Release 1.0.2 for Sun SPARC Solaris
Part Number A86239-01
Library |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle9i Application Server Installation Guide Release 1.0.2 for Sun SPARC Solaris Part Number A86239-01 |
|
This appendix guides you through the steps required to run component-specific configuration assistants to configure Oracle9i Application Server. It contains instructions on manually launching, and running the configuration assistants to configure the components you chose not to configure during installation.
This section contains instructions on manually launching, and running configuration assistants for the following components:
Before you can run the Oracle Database Cache Configuration Assistant, you need to configure the ora_icache_origin service manually.
The tnsnames.ora in the ORACLE_HOME/network/admin directory has the following entry after installation:
ora_icache_origin =(DESCRIPTION =(ADDRESS_LIST =(ADDRESS = (PROTPCOL = TCP) (HOST = <ORIGINHostName>) (PORT = originPortNumber>))) (CONNECT_DATA =(SERVICE_NAME = <originServiceName>)))
Fill in the origin host name, port and service name in tnsnames.ora file as per the above example before running the following command to launch the Oracle Database Cache Configuration Assistant:
prompt> <ORACLE_HOME>/bin/wtacca -create -custom
The following steps guide you through the Oracle Database Cache Configuration Assistant:
The Welcome screen introduces you to the Oracle Database Cache Wizard.
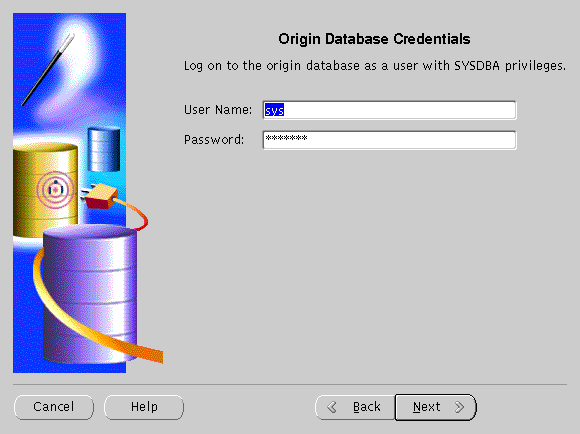
The Oracle Database Credentials screen specifies the database that is the original and primary storage for the data that you cache on the middle-tier node.

The Summary screen provides information about the origin database, cache node, port number, cache name, memory and disk space allocated.
The Cache Configuration Assistant Progress screen informs you of the results of the configuration.
The following command launches the Oracle Internet File System Configuration Assistant:
prompt> <ORACLE_HOME>/ifs1.1/bin/ifsconfig
The following steps guide you through the Oracle Internet File System Configuration Assistant:
The Welcome screen introduces you to the Oracle Internet File System Configuration Assistant and allows you to review the licensing agreement before you can proceed to configure Oracle Internet File System.
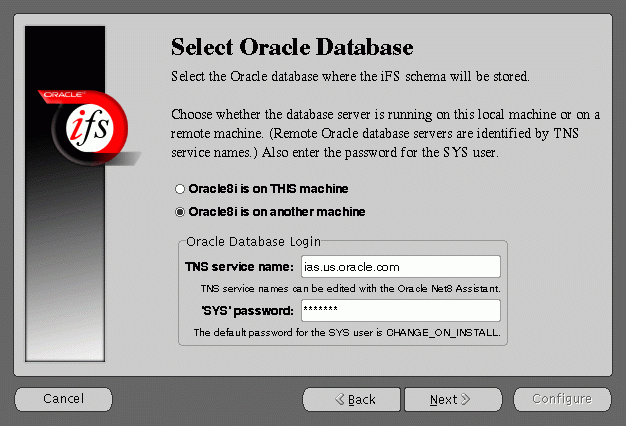
Select Oracle Database screen allows you to choose where the Oracle Internet File System schema will be stored. Select whether the origin database is on the local machine or on the remote machine other than the Oracle Internet File System server machine currently being configured.
If you select Oracle8i on THIS machine, then you will have to fill in the SYS password field.
If you select Oracle8i on another machine, then you will have to enter the TNS service name and the SYS password in their respective fields.
If an error occurs, you will be required to correct the database connection information before continuing.
