Release 8.1.6
A77132-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Spatial User's Guide and Reference Release 8.1.6 A77132-01 |
|
This chapter contains descriptions of the geometry functions, which can be grouped into the following categories:
This group also includes the following deprecated functions: SDO_POLY_DIFFERENCE, SDO_POLY_INTERSECTION, SDO_POLY_UNION, SDO_POLY_XOR
The geometry functions are listed Table 7-1, and some usage information follows the table.
|
Note: The SDO_POLY_xxx functions are deprecated and will not be supported in future versions of Oracle Spatial. You should use instead the corresponding "generic" (not restricted to polygons) SDO_xxx functions: SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE, SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION, SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION, and SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR. |
The following usage information applies to the geometry functions. (See also the Usage Notes under the reference information for each function.)
Examines two geometry objects to determine their spatial relationship.
SDO_GEOM.RELATE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
mask IN VARCHAR2,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN VARCHAR2;
or
SDO_GEOM.RELATE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
mask IN VARCHAR2,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN VARCHAR2;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Specifies a list of relationships to check. See the list of keywords in the Usage Notes.
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
The MDSYS.SDO_GEOM.RELATE function can return the following types of answers:
SDO_GEOM.RELATE is in the SELECT clause of the SQL statement.
The following mask relationships can be tested:
Values for mask can be combined using a logical Boolean operator OR. For example, `INSIDE + TOUCH' returns 'INSIDE + TOUCH' or 'FALSE' depending on the outcome of the test.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example checks if there is any spatial interaction between geometry objects cola_b and cola_d. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
SELECT SDO_GEOM.RELATE( c_b.shape, m.diminfo, 'anyinteract', c_d.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_b, cola_markets c_d, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_b.name = 'cola_b' AND c_d.name = 'cola_d'; SDO_GEOM.RELATE(C_B.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,'ANYINTERACT',C_D.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FALSE
None.
Returns the area of a two-dimensional polygon.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function works with any polygon, including polygons with holes.
This function does not support the units parameter that is included with the LOCATOR_WITHIN_DISTANCE operator of interMedia Locator, which is a component of the Oracle interMedia product.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example returns the areas of geometry objects stored in the cola_markets table. The first statement returns the areas all objects; the second returns just the area of cola_a. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the areas of all cola markets. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE'; NAME SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------- ------------------------------------ cola_a 24 cola_b 16.5 cola_c 5 cola_d 12.5663706 -- Return the area of just cola_a. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_a'; NAME SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------- ------------------------------------ cola_a 24
None.
Generates a buffer polygon around a geometry object.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER(
geom IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
distance IN NUMBER,
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Euclidean distance value.
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function returns a geometry object representing the buffer polygon.
This function creates a rounded buffer around a point, line, or polygon. The buffer within a void is also rounded, and is the same distance from the inner boundary as the outer buffer is from the outer boundary. See Figure 1-11 for an illustration.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
This function does not support the units parameter that is included with the LOCATOR_WITHIN_DISTANCE operator of interMedia Locator, which is a component of the Oracle interMedia product.
The following example returns a polygon representing a buffer of 1 around cola_a. Note the "rounded" corners (for example, at .292893219,.292893219) in the returned polygon. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Generate a buffer of 1 unit around a geometry. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER(c.shape, m.diminfo, 1) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_a'; NAME -------------------------------- SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,1)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, SDO_POINT(X, Y, Z) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cola_a SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1005, 8, 1, 2, 2, 5, 2, 1, 7, 2, 2, 11, 2, 1, 13, 2, 2, 17, 2, 1, 19, 2, 2, 23, 2, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY( 0, 1, .292893219, .292893219, 1, 0, 5, 0, 5.70710678, .292893219, 6, 1, 6, 7, 5. 70710678, 7.70710678, 5, 8, 1, 8, .292893219, 7.70710678, 0, 7, 0, 1))
Returns the centroid of a polygon. (The centroid is also known as the "center of gravity.")
