Release 3.0
Part Number A86707-02
Library |
Service |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle9i Application Server Oracle Portal Configuration Guide Release 3.0 Part Number A86707-02 |
|
This chapter provides information about Oracle Portal after installation and the configuration tasks that you can perform.
|
See: For information about installing Oracle Portal with Oracle9i Application Server, see the "Oracle9i Application Server Installation Guide". |
Specific topics covered include:
Oracle Portal is installed primarily in the Oracle8i database, with some supporting components installed on the middle tier in Oracle9i Application Server.
If you install Oracle Portal in the default mode, five schemas are created. The default base schema name is portal30 which you can change at installation time.
|
Note: The portal30 and the portal30_sso schemas are highly privileged database schemas. For more information, see the "Using the PL/SQL Gateway" guide provided with Oracle9i Application Server. |
With each Oracle Portal installation, a default set of accounts is created. Assuming that the product is installed in a schema named portal30, the following default accounts are created:
|
See also:
Task topics in the "Working with Users" folder from the Oracle Portal Online Help content area. |
The following groups are created at installation time:
|
See also:
Task topics in the "Understanding Users" folder from the Oracle Portal Online Help content area. |
After you have successfully installed Oracle Portal, you can access it by entering the following in your browser:
http://<hostname>:<portnumber>/pls/<dad>
You will be prompted to enter the Single Sign-On (SS0) username and password before gaining access to Oracle Portal. The defaults are as follows:
Username: portal30
Password: portal30
You can choose to install and display the Oracle Portal user interface in any of the 24 supported languages from your browser. To install support for a given language, you must run the wwvseedus.sql and langinst.csh scripts. Once the language is installed you use the Set Language portlet to choose which language Oracle Portal should use.
The supported languages and their abbreviations are listed in the following table:
To install support for a given language in Oracle Portal:
ORACLE_HOME/portal30/admin/plsql directory.
UNIX
langinst.csh <-s portal_schema> <-p portal_password> <-o sso_schema> <-d sso_ password> <-c portal_connect_string>
-l <language> -available
Windows NT
langinst.cmd <-s portal_schema> <-p portal_password> <-o sso_schema> <-d sso_ password> <-c portal_connect_string> -l <language> -available
Example
langinst.csh -s portal30 -p portal30 -o portal30_sso -d portal30_sso -c orcl
-l cs -available
where
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The database schema for the Oracle Portal database objects.
Default = |
|
|
The Oracle database password for the Oracle Portal schema. Default = <portal_schema> |
|
|
The Oracle database schema for Login Server objects.
Default = |
|
|
The Oracle database password for Login Server schema.
Default = |
|
|
The connect string for the database in which the Oracle Portal schema is installed. You need to provide the connect string only if the schema is located on a remote database. |
|
|
The abbreviation for the language you want to install. See Table 2-5, "Supported languages and abbreviations" above. |
|
|
(Required) Ensures that the tabs are translated. |
Typically, it makes sense to add the Set Language portlet to your content area home page, but you could add it to any page. The Set Language portlet can be added to a page just like any other portlet. Refer to the Oracle Portal online help content area for instructions on how to add portlets to pages.
Notes:
This section describes how to use Oracle Universal Installer to deinstall Oracle products (which deinstalls them from the Oracle Universal Installer inventory) instead of removing them manually.
To deinstall Oracle Portal:
The Welcome window for Oracle Universal Installer appears.
The Inventory dialog box appears.
The Inventory Confirmation window appears.
The products are deinstalled from your computer. The Inventory dialog box appears without the deinstalled products.
If you need to delete a single Oracle Portal schema or the Login Server, you can do so from the Oracle Portal Configuration Assistant - Step 1 of 6: Installation Options.
To deinstall an Oracle Portal schema or the Login Server:
Windows NT
UNIX
Click the option to Deinstall Oracle Portal or the Login Server.
Oracle Portal and the Login Server can be configured to run in HTTPS mode if your portal requires increased security. For optimal performance, you can also choose to have a mixed configuration where Oracle Portal is run in HTTP mode and the Login Server is run in HTTPS mode.
The Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is responsible for securing Web HTTP communication between a browser and a Web server in plain HTTP over SSL (named HTTPS). Enabling SSL to work with the Oracle HTTP Server is handled by the mod_ssl package which is provided with the Apache Web server. It uses the URL scheme HTTPS rather than HTTP and a different server port.
For more information about enabling and disabling SSL, visit the Apache interface to mod_SSL at the following location:
http://www.modssl.org
In the Login Server, if you need to specify URL prefixes and ports, for example, if you are working with the ssodatan script (which configures your login via the Single Sign-On server) or ssodatax script, or running the Oracle Universal Installer, you would specify https:// and an https port; instead of specifying an http:// and an http port.
When configuring the Login Server for HTTPS, Oracle Portal still requires access to an HTTP port to use UTL_HTTP to connect to the Login Server for some of the communication that it requires. You can specify an available HTTP port from the Global Settings page in the Services portlet.
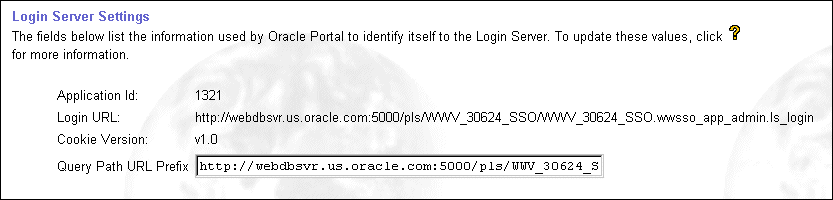
In the Query Path URL Prefix field, enter the URL prefix which is used to construct the URLs for these internal connections to the Login Server. You must specify an available HTTP port for this URL prefix.
For increased security, refer to the Apache documentation for information on restricting access to the HTTP ports to the portal so that only HTTPS connections from Oracle Portal database's IP address (which is performing a UTL_HTTP callout) is accepted.
With HTTPS, you must use certificates for increased security in Oracle Portal. In this case, the Parallel Servlet must be aware of which port(s) are operating under HTTPS. To set this up, you must edit the zone.properties file which is located in the following location by default:
| Operating System | Location |
|---|---|
|
Windows NT |
<ORACLE_HOME>\Apache\Jserv\servlets\zone.properties |
|
UNIX |
<ORACLE_HOME>/Apache/Jserv/etc/zone.properties |
Add the following line to the zone.properties file:
servlet.page.initArgs=httpsports=<port1>:<port2>:. . . :<portn>
Each port in this list will operate using the HTTPS protocol, and must have a certificate created on the Oracle HTTP Server powered by Apache on that port.
|
|
 Copyright © 2000 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|