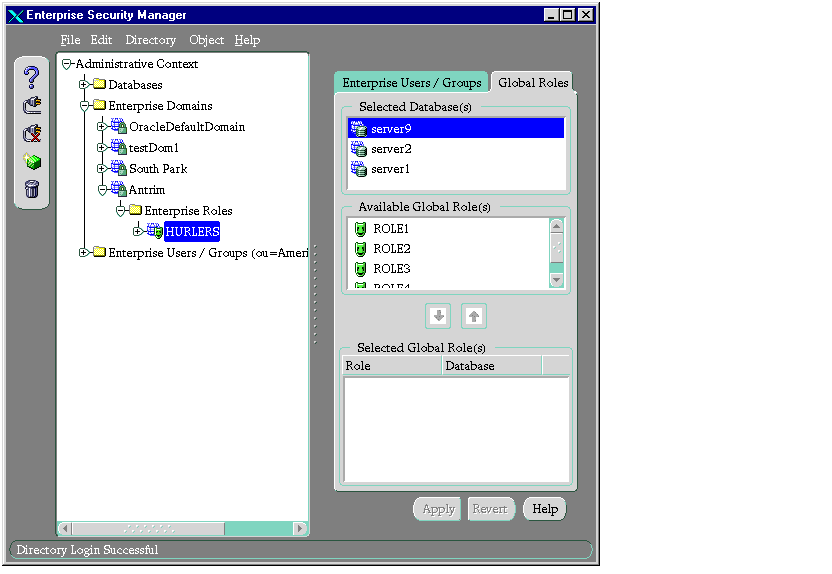
If no database service has been configured:
- In the Global Roles tab page, in the Selected Databases field, right-click the database name.
- Choose Reconnect.
- Specify a new service name.
Note:
Although Oracle Enterprise Security Manager provides this database configuration convenience, be sure to properly configure the Oracle Enterprise Security Manager Net8 client environment to support connectivity to databases as they are named in the directory server.
|
- In the Available Role(s) field, select an available role.
- Click the down arrow button to move the role into the Selected Global Role(s) area.
- Repeat steps 9 through 12 for each database from which you want to select one or more roles.
- Click Apply.
You have created an enterprise role within an enterprise domain of databases and can assign this enterprise role to any enterprise user.
Assigning Enterprise Users to an Enterprise Role
To assign an enterprise user to an enterprise role:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains > enterprise_domain_name > Enterprise Roles.
- In the navigator pane, select the enterprise role. The corresponding group of tabs pages appears in the right pane.
- In the right pane, select the Enterprise/Users Groups tab.
- In the Available window, select the enterprise users you want to assign to the role.
- Click the down arrow button. The enterprise users appear in the Selected window.
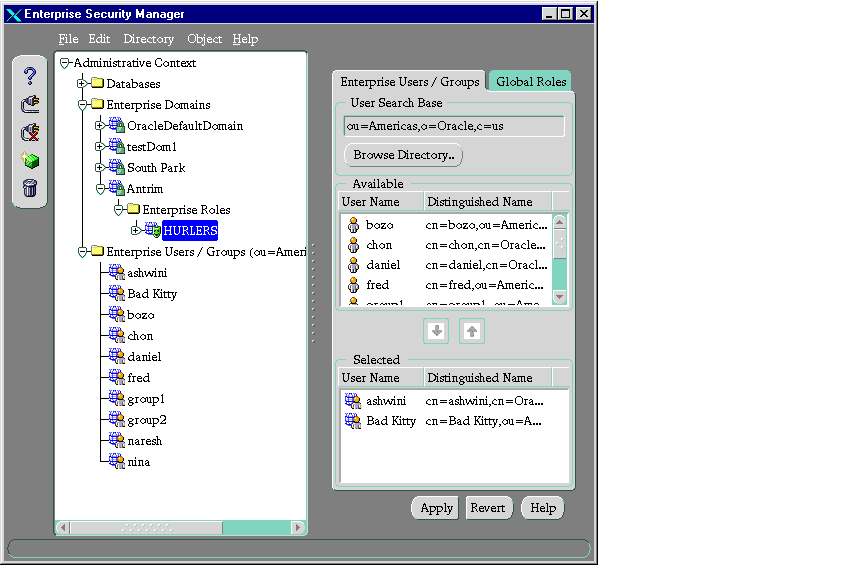
- Click Apply. The enterprise users appear under the Enterprise Role node in the navigator pane.