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CENTROID(
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CENTROID(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function returns a null value if geom is not a polygon or if geom is a multipolygon.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example returns a geometry object that is the centroid of cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the centroid of a geometry. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_CENTROID(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_c'; NAME -------------------------------- SDO_GEOM.SDO_CENTROID(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, SDO_POINT(X, Y, Z) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cola_c SDO_GEOMETRY(2001, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY( 4.73333333, 3.93333333))
None.
Returns a polygon-type object that represents the convex hull of a geometry object.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CONVEXHULL(
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CONVEXHULL(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
The convex hull is a simple convex polygon that completely encloses the geometry object. Spatial uses as few straight-line sides as possible to create the smallest polygon that completely encloses the specified object. A convex hull is a convenient way to get an approximation of a complex geometry object.
The geometry object (geom) cannot be a circle.
This function returns a null value if geom is of point type or has fewer than three points or vertices.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example returns a geometry object that is the convex hull of cola_c (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1. This specific example, however, does not produce useful output -- the returned polygon is identical to the input polygon -- because the input polygon is already a simple convex polygon.)
-- Return the convex hull of a polygon. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_CONVEXHULL(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_c'; NAME -------------------------------- SDO_GEOM.SDO_CONVEXHULL(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, SDO_POINT(X, Y, -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cola_c SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1003, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARR AY(6, 3, 6, 5, 4, 5, 3, 3, 6, 3))
None.
Returns a geometry object that is the topological difference (MINUS operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
In Figure 7-1, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_DIFFERENCE is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).
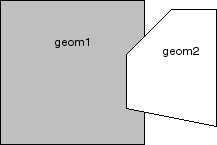
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
You should use this function instead of the deprecated function SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_DIFFERENCE.
The following example returns a geometry object that is the topological difference (MINUS operation) of cola_a and cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the topological difference of two geometries. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE(c_a.shape, m.diminfo, c_c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_a, cola_markets c_c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_a.name = 'cola_a' AND c_c.name = 'cola_c'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE(C_A.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,C_C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_ -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1003, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARR AY(1, 7, 1, 1, 5, 1, 5, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 7, 1, 7)
Note that in the returned polygon, the SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY starts and ends at the same point (1, 7).
Computes the distance between two geometry objects. The distance between two geometry objects is the distance between the closest pair of points or segments of the two objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DISTANCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN NUMBER;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DISTANCE(
Geometry object whose distance from geom2 is to be computed.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Geometry object whose distance from geom1 is to be computed.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function does not support the units parameter that is included with the LOCATOR_WITHIN_DISTANCE operator of interMedia Locator, which is a component of the Oracle interMedia product.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example returns the shortest distance between cola_b and cola_d. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the distance between two geometries. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_DISTANCE(c_b.shape, m.diminfo, c_d.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_b, cola_markets c_d, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_b.name = 'cola_b' AND c_d.name = 'cola_d'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_DISTANCE(C_B.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,C_D.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------------------------------------- .846049894
Returns a geometry object that is the topological intersection (AND operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
In Figure 7-2, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_INTERSECTION is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).

If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
You should use this function instead of the deprecated function SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_INTERSECTION.
The following example returns a geometry object that is the topological intersection (AND operation) of cola_a and cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the topological intersection of two geometries. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION(c_a.shape, m.diminfo, c_c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_a, cola_markets c_c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_a.name = 'cola_a' AND c_c.name = 'cola_c'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION(C_A.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,C_C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SD -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1003, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARR AY(4, 5, 3, 3, 5, 3, 5, 5, 4, 5))
Note that in the returned polygon, the SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY starts and ends at the same point (4, 5).
Returns the length or perimeter of a geometry object.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
If the input polygon contains one or more holes, this function calculates the perimeters of the exterior boundary and all holes. It returns the sum of all the perimeters.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
This function does not support the units parameter that is included with the LOCATOR_WITHIN_DISTANCE operator of interMedia Locator, which is a component of the Oracle interMedia product.
