Release 9.0.1
Part Number A88784-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle interMedia Annotator User's Guide Release 9.0.1 Part Number A88784-01 |
|
This chapter supplies information on Oracle interMedia Annotator, which extracts information (or metadata) from media sources of certain formats and inserts the metadata, along with the media source, into an Oracle database.
interMedia Annotator uses Oracle interMedia.
When managing multimedia data in an object-relational database system, you will likely face the problem of how to extract, process, and manage metadata associated with your media sources. Metadata, which typically consists of text-based information that describes the media source, is usually embedded within the media source using a proprietary format, and is therefore not always easily accessible. To be able to efficiently manage and use metadata, you must be able to extract it from many different types of media sources. After extraction, you must have a consistent, accurate representation of the metadata, regardless of the original media source.
Oracle interMedia Annotator is a Java-based engine that is used to organize a set of multimedia content and metadata and upload it to an Oracle database.
You can use Annotator to parse a media source, extract its metadata, and group the metadata into an organized structure called a logical annotation (or annotation). Every annotation is organized as a set of text attributes and optional samples. An attribute provides information about the media source, either its data format (such as MIME type or format) or data content (such as song title or movie director). Samples are multimedia data (such as audio clips or closed captions) extracted from the media source.
You can use interMedia Annotator to parse your audio, image, or video files (see Appendix B for a list of supported file formats) and extract attributes to build an annotation.
interMedia Annotator also creates a separate annotation for each track of the media source. For example, for a media source containing a movie, interMedia Annotator can create separate annotations for the video data and audio data; those annotations would be sub-annotations of the movie annotation.
You can use interMedia Annotator to insert the annotation along with the media source into an Oracle database. Once the annotation is in the database, you can use Oracle9i Text to query the annotation.
You can use the interMedia Annotator functions in one of two ways. If you want to become more familiar with interMedia Annotator, or if you have simple needs that do not require writing a Java application, you can use the graphical user interface (GUI) of the interMedia Annotator utility to generate annotations. The Annotator GUI is built on the Annotator Java-based engine.
For example, users who are responsible for creating and storing movie trailers can use the Annotator GUI to upload the movie trailers to an Oracle database. The Annotator GUI can automate the process of extracting metadata and uploading both the metadata and the movie trailer to an Oracle database in a few clicks. Once the content is uploaded, the movie trailers can be searched, published, or streamed through an application, such as the MediaFinder sample application.
See Part I, "interMedia Annotator GUI" for more information on the interMedia Annotator GUI.
Additionally, if you are an application developer who needs to organize related multimedia files, you can use the interMedia Annotator engine Java APIs to integrate the Annotator functions into your application. You can also use the interMedia Annotator engine APIs as a tool for bulk loading many multimedia files into the database.
For example, in the scenario presented previously, if you have a large number of movie trailers to store, you might not want to click through the GUI for every movie trailer. Instead, you can write a custom Web-based application to parse the movie trailers, generate annotations for each trailer, and upload the movie trailers to an Oracle database automatically.
See Part II, "interMedia Annotator Java-Based Engine" for more information on the interMedia Annotator Java engine.
interMedia Annotator is extensible; you can use the Annotator parser Java APIs to write a custom parser for your media source files, or create your own annotation types.
For example, a real-estate company might maintain a list of properties to be sold, with each entry containing a picture of the exterior, a short movie of the interior, a technical document, selling price, and other information.
Using the extensibility features of Annotator, a developer can easily create a Web-based application to allow selling agents to supply the entry, including the multimedia files, and upload them to Oracle as a property content unit. The developer can define a new annotation type named property, containing the name, selling price, closing date, and other text information. The new annotation type can include an image sub-annotation describing the picture of the exterior or a movie sub-annotation describing the movie of the interior of the house. The developer can also write a new parser to create the property annotation.
See Part III, "interMedia Annotator Extensibility" for more information on extending interMedia Annotator.
The main functions of interMedia Annotator are to build a logical annotation from a media source and to then upload both the annotation and the source file to an Oracle database. Users can then query the media data in the database based on information in the annotation.
Figure 1-1 provides an overview of this process. This process can be performed either by the Annotator GUI or a custom-written Java application using the Annotator Java APIs.
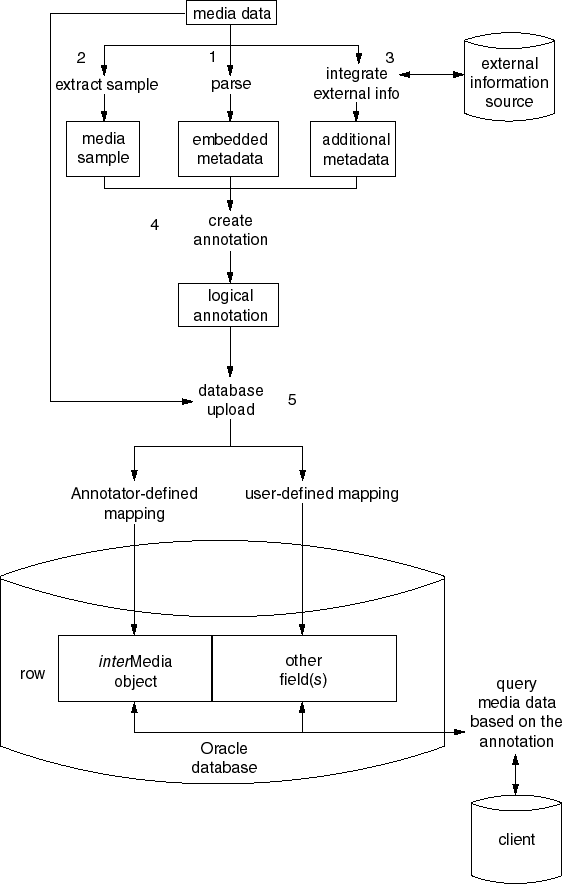
You can use interMedia Annotator to perform the following operations, in this order:
Applications can further customize the annotation at this point.
interMedia Annotator will upload the media source and the annotation (in XML format) into an interMedia object in the database. interMedia Annotator can also upload individual attributes from the annotation into other columns of the database. You specify the interMedia object to which you will upload, along with the rest of the information to be uploaded, in a PL/SQL Upload Template. You can create a template using a text editor or the PL/SQL Template Wizard.
See Chapter 4 and Chapter 7 for more information on the upload process.
Once you have completed these steps, you will be able to query the information in the annotation in order to use information about the media source that cannot be directly extracted. You can also build indexes on the information in the annotation using Oracle9i Text.
To use interMedia Annotator, you must have access (either local or remote) to an Oracle database with Oracle interMedia, and an Oracle JDBC driver (either Thin or OCI) for Oracle 8.1.5 or later.
To use interMedia functions in your Java applications, you should use the Java Development Kit 1.1.7 or later.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|