10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10316-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server TopLink Mapping Workbench User's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10316-01 |
|
The Oracle Application Server TopLink Mapping Workbench project ( .mwp file) stores the information about how classes map to database tables. These are language-independent XML files, different from the deployment XML files generated by the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench, that are read in by the application using the XMLProjectReader class.
You can edit each component of the project, including:
The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench displays projects and their contents in the Navigator pane. When you select a project, its attributes display in the Editor pane. The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench can log runtime XML calls (in the mw_xml.log file) to help troubleshoot projects (see "General Preferences" for more information).
Use this procedure to create a new OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project.
 on the toolbar. The Create New Project dialog box appears.
on the toolbar. The Create New Project dialog box appears.
You can also create a new project by choosing File > New Project.
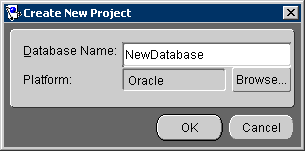
To select a different database, click Browse. See "Working with Databases" for more information.
|
Note:
Always use a new folder to save a project. After creating the |
The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench window appears, showing the project name in the Navigator pane. Continue with "Working with Project Properties".
Use this procedure to open an existing project.
|
Caution: To upgrade from a previous version of OracleAS TopLink, you must follow specific upgrade procedures and use the Package Rename tool. Refer to the Oracle Application Server TopLink Release Notes and Oracle Application Server TopLink Getting Started Guide for more information. |
 on the toolbar. The Choose a File dialog box appears. You can also open a project by choosing File > Open Project from the menu.
on the toolbar. The Choose a File dialog box appears. You can also open a project by choosing File > Open Project from the menu.
.mwp) to open and click Open. The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench displays the project information. If you open an OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench version 3.x project that contains EJBs, the Potential EJB Descriptors dialog box appears.
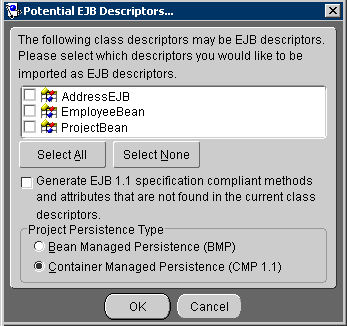
You can also specify whether the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench generates methods and attributes that comply with the EJB specification if they are not found within the current class descriptor(s).
The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench does not automatically save your project. Be sure to save your project often to avoid losing data.
Click the Save Selected Project button
 or Save All Projects button
or Save All Projects button
 to save your project(s). You can also save a project by choosing File > Save Project or File > Save All from the menu.
to save your project(s). You can also save a project by choosing File > Save Project or File > Save All from the menu.
|
Caution:
Do not rename the |
If the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench interface becomes corrupt, use the Refresh Tree option to refresh the Navigator pane.
Choose File > Refresh from the menu, or press Ctrl+T.
Use the Project Status Report to display a list of all warnings and errors in the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project. This report will quickly identify any incomplete mappings and indicate the project's current status.
Choose Tools > Generate Project Status Report from the menu. The Project Status Report dialog box appears, displaying the status of each OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project.
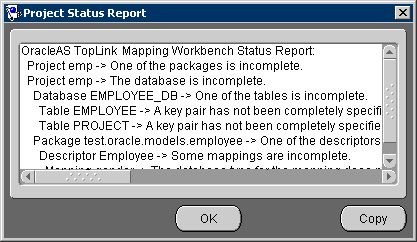
Text description of the illustration statrpt.gif
See "Error Messages" for information on each reported error.
To copy the report to another application (such as a text editor or e-mail message), click Copy.
Each project in the Navigator pane contains different editable parameters. To edit the project's properties, select the project object in the Navigator pane. The following tabs appear in the Editor pane.
Use the project's General tab to specify the default persistence type and class path information. Each OracleAS TopLink project uses a class path -- a set of directories, .jar files, and .zip files -- when importing Java classes and defining object types.
To create a descriptor for a persistent class, the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench reads a compiled Java .class file to read its attributes and relationships.
