10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10314-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server Reports Services Publishing Reports to the Web 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10314-01 |
|
Single Sign-On enables you to establish a unique identity for each user, and tie that identity to the resources and data sources unique to that user. For example, a user might log into an environment such as OracleAS Portal, which enables them to access certain reports and printers for which they have the necessary privileges. When they choose to run a report from this environment, they can access the necessary data sources for the report because their data source credentials are stored with the single user identity used to login to OracleAS Portal. Thus, logging in once provides them access to all of the resources and data sources they require to run their reports.
Because OracleAS Reports Services provides a flexible approach to security, you can implement many variations of the configuration described above. For example, you might choose not to store data source credentials with the single user identity. Or you might prefer to use direct URLs for launching reports rather than a platform like OracleAS Portal. If your reports are public and do not require any security, then you might choose to turn off report security altogether.
This chapter describes how you can implement and administer various configurations of OracleAS Single Sign-On with OracleAS Reports Services.
OracleAS Single Sign-On can be implemented only in a secure server environment. This means that you must have a security policy in place in your Reports Server configuration file before you can consider implementing OracleAS Single Sign-On with OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note:
Security settings are discussed in the following places: Chapter 3, "Configuring OracleAS Reports Services" tells you how to specify the Java class that defines the security policy for the server; Chapter 11, "Deploying Reports in OracleAS Portal" tells you how to deploy OracleAS Reports Services reports in OracleAS Portal; Appendix A, "Command Line Options" provides information about the |
With OracleAS Single Sign-On, your administrator establishes a user identity for each user. The administrator does this in the Oracle Internet Directory, through its user interface, the Oracle Delegated Administration Services. You can access Oracle Delegated Administration Services standalone or through OracleAS Portal. In either case, the information is saved to the Oracle Internet Directory.
The user identity is comprised of the user name and password. Once users are established, data source connection strings may be associated with them. At login, users must enter their user names and passwords (their user identities), which will in turn give them access to all of the data sources associated with those identities. OracleAS Single Sign-On issues a session cookie that effectively acts as a key that opens all authorized doorways for that session.
|
Note:
For detailed information about the requirements and procedures required for setting up SSO-related components, such as the Oracle Internet Directory, see the Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide and the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide on the Oracle Application Server documentation CD and on the Oracle Technology Network, ( |
By default, the Reports Server is secured and, to run a report, you must login with a valid Single Sign-On userid and password. The Reports Server is configured by default with the OracleAS Single Sign-On instance installed as part of Oracle Application Server. The Oracle Internet Directory instance installed with Oracle Application Server is used as the default repository for user and group information. If you want to configure the Reports Server to use a different Oracle Internet Directory instance or disable security, refer to Administering OracleAS Single Sign-On. For information on how to add users to the Oracle Internet Directory, refer the Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide. In addition, for each Oracle Application Server installation, the Reports Server instances connect to the Oracle Internet Directory as an application entity that is unique to the Oracle Application Server installation. For more information on this behavior, refer to Connecting to the Oracle Internet Directory.
If a user is not already logged in to OracleAS Single Sign-On, they are prompted to login when they attempt to run a report to the Reports Server via rwservlet. If the user parameters for a report include SSOCONN, OracleAS Single Sign-On will search for the user's data source credentials in the Oracle Internet Directory. If none are found, then OracleAS Single Sign-On prompts the user to create a new resource. For more information on rwservlet, refer to rwservlet. For more information about SSOCONN, refer to SSOCONN.
The Reports Server is also configured to operate with OracleAS Portal by default. You can optionally add reports to the portal and enable users to launch them from the portal. Since users must login to the portal in this case, they are not prompted to login again when they launch their reports because they have already been identified to OracleAS Single Sign-On by logging in to the portal.
You can also optionally define access controls for resources associated with the Reports Server (e.g., reports, printers, Reports Servers, and calendars) in OracleAS Portal. To control access to resources, you must add them to the portal and specify their access options. The resource access controls you specify in OracleAS Portal apply to reports that you run outside of the portal as well. For example, if a user tries to run a report through rwservlet, it will be subject to any access controls you have put in place through OracleAS Portal.
|
See Also:
Deploying Reports in OracleAS Portal For more information about the integration between OracleAS Portal and OracleAS Reports Services. |
This section describes some of the administrative tasks you may need to perform as you maintain security for OracleAS Reports Services.
