| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5.0) Part Number E14500-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5.0) Part Number E14500-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter explains how you can patch Oracle Database. In particular, this chapter covers the following:
This section helps you get started with this chapter by providing an overview of the steps involved in patching Oracle Database. Consider this section to be a documentation map to understand the sequence of actions you must perform to successfully patch Oracle Database. Click the reference links provided against the steps to reach the relevant sections that provide more information.
Table 15-1 Getting Started with Patching Oracle Database
| Step | Description | Reference Links |
|---|---|---|
 |
Understanding the Deployment Procedure Understand the Deployment Procedure that is offered by Enterprise Manager Grid Control for patching Oracle Database. Know how the Deployment Procedure functions, what use cases it covers, and so on. |
To learn about the Deployment Procedure, see Deployment Procedures. |
 |
Knowing About the Supported Releases Know what releases of Oracle Database can be patched by the Deployment Procedure. |
To learn about the releases supported by the Deployment Procedure, see Supported Releases. |
 |
Selecting the Patching Mode Identify whether the host that runs Enterprise Manager Grid Control has an Internet connection to connect to My Oracle Support. If it has, then choose to patch in online mode. Otherwise, choose to patch in offline mode. |
|
 |
Understanding the Deployment Phases The Deployment Procedure consists of a series of interview screens that take you through the different deployment phases and capture the required information. Understand the different phases involved and know what information is captured in each phase. |
|
 |
Meeting the Prerequisites Before you run any Deployment Procedure, you must meet the prerequisites, such as setting up of the environment for online or offline patching, applying mandatory patches, setting up of Oracle Software Library, and so on. |
|
 |
Running the Deployment Procedure Run the Deployment Procedure to successfully patch Oracle Database. |
|
Enterprise Manager Grid Control offers the following Deployment Procedures for patching Oracle Database:
Patch Oracle Database
Note:
If the Oracle home of the database you are patching also has an ASM installed, then the Deployment Procedure patches only the database instance, but appropriately shuts down the ASM instance before patching the database and restarts it after the operation is complete.
The Deployment Procedure leaves several .log and .lst files per database instance in the Oracle home of the database being patched. For example, with a databases named UPGRD1, the following files will be left in the oracle home after patching:
-rw-r----- 1 oraets92 oinstall 0 Mar 27 12:19 UPGRD1_is_running.lst-rw-r----- 1 oraets92 oinstall 86 Mar 27 12:18 UPGRD1_shutdown.log-rw-r----- 1 oraets92 oinstall 401 Mar 27 12:19 UPGRD1_shutdown.lst
You cannot avoid the creation of these log files. If you want to delete them, you can either navigate to the Oracle home directory and manually delete them or customize the Deployment Procedure to include a step to automatically delete them.
Using this Deployment Procedure, you can patch the following releases of Oracle Database:
Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1.x.x)
Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2.x.x)
Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1.x.x)
This section describes how you can patch a standalone Oracle Database in online mode, that is, by connecting to My Oracle Support. This option is best suited when you have an Internet connection on the host where Enterprise Manager Grid Control is running.
This section covers the following:
The following describes the different phases involved in this Deployment Procedure:
Table 15-2 Deployment Phases Involved in Patching Oracle Database in Online Mode
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Software Updates Allows you to select the software updates (patches and patch sets) you want to apply, upgrade OPatch, black out associated targets, apply SQL script, and run OPatch options. |
 |
Target List Allows you to select the database targets you want to patch. |
 |
Oracle Configuration Manager Allows you to configure Oracle Configuration Manager so that security updates can be sent. |
 |
Credentials Allows you to specify Oracle home credentials required to patch database Oracle homes, and host credentials to access the hosts where the database are present. |
 |
Schedule Allows you to schedule the Deployment Procedure to run immediately or later. |
 |
Review Allows you to review the details you have provided for patching the selected databases. |
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the following prerequisites:
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in the following sections:
Ensure that you run the patchability report to understand whether the Oracle Database you want to patch is suitable for this patching operation. In the report, if the Oracle Database you want to patch appears as a target that cannot be patched, then resolve the conflicts to make it a target that can be patched. For more information about the patchability report, and to understand how you can diagnose the issues with an Oracle Database target and take corrective actions, see Appendix H, "About Patching Automation Reports".
Ensure that you run the prerequisite checker Deployment Procedure as described in Running Patch Prerequisite Checker for Standalone Database.
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has the privileges to run the Deployment Procedure and its commands on the target hosts. If you do not have the privileges to do so, that is, if you are using a locked account, then request your administrator (a designer) to either customize the Deployment Procedure to run it as another user or ignore the steps that require special privileges. For information about customization, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
To patch a standalone Oracle Database, follow these steps:
In Grid Control, click the Deployments tab.
On the Deployments page, in the Deployment Procedure Manager section, click Patch Procedures.
On the Deployment Procedure Manager page, in the Procedures subtab, from the table, select Patch Oracle Database. Then click Schedule Deployment.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Software Updates page of the Deployment Procedure.
On the Software Updates page, do the following:
In the Select Stage Location section, retain the default selection, that is, Enter Stage Location that has the value %emd_root%/EMStage.
This default value refers to a location on the target host where the database to be patched is running. The software updates are downloaded from My Oracle Support to Oracle Software Library, and then staged in this location on the target hosts.
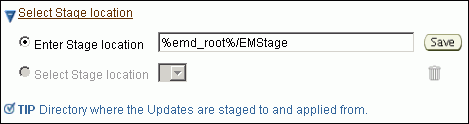
You can modify the location if you want to, and click Save. If you save multiple custom locations, then the Select Stage Location option gets enabled and allows you to select any of the saved custom locations the next time you visit the same page.
Instead of %emd_root%, you can also specify %oracle_home% to indicate the current home location being patched or %perlbin% to indicate the location of perl binary used by Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent).
In the Standalone Database Updates section, click Add to search and select software updates from My Oracle Support. Alternatively, if you have a text file that contains details about the patches, then click Upload From File to select and upload that text file.
On clicking Add, Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Search and Select Software Updates page. On this page, select Search My Oracle Support, specify the details of the patches you want to search, and click Go.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control connects to My Oracle Support, searches the patches, and displays details about them on the Search and Select Software Updates page. Select the ones you want to apply using the Deployment Procedure, and click Select.
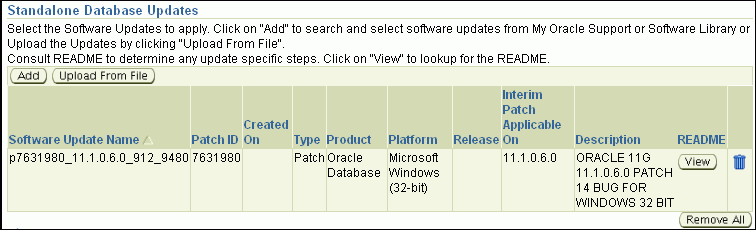
On clicking Upload From File, Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Upload File page. On this page, select Upload from Local Machine or Upload from Software Library depending on where the text file is available, click Browse to search and select that file, and then click Upload.
In the Upgrade OPatch section, retain the default selection so that the OPatch software on the target hosts are upgraded before the patches are applied on the database targets.