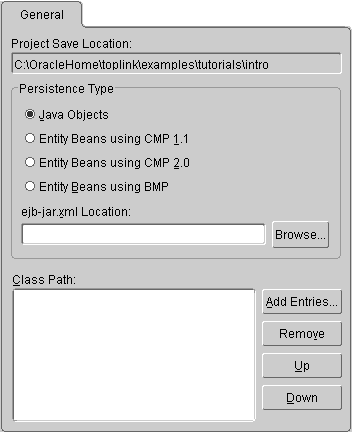
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Project Save Location |
Location of the project's |
|
Persistence Type |
Specify the project's persistence type. For EJB projects, specify the location of the |
|
ejb-jar.xml Location |
Location of the Note: This field applies for EJB projects only. |
|
Class Path |
Location of the classes and packages for this project. See "Working with Classes" for information.
To create a relative class path, select an entry and edit the path, as necessary. The path will be relative to the Project Save Location. |
You can create an OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project based on information in the ejb-jar.xml file. Use this file to map the EJB 2.0 Container Managed Persistence (CMP) entity beans' virtual fields (called Container Managed Fields, defined by <cmp-field> tag) or relationships (called Container Managed Relationship, defined by <cmr-field> tag) to database tables. You must specify an .xml file or a .jar file that contains an ejb-jar.xml file.
The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench defines all descriptors for entity classes (as defined in the ejb-jar.xml file) as EJB descriptors
![]() . The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench does not create (or remove) descriptors for the interfaces and primary key class for the entity when refreshing from the
. The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench does not create (or remove) descriptors for the interfaces and primary key class for the entity when refreshing from the ejb-jar.xml.
|
Note:
The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench creates class descriptors for entity classes not defined in the |
To update your project from the .xml file, right-click an EJB descriptor and select Update Descriptors from ebj-jar.xml. You can also update the project by choosing Selected > Update Descriptors from ebj-jar.xml from the menu. See "Working with the ejb-jar.xml File" for more information.
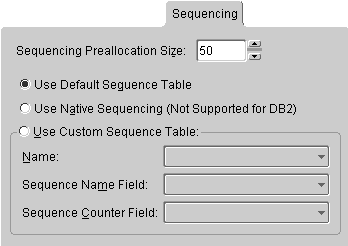
Sequence numbers are artificial keys that uniquely identify the records in a table. Use the project's Sequencing tab to specify default sequencing properties for all descriptors in the project. See "Working with Sequencing" for more information.
Use the project's Default tab to specify the default identity map, existence checking, and field access method.
Use the project's Default tab to specify the default:
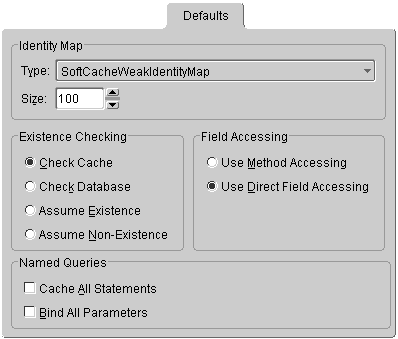
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Identity Map |
Use the Type drop-down list to select the default identity map and its Size for descriptors in this project (see "Working with Identity Maps"). |
|
Existence Checking |
Specify the type of existence checking to use. |
|
Field Accessing |
Specify whether the descriptors use Method or Direct field accessing (see "Specifying Direct Access and Method Access"). |
|
Named Queries |
Specify if OracleAS TopLink Caches All Statements or Binds All Parameters for named queries. See "Named Queries" for more information, including how to override this setting for specific queries. |
To rename your packages, you must edit each of the project's associated .xml files in the following subdirectories:
You must also edit the package and class names in the .mwp file. After changing the package names in all files, open the project in the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench. OracleAS TopLink now uses the new package name.
Use the project's Options tab to specify the default file names, class names, and directories, when exporting or generating Java source code and deployment XML. In addition, you can specify the primary key name and primary key search pattern (database schema) to use when generating tables. The resulting tables and columns will conform to the naming restrictions of the project's target database.