To take advantage of OracleAS Single Sign-On out-of-the-box, the SINGLESIGNON parameter in the rwservlet configuration file (rwservlet.properties) is set to YES, which indicates that you will use OracleAS Single Sign-On to authenticate users. You may change this parameter to NO, if you choose not to use OracleAS Single Sign-On. If you choose NO, the Reports Server authenticates users by itself (i.e., the same mechanism used in Oracle Reports6i). The rwservlet configuration file is usually found in:
ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf
The SINGLESIGNON value is usually commented out after installation, but the default value is YES.
Reports Server security is turned on and off in the Reports Server configuration file. By default, the Reports Server configuration file, ORACLE_HOME/reports/conf/servername.conf, contains a security element like the following:
<security id="rwSec" class="oracle.reports.server.RWSecurity"><!--property name="securityUserid" value="portal_id/portal_password@portal_ schema" confidential="yes" encrypted="no"--> <property name="oidEntity" value="%REPORTS_OID_ENTITY%" confidential="yes" encrypted="no"/></security>
This security element is referenced by default from the two default job elements in the configuration file to indicate that Reports Server security should be enforced:
<job jobType="report" engineId="rwEng" securityId="rwSec"/> <job jobType="report" engineId="rwEngURL" securityId="rwSec"/>
To disable Reports Server security, you must remove or comment the security element as well as the secuirtyId attributes from the job element specifications.
To enable data source security through OracleAS Single Sign-On, you must do the following:
SSOCONN in the URL that launches the report.
If you wish to implement data source security through OracleAS Single Sign-On for your own pluggable data sources, you need to perform the following additional task:
The sections that follow explain how to perform these operations.
To enable data source security through OracleAS Single Sign-On, the URL must contain or reference (i.e., via the key map file) a OracleAS Single Sign-On parameter (SSOCONN) with a value of the form:
key_name/data_source_type/parameter_name
key_name maps to a string stored in the Oracle Internet Directory that provides the necessary information to connect to the database. When Oracle Reports encounters a key_name, it checks to see if the current user has a corresponding key stored in the Oracle Internet Directory. If so, Oracle Reports uses the string stored in that key to connect to the data source. If not, Oracle Reports checks to see if the key_name maps to a publicly available key. If so, Oracle Reports uses that key. If not, Oracle Delegated Administration Services prompts the user to create a new resource.
|
See Also:
Populating the Oracle Internet Directory For more information about populating the Oracle Internet Directory with resources |
data_source_type is the kind of data source to which you are connecting. data_source_type lets Oracle Reports know what format to expect in the string associated with key_name. data_source_type must be a valid resource type stored in the Oracle Internet Directory. Oracle Reports provides default resource types for the following:
You can also create addition resource types in the Oracle Internet Directory for your own pluggable data sources.
parameter_name specifies the Oracle Reports system or user parameter to be used to pass the connection string to Oracle Reports. For example, in the case of the OracleDB data source, Oracle Reports receives the connection string via the USERID parameter and uses it to connect to the specified Oracle database. Similarly, for the EXPRESSPDS, the EXPRESS_SERVER parameter is used and, for the jdbcpds, p_jdbcpds is used. If you have your own custom pluggable data sources, you would need to define your own user parameter for passing the connection string to Oracle Reports and specify it as parameter_name for SSOCONN.
In the case of an Oracle database, the URL to call a report with SSOCONN would look something like the following:
http://myhost.mycompany.com:7779/reports/rwservlet?server=rs_cped &report=my.rdf&destype=cache&ssoconn=mykey/OracleDB/userid&desformat=html
In the case of an Oracle Express database, the Single Sign-On value would look something like the following:
http://myhost.mycompany.com:7779/reports/rwservlet?server=rs_cped &report=exppds.rdf&destype=cache&ssoconn=exptest1/EXPRESSPDS/express_server&desformat=html
In the case of a JDBC data source, the Single Sign-On value would look something like the following:
http://myhost.mycompany.com:7779/reports/rwservlet?server=rs_cped &report=Jdbcthin.rdf&destype=cache&desformat=html&ssoconn=jd1/jdbcpds/p_jdbcpds
In this case, jd1 is an Oracle Internet Directory resource name.
|
See Also:
Configuring and Using the JDBC PDS For more information on how to configure a JDBC data source. |
SSOCONN in a command line, you cannot:
authid in the same command line.
SINGLESIGNON set to NO in rwservlet.properties.
Doing any of the above with SSOCONN in the command line results in an error.