The following example returns the perimeters of geometry objects stored in the cola_markets table. The first statement returns the perimeters all objects; the second returns just the perimeter of cola_a. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the perimeters of all cola markets. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE'; NAME SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------- -------------------------------------- cola_a 20 cola_b 17.1622777 cola_c 9.23606798 cola_d 12.5663706 -- Return the area of just cola_a. SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_a'; NAME SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------- -------------------------------------- cola_a 20
None.
Returns a point that is guaranteed to be on the surface of a polygon geometry object.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POINTONSURFACE(
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POINTONSURFACE(
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function returns a point geometry object representing a point that is guaranteed to be on the surface of geom.
The returned point can be any point on the surface. You should not make any assumptions about where on the surface the returned point is, or whether the point is the same or different when the function is called multiple times with the same input parameter values.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example returns a geometry object that is a point on the surface of cola_a. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return a point on the surface of a geometry. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_POINTONSURFACE(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_a'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_POINTONSURFACE(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, SDO_POINT(X, -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SDO_GEOMETRY(2001, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY( 1, 1))
None.
Returns a geometry object representing the difference (A minus B) of two polygon objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_DIFFERENCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
The SDO_POLY_DIFFERENCE function is deprecated and will not be supported in future releases of Oracle Spatial. You should use instead the SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE function.
This function returns an empty geometry if any of the following occurs:
Returns a geometry object representing the intersection (A and B) of two polygon objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_INTERSECTION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
The SDO_POLY_INTERSECTION function is deprecated and will not be supported in future releases of Oracle Spatial. You should use instead the SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION function.
This function returns an empty geometry if any of the following occurs:
Returns a geometry object representing the union (A or B) of two polygon objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_UNION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
The SDO_POLY_UNION function is deprecated and will not be supported in future releases of Oracle Spatial. You should use instead the SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION function.
This function returns an empty geometry if any of the following occurs:
Returns a geometry object representing the symmetric difference (A xor B) of two polygon objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_XOR(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Polygon geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
The SDO_POLY_XOR function is deprecated and will not be supported in future releases of Oracle Spatial. You should use instead the SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR function.
This function returns an empty geometry if any of the following occurs:
Returns a geometry object that is the topological union (OR operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
In Figure 7-3, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_UNION is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).
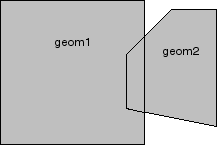
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
You should use this function instead of the deprecated function SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_UNION.
The following example returns a geometry object that is the topological union (OR operation) of cola_a and cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the topological intersection of two geometries. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION(c_a.shape, m.diminfo, c_c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_a, cola_markets c_c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_a.name = 'cola_a' AND c_c.name = 'cola_c'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION(C_A.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,C_C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1003, 1), SDO_ORDINATE_ARR AY(5, 5, 5, 7, 1, 7, 1, 1, 5, 1, 5, 3, 6, 3, 6, 5, 5, 5))
Note that in the returned polygon, the SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY starts and ends at the same point (5, 5).
Returns a geometry object that is the topological symmetric difference (XOR operation) of two geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_XOR,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
or
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
In Figure 7-4, the shaded area represents the polygon returned when SDO_XOR is used with a square (geom1) and another polygon (geom2).

If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
You should use this function instead of the deprecated function SDO_GEOM.SDO_POLY_XOR.
The following example returns a geometry object that is the topological symmetric difference (XOR operation) of cola_a and cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Return the topological symmetric difference of two geometries. SELECT SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR(c_a.shape, m.diminfo, c_c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_a, cola_markets c_c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_a.name = 'cola_a' AND c_c.name = 'cola_c'; SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR(C_A.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,C_C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO)(SDO_GTYPE, SDO_SRID, S -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SDO_GEOMETRY(2007, NULL, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1, 1003, 1, 11, 1003, 1), SDO _ORDINATE_ARRAY(5, 5, 5, 3, 6, 3, 6, 5, 5, 5, 1, 7, 1, 1, 5, 1, 5, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5 , 5, 5, 5, 7, 1, 7))
Note that in the returned polygon is a multipolygon (SDO_GTYPE = 2007), and the SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY describes two polygons: one starting and ending at (5, 5) and the other starting and ending at (1, 7).