Removing a Database from an Enterprise Domain
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains.
- In the navigator pane, select the name of the enterprise domain from which you want to remove a database.
- In the Databases tab page, in the Selected window, select the database you want to remove from the enterprise domain.
- Click the up button to move the database from the Selected window to the Available window.
- Click Apply.
Deleting an Enterprise Domain
You must first delete all enterprise roles from the enterprise domain before you can delete the selected enterprise domain. Otherwise a message window will display informing you that you need to delete one or more enterprise roles.
To delete an Enterprise Domain:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Contexts > Enterprise Domains.
- In the navigator pane, select the name of the enterprise domain you want to delete.
- Click the Delete Object button to the left of the navigator pane.
A window asks you to confirm the deletion.
- Click Yes.
- The selected enterprise domain is removed from the enterprise domains tree.
Administering Enterprise Users
This section discusses the following tasks:
Creating a New Enterprise User
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager allows you to create new enterprise users if the users do not already exist in the directory server. To do this.
- From the menu bar, select Object > Create. The Create Directory Object dialog box appears.
- In the Type menu, select Enterprise User.
- In the Name field, enter the name of the enterprise user you want to create.
- In the Base field, accept the default, or enter a new search base as described in "Browsing the Directory".
- Click Create. The enterprise user you created appears in the navigator pane under the Enterprise Users/Groups node. When you select the new enterprise user, the corresponding tab page appears in the right pane.
Note:
In the above procedure, the directory user entry that Oracle Enterprise Security Manager creates is associated with only the top and person object classes. If you want to associate that user entry with other object classes, you must do so in an separate procedure.
|
Granting an Enterprise Role to an Enterprise User
Once you have created an enterprise user, you can assign enterprise roles to that user.
You can grant many enterprise roles to enterprise users, and these roles can exist in different enterprise domains. You can grant these roles in two ways:
When a database needs to authorize a global user, it searches the directory for those enterprise role(s) within its enterprise domain that are granted to that user.
To grant an enterprise role to an enterprise user:
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Users.
- Select the name of an enterprise user. The corresponding group of tab pages appears in the right pane.
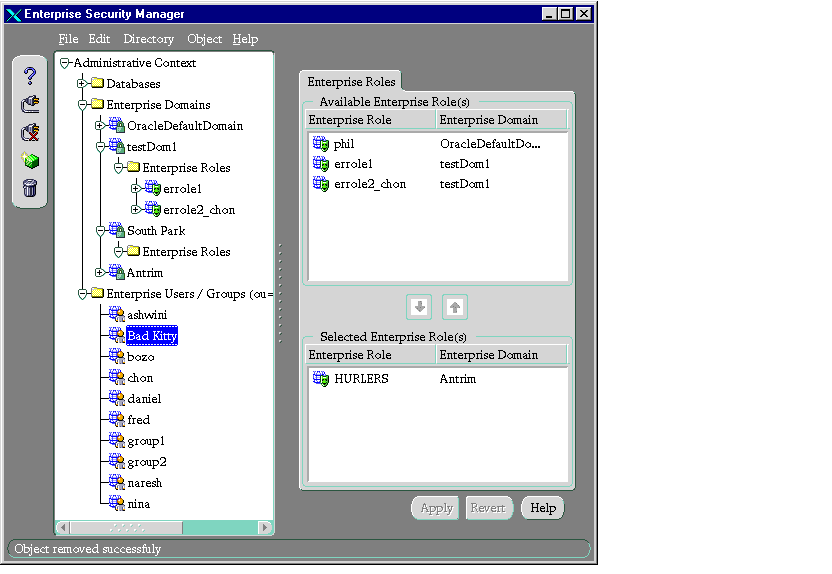
- In the Available Enterprise Role(s) window, select an enterprise role you want to grant to the enterprise user.