For data source security to function with OracleAS Single Sign-On, you need to store the data connection information for each user in the Oracle Internet Directory or make the resource a default one available to every user. You can populate Oracle Internet Directory with this information in any one of the following ways:
If you only need to enter credentials for a small number of users (e.g., for a development environment), you can use Oracle Delegated Administration Services to directly enter connection string information into the Oracle Internet Directory for each user.
|
Note: Before a user can access Oracle Delegated Administration Services, an administrator must have already entered a user identity in the Oracle Internet Directory for the user. This step can be done by batch loading information that is already entered into an LDAP directory in some other source.
See the Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide for information on batch loading. You'll find it on the Oracle Application Server documentation CD and on the Oracle Technology Network, ( |
During Oracle Application Server installation, you specify the location of Oracle Delegated Administration Services. You use this URL to access Oracle Delegated Administration Services for administrative purposes. Once in Oracle Delegated Administration Services, you enter the information via the Resource Access Information section of the Preferences tab for the user. See Figure 10-1. Note that, for the Preferences tab to appear, there must already be a resource in place.
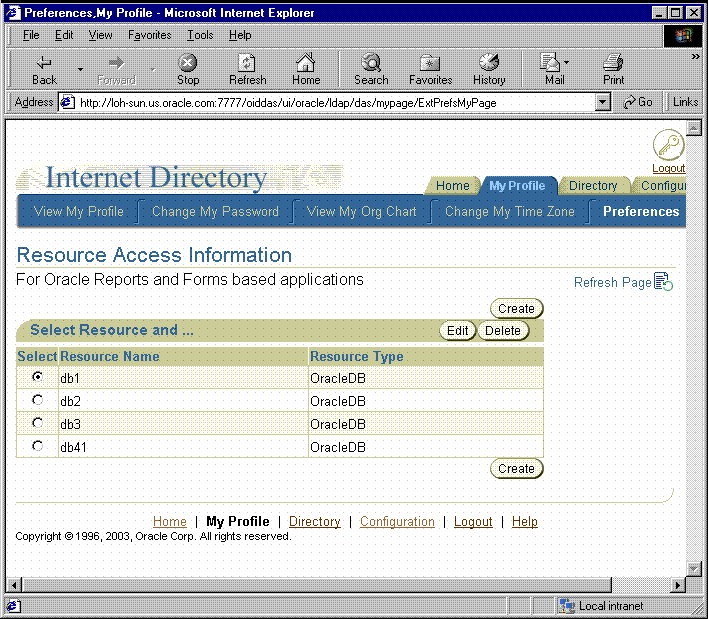
If you need to enter data source information for a large number of users, you should use either the user prompt or batch methods of populating the Oracle Internet Directory.
If you prefer to have users enter their own connection string information, you do not have to pre-populate the Oracle Internet Directory with data source connection information at all. If you use SSOCONN when launching the report but the Oracle Internet Directory does not already contain a connection string for the key and the key is not publicly available to all users, the Oracle Delegated Administration Services Create Resource page is displayed to the user, who must enter their data source connection string. See Figure 10-2. Oracle Delegated Administration Services stores the string entered by the user in the Oracle Internet Directory for future use and rwservlet uses the newly entered connection string for the data source connection string of the report.
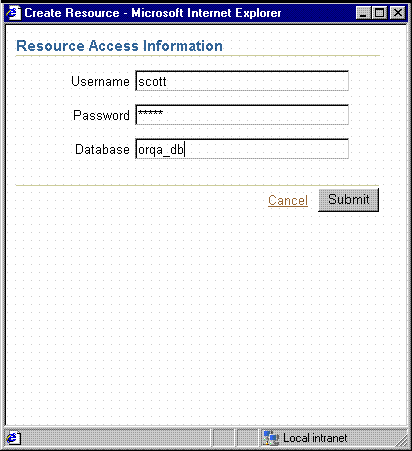
Resources for OracleAS Reports Services are created in the Oracle Internet Directory under the following entry:
orclresourcename=resource_name, cn=Resource Access Descriptor, orclownerguid=guid, cn=Extended Properties, cn=OracleContext, dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=comFoot 1
You need to create orclownerguid=guid in the above Oracle Internet Directory entry before you can proceed with the batch loading of resources. If you used Oracle Delegated Administration Services to create your users, orclownerguid=guid was created automatically and you can proceed to Batch Loading Resources.