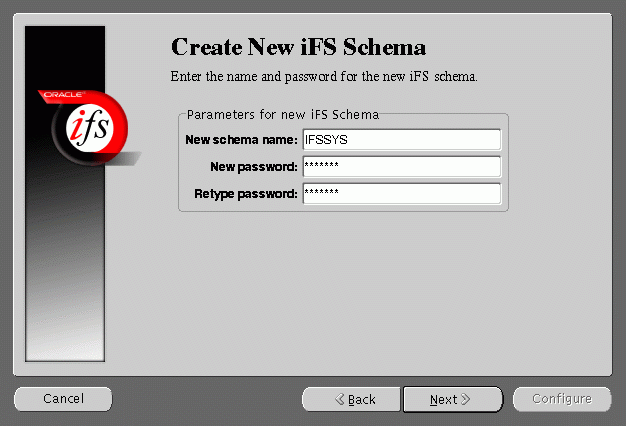
Create New iFS Schema screen allows you to specify an Oracle database username and password for the new schema.
If you choose to create a new schema with the same name as an existing schema, a warning message appears. Creating a new schema with the same name as an existing schema will drop the existing schema.
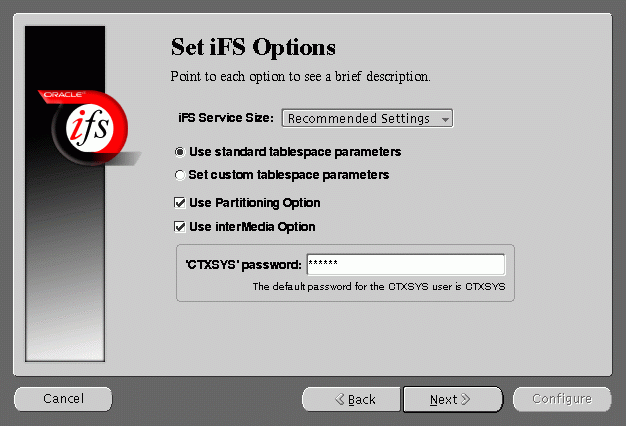
Set iFS Options screen allows you to set certain schema options and to select a service size for your Oracle Internet File System server. There are two choices for the Oracle Internet File System server size:
If you are creating a new Oracle Internet File System schema, then you can choose whether to use standard tablespace parameters, or to specify custom tablespace parameters.
- Primary: Stores metadata for documents. information about users and groups, and other Oracle Internet File System data.
- Non-Indexed Medias: Stores the LOB data for documents that are not indexed by interMedia, such as image, audio, and video files.
- Indexed Media: Stores the LOB data documents that are indexed by interMedia, such as text and word processing files.
- interMedia Index: Stores the Oracle indexed on interMedia data.
- interMedia Keymap: Stores the mapping between interMedia Text information and Oracle Internet File System information.
- interMedia Data: Stores the interMedia data about Oracle Internet File System documents.
- Partioning Option: Improves performance. Available only with Oracle8i Enterprise Edition.
- interMedia Option: If you have installed interMedia Text, then select this option to use interMedia Text for searching document contents.
- CTXSYS: If you choose the interMedia Text option, then enter the password for the interMedia CTXSYS account. The default password is CTXSYS.
If you have chosen to use interMedia Text, the Configuration Assistant will verify the interMedia configuration when you click the Next button. If an error occurs. then you will not be able to choose the interMedia Text option unless you rectify the error.
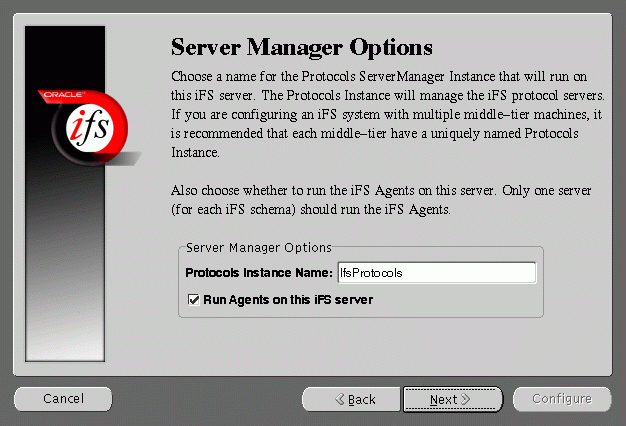
Server Manager Options screen allows you to enter a name for the Protocols Server Manager Instance that will run on this Oracle Internet File System server.