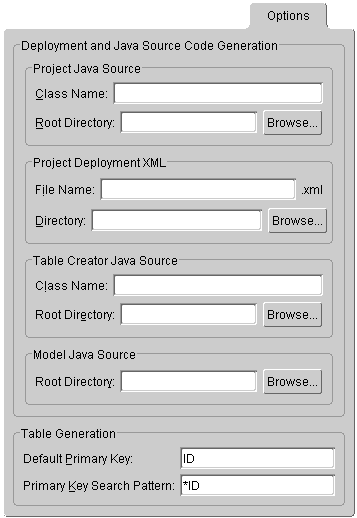
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Deployment and Java Source Code Generation |
Specify the defaults to use when exporting project information. Directories are relative to the project location and will contain folders for each generated package. |
|
Java class name and project root directory when generating Java source. See "Exporting Project to Java Source" for more information. |
|
|
Filename ( |
|
|
Java class name and project root directory when generating table source. See "Exporting Table Creator Files" for more information. |
|
|
Project root directory when generating Java model source. See "Generating Java Code for Descriptors" for more information. |
|
|
Table Generation |
|
|
Default name to use when generating primary keys. |
|
|
Default search pattern to use when generating primary keys. |
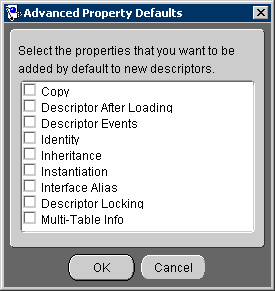
In addition to a descriptor's standard property tabs, you can specify advanced properties for each descriptor (see "Working with Advanced Properties" for more information). You can also specify which of these advanced properties appear, by default, for new descriptors.
You can also set the default advanced properties by choosing the project object and choosing Selected > Set Advanced Property Defaults from the menu.
This section describes how to create descriptors from Java classes and packages and includes information on the following:
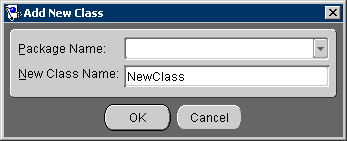
Use this procedure to create new classes and packages from within the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench.
You can also choose Selected > Create New Class from the menu.
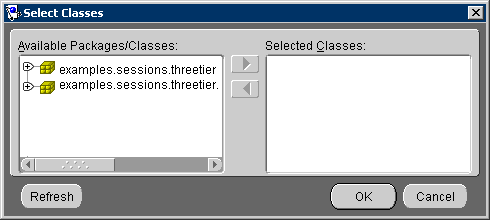
Use this procedure to update or refresh the classes in the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project.
 . The Select Classes dialog box appears.
. The Select Classes dialog box appears.
You can also update the classes by choosing Selected > Add/Refresh Classes from the menu.
|
Note: The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench creates class descriptors for each package/class. See "Specifying Descriptor Types" for to change the descriptor type. |
Select on the descriptor and click the Remove Class button
 , or choose Selected > Remove Class from the menu.
, or choose Selected > Remove Class from the menu.
To use your project with the Oracle Application Server TopLink Foundation Library, you must either generate deployment XML or export the project to Java source code. The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench can generate and export the following project information:
|
Note: When exporting Java source and deployment XML, the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench writes the password using JCE encryption (when using JDK 1.4). Refer to the Oracle Application Server TopLink Getting Started Guide for information on using password encryption with pre-JDK 1.3. Use the OracleAS TopLink Sessions Editor to specify custom password encryption (see "Setting Login Properties"). |
Use this procedure to convert the project to Java code. Generally, this generated code executes faster and deploys easier than XML files.
Right-click the project in the Navigator pane and choose Export > Project to Java Source from the pop-up menu.
You can also click the Export to Java Source button
 , or choose File > Export > Export to Java Source or Selected > Export > Export to Java Source from the menu.
, or choose File > Export > Export to Java Source or Selected > Export > Export to Java Source from the menu.
