| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5.0) Part Number E14500-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5.0) Part Number E14500-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter explains how you can provision Oracle RAC. In particular, this chapter covers the following:
This section helps you get started with this chapter by providing an overview of the steps involved in provisioning Oracle RAC. Consider this section to be a documentation map to understand the sequence of actions you mOracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patchingust perform to successfully provision Oracle RAC. Click the reference links provided against the steps to reach the relevant sections that provide more information.
Table 5-1 Getting Started with Provisioning Oracle RAC
| Step | Description | Reference Links |
|---|---|---|
 |
Understanding the Deployment Procedure Understand the Deployment Procedure that is offered by Enterprise Manager Grid Control for provisioning Oracle RAC. Know how the Deployment Procedure functions, what use cases it covers, what core components it deletes or scales down, and so on. |
To learn about the Deployment Procedure, see Deployment Procedures. To learn about the core components that are provisioned, see Core Components Deployed. |
 |
Knowing About The Supported Releases Know what releases of Oracle RAC can be provisioned by the Deployment Procedure. |
To learn about the releases supported by the Deployment Procedure, see Supported Releases. |
 |
Selecting the Use Case This chapter covers a few use cases for provisioning Oracle RAC. Select the use case that best matches your requirement. |
|
 |
Understanding the Deployment Phases The Deployment Procedure consists of a series of interview screens that take you through the different deployment phases and capture the required information. Understand the different phases involved and know what information is captured in each phase. |
|
 |
Meeting the Prerequisites Before you run any Deployment Procedure, you must meet the prerequisites, such as setting up of the provisioning environment, applying mandatory patches, setting up of Oracle Software Library. |
|
 |
Running the Deployment Procedure Run the Deployment Procedure to successfully provision Oracle RAC. |
|
Enterprise Manager Grid Control offers the following Deployment Procedures for provisioning Oracle RAC:
Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For UNIX
Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For Windows
Note:
When you run the Deployment Procedures to provisioning Oracle RAC on a shared file system, the software binaries are installed in the shared location, but the configuration happens only on one node and not on all nodes. This is an expected behavior. To configure other nodes, run the One Click Extend Cluster Database procedure to extend the Oracle RAC stack to other nodes.When you provision Oracle RAC, essentially, the Deployment Procedures deploy the following core components:
Oracle Clusterware
Oracle RAC Database
Optionally, Automatic Storage Management (ASM)
You can deploy ASM either in the same Oracle home as the one for Oracle RAC Database, or in a completely different Oracle home (recommended).
Using these Deployment Procedures, you can provision the following releases of Oracle RAC:
Oracle RAC Database 10g Release 2 (10.2.x.x)
Oracle RAC Database 11g Release 1 (11.1.x.x)
This section describes how you can clone an existing Oracle RAC installation that is running on a host monitored by Enterprise Manager Grid Control.
This section covers the following:
The following describes the different phases involved in this Deployment Procedure:
Table 5-2 Deployment Phases Involved in Cloning an Existing Oracle RAC
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Select Source Allows you to select an existing Oracle RAC installation that you want to clone. |
 |
Select Hosts Allows you to select the target hosts, which should form the cluster, and the network interfaces (public and private). |
 |
Credentials and Schedule Allows you to specify host credentials required for accessing the hosts where the existing Oracle RAC needs to be cloned, and schedule the Deployment Procedure to run immediately or later. |
 |
Configure Cluster Allows you to specify configuration values for the cluster, create new starter database, and enable backup and recovery options. |
 |
Storage Allows you to specify a partition name and mount location, and select a mount format and storage device for storing data. |
 |
Configuration Allows you to provide additional parameters for configuring the clusterware. |
 |
Oracle Configuration Manager Allows you to configure Oracle Configuration Manager so that security updates can be sent. |
 |
Review Allows you to review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC. |
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the following prerequisites.
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in the following sections:
If you want to clone Oracle RAC 11g Release 1 (11.1.0.6) on Solaris platforms, then apply patch# 6486988 on the Oracle home that needs to be cloned.
Ensure that the target hosts have the necessary hardware and software required for Oracle RAC. The hardware requirements include setting up of the following:
Private Network: The network interface cards must be installed on each node and connected to each other.