Performs a consistency check for valid geometry types. The function checks the representation of the geometry from the tables against the element definitions.
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY(
or
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY(
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
If the geometry is valid, this function returns TRUE.
If the geometry is not valid, this function returns one of the following
This function checks for the following:
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example validates the geometry of cola_c. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Is a geometry valid? SELECT c.name, SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY(c.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c.name = 'cola_c'; NAME -------------------------------- SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY(C.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- cola_c TRUE
Examines a geometry column to determine if the stored geometries follow the defined rules for geometry objects.
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_LAYER(
geom_table IN VARCHAR2,
geom_column IN VARCHAR2,
pkey_column IN VARCHAR2,
result_table IN VARCHAR2);
Geometry table.
Geometry object column to be examined.
The primary key column. This can be the rowid or any other single-column primary key; however, the specified column must be numeric (NUMBER data type).
Result table to hold the validation results.
This procedure populates the result table with validation results. (VALIDATE_LAYER is a procedure, not a function.)
An empty result table (result_table parameter) must be created prior to calling this procedure. The format of the result table is: (pkey_column NUMBER, result VARCHAR2(10)).
In the result table, for each pkey_column the result column contains TRUE if the geometry is valid. If it is invalid, the result column for that geometry contains an Oracle error message number. You can then look up this error message to determine the cause of the failure.
This procedure checks for the following:
The following example validates the geometry objects stored in the shape column of the cola_markets table. The example includes the creation of the results table. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Is a layer valid? (First, create the results table.) CREATE TABLE val_results (mkt_id number, result varchar2(10)); EXECUTE SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_LAYER('COLA_MARKETS','SHAPE','MKT_ID','VAL_RESULTS'); PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SELECT * from val_results; MKT_ID RESULT ---------- ---------- 1 TRUE 2 TRUE 3 TRUE 4 TRUE
Determines if two spatial objects are within some specified Euclidean distance from each other.
SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim1 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY,
distance IN NUMBER,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
dim2 IN MDSYS.SDO_DIM_ARRAY
) RETURN VARCHAR2;
or
SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE(
geom1 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
distance IN NUMBER,
geom2 IN MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY,
tolerance IN NUMBER
) RETURN VARCHAR2;
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom1, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Euclidean distance value.
Geometry object.
Dimensional information array corresponding to geom2, usually selected from one of the xxx_SDO_GEOM_METADATA views (see Section 2.4).
Tolerance value (see Section 1.5.4).
This function returns TRUE for object pairs that are within the specified distance, and FALSE otherwise.
The distance between two extended objects (for example, nonpoint objects such as lines and polygons) is defined as the minimum distance between these two objects. Thus the distance between two adjacent polygons is zero.
If the function format with tolerance is used, all geometry objects must be defined using 4-digit SDO_GTYPE values (explained in Section 2.2.1).
The following example checks if cola_b and cola_d are within 1 unit apart at the shortest distance between them. (The example uses the definitions and data from Section 2.1.)
-- Are two geometries within 1 unit of distance apart? SELECT SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE(c_b.shape, m.diminfo, 1, c_d.shape, m.diminfo) FROM cola_markets c_b, cola_markets c_d, user_sdo_geom_metadata m WHERE m.table_name = 'COLA_MARKETS' AND m.column_name = 'SHAPE' AND c_b.name = 'cola_b' AND c_d.name = 'cola_d'; SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE(C_B.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO,1,C_D.SHAPE,M.DIMINFO) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TRUE
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|