Release 1 (9.0.1) for Windows
Part Number A90163-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i Database Getting Started Release 1 (9.0.1) for Windows Part Number A90163-01 |
|
This chapter describes use of the registry for various Oracle9i for Windows components. It also lists the recommended values and ranges for configuration parameters.
This chapter contains these topics:
Oracle9i for Windows uses configuration parameters to locate files and specify runtime parameters common to all Oracle products. When an Oracle program or application requires a translation for a particular configuration variable, Oracle9i for Windows uses the associated parameter. All Oracle parameters are stored in the registry.
Oracle9i for Windows stores its configuration information in a repository (the registry) that is organized in a tree format. The tree format consists of keys in the registry and parameter values for the keys. Keys and parameter values can be viewed and modified in the Registry Editor.
Keys are folders that appear in the left pane of a Registry Editor window. A key contains subkeys or parameters.
Parameters in the Registry Editor appear as a string, consisting of three components:
For example, parameter ORACLE_SID can have the following entry in the registry:
ORACLE_SID:reg_sz:orcl1
Value classes for Oracle9i for Windows parameters are:
REG_SZ, REG_EXPAND_SZ (for an expandable string), or a REG_MULTI_SZ (for multiple strings) prefix to identify a parameter value entry as a data string
REG_DWORD prefix to identify a value entry as a dword (hexadecimal data) entry
Most Oracle9i for Windows parameter values are string types. Use Oracle Universal Installer defaults when a type is not given.
This section describes the Oracle9i for Windows registry parameters for the following keys. Other products, such as Oracle Enterprise Manager, have additional keys and parameters that are not described in this chapter.
To modify these registry values, see "Modifying a Registry Value with regedt32" in this manual.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID
Each time you install Oracle products into a new Oracle home on your computer, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID is created and ID is incremented. This subkey contains parameter values for most Oracle products.
|
Note: See Chapter 6, "Multiple Oracle Homes and Optimal Flexible Architecture" in this manual for details on the PATH variable and registry values when you are working with multiple Oracle homes. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID includes the following parameters for an Oracle home directory. Depending on the products you install, additional parameters can also be created. See your Windows development manuals.
MSHELP_TOOLS
Specifies the location of the Windows help files. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\mshelp.
NLS_LANGSpecifies the supported language, territory, and character set. This parameter specifies the language in which messages appear, the territory and its conventions for calculating week and day numbers, and the character set displayed. Oracle Universal Installer sets this value during installation based on the language setting of the operating system. See the Oracle9i Database Globalization Support Guide for a list of values.
ORA_CWDSpecifies the current working directory. For example, if you set this parameter and then use ORADIM, a log file called oradim.log is created in this directory. This parameter must be manually set.
ORA_SID_AUTOSTART
Starts the database when the OracleServiceSID service is started. The default value is true.
ORA_SID_PFILE
Specifies the full path to the initialization parameter file (init.ora). The default value is ORACLE_BASE\admin\DB_NAME\pfile\init.ora
ORA_SID_SHUTDOWN
When set to true, the default value, this parameter shuts down the Oracle database identified by SID when OracleServiceSID is stopped.
ORA_SID_SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT
Sets the maximum time (in seconds) to wait for the shutdown to complete before the service for a particular SID stops. The default value is 30.
ORA_SID_SHUTDOWNTYPE
Specifies the mode in which the database is shut down when you stop OracleServiceSID. The valid values are a (abort), i (immediate), and n (normal). The default value is i.
ORA_TZFILESpecifies the location of the timezone file. Each file contains:
ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\oracore\zoneinfo\timezone.dat is the default. It contains the most commonly used timezones and is smaller for better database performance. The optional file, timezlrg.dat, includes timezones not defined in the default; but its use may affect database performance. To enable use of the optional file, the database administrator must:
ORA_TZFILE to the full path name of the location of timezlrg.dat file.
To view the timezone names, use SQL*Plus to make the following query:
SELECT * from v$timezone_names
Once the larger file is used, it must stay in use unless the user is sure that no data uses one of the added timezones. Also, all databases that share information must use the same timezone file.
