Release 2.2
Part Number A85247-01
Library |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide Release 2.2 Part Number A85247-01 |
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager is a system management tool which provides an integrated solution for centrally managing your heterogeneous environment. Oracle Enterprise Manager combines management applications such as the Console, Oracle Management Servers, Oracle Intelligent Agents, common services, and tools to provide an integrated, comprehensive systems management platform for managing Oracle products.
This introduction discusses the topics listed below:
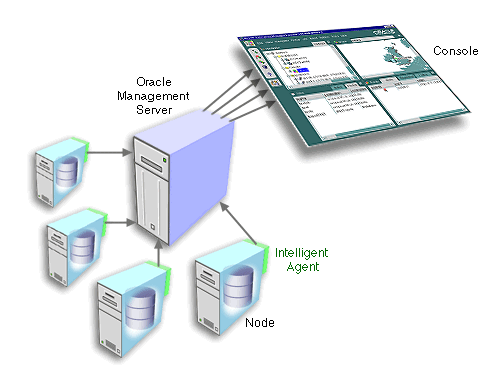
Oracle Enterprise Manager is based on a highly scalable three-tier model.
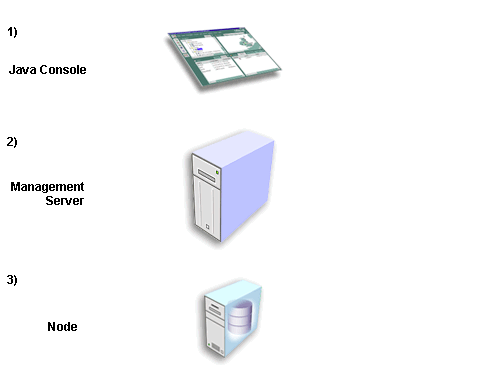
The first tier, the client, consists of a Java-based Console and integrated applications.
The second tier is the Management Server or designated group of Management Servers which manages the flow of information between the clients and targets.
The third tier is comprised of targets, such as databases, nodes, or other managed services. An Intelligent Agent resides on each target node and monitors the services in the target for registered events (potential problem occurrences) and executes jobs sent by the Console via the Oracle Management Server(s). Only one Intelligent Agent can run on a single machine, regardless of the number of services on that machine.
Oracle Enterprise Manager's three main components are listed below:
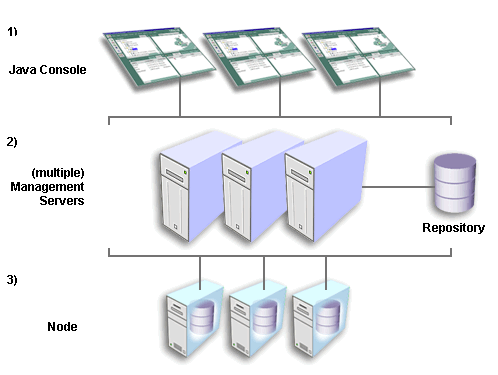
A repository is a set of tables in a database containing the internal state information of Enterprise Manager for the managed environment and information about the management packs. It is used as a back-end store by the Oracle Management Servers, providing distributed control between clients and managed nodes.
An Enterprise Manager repository is owned by a database user. During repository creation a repository's user name is entered that will be used to create this database user.
The name of the repository user will also be the name of this repository, and this name will be used throughout the network to identify all the objects in this repository. The name of the repository must be a unique schema name across the entire managed network.
If the repository user name and encrypted password are saved during repository creation, the Management Server uses them to login to the repository; if they are not saved, the Management Server prompts the user for a user name and password before it starts up.
An Oracle Enterprise Manager administrative user is an account that provides users permission to perform administrative tasks and access administrative information. An administrative account is usually created for each person on an administrative team. Preferences, such as preferred credentials, login password, and email and paging notification schedules, must be set for each administrator. Generally each person has a single administrative user account through which he administers several to many targets.