If you have not defined deployment and source code generation defaults (see "Working with Project Options") the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench prompts for a project class name and source directory.
|
Note: If your OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project uses UTF-8 character set, you must use a compatible JDK when compiling the exported Java source. |
Use this procedure to generate XML files from your project that can be read by the OracleAS TopLink Foundation Library. Using this option reduces development time by eliminating the need to regenerate and recompile Java code each time the project changes.
Right-click the project in the Navigator pane and choose Export > Deployment XML from the pop-up menu.
You can also click the Export to Deployment XML button
 or choose File > Export > Generate Deployment XML or Selected > Export > Generate Deployment XML from the menu.
or choose File > Export > Generate Deployment XML or Selected > Export > Generate Deployment XML from the menu.
If you have not defined deployment and source code generation defaults (see "Working with Project Options") the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench prompts for a filename and directory.
Use this procedure to create Java source code to generate database tables.
Right-click the project in the Navigator pane and choose Export > Export Table Creator Java Source from the pop-up menu.
You can also choose File > Export > Table Creator Java Source or Selected > Export > Table Creator Java Source from the menu.
If you have not defined deployment and source code generation defaults (see "Working with Project Options") the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench prompts for a class name and root directory.
Use this procedure to generate the project model's Java source.
Right-click the project, package, or specific descriptor in the Navigator pane and choose Export > Export Java Model Source from the pop-up menu. The OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench creates a .java file for each selected descriptor.
You can also choose File > Export > Export Java Model Source or Selected > Export > Java Model Source from the menu.
If you have not defined deployment and source code generation defaults (see "Working with Project Options") the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench prompts for a root directory.
|
Note: If your OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project uses UTF-8 character set, you must use a compatible JDK when compiling the exported Java source. |
For OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench projects that use EJB 2.0 CMP persistence, use the ejb-jar.xml file to store persistence information for the application server. With the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench, you can import information from an existing ejb-jar.xml file into your project, or you can create/update the ejb-jar.xml from your project.
Each OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project uses a single ejb-jar.xml file. For each entity from the file, you should have an EJB descriptor in the project. All entities must use the same persistence type.
As you make changes in your project, you can update the ejb-jar.xml file to reflect your project. Additionally, if you edit the ejb-jar.xml file outside the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench, you can update your project to reflect the current file.
Table 2-1 describes how fields in the ejb-jar.xml file correspond to specific functions in the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench:
| ejb-jar.xml | OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench |
|---|---|
|
|
Bean attribute mapped to the primary key in the database table (see "Setting Descriptor Information") |
|
|
EJB descriptor information on the EJB Info tab (see "Displaying EJB descriptor Information") |
|
|
Descriptor Alias field on the Name Queries tab (see "Named Queries") |
|
|
Nonrelational attributes on the Descriptor Info tab (see "Setting Descriptor Information") |
|
|
Persistence Type field on the General tab (see "Working with General Project Properties") The persistence-type is set to container. |
|
|
Queries listed in Queries tab (see "Specifying Queries and Named Finders") Note: The findByPrimaryKey query is not in the ejb-jar.xml file, as per the EJB 2.0 specification. |
|
|
One-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many mappings (see "Working with Relationship Mappings") |
Use this procedure to update the ejb-jar.xml file, based on the current OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench information. Use the EJB preferences to specify whether the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench automatically updates the ejb-jar.xml file when you save the project.
|
Note:
You can also write the information to a |
Choose Selected > Write Project to ejb-jar.xml from the menu. You can also right-click the project in the Navigator pane and choose Write Project to ejb-jar.xml from the pop-up menu.
ejb-jar.xml, the system prompts you to create a new file.
ejb-jar.xml file but not yet read into the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench (for example, you changed the file outside the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench), then the system prompts you to read the file before writing the changes.
Use this procedure to read the ejb-jar.xml information and update your OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench project.
|
Tip:
To automatically create EJB descriptors in the OracleAS TopLink Mapping Workbench for all entities, read the |
Choose Selected > Update Project from ejb-jar.xml from the menu. You can also right-click the project in the Navigator pane and choose Update Project from ejb-jar.xml from the pop-up menu.
|
|
 Copyright © 1997, 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|