Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 8 of 8
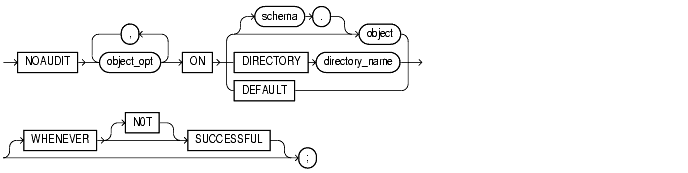
To stop auditing previously enabled by the AUDIT schema_objects statement.
|
See Also:
|
The object on which you stop auditing must be in your own schema or you must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege. In addition, if the object you chose for auditing is a directory, even if you created it, you must have the AUDIT ANY system privilege.
|
object_opt |
stops auditing for particular operations on the object. For a list of these options, see Table 7-3. |
|
|
|
identifies the object on which auditing is stopped. If you do not qualify object with schema, Oracle assumes the object is in your own schema. |
|
|
object |
must a table, view, sequence, stored procedure, function, or package, snapshot, or library. |
|
|
|
For information on auditing specific schema objects, refer to "AUDIT schema_objects". |
|
|
|
identifies the name of the directory on which auditing is being stopped. |
|
|
|
removes the specified object options as default object options for subsequently created objects. |
|
|
|
stops auditing only for SQL statements that complete successfully. NOT stops auditing only for statements that result in Oracle errors. |
|
|
|
If you omit the |
|
If you have chosen auditing for every SQL statement that queries the EMP table in the schema SCOTT, you can stop auditing for such queries by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT SELECT ON scott.emp;
You can stop auditing for queries that complete successfully by issuing the following statement:
NOAUDIT SELECT ON scott.emp WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
This statement stops auditing only for successful queries. Oracle continues to audit queries resulting in Oracle errors.
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|