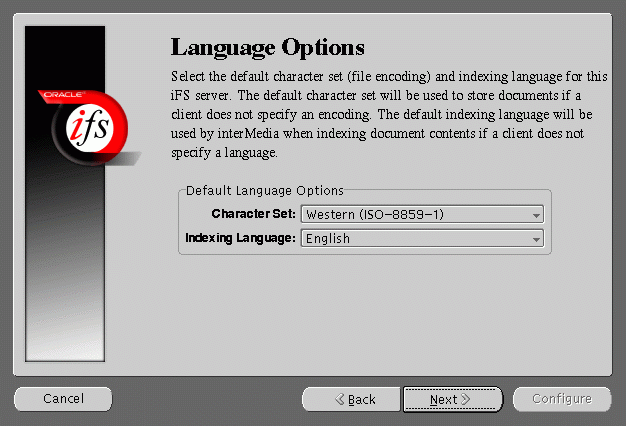
Language Options screen allows you to select the Character set and indexing language for this Oracle Internet File System server.
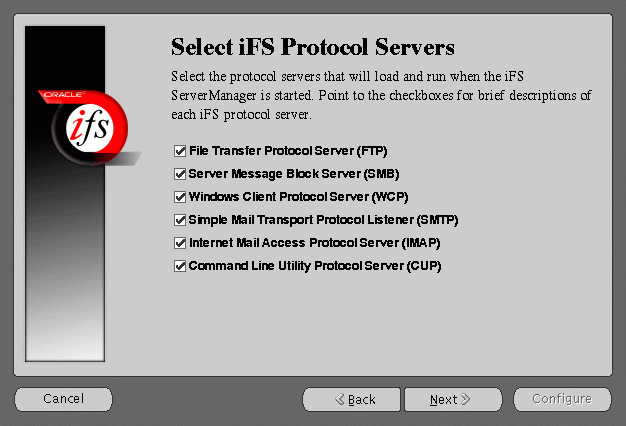
Select iFS Protocol Servers screen allows you to select the protocol servers to configure for this Oracle Internet File System server. The following protocol servers are available:
For more information on configuration of these protocols, refer to Oracle Internet File System Setup and Administration Guide.
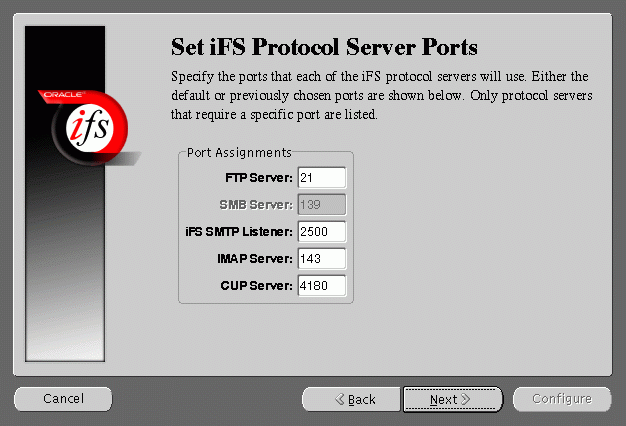
Set iFS Protocol Server Ports screen allows you to set port numbers for the protocol servers you selected in the previous screen. The following is a list of protocol servers and their default port numbers:
When you click the Next button, the port availability on your computer is tested. If a port is already in use, a warning screen appears. A common port conflict can arise because the standard Solaris installation includes a FTP server on port 21, which conflicts with the Oracle Internet File System FTP server. You must resolve such conflicts before starting the Oracle Internet File System protocol servers.
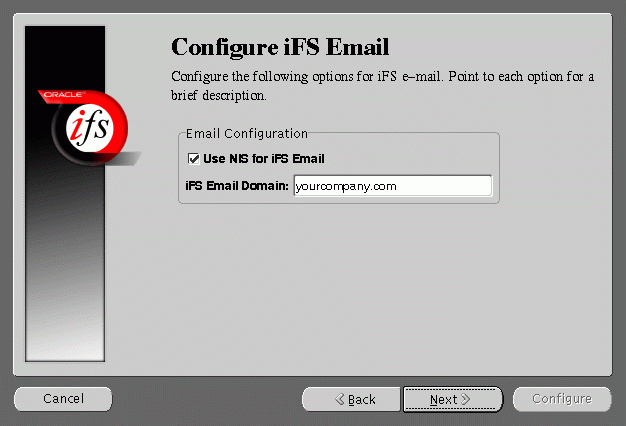
Configure iFS Email screen allows you to enter the iFS Email domain.