- Click the down arrow button.
- The selected role is moved from the Available Role(s) list to the Selected Role(s) list.
- Click Apply.
Deleting an Enterprise User
Note:
You can delete an enterprise user only if that user has no enterprise roles.
|
- Expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Users/Groups.
- Select the enterprise user you want to delete.
- On the menu bar, click Object > Delete. An alert asks you to confirm the deletion.
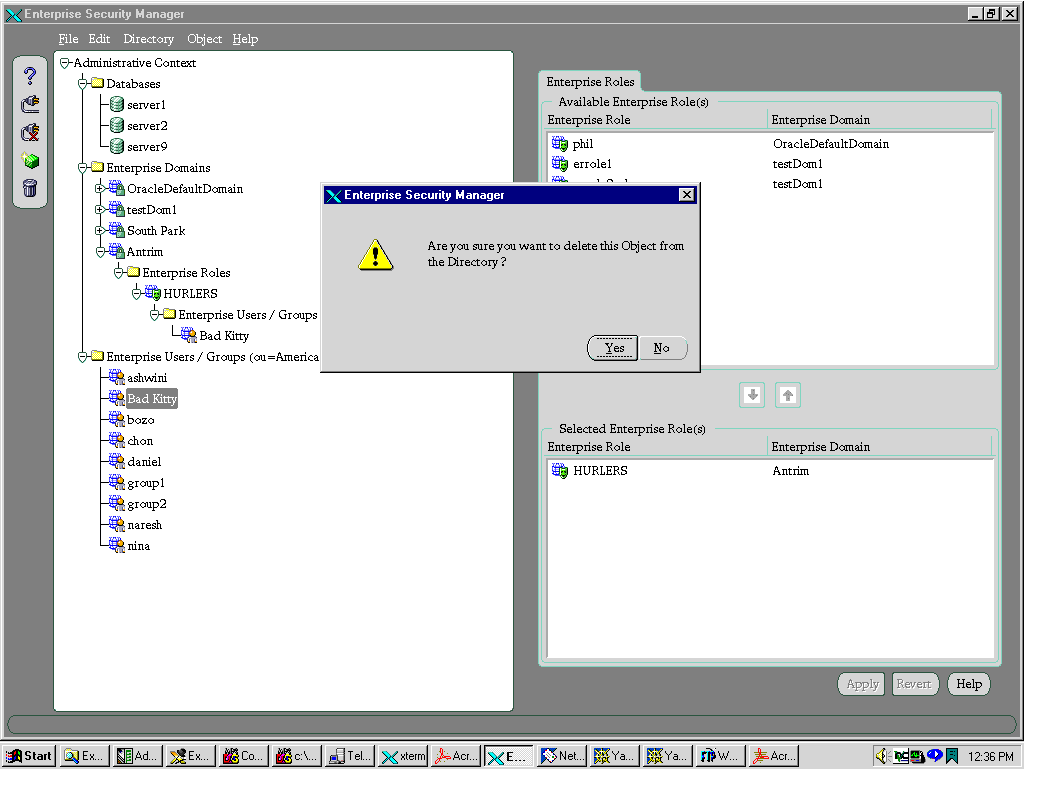
- Click Yes. The enterprise user is deleted from the tree in the navigator pane.
Managing Security Administrators
Use Oracle Enterprise Security Manager to define various administrators as described in the following sections:
Managing Database Security Administrators
To manage database security administrators, you must be a member of the Database Security Administrators group.
To specify a user to be a database security administrator:
- In the navigator pane, select Administrative Contexts.
- In the right pane, select the Database Security Administrators tab.
Enterprise user names appear in the Available field.
