10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B12118-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle® Internet Directory Administrator's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B12118-01 |
|
Directory Replication Concepts, 3 of 12
This section contains these topics:
Full replication involves propagating the entire DIT to another node. This type of replication ensures the high availability of the entire directory. You can also use it to distribute operations on the entire directory among different nodes.
Full replication can be based on either Oracle9i Advanced Replication or LDAP.
Partial replication enables you to propagate one or more subtrees, rather than the entire DIT, to another node. Decentralizing a directory in this way enables you to balance the workload between servers and build a highly available distributed directory complete with fault tolerance and failover. Because it brings data closer to the client, partial replication reduces response time and improves performance. You can configure partial replication by using the Replication Environment Management Tool.
Partial replication is LDAP-based only. It does not use Oracle9i Advanced Replication.
Figure 24-1 shows an example of partial replication.
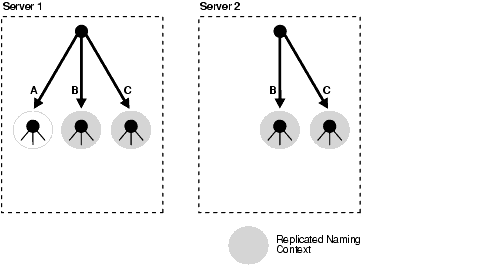
In a partial replication scenario, one or more naming contexts, but not the entire directory, are replicated. For example, in Figure 24-1, Server 1 contains three naming contexts: A, B, and C. Naming contexts B and C are replicated to Server 2, but naming context A is not.
Table 24-1 compares the two types of replication.
|
|
 Copyright © 1999, 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|