Begin iFS Configuration screen informs the users of the configuration process, and displays the location for the log files.
Once you have started the configuration process, a progress window appears. indicating the progress of the Oracle Internet File System configuration. If an error occurs, check the log files that are displayed on the Begin iFS Configuration screen.
A dialog box appears noting that the configuration was successfully completed. You are then prompted to run the ifssetup script as a root user. The script is located in the ORACLE_HOME/ifs/bin directory. This script will configure your system for Oracle Internet File System email, if this option was selected.
The following command launches the Oracle Portal Configuration Assistant:
prompt> <ORACLE_HOME>/assistants/opca/launch.sh
The following steps guide you through the Oracle Portal Configuration Assistant:

The Installation Options screen allows you to install and deinstall Oracle Portal. Selecting "Install Oracle Portal and the Login Server" installs the Oracle Portal schema and the Login Server onto your database.
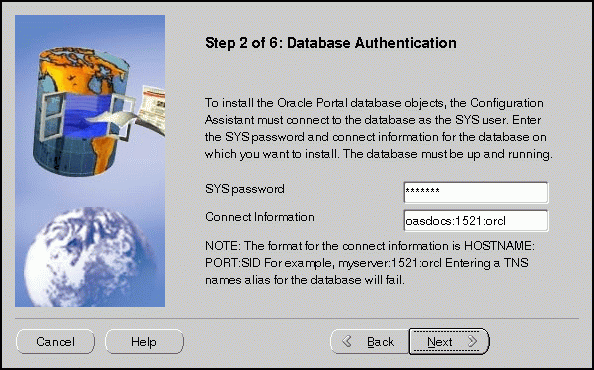
The Database Authentication screen allows you to specify the database connection information granting the Configuration Assistant database access to install the Oracle Portal database objects.
CHANGE_ON_INSTALL, is automatically created and granted the DBA role.
HOSTNAME:PORT:SID
Example: oasdocs:1521:orcl
where hostname is the domain name and machine where you want to install Oracle Portal, port is the port number on which the Oracle8i database is running, and SID is the database name which uniquely identifies a node's instance. The default SID name is orcl.
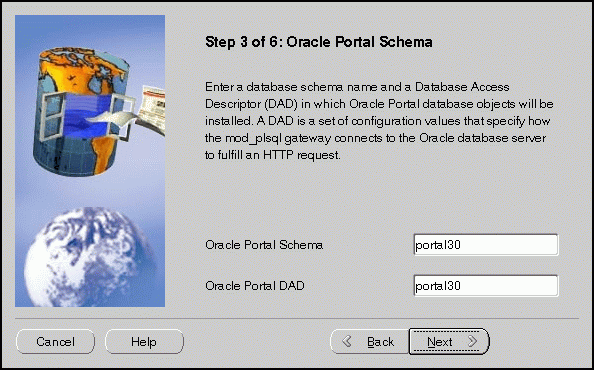
Oracle Portal Schema screen allows you to enter the Schema and DAD name. These must match the Oracle Portal Schema and DAD name you entered during the installation process on the Apache Listener Configuration for Oracle Portal (DAD and Schema name) screen. The default is portal30.
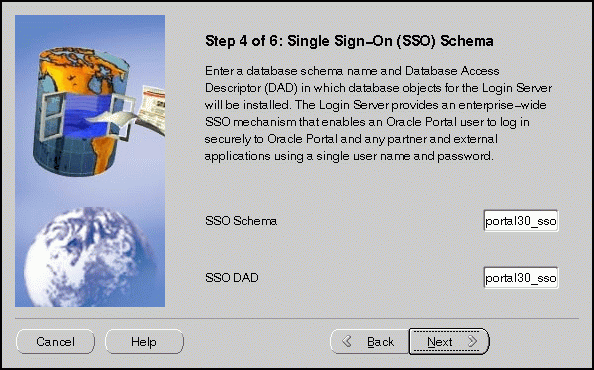
Single Sign-On Schema screen allows you to enter the SSO Schema and DAD name. These must match the SSO Schema and DAD name you entered during the installation process on the Apache Listener Configuration for Oracle Portal (Login Server) screen. The default is portal30_sso.