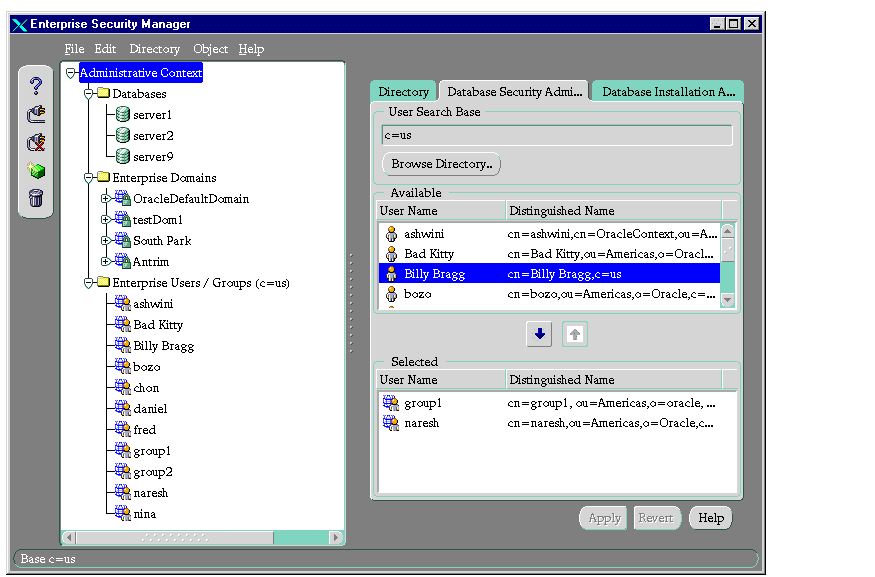
- Select the enterprise user you want to specify as an administrator.
- Click the down arrow to move the user to the Selected window.
- Click Apply.
Managing Database Installation Administrators
To manage database installation administrators, you must be a member of the Database Security Administrators group.
To specify a user to be a database installation administrator:
- In the navigator pane, select Administrative Contexts.
- In the right pane, select the Database Installation Administrators tab.
Enterprise user names appear in the Available field.
- Select the enterprise user you want to specify as an administrator.
- Click the down arrow to move the user to the Selected window.
- Click Apply.
Managing Database Administrators
To manage database administrators, you must be either a member of the Database Security Administrators group or a database administrator for this particular database.
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Database.
- Select the database for which you want to assign administrators. The corresponding group of tab pages appears in the right pane.
- Select the Database Administrators tab. The Available window displays user names of enterprise users available in the current user search base.
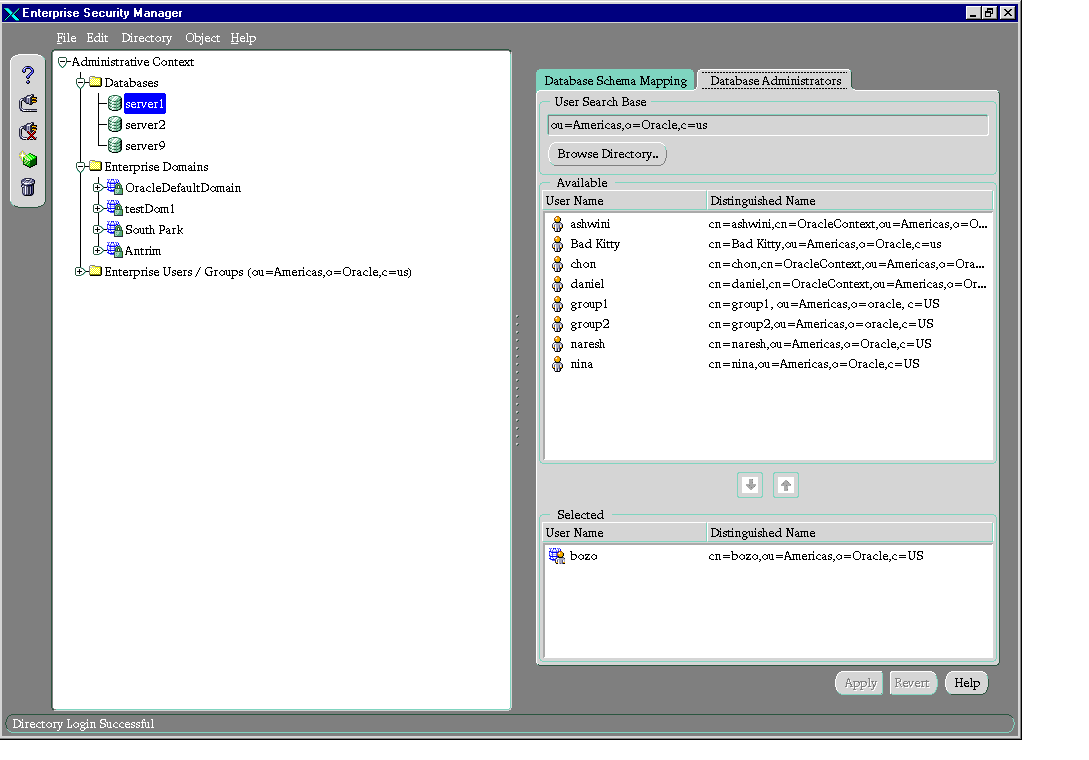
- Select the enterprise user you want to specify as an administrator.