If you seeded users into the Oracle Internet Directory with an LDIF file, then, before following the steps in Batch Loading Resources, you need to complete the following steps:
Depending on how your users are created in the Oracle Internet Directory, you can use any number of methods to get their GUIDs. You can get user GUIDs using the Oracle Internet Directory LDAP API. You can also get it using the ldapsearch command:
D:\ora9ias\BIN>ldapsearch -h host_name -p port_num -L -D cn=orcladmin -w orcladmin's_password -b "cn=users,dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=com" -s sub "objectclass=*" dn orclguid
orclownerguid=guid under cn=Extended Properties, cn=OracleContext, dc=us, dc=oracle, dc=com.
orclownerguid=guid, proceed to Batch Loading Resources.
Follow the steps below to batch load data source resources for your users:
orclresourcename=resource_name, cn=Resource Access Descriptor under orclownerguid=guid, cn=Extended Properties, cn=OracleContext, dc=us, dc=oracle, dc=com, where orclownerguid=guid is the GUID created in Before You Begin.
If you want to make a resource publicly available to all of your users, you can do so by following these steps:
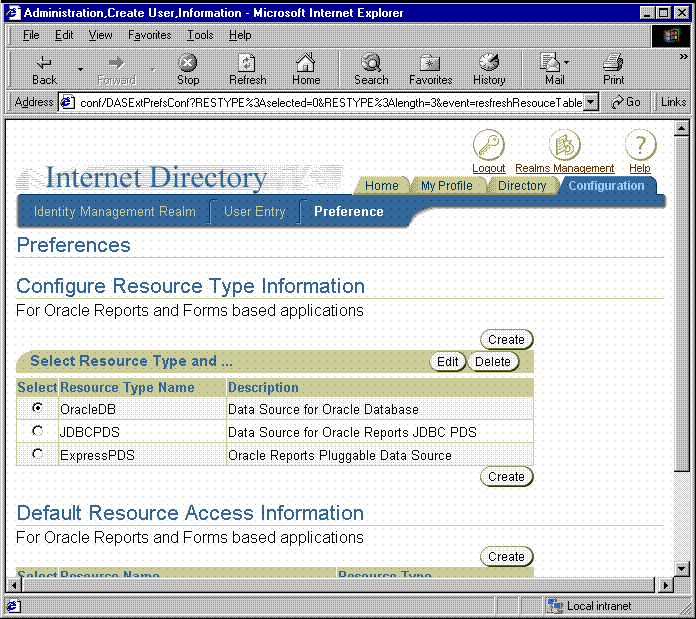
scott/tiger@mydb.
That resource should now appear under Default Resource Access Information and be available to all users.
If you want to add a new resource type to support your own pluggable data source, you need to perform the following procedure:
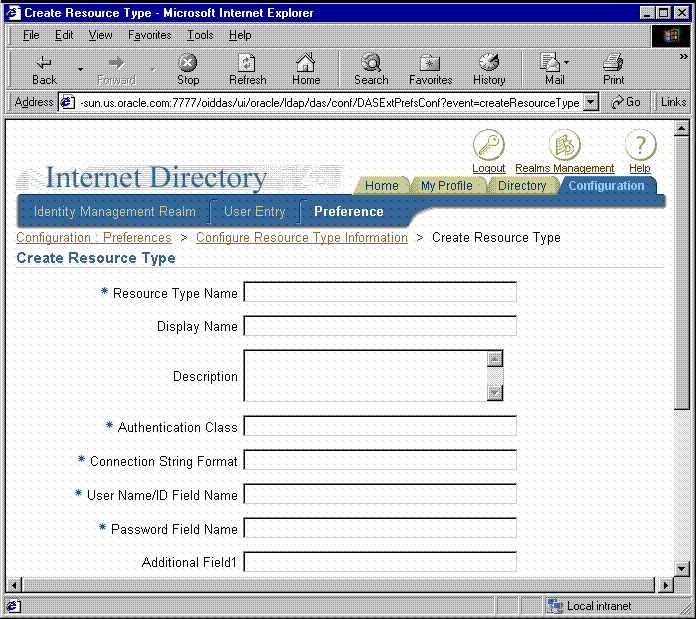
Table 10-1 Create Resource Type Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
Resource Type Name |
Is the name of the new resource type. This name is used when you need to reference the resource type, for example, in the |
|
Display Name |
Is the name to be used when the resource type appears in the user interface. |
|
Description |
Is a textual description that explains the purpose of the resource type and any other documentary information you want to enter for it. |
|
Authentication Class |
Leave this field blank. |
|
Connection String Format |
Defines how OracleAS Reports Services should construct the connection string using the values stored in Oracle Internet Directory for the resource. For example: for the Oracle database or a JDBC data source your connection string format might be:
This string indicates that the user name is followed by a slash, the password, an at sign ( for Oracle Express your connection string format might be:
This string indicates that
|
|
User Name/ID Field Name |
Is the display name of the user name field that contains the value for |
|
Password Field Name |
Is the display name of the password field that contains the value for |
|
Additional Field 1-3 |
Is the display name of the additional fields, which contain the values of |
data_source_type portion of the SSOCONN argument.
