Release 9.0.1 for Windows NT and Windows 2000
Part Number A90174-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Legato Storage Manager Administrator's Guide Release 9.0.1 for Windows NT and Windows 2000 Part Number A90174-01 |
|
Many of the problems that LSM users report when they set up and configure LSM are actually problems with the communications in their networks. This section contains a procedure for testing the communications in a network.
ping to establish basic connectivity. See "How to Use ping to Verify Network Connections".
Legato recommends that you troubleshoot IP problems using only host tables. Troubleshooting using only host tables does not mean you cannot use your name service (for example, DNS) with LSM. Test using only host tables to determine whether you have LSM installed correctly. After you know LSM works with host tables, you can enable whatever name server you are using.
To configure host tables on a server or client:
127.0.0.1 localhost loopback 123.456.789.111 client client.domain.com 123.456.789.222 server server.domain.com
127.0.0.1 localhost loopback 123.456.789.111 server server.domain.com 123.456.789.222 client client.domain.com
Notes for host table configuration:
On Windows, the host tables reside in C:\system32\drivers\etc\hosts.
Host tables can be used in addition to DNS where necessary, but it is simplest to temporarily disable DNS for troubleshooting purposes.
After you have created the host tables, test with ping. Use just the steps marked with an asterisk (*) if the server is the only client.
On the LSM client:
ping the client short name (host name) from the client
ping the client long name (host name plus domain information) from the client
ping the client IP address from the client
ping the server short name from the client
ping the server long name from the client
ping the server IP address from the client
The following example shows pinging the client short name and client long name from an LSM client called mars in the oak domain:
pingmarspingmars.oak.com
On the LSM Server:
ping the server short name from the server *
ping the server long name from the server *
ping the server IP address from the server *
ping the client short name from the server
ping the client long name from the server
ping the client IP address from the server
If you are using switches or routers from any vendor, make sure that the switch or router firmware is dated after August 1995 (wherever they exist on your network) to ensure that RPC traffic is handled properly. Most of the switch and router vendors with whom we have worked have significantly improved their handling of RPC traffic since August 1995.
You establish communication between the LSM Server and the Oracle Server (as an LSM client) by assigning values in both the Set Up Server dialog box and the Client dialog box in the LSM Administrator GUI. To help you understand how these values work together, this section discusses communication issues internal to LSM. LSM relies on full and accurate configuration of the network to implement features that protect data and ensure security.
Configure your server by using the Set Up Server dialog box (Figure B-1). Here you make choices that affect the performance and security of your backups, such as setting the server parallelism, enabling concurrent devices, and adding or changing LSM administrators.
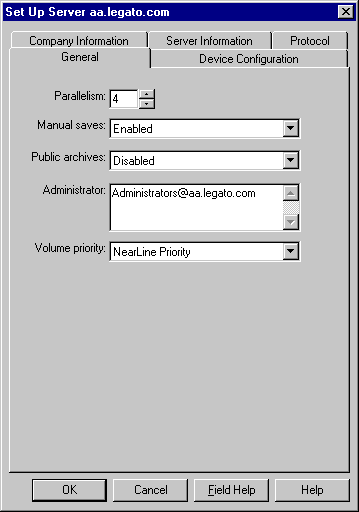
Click Set Up Server in the Server window of the LSM Administrator GUI to open the Set Up Server dialog box. The Set Up Server dialog box contains overlapping tabs containing resource attributes to configure your LSM server. Many of these attributes are determined when you initially install your LSM Server software.
Some attributes are read-only, or contain information more advanced and detailed than most LSM users need, particularly if Hidden Attributes is enabled. Technical support engineers might request that you provide information displayed in these attributes to understand your system configuration. Click Field Help to learn more about each attribute.
The following sections address various communication issues using LSM.
Your Windows LSM server gets its host name from its TCP/IP setup. You can access both the server and domain name through the Windows control panel. This name is not necessarily the computer name that is common to other Windows applications.
To access your server and domain names, follow these steps:
In a pure Windows environment, you may find using WINS or LMHOSTS is adequate for using LSM. However, using LSM with other types of clients requires using a local host file or DNS name resolution.
You must add the LSM server name to either the local HOSTS file located in C:\system32\drivers\etc or the Domain Name Server (DNS) which contains the names of all the servers on your network.
The Backup Operators local group provides its members the rights necessary to backup and recover data from a Windows system. A user requesting a backup must be in the Backup Operators or Administrators group of the domain into which they are logged. The Backup Operators group is assigned on a computer-by-computer basis. It is not assigned globally by the domain. If you are having trouble performing tasks on one LSM Server but not another, check the problematic computer's Backup Operators group to ensure you are properly assigned.
Typically, addresses for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) clients change because they use dynamic addressing. If your LSM Server is a DHCP client, you must reserve a static TCP/IP address on your DHCP server. If the address changes, the authorization code for that LSM Server becomes invalid.
In the Windows operating system, the service named NetWorker Backup and Recover Server is normally started by the Windows System account. This allows the LSM services to be running even if no one is logged onto that system.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|