Enterprise Manager Grid Control uses OPatch software to apply the one-off patches. It is assumed that this software is already available on the target hosts managed by Oracle Management Agents (Management Agent), but Oracle recommends you to retain the selection so that the existing software is upgraded to the latest release.
In the Black Out Associated Targets section, retain the default selection so that all targets associated with the database to be patched are blacked out while the patching is in progress.

For example, if the Oracle Database to be patched is running in an Oracle home location where Oracle ASM is running, then before patching that Oracle Database, all associated targets such as Oracle Listener and Oracle ASM instances will be blacked out.
In the Apply SQL Script section, retain the default selection so that the default SQL script that is packaged with the patch is used for modifying the schemas.

If you want to run any custom script, then select Enter the script to apply SQL and specify the full path to the location where the custom script is available. For example, %oracle_home%/rdbms/admin/catupgrd.sql .
The variables you can use for the directory location are %emd_root% to indicate a location on the target host, %oracle_home% to indicate the current home location being patched, or %perlbin% to indicate the location of perl binary used by the Management Agent.
You have an option of running both the scripts by selecting both these options or one of the scripts by selecting only one of these options. If you select both these options, then both the scripts are run, that is, the default script runs first and then the custom script runs.
In the Advanced OPatch Options section, specify any opatch-related options you want to pass while running this Deployment Procedure. For example, if you want the Deployment Procedure to ignore duplicate patches, then specify -skip_duplicate.