As you may recall from Chapter 9, "Securing OracleAS Reports Services", OracleAS Reports Services must connect to the Oracle Internet Directory to verify user privileges and obtain existing data source connection information. In connecting to the Oracle Internet Directory, you must consider:
When OracleAS Reports Services connects to the Oracle Internet Directory, it does so as an application entity. By default, each OracleAS Reports Services application entity is unique to its Oracle Application Server installation. Every Reports Server started from the same Oracle Application Server installation (i.e., ORACLE_HOME) uses the same application entity to connect the Oracle Internet Directory. This setup ensures that each Reports Server can only access information in the Oracle Internet Directory that is relevant to its instance of Oracle Application Server.
For example, suppose you have two instances of Oracle Application Server, one for your Finance group and one for your Human Resources group. A Reports Server from the Finance group's Oracle Application Server instance would be prevented from accessing information relevant only to the Human Resources group, and vice versa. Thus, information stored in the Oracle Internet Directory is more secure by default.
In previous releases of OracleAS Reports Services, all Reports Servers connected to the Oracle Internet Directory as the same application entity. As a result, it was not possible to restrict a Reports Server's access to information in the Oracle Internet Directory.
To revert to the less restrictive security mode, refer to the OracleAS Reports Services chapter of the Oracle Application Server Release Notes.
By default, the Reports Server is configured to use the Oracle Internet Directory instance installed with Oracle Application Server. If you are building your system anew, this arrangement is fine. If, however, you have an existing Oracle Internet Directory instance that you want to use for the Reports Server, you have to make some adjustments to your configuration.
Changing Oracle Internet Directory instances, though, must be done as part of a complete change of your Oracle Application Server middle tier. For more information about this process, please refer to the chapter on reconfiguring application server instances in the Oracle Application Server 10g Administrator's Guide.
You can merge serveral application entities so that the Reports Servers installed in separate ORACLE_HOMEs can share available SSOCONN resources. To achieve this merge, you must execute an ldif file with the ldapmodify command. The ldif file should contain the following:
dn: dn of the group which represents the logical grouping of all report instances changetype: modify add: uniquemember uniquemember: dn of the Reports Application Entity
where:
dn of the group which represents the logical grouping of all report instances=cn=Virtual Application Group, orclApplicationCommonName=reports_ application_entity_nameFoot 2, cn=Reports, cn=Products, cn=OracleContext
and
dn of the Reports Application Entity =orclApplicationCommonName=reports_ application_entity_name, cn=Reports, cn=Products, cn=OracleContext
The default configuration for Oracle Application Server Forms Services does not run in OracleAS Single Sign-On (SSO) mode. The default configuration for OracleAS Reports Services does run in SSO mode.
Forms applications calling integrated OracleAS Reports Services using the RUN_REPORT_OBJECT built-in will not experience any problems when OracleAS Forms Services is running in non-SSO mode and OracleAS Reports Services is running in SSO mode as long as the Reports Server and the requested report are not registered in OracleAS Portal.
Other Requirements:
rwserver server=Reports Server name
REPORTS_PATH, must be modified in the file ORACLE_HOME/bin/reports.sh to reference the path of the reports to be run.
server_name.conf located in the ORACLE_HOME/server/conf/ directory.
ORACLE_HOME/server/conf/reports_server_name.conf by commenting out the <security> tag and removing securityId from the <job> tags.
Table 10-2 lists the possible Forms/Reports combinations and expected results:
1
dc=us,dc=oracle,dc=com is merely an example in this instance. You would normally enter your own values for these items.
2
Where reports_application_entity_name is in the format, reportsApp_hostname_GUID. For example, reportsApp_serv1.us.oracle.com_C7543D42A9E26726E034080020A46EE2
|
|
 Copyright © 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|