Shared Storage Between Nodes: The shared storage is required for OCR, Voting disks and the data files.
Ensure that the Virtual IPs are set up in the DNS. If you choose to set up the Virtual IPs locally, then the IP addresses can be specified using the Deployment Procedure, and the procedure will set them up for you.
If you want to use standard response files while provisioning the database, then edit the dbca.rsp file available on the installation medium, and store it in a location accessible from the target hosts. The file may be on the target host or on a shared location.
To understand how response files work, see the Oracle Database Installation Guide for Linux available at one of these URLs:
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db111/homepage
If you want to use a custom template to create a structure for the database, then create a template (a .dbt file), and store it in a location accessible from the target hosts. The file may be on the target host or on a shared location.
To understand how a template can be created and used for creating databases, see Appendix D, "Creating Templates for Oracle Database".
Ensure that operating system users such as oracle and crsuser are available on all nodes of the cluster. These users must be a part of the relevant operating system groups such as dba and oinstall.
For more information, see Oracle Clusterware Installation Guide available at:
Ensure that the User IDs for operating system users and the Group IDs for operating system groups are identical on all nodes of the cluster.
Ensure that you do NOT use an NIS-based operating system user.
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has the privileges to run the Deployment Procedure and its commands on the target hosts. If you do not have the privileges to do so, that is, if you are using a locked account, then request your administrator (a designer) to either customize the Deployment Procedure to run it as another user or ignore the steps that require special privileges. For information about customization, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has write permission on the staging areas used for placing software binaries of Oracle RAC database.
Deployment Procedures allow you to use staging locations for quick file-transfer of binaries and prevent high traffic over the network. While providing a staging location, ensure that the operating system user you use has write permission on those staging locations. For information about staging area, see Staging Area.
Compare the configuration of the source and target hosts and ensure that they have the same configuration. If the configurations are different, then contact your system administrator and fix the inconsistencies before running the Deployment Procedure.
To compare the configuration of the hosts, in Grid Control, click Targets and then Hosts. On the Hosts page, click the name of the source host to access its Home page, and then click the Configuration tab. On the Configuration page, click Compare Configuration and select the target host.
While selecting the source, remember to remove sqlnet.ora from the list of files mentioned in Files to Exclude.
Ensure that the umask value on the target host is 022.
To clone an existing Oracle RAC installation, follow these steps:
In Grid Control, click the Deployments tab.
On the Deployments page, in the Deployment Procedure Manager section, click RAC Provisioning Procedures.
On the Deployment Procedure Manager page, in the Procedure subtab, from the table, select one of the following, and click Schedule Deployment.
To run the Deployment Procedure on UNIX platforms, Select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For UNIX.
To run the Deployment Procedure on Microsoft Windows platforms, select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For Windows.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Select Source page of the Deployment Procedure.
On the Select Source page, do the following:
In the Select Source section, select Select from Existing Installations. Then click the torch icon for Reference Host and select the host on which the existing Oracle RAC installation is running. Once you select the reference host, the application automatically displays the working directory and the details of the selected Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Database.
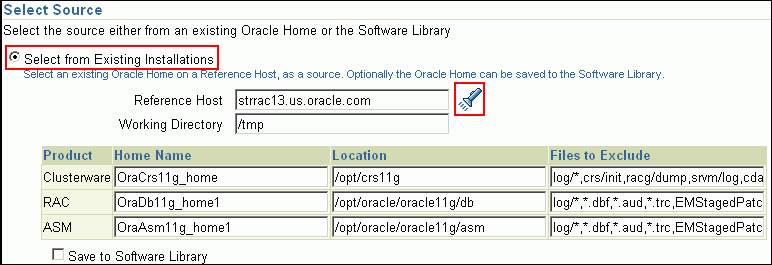
If you want to save the selected Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Database as gold images in the Software Library, then click Save to Software Library. Oracle Clusterware is saved as a Clusterware Clone component type and Oracle Database is stored as a Database Clone component type, respectively.
Note:
Maintain different locations as working directories in case a shared disk is used between the source host and the destination host.
Remove sqlnet.ora from the list of files mentioned in Files to Exclude. If you do not remove it, the Oracle RAC database configuration will fail.