The following are the options you can specify:
-skip_duplicate, skips duplicate patches
-skip_conflict, skips conflicting patches
-skip_missing_component, skips patches whose components are missing
-invPtrLoc, the location of oraInst.loc file
Note:
If you want to specify multiple options, then separate the list with a white space. For example,-skip_duplicate -skip_conflictClick Next.
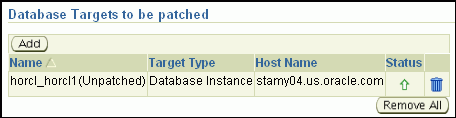
On the Target List page, in the Database Targets to be Patched section, click Add to add the database targets you want to patch. Then click Next.
On the Oracle Configuration Manager page, do the following:
If the host where the database is being patched has a direct connection to the Internet, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password.
An e-mail address is required so that security updates and install updates can be sent. You can specify any e-mail address, but Oracle recommends you to specify the My Oracle Support user name. For example, john.mathew@xyz.com.
If the My Oracle Support password is incorrect, you will be allowed two more attempts. However, if your password is incorrect in all three attempts or if it is left blank, then you are registered anonymously, which means, the configuration information will be collected and uploaded to My Oracle Support but the uploaded information will not be associated with your My Oracle Support account. Therefore, if you log in to My Oracle Support with your credentials, you will not see this information displayed against your account. However, if you had specified an e-mail address, then you will continue to receive security updates and other notifications from Oracle to that e-mail address.
If the host where the database is being patched has an indirect connection to the Internet through a proxy server, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password, and then in the Connection Details section, specify the proxy server details.
Note:
You can change the proxy server settings any time after the Deployment Procedure ends. To do so, run theconfigCCR command from the /ccr/bin/ directory within the Oracle home directory of the provisioned database.If the host where the database is being patched does not have a direct or indirect connection to the Internet, then specify the e-mail address and leave the other fields blank.
In this case, after you complete the installation process, manually collect the configuration information and upload it to My Oracle Support. To understand how the configuration information can be manually collected and uploaded, see the steps outlined in Manually Collecting and Uploading Configuration Information to My Oracle Support.
On the Credentials page, in the Home Credentials section, specify the Oracle home credentials required to patch database Oracle homes, and in the Host Credentials section, specify the operating system credentials to log in to the hosts where the databases are present. Then click Next.
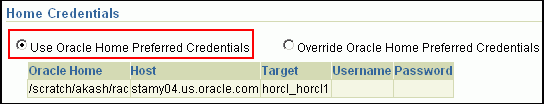
Note:
When there are Oracle home active steps, the Home Credentials section appears. When there are host-level active steps, the Host Credentials section appears. When Oracle home active steps and host-level active steps are present, both the sections appear.For both sections, choose to use the preferred credentials so that the credentials stored in the Management Repository can be used.
Of course, you can always override the preferred credentials with a new set of credentials. If you choose to do so, you can specify either a common set of credentials to be used across Oracle homes and hosts, or a unique set of credentials for each Oracle home and host.
After specifying a new set of credentials to override the preferred credentials, click Save OH Credential if you want to store the new credentials in the Management Repository.
On the Schedule page, schedule the Deployment Procedure to run either immediately or later.
For Instance Name, specify a unique name for this Deployment Procedure instance so that it can be tracked later and reused with the same settings.
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for patching the selected databases, and click Deploy.
Note:
If you have not applied the one-off patch as described in Applying One-Off Patch to Introduce Analyze Mode and Reports, then the Deploy button on the Review page appears as Submit.This section describes how you can patch a standalone Oracle Database in offline mode, that is, without connecting to My Oracle Support. This option is best suited when you do not have an Internet connection on the host where Enterprise Manager Grid Control is running.
This section covers the following:
The following describes the different phases involved in this Deployment Procedure:
Table 15-3 Deployment Phases Involved in Patching Oracle Database in Offline Mode
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Software Updates Allows you to select the software updates (patches and patch sets) you want to apply, upgrade OPatch, black out associated targets, apply SQL script, and run OPatch options. |
 |
Target List Allows you to select the database targets you want to patch. |
 |
Credentials Allows you to specify Oracle home credentials required to patch database Oracle homes, and host credentials to access the hosts where the database are present. |
 |
Schedule Allows you to schedule the Deployment Procedure to run immediately or later. |
 |
Review Allows you to review the details you have provided for patching the selected databases. |
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the following prerequisites:
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in the following sections:
Ensure that you run the patchability report to understand whether the Oracle Database you want to patch is suitable for this patching operation. In the report, if the Oracle Database you want to patch appears as a target that cannot be patched, then resolve the conflicts to make it a target that can be patched. For more information about the patchability report, and to understand how you can diagnose the issues with an Oracle Database target and take corrective actions, see Appendix H, "About Patching Automation Reports".
Ensure that you run the prerequisite checker Deployment Procedure as described in Running Patch Prerequisite Checker for Standalone Database.
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has the privileges to run the Deployment Procedure and its commands on the target hosts. If you do not have the privileges to do so, that is, if you are using a locked account, then request your administrator (a designer) to either customize the Deployment Procedure to run it as another user or ignore the steps that require special privileges. For information about customization, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
To patch a standalone Oracle Database, follow these steps:
In Grid Control, click the Deployments tab.
On the Deployments page, in the Deployment Procedure Manager section, click Patch Procedures.
On the Deployment Procedure Manager page, in the Procedures subtab, from the table, select Patch Oracle Database. Then click Schedule Deployment.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Software Updates page of the Deployment Procedure.
On the Software Updates page, do the following:
In the Select Stage Location section, retain the default selection, that is, Enter Stage Location that has the value %emd_root%/EMStage.
This default value refers to a location on the target host where the database to be patched is running. The software updates are downloaded from My Oracle Support to Oracle Software Library, and then staged in this location on the target hosts.