Administrative user accounts are created by the super administrator. Oracle Enterprise Manager is installed with a default super administrator account which can be used for the initial login. The super administrator account is sysman and the initial password is oem_temp. The password must be changed after the initial login. The super administrator account is similar to root on UNIX or Administrator on Windows NT and is a user which cannot be deleted or renamed.
|
Note: Administrator user accounts are specific to Oracle Enterprise Manager and are different than Oracle database users. |
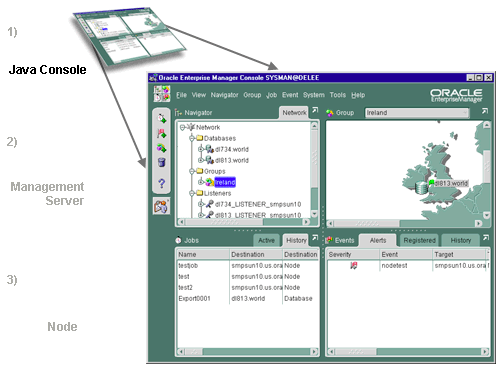
The Console, a graphical interface for administrators and the central launching point for all applications (including the integrated applications), is a Java-based application that can be run as either a "thin" or "fat" client. Thin clients use a web browser to connect to a server where Console files are installed, whereas fat clients require Console files to be installed locally.
However you run the Console, it relies on the Oracle Management Server and the Oracle Intelligent Agent to perform system management tasks.
The Management Server is the core of the Enterprise Manager framework. It provides administrative user accounts, processes management functions such as jobs and events, and manages the flow of information between the tiers.
As the number of nodes and managed services in your network increases or if the current Management Server is overloaded, you can add more Oracle Management Servers to the middle tier to share and balance the workload. These additional Management Servers provide fault-tolerance in the case where one Management Server becomes unavailable. All Management Servers administering the same set of managed nodes share a single Repository, which stores all system data, application data, and the state of managed nodes throughout the environment.
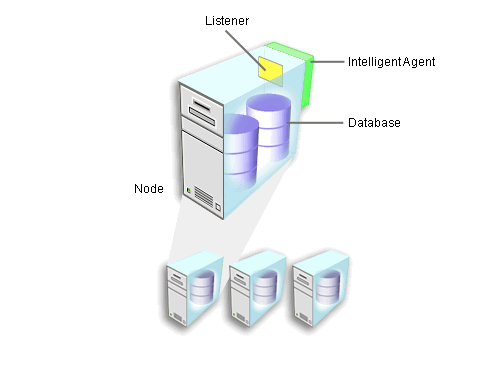
An Oracle Intelligent Agent is a process on a managed server, which monitors registered events and runs scheduled jobs against all discovered services on that server. Only one Intelligent Agent is required per node regardless of the number of services present on that machine. Intelligent Agents function independently of the database or services they support, as well as being independent of the Management Server and Console clients.
There are two types of discovery:
Without the Intelligent Agent discovery, there is no Console discovery. Both discoveries must be successful and must happen in the correct order for the services to appear in the Console Navigator.
When you use the Discovery Wizard in the Console, the Management Server contacts the Intelligent Agent installed on that node to discover the Oracle services installed on the node.
When the Intelligent Agent starts, it performs its service discovery by scanning the system for Oracle services to manage. The Intelligent Agent records the service discovery. When the Console requests a discovery of the node, the Intelligent Agent transmits the service discovery information it has detected to the Management Server.
The Management Server then places the new information in the repository, and updates the Console Navigator, displaying a view of all nodes and their respective services.
Service discovery allows administrators to run jobs and monitor for events on those nodes and allows the information to be centrally managed by the Consoles.
A managed node is any machine that is being monitored by an Intelligent Agent that has been discovered by the Console.
Every service running on a managed node is a managed service or target. Multiple services (targets) can exist on a single machine (node).
This section contains information about:
Each administrator can set up specific usernames, passwords, and roles (NORMAL, SYSOPER, or SYSDBA) for nodes, listeners, databases, and other services that you administer in the network.
After you set up preferred credentials, you are no longer prompted for credentials when connecting to the managed targets.
The Preferred credentials you set up through the Console also allow you to use the job and event system for targets where credentials are required. All login credentials set up through the Console are encrypted in the repository.
DBA Studio stores a list of databases that are displayed in the DBA Studio navigator tree. If preferred credentials are specified for any of these databases, the username, encrypted password, and role are added to a local file.
Saving or editing preferred credentials is an option which enables you to store login information, such as username, password, and role (NORMAL, SYSOPER, or SYSDBA). Passwords are always stored in encrypted format. This login information is used when a connection is established for the database instead of having to type a username and password each time.
You can run Oracle Enterprise Manager components in any configuration depending on your management environment. For example, you can run each tier on separate machines or run all three tiers on one machine.
Running Enterprise Manager components on separate machines requires the following:
Machine running only the Console and DBA Management Pack:
Running the entire Enterprise Manager bundle (Console, DBA Management Pack, Oracle Management Server and database repository) from a single machine requires the following:
Running the Enterprise Manager Console from a web browser requires 128 MB RAM.
Downloading Enterprise Manager from the webserver requires 50 MB of disk space.