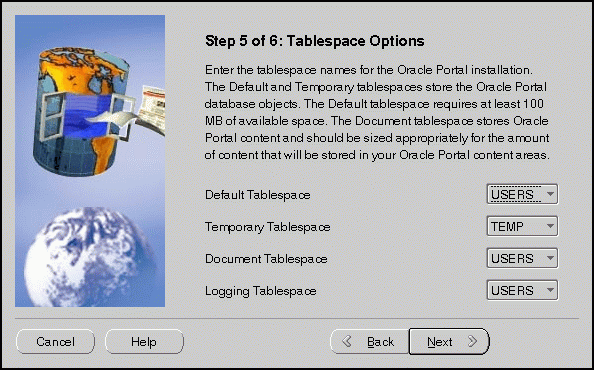
Tablespace Options screen allows you to enter the tablespace names for Oracle Portal. Choose from the list of tablespaces. For more information, refer to Table A-1.
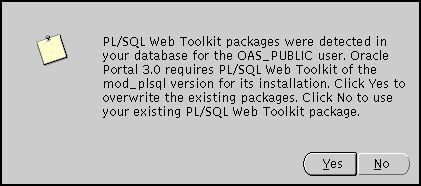
PL/SQL Web Toolkit screen appears only if the configuration assistant detects that PL/SQL Web Toolkit packages already exist on your machine. Click Yes to overwrite the existing packages, or click No to keep the existing PL/SQL Web Toolkit packages.
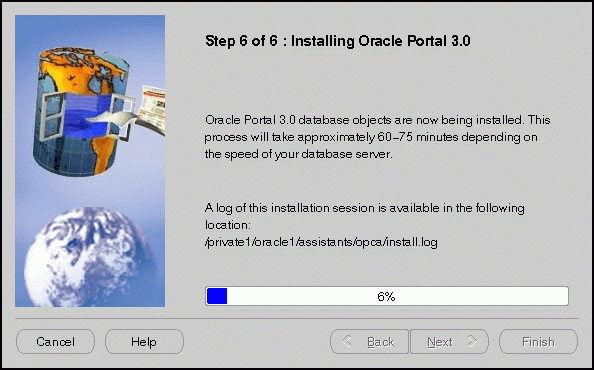
Installing Oracle Portal screen displays a database objects installation progress bar. Please be patient and refrain from using your machine while this is underway. This process may a long time to complete.

Summary screen appears at the end of installation. It reveals information about accessing the Oracle Portal Home page, Login Server page and the gateway settings page. For your convenience, make note of this information before clicking OK.
<ORACLE_HOME>/assistants/opca/install.log
The following command launches the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant:
prompt> <ORACLE_HOME>/bin/emca
The following steps guide you through the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Assistant:
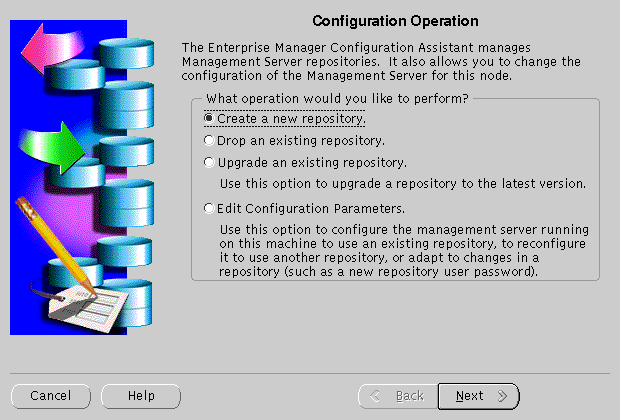
Configuration Operation Screen allows you to create, drop, or upgrade a repository. It also enables you to edit your configuration parameters.