Click Next.
On the Select Hosts page, do the following:
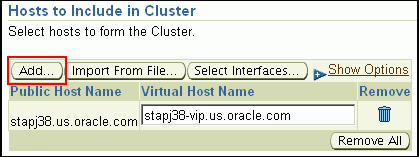
In the Hosts to Include in Cluster section, click Add and select the target hosts that should form the cluster. To see more details about the selected hosts, click Show Options.
Note:
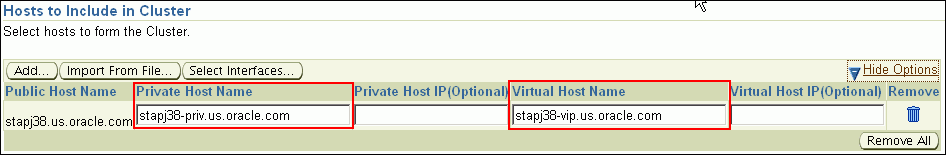
When you click Add, the Select Target pop-up window appears. On this page, by default, the Show Suitable Hosts option is selected and the table lists only those hosts that are best suited for provisioning. If you do not find the host you want to add, then select Show All Hosts to view a complete list of hosts.By default, Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are automatically prefilled with values. Edit them and specify values that match with your environment. Optionally, you can also specify their IP addresses.
Note:
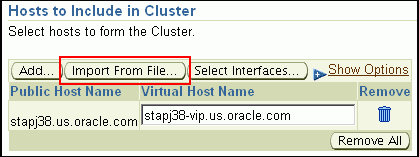
If the prefilled, default values of Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are incorrect, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".If you already have these details stored in cluster configuration file, then click Import From File to select that cluster configuration file. This file typically contains information about the new hosts to be added. To understand how a cluster configuration file looks, see the sample file shown in Sample Cluster Configuration File.
To configure the private and public network interfaces, click Select Interfaces. By default, the interfaces that have the same name and subnet for the selected target hosts are displayed. However, you can also choose to view all the interfaces for the selected target hosts. You can either select one of the existing interfaces or specify a completely new one if the interface you want to use does not exist.
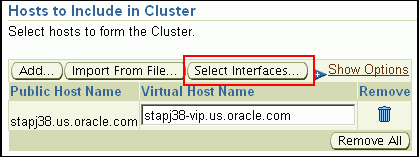
In the Network Interface Configuration section, review the details of the private and public interfaces.
Click Next.
On the Credentials/Schedule page, do the following:
In the Reference Host Credentials section, retain the default selection, that is, Use Preferred Credentials.
Note:
You can optionally override these preferred credentials. The credentials you specify here are used by the Deployment Procedure to run the provisioning operation. If this environment is secure and has locked accounts, then make sure that:The credentials you specify here have the necessary privileges to switch to the locked account for performing the provisioning operation.
The Deployment Procedures has been customized to support locked environments.
For more information, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
From the Host Credentials list, select Different for each Oracle Home if you want to use different operating system credentials for each Oracle home, or Same for all Oracle Homes if you want to use the same set of credentials for all Oracle homes. Depending on the selection you make, specify the credentials. Ensure that the users belong to the same group (dba/oinstall).
In the Target Host(s) Credentials section, provide the credentials as described in Step 6 (a).
Note:
If you are using vendor clusterware, then ensure thatroot and the operating system users, such as oracle and crsuser, owning the clusterware and various Oracle homes are a part of the operating system groups required by the vendor clusterware.
For example, if your system uses High Availability Cluster Multiprocessing (HACMP) clusterware, then create or check for the existence of the group hagsuser. Ensure that the relevant operating system users and root user are members of this group.
For more information, refer to the Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation and Configuration Guide.
In the Schedule section, schedule the Deployment Procedure to run either immediately or later.
Click Next.
On the Configure Cluster page, do the following:
In the Cluster Name and Location section, review the default name and location details provided for Oracle Clusterware and Oracle RAC Database. While Oracle recommends you to retain the default values, you can always edit them to provide custom values.
For security purposes, the clusterware configuration sets the ownership of Oracle Clusterware home and all its parent directories to be owned by root. Hence, Oracle recommends you to install Oracle Clusterware outside the Oracle base of the Oracle RAC home.