ORACLE_AFFINITYSpecifies the Windows NT processor affinity of each thread within the Oracle process. This parameter must be manually added. Oracle Corporation recommends consulting Oracle Support Services before changing this parameter. The format is:
name1:cpumask1;name2:cpumask2
Each name setting must be the name of a background thread, user for non-background (shadow) threads, or def for any thread type not handled specifically.
The name mask sets the affinity mask of the Oracle process. Valid background thread names include DBW0, LGWR, PMON, SMON, ARCH, RECO, CKPT, TRWR, SNP0 through SNP9, P000 through P481, and any other name found in the NAME column of the v$bgprocess data dictionary view.
Each affinity setting must be a valid affinity mask (or its numeric equivalent) for the corresponding name. Process affinity masks are used only when Oracle services are first started. Each thread's affinity is set only when the individual thread is started (for example, at database startup time for the background threads).
ORACLE_BASE
Specifies the top-level Oracle directory (for example, C:\oracle) that contains ORACLE_HOME, \admin, and \oradata. The default is ORACLE_BASE.
ORACLE_GROUP_NAME
Specifies the name of the group containing icons of the Oracle products installed. The parameter is added to your registry when you first install Oracle products, even if Oracle Universal Installer does not create a program group for the Oracle products you have installed (for example, if you have installed only Oracle Net software). The default value is Oracle - HOME_NAME.
ORACLE_HOMESpecifies the Oracle home directory in which Oracle products are installed. This directory is immediately beneath the Oracle base directory in the Oracle directory hierarchy. The default value is the drive letter and name that you specify during installation.
ORACLE_HOME_KEY
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE location of Oracle parameters. The default value is software\oracle\HOMEID.
ORACLE_HOME_NAMESpecifies the home name of the Oracle home directory in which Oracle products are installed. The default value is the name that you specify during installation.
ORACLE_PRIORITY Determines the Windows NT scheduling priorities of the threads within the Oracle database management system process. The format is:
name1:priority1;name2:priority2 . . .
The name class sets the priority class of the Oracle process. Threads can be assigned priority either collectively or individually. The collective name user designates non-background (shadow) threads; the collective name def designates any thread type not handled specifically. Valid individual background thread names include DBW0, LGWR, PMON, SMON, ARCH0, RECO, CKPT, TRWR, SNP0 through SNP9, and any other name found in the NAME column of the v$bgprocess data dictionary view.
The default value is class:normal; def:normal.
ORACLE_SIDSpecifies the name of the Oracle database instance on the host computer. The value of this parameter is the SID for the instance. The default value is specified by the entry in the Database Identification window of Oracle Universal Installer.
RDBMS_ARCHIVE
Specifies the location of the backup database files. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\database\archive.
OSAUTH_PREFIX_DOMAIN
Enables user authentication. When set to true, enables the server to differentiate between one username and another, whether they are local users, domain users, or domain users on another domain in your network. When set to false, the domain is ignored, and the local user becomes the default value of the operating system user returned to the server. The default value is false.
OSAUTH_X509_NAME
Enables client users to access the Oracle9i database as X.509-compliant enterprise users. This parameter is required only if you want to use enterprise users and roles in an Oracle9i database computer running in a Windows 2000 domain. The default value is false.
RDBMS_CONTROL
Specifies the location of the backup database control files. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\database.
SQLPATH
Specifies the location of SQL scripts. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\dbs.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLEThis subkey contains the following parameters:
INST_LOC
Specifies the location of Oracle Universal Installer files. The default value is System Drive:\program files\oracle\inventory.
OO4O
Specifies the location of Oracle Objects for OLE message files. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\oo4o\mesg.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\ALL_HOMESThis subkey provides general information on each Oracle home directory on a computer.
DEFAULT_HOMESpecifies the default Oracle home name (that is, the first Oracle home installed on your computer). The default value is the name that you specify during installation. You can also use an Oracle tool to change the default home name. See "Using Oracle Home Selector" in this manual.
HOME_COUNTER
Specifies the number of installed Oracle homes. The default value is 1.