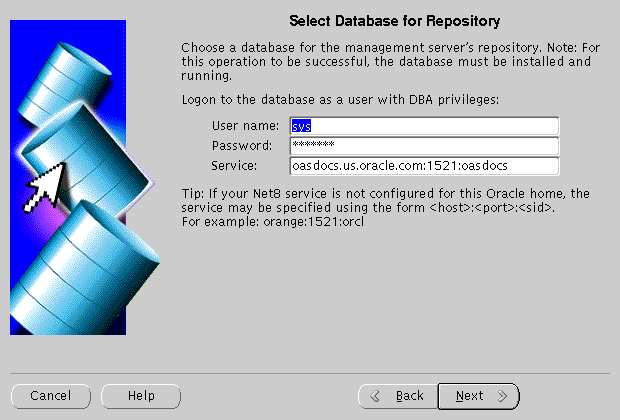
Select Database for Repository screen allows you to enter database information for the management server's repository. Be sure to log in as a user with DBA privileges.
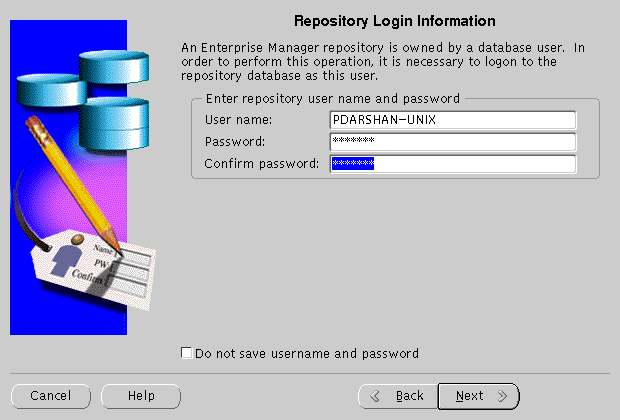
Repository Login Information screen allows you to enter the login username and password for the database user.
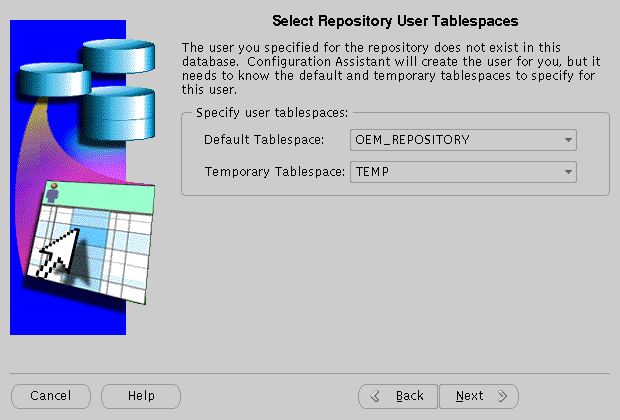
Select Repository User Tablespaces screen allows you to select the default and temporary tablespace for the new repository user. Use the drop-down button to select the default and temporary tablespace.

Create Repository Summary screen displays all your repository settings. Be sure to verify them for accuracy.
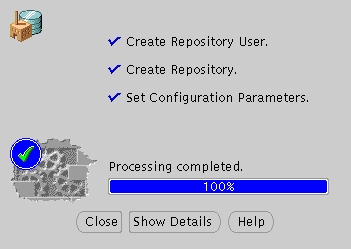
Configuration screen indicates the progress the configuration assistant has made as it creates the repository. Click on Show Details if you get an error.
The following command launches the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant:
prompt> <ORACLE_HOME>/bin/dbassist
The Oracle Database Configuration Assistant creates a database that is used as a container for Oracle 8i JVM. The following screen appears as the configuration assistant creates the database:
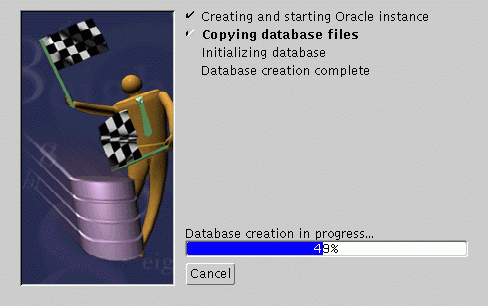
Oracle Database Configuration Assistant does not require any user input. Once the database creation process ends, the following screen appears.
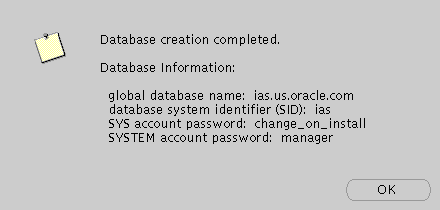
The Database Information screen displays database information such as global database name, database SID, SYS account password, and SYSTEM account password. Make a note of this information and click OK. You have completed the database creation process.
|
|
 Copyright © 2000 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|