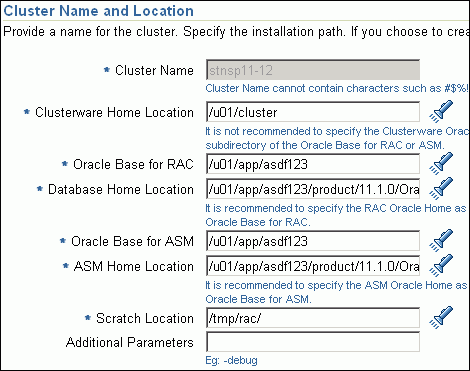
The default cluster name you see here is based on the host cluster name you provided in the Agent Deploy application in Enterprise Manager Grid Control, while deploying Management Agents on a cluster. The scratch location you see here is a temporary location on the target host where temporary files are placed before provisioning and configuring Oracle RAC.
For Additional Parameters, specify any additional parameters you want to run while installing Oracle Clusterware. For example, -debug.
You can specify any Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) parameter that can be used in this provisioning operation. Using these parameters, you can even change the installation type of the database. For example, INSTALL_TYPE=SE. Ensure that the parameters are separated by white space.
Note:
If you do not see a default cluster name in the Cluster Name field, then you might have selected nodes that are not master nodes of the cluster. In this case, manually specify a cluster name, but ensure that the name you specify is the same host cluster name you provided in the Agent Deploy application in Enterprise Manager Grid Control, while deploying Management Agents on that cluster.
If this entire section (Cluster Name and Location section) is disabled, then it is clear that each node has a Management Agent, but they were NOT installed using the Cluster Install option available in the Agent Deploy application. To resolve this issue, ensure that you convert the standalone Management Agents to a cluster agent. For more information, see Appendix I, "Converting Standalone Oracle Management Agent to Cluster Agent".
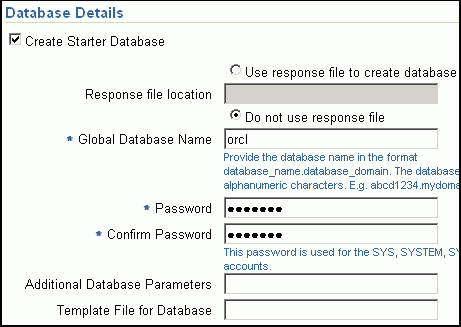
In the Database Details section, retain the default selection for creating a starter database.
Note:
If the database creation steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this section.If you want to create a general-purpose database, then leave all the fields in this section blank. Otherwise, provide the required details as described in this step.
If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be available on the target host, in a shared location accessible from the target host, in the Software Library, or in a location where an existing database is running.
Note:
From the Software Library or from the location where an existing database is running, only a.dbt template file can be used. However, from the target host or a shared location, any template file can be used.If you do not have a custom response file, then select Do not use response file, and provide the global database name, the credentials, and the additional parameters you want to run while creating the starter database.
Note:
Ensure that the database name you specify is in the format database_name.database_domain. It must have 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters. For example, orcl.mydomain.com. Also note that the credentials you provide are used for SYS, SYSTEM, SYSMAN, and DBSNMP accounts.If you want to use the structure of an existing database and have a custom template to structure the new database, then in Template File for Database, specify the full path to a location where the template file is available. The file may be available on the target host or on a shared location accessible from the target host.
Note:
If you do not store the response files and templates in a central location, you can always customize the Deployment Procedure to add another step that copies the response file or template to the target host before invoking the configuration tools to create the database.In the Backup and Recovery Details section, retain the default selection, that is, Do not Enable Automated Backups if you do not want to have backups taken.
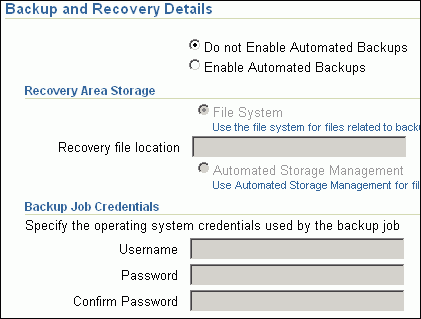
Alternatively, if you want to enable automated backups, select Enable Automated Backups, specify the full path to a directory location from where the backed-up files can be recovered, and provide the operating system credentials for running the backup job. Note that recovery location is the same location as the backup location because this where the files are backed up and also recovered from.
