Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 11 of 20
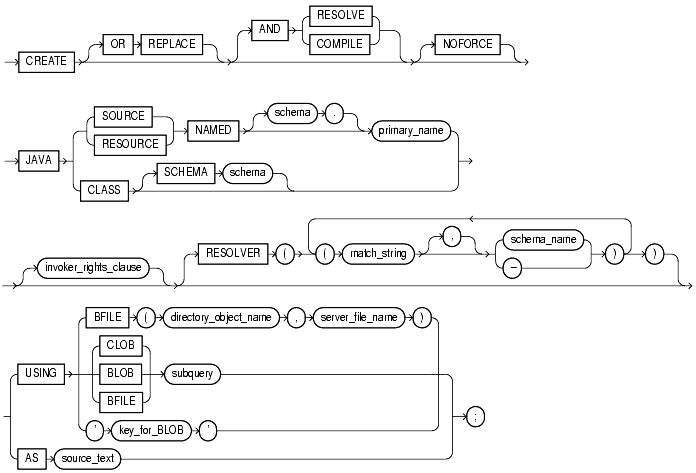

To create a schema object containing a Java source, class, or resource. For information on the following topics, see these books:
To create or replace a schema object containing a Java source, class, or resource in your own schema, you must have CREATE PROCEDURE system privilege. To create such a schema object in another user's schema, you must have CREATE ANY PROCEDURE system privilege. To replace such a schema object in another user's schema, you must also have ALTER ANY PROCEDURE system privilege.
|
|
re-creates the schema object containing the Java class, source, or resource if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing object without dropping, re-creating, and regranting object privileges previously granted.
If you redefine a Java schema object and specify |
|
|
|
Users who had previously been granted privileges on a redefined function can still access the function without being regranted the privileges. |
|
|
|
are synonymous keywords. They specify that Oracle should attempt to resolve the Java schema object that is created if this statement succeeds.
Restriction: You cannot specify this clause for a Java resource. |
|
|
|
rolls back the results of this |
|
|
|
loads a Java source file. |
|
|
|
loads a Java class file. |
|
|
|
loads a Java resource file. |
|
|
|
is required for a Java source or resource. The primary_name must be enclosed in double quotation marks.
If you do not specify schema, Oracle creates the object in your own schema. |
|
|
|
Restrictions: |
|
|
|
applies only to a Java class. This optional clause specifies the schema in which the object containing the Java file resides. If you do not specify schema and you do not specify |
|
|
invoker_rights_clause |
specifies whether the methods of the class execute with the privileges and in the schema of the user who owns the class or with the privileges and in the schema of This clause also determines how Oracle resolves external names in queries, DML operations, and dynamic SQL statements in the member functions and procedures of the type. See Also: Oracle8i Java Stored Procedures Developer's Guide. |
|
|
|
|
specifies that the methods of the class execute with the privileges of
This clause also specifies that external names in queries, DML operations, and dynamic SQL statements resolve in the schema of |
|
|
|
specifies that the methods of the class execute with the privileges of the owner of the schema in which the class resides, and that external names resolve in the schema where the class resides. |
|
|
specifies a mapping of the fully qualified Java name to a Java schema object, where
This mapping is stored with the definition of the schema objects created in this command for use in later resolutions (either implicit or in explicit ALTER ... RESOLVE statements). |
|
|
|
determines a sequence of character (CLOB or BFILE) or binary (BLOB or BFILE) data for the Java class or resource. Oracle uses the sequence of characters to define one file for a Java class or resource, or one source file and one or more derived classes for a Java source. |
|
|
|
|
identifies a previously created file on the operating system (directory_object_name) and server file (server_file_name) containing the sequence. |
|
|
|
supplies a query that selects a single row and column of the type specified ( |
|
|
key_for_BLOB |
supplies the following implicit query: SELECT LOB FROM CREATE$JAVA$LOB$TABLE WHERE NAME = 'key_for_BLOB';
Restriction: To use this case, the table |
|
AS source_text |
determines a sequence of characters for a Java or SQLJ source. |
|
The following statement creates a schema object containing a Java class using the name found in a Java binary file:
CREATE JAVA CLASS USING BFILE (bfile_dir, 'Agent.class');
This example assumes the directory object bfile_dir, which points to the operating system directory containing the Java class Agent.class, already exists. In this example, the name of the class determines the name of the Java class schema object.
The following statement creates a Java source schema object:
CREATE JAVA SOURCE NAMED "Hello" AS public class Hello { public static String hello() { return "Hello World"; } };
The following statement creates a Java resource schema object named APPTEXT from a BFILE:
CREATE JAVA RESOURCE NAMED "appText" USING BFILE (bfile_dir, 'textBundle.dat');
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|