Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 11 of 11
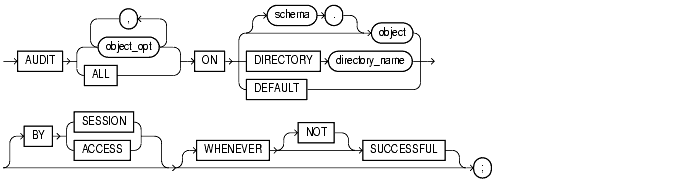
To track operations on a specific schema object. To choose particular SQL statements for auditing, see "AUDIT sql_statements".
Auditing keeps track of operations performed by database users. Auditing options established by the AUDIT schema_objects statement apply to current sessions as well as to subsequent sessions. For information on discontinuing auditing operations, see "NOAUDIT schema_objects".
The object you choose for auditing must be in your own schema or you must have AUDIT ANY system privilege. In addition, if the object you choose for auditing is a directory object, even if you created it, you must have AUDIT ANY system privilege.
|
object_opt |
specifies a particular operation for auditing. Table 7-3 shows each object option and the types of objects to which it applies. The name of each object option specifies a SQL statement to be audited. For example, if you choose to audit a table with the |
|
|
|
is a shortcut equivalent to specifying all object options applicable for the type of object. You can use this shortcut rather than explicitly specifying all options for an object. |
|
|
schema |
is the schema containing the object chosen for auditing. If you omit schema, Oracle assumes the object is in your own schema. |
|
|
object |
identifies the object chosen for auditing. The object must be a table, view, sequence, stored procedure, function, package, materialized view, or library. |
|
|
|
You can also specify a synonym for a table, view, sequence, procedure, stored function, package, or materialized view. |
|
|
|
establishes the specified object options as default object options for subsequently created objects. Once you have established these default auditing options, any subsequently created object is automatically audited with those options. The default auditing options for a view are always the union of the auditing options for the view's base tables. You can see the current default auditing options by querying the
If you change the default auditing options, the auditing options for previously created objects remain the same. You can change the auditing options for an existing object only by specifying the object in the |
|
|
|
identifies the name of the directory chosen for auditing. |
|
|
|
causes Oracle to write a single record for all operations of the same type on the same object issued in the same session. This is the default. |
|
|
|
causes Oracle to write one record for each audited operation. |
|
|
|
chooses auditing only for SQL statements that complete successfully. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you omit the |
|
To choose auditing for every SQL statement that queries the EMP table in the schema SCOTT, issue the following statement:
AUDIT SELECT ON scott.emp;
To choose auditing for every statement that successfully queries the EMP table in the schema SCOTT, issue the following statement:
AUDIT SELECT ON scott.emp WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
To choose auditing for every statement that queries the EMP table in the schema SCOTT and results in an Oracle error, issue the following statement:
AUDIT SELECT ON scott.emp WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
To choose auditing for every statement that inserts or updates a row in the DEPT table in the schema BLAKE, issue the following statement:
AUDIT INSERT, UPDATE ON blake.dept;
To choose auditing for every statement that performs any operation on the ORDER sequence in the schema ADAMS, issue the following statement:
AUDIT ALL ON adams.order;
The above statement uses the ALL shortcut to choose auditing for the following statements that operate on the sequence:
ALTER SEQUENCE
AUDIT
GRANT
CURRVAL or NEXTVAL
To choose auditing for every statement that reads files from the BFILE_DIR1 directory, issue the following statement:
AUDIT READ ON DIRECTORY bfile_dir1;
The following statement specifies default auditing options for objects created in the future:
AUDIT ALTER, GRANT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON DEFAULT;
Any objects created later are automatically audited with the specified options that apply to them, provided that auditing has been enabled:
ALTER, GRANT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements issued against the table.
GRANT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements issued against the view.
ALTER or GRANT statements issued against the sequence.
ALTER or GRANT statements issued against it.
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|