- Click the down arrow to move the user to the Selected window.
- Click Apply.
Managing Enterprise Domain Administrators
To manage enterprise domain administrators, you must be either a member of the Database Security Administrators group of a domain administrator for this particular domain.
- In the navigator pane, expand Administrative Context > Enterprise Domains.
- Select the enterprise domain for which you want to assign administrators. The corresponding group of tab pages appears in the right pane.
- Select the Enterprise Domain Administrators tab. The Available window displays user names of enterprise users available in the current user search base.
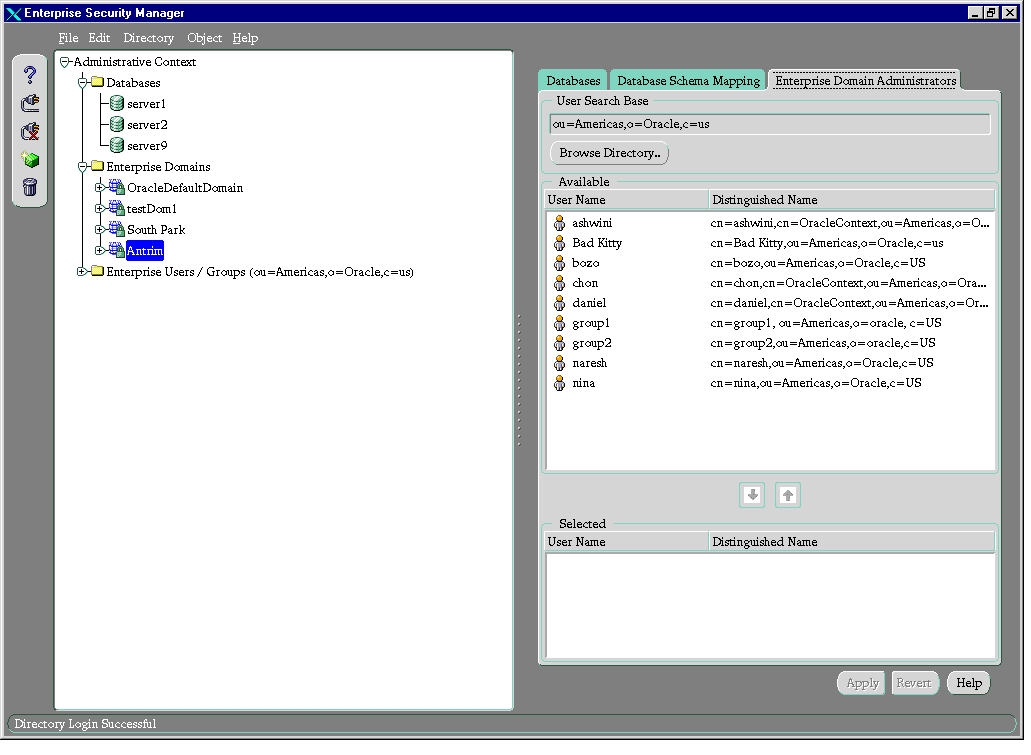
- Select the enterprise user you want to specify as an administrator.
- Click the down arrow to move the user to the Selected window.
- Click Apply.