LAST_HOME
Displays the ID number of the most recently installed Oracle home. For example, if HOME0 was the most recently installed Oracle home, then the number 0 appears. The default value is 0.
IDx
This subkey corresponds to the HOMEID of the same number (for example, HOME0 for the first installation, HOME1 for the second installation, and so on). IDx contains NAME and PATH parameters. The values that appear are determined by what you enter during installation in the File Locations window of Oracle Universal Installer.
NAME specifies the home name of the Oracle home for IDx. This is the value that you specify during installation when prompted for an Oracle home name.
PATH specifies the Oracle home directory for IDx. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet registry address contains four keys:
The first three are used by the operating system. You can edit only the Services subkey, which contains:
Oracle Performance Monitor for Windows NT parameters appear in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CURRENTCONTROLSET\SERVICES\ORACLE9\PERFORMANCE.
For Oracle Performance Monitor for Windows NT to display information for Oracle performance objects, it must log into the database. Modify the following parameters if the default information is not applicable or if you want to access another database:
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=BEQ)(PROGRAM=oracle9)(ARGV0=oracle9SID)(ARGS='(DESCRIPTION=(LOCAL=YES)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=beq)))')))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=SID)))
Password displays the encrypted password for the username to access the database. The default value is MANAGER (encrypted).
Username displays the username to access the database. The default value is SYSTEM.
Oracle Performance Monitor for Windows NT requires the following parameters as entry points:
Close specifies the close entry point for the DLL. The default value is CloseOracle9PerformanceData.
Collect specifies the collect entry point for the DLL. The default value is CollectOracle9PerformanceData.
Library specifies the name of the Oracle Performance Monitor DLL. The default value is oraperf.dll
Open specifies the open entry point for the DLL. The default value is OpenOracle9PerformanceData.
The following parameters specify the Oracle Performance Monitor for Windows NT log file and object configuration files:
LOGFILE specifies the name of the Oracle Performance Monitor log file. This log file reports any errors, such as Oracle objects not appearing or database access problems. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\dbs\operf90.log.
PERF_FILE_NAME specifies the location of the perf.ora file, which contains all the performance objects displayed by Oracle Performance Monitor. The default value is ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\dbs\perf90.ora
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CURRENTCONTROLSET\SERVICES subkey contains additional subkeys that correspond to each Oracle service.
Each service subkey contains the following parameters:
DisplayName specifies the service name of the instance whose SID is SID. The default value is the name of the service. For example, OracleServiceORCL1, where ORCL1 is the SID.
ImagePath specifies the fully qualified path name of the executable started by the service and any command-line arguments passed into the executable at runtime. The default value is the path to the executable file of the product.
ObjectName specifies the logon user account and computer to which the service should log on. The default value is LocalSystem.
Oracle Real Application Clusters registry values are based on Oracle Corporation's Operating System Dependent (OSD) clusterware. If you are not using the Oracle OSDs, then some of this information may not be applicable to your particular cluster environment.
The registry values are first listed and described (where necessary). Data types and default values are displayed in Table 9-1, " Oracle Real Application Clusters Registry Parameters"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\OSD9IThis subkey contains the following required and optional values:
CMDLL specifies the full path of the Cluster Manager (CM) DLL.
IODLL specifies the full path of the I/O DLL.
IPCDLL specifies the full path of the Inter-Process Communication (IPC) DLL.
STARTDLL specifies the full path of the Startup DLL.
This subkey contains the Cluster Manager registry values. These values are updated when the Oracle OSD clusterware is installed.
ClusterID
ClusterName
CmDiskFile
CmHostName is for public host names used by the local Cluster Manager. Useful in a multihost environment, when more than one network is available on the node.
DefinedNodes specifies the names for the nodes in a private network. The Oracle OSD clusterware uses these addresses for its interconnect traffic.
MissCount defines the number of check-in intervals that can be missed before a Cluster Manager and its related node are declared down by the cluster.
PollInterval defines the check-in time among Cluster Managers on different nodes. Each Cluster Manager is expected to send at least one status packet to all other nodes for each poll interval.
PublicNames specifies the public node names in the public network (known as DNS host names).