In the ASM Instance Details section (appears only if you had selected to deploy ASM), retain the default selection, that is, Create ASM Instance, and specify the credentials, additional ASM parameters to be used, and the ASM disk string to be used.
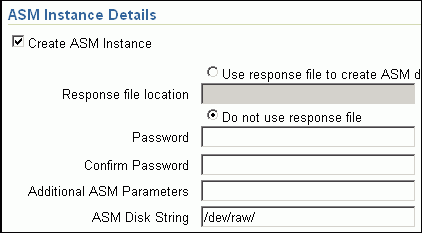
Important:
If you are provisioning Oracle Database 10g and Oracle ASM 10g, then ensure that you specify the same password for database as well as ASM.If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create ASM database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be availableon the target host or on a shared location accessible fromt he target hosts.
If you do not want to use a response file, then select Do not use response file.
Click Next.
On the Storage page, do the following:
In the Shared Storage Configuration section, provide details about the storage devices and click Next. Specify the partition name and the mount location, and select the mount format and a storage device for storing data. While partition name is the path to the location where the device is installed, mount location is the mount point that represents the partition location.
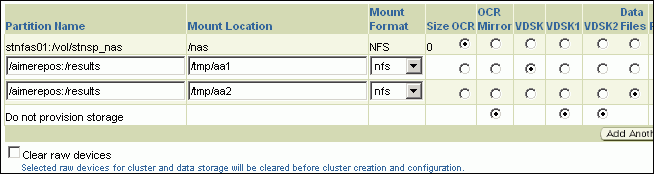
While configuring the storage device, at a minimum, you must have a partition for at least OCR, Voting Disk, and data files. You cannot designate the same storage device to multiple partitions.
Oracle recommends designating the OCR and the OCR Mirror devices to different partitions. Similarly, Oracle recommends designating the Voting Disk, Voting Disk1, and Voting Disk2 to different partitions.
Before clicking Next, do the following:
- If you want to clear the data on selected raw devices before creating and configuring the cluster, then select Clear raw devices.
- If you have configured only for a few storage devices, then select Do not provision storage for others that you do not want to provision.
- Specify the ASM disk string to be used.
In the Options section, select the ASM redundancy mode. The default is None, which requires 7 GB of space. While Normal requires 16 GB of space, High requires 32 GB.
(Optional) On the Advanced Configuration page, do the following:
Note:
If the configuration steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this page.In the Bonding Interface (Private Interconnect) section, select Configure Bonding Interface if you want to configure the bonding interface. To bind the interfaces, specify details as described in Table 5-5.
In the Sysctl File Configuration section, select Configure Sysctl file if you want to configure the sysctl.conf file. Specify the mode of editing the system configuration file and the location of the reference system configuration file used for modifying the kernel parameters.
The default mode is append. You can however select edit to modify, and replace to replace the current sysctl.conf file.
Ensure that the reference file you specify is available in a shared location accessible by the Oracle Management Service.
On the Configure Oracle Home page, do the following:
If the host where the database is being provisioned has a direct connection to the Internet, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password.
An e-mail address is required so that security updates and install updates can be sent. You can specify any e-mail address, but Oracle recommends you to specify the My Oracle Support user name. For example, john.mathew@xyz.com.
If the My Oracle Support password is incorrect, you will be allowed two more attempts. However, if your password is incorrect in all three attempts or if it is left blank, then you are registered anonymously, which means, the configuration information will be collected and uploaded to My Oracle Support but the uploaded information will not be associated with your My Oracle Support account. Therefore, if you log in to My Oracle Support with your credentials, you will not see this information displayed against your account. However, if you had specified an e-mail address, then you will continue to receive security updates and other notifications from Oracle to that e-mail address.
If the host where the database is being provisioned has an indirect connection to the Internet through a proxy server, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password, and then in the Connection Details section, specify the proxy server details.
Note:
You can change the proxy server settings any time after the Deployment Procedure ends