You can modify the location if you want to, and click Save. If you save multiple custom locations, then the Select Stage Location option gets enabled and allows you to select any of the saved custom locations the next time you visit the same page.
Instead of %emd_root%, you can also specify %oracle_home% to indicate the current home location being patched or %perlbin% to indicate the location of perl binary used by Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent).
In the Standalone Database Updates section, click Add to search and select software updates from Oracle Software Library (Software Library). Alternatively, if you have a text file that contains details about the patches, then click Upload From File to select and upload that text file.
On clicking Add, Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Search and Select Software Updates page. On this page, select Search Software Library, specify the details of the patches you want to search, and click Go.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control searches the patches in the Software Library, and displays details about them on the Search and Select Software Updates page. Select the ones you want to apply using the Deployment Procedure, and click Select.
On clicking Upload From File, Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Upload File page. On this page, select Upload from Local Machine or Upload from Software Library depending on where the text file is available, click Browse to search and select that file, and then click Upload.
In the Upgrade OPatch section, retain the default selection so that the OPatch software on the target hosts are upgraded before the patches are applied on the database targets.

Enterprise Manager Grid Control uses OPatch software to apply the one-off patches. It is assumed that this software is already available on the target hosts managed by Oracle Management Agents (Management Agent), but Oracle recommends you to retain the selection so that the existing software is upgraded to the latest release.
In the Black Out Associated Targets section, retain the default selection so that all targets associated with the database to be patched are blacked out while the patching is in progress.

For example, if the Oracle Database to be patched is running in an Oracle home location where Oracle ASM is running, then before patching that Oracle Database, all associated targets such as Oracle Listener and Oracle ASM instances will be blacked out.
In the Apply SQL Script section, retain the default selection so that the default SQL script that is packaged with the patch is used for modifying the schemas.

If you want to run any custom script, then select Enter the script to apply SQL and specify the full path to the location where the custom script is available. For example, %oracle_home%/rdbms/admin/catupgrd.sql .
The variables you can use for the directory location are %emd_root% to indicate a location on the target host, %oracle_home% to indicate the current home location being patched, or %perlbin% to indicate the location of perl binary used by the Management Agent.
You have an option of running both the scripts by selecting both these options or one of the scripts by selecting only one of these options. If you select both these options, then both the scripts are run, that is, the default script runs first and then the custom script runs.
In the Advanced OPatch Options section, specify any opatch-related options you want to pass while running this Deployment Procedure. For example, if you want the Deployment Procedure to ignore duplicate patches, then specify -skip_duplicate.

The following are the options you can specify:
-skip_duplicate, skips duplicate patches
-skip_conflict, skips conflicting patches
-skip_missing_component, skips patches whose components are missing
-invPtrLoc, the location of oraInst.loc file
Note:
If you want to specify multiple options, then separate the list with a white space. For example,-skip_duplicate -skip_conflictClick Next.
On the Target List page, in the Database Targets to be Patched section, click Add to add the database targets you want to patch. Then click Next
On the Oracle Configuration Manager page, click Next.
On the Credentials page, in the Home Credentials section, specify the Oracle home credentials required to patch database Oracle homes, and in the Host Credentials section, specify the operating system credentials to log in to the hosts where the databases are present. Then click Next.

Note:
When there are Oracle home active steps, the Home Credentials section appears. When there are host-level active steps, the Host Credentials section appears. When Oracle home active steps and host-level active steps are present, both the sections appear.For both sections, choose to use the preferred credentials so that the credentials stored in the Management Repository can be used.
Of course, you can always override the preferred credentials with a new set of credentials. If you choose to do so, you can specify either a common set of credentials to be used across Oracle homes and hosts, or a unique set of credentials for each Oracle home and host.
After specifying a new set of credentials to override the preferred credentials, click Save OH Credential if you want to store the new credentials in the Management Repository.
On the Schedule page, schedule the Deployment Procedure to run either immediately or later.
For Instance Name, specify a unique name for this Deployment Procedure instance so that it can be tracked later and reused with the same settings.
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for patching the selected databases, and click Deploy.
Note:
If you have not applied the one-off patch as described in Applying One-Off Patch to Introduce Analyze Mode and Reports, then the Deploy button on the Review page appears as Submit.