ServiceName
This subkey contains the Inter-Process Communication (IPC) registry values. These values are updated when the Oracle OSD clusterware is installed.
DeviceNic is for use with Virtual Interface Architecture (VIA) hardware. Nic refers to the Network Interface Card.
InstanceID contains the VIA MAC addresses of all the nodes.
To edit Oracle-related settings:
C:\> regedt32
regedt32 in the Open field, and click OK.
The Registry Editor window appears.
The left-hand side of the window shows the hierarchy of registry keys, and the right-hand side of the window shows various values associated with a key.
The String Editor dialog box appears:
To add a parameter to the registry:
C:\> regedt32
regedt32 in the Open field, and click OK.
The Registry Editor window appears.
The Add Value dialog box appears:
The String Editor dialog box appears:

The Registry Editor adds the parameter.
Instead of using regedt32 to add, edit, and delete parameters for an Oracle home, you can use the Oracle Home Configuration snap-in, one of several snap-ins included as part of Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT. You must have Microsoft Management Console on your computer to use this product. The Oracle home parameters are located in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID key.
See "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID" in this manual for more information about the Oracle home parameters.
To start the Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT:
Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT starts.
To add an Oracle home parameter:
The Add Value dialog box appears.
To change the default SID, select the SID from the Default SID list in the Properties dialog box. To edit one of the other parameters:
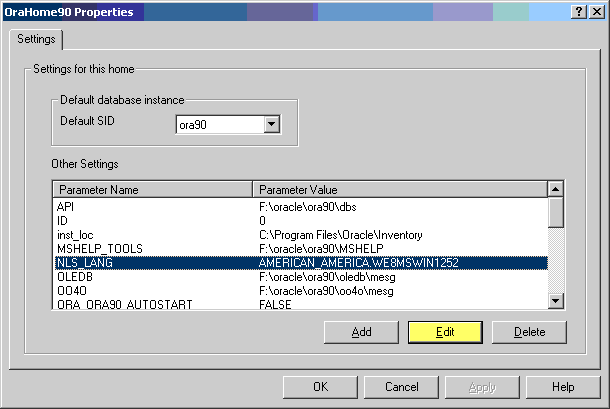
Text description of the illustration admin4.gif
The Edit Value dialog box appears.
To delete an Oracle home parameter:
Instead of using regedt32 to modify Oracle Performance Monitor's Hostname, Password, and Username parameters, you can use Oracle's OPERFCFG utility or Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT.
|
See Also:
"Parameters for Oracle Performance Monitor for Windows NT" in this manual for more information about the |
The OPERFCFG utility is an Oracle tool that you run from the MS-DOS command prompt. Use this syntax:
operfcfg [-U username] [-P password] [-D database_name]
where:
username is the username registry parameter value that Oracle Performance Monitor uses to log into the database. You must have a DBA privilege on this database.
password is the password registry parameter value for the username.
database_name is the net service name that Oracle Performance Monitor uses to connect to the database. It affects the Hostname registry parameter. The net service name corresponds to the SID of the database that you want to monitor. The -D command can be specified without providing a database name value.
The -U, -P, and -D commands are all optional.
The following examples illustrate the use of the OPERFCFG utility. First, to change the username to dba_admin, the password to frank, and leave the database name at its current value, you would enter:
C:\> operfcfg -U dba_admin -P frank
To change the username to dba_admin, the password to frank, and the database name to prod, you would enter:
C:\> operfcfg -U dba_admin -P frank -D prod
To change the password to frank for the current username and database name, you would enter:
C:\> operfcfg -P frank
In the final example, you change the Hostname parameter to a blank value, causing the Oracle Performance Monitor to connect to the default database on the computer. The current username and password must be valid user accounts on this database. Enter:
C:\> operfcfg -D
The Oracle Performance Monitor snap-in is part of the Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT. You must have Microsoft Management Console on your computer in order to use this product.
To use the Oracle Performance Monitoring snap-in:
> Configuration and Migration Tools > Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT.
Oracle Administration Assistant for Windows NT starts.
The Performance Monitor Properties dialog box appears.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|