The default Enterprise Manager package (using a single Oracle Management Server in your environment) is tuned to best support an environment with the following characteristics:
If the available Management Servers are CPU-bound (the CPU usage is exhausted), adding additional Management Servers is an alterative to increasing the capacity of the nodes that run the Management Servers.
To improve performance when the number of Consoles, jobs or events increases, Oracle recommends increasing resource capacity on the Repository database machine.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Release 2.2 is certified on the following operating systems:
The Management Server is not certified on Windows 95 or Windows 98.
Browser-based Oracle Enterprise Manager is only supported on the following operating systems: Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, and Windows 2000.
The tables below outline the steps needed for various Enterprise Manager configurations:
Details of the steps involved can be found in the indicated sections.
The following configuration may be used for most small to medium-sized environments. Small to medium-sized environments are environments which administer fewer than 64 managed nodes.
In this configuration, the middle-tier and client-tier Oracle Enterprise Manager components are on the same node.
|
Note: The information below is for new installations. For guidelines to upgrading your Oracle Enterprise Manager framework and Management Packs from previous 2.x releases to Release 2.2, refer to "Upgrading Your Oracle Enterprise Manager Framework and Management Packs" on page 1-19. |
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release. |
|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release or the installation guide provided with the separately licensable packs. |
|
Refer to "Creating a Release 2.2 Repository" on page 2-1 to create a repository using the Oracle Enterprise Configuration Assistant. |
|
|
Refer to "Starting the Enterprise Manager Console" on page 6-3. |
The following configuration is best for large environments with many managed databases and services. Large environments are environments which administer more than 64 managed nodes.
|
Note: The information below is for new installations. For guidelines to upgrading your Oracle Enterprise Manager framework and Management Packs from previous 2.x releases to Release 2.2, refer to "Upgrading Your Oracle Enterprise Manager Framework and Management Packs" on page 1-19. |
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Use an existing database for the Oracle Management Server repository or install and use a new Oracle database.
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release. Refer to "Creating a Release 2.2 Repository" on page 2-1 to create a repository using the Oracle Enterprise Configuration Assistant. |
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Install the Oracle Enterprise Manager client software in a new ORACLE_HOME. If you are installing from the database CD, choose the install type: Oracle8i Client->Administrator. If you are installing from the separately licensable packs CD, choose the install type: Oracle Enterprise Manager Packs and Management Infrastructure. |
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release or the installation guide provided with the separately licensable packs. |
|
Launch the Console (client), and at the login, point to the Management Server. |
Refer to "Starting the Enterprise Manager Console" on page 6-3. |
|
Note: If you want to have multiple clients working concurrently, install the client software on multiple clients. |
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release or the installation guide provided with the separately licensable packs. |
|
Refer to "Adding Additional Management Servers" on page 4-1. |
|
The upgrade of the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework (Console, Management Server, repository, and Intelligent Agent) and Management Packs from previous 2.x releases to Release 2.2 must be performed in the order documented below.
| Procedure | Reference |
|---|---|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release and the installation guide provided with the separately licensable packs. |
|
|
Refer to "Upgrade a Release 2.0 or 2.1 Repository to a Release 2.2 Repository" on page B-1 |
|
|
Refer to "Upgrading the Intelligent Agent and Data Gatherer" on page C-1. |
|
Refer to "Upgrading the Intelligent Agent and Data Gatherer" on page C-1. |
An Oracle Enterprise Manager Release 1.x repository schema is not the same as an Oracle Enterprise Manager "shared" Release 2.2 repository schema. In Enterprise Manager Release 1.x, each administrator had a separate repository schema which contained the current view of the network and user-specific information. In Enterprise Manager Release 2.2, administrators have accounts within a single shared repository schema, and all individual preferences are stored in the administrator's account.
Each Release 1.x repository must be separately migrated to a new Release 2.2 repository.
The procedures below highlight the basic steps for migrating a repository.
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release. |
|
|
Refer to the installation guide provided with the database release or the installation guide provided with the separately licensable packs. |
|
Refer to "Creating a Release 2.2 Repository" on page 2-1 to create a repository using the Oracle Enterprise Configuration Assistant. |
|
|
Refer to "Starting the Enterprise Manager Console" on page 6-3. |
| Procedure | Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Run the Release 2.2 Oracle Enterprise Manager Migration Assistant to migrate data you are using in your V1.x environment from one or multiple private repositories into a specific user in your new Release 2.2 repository. |
Refer to "Migrating a Release 1.x Repository to a Release 2.2 Repository" on page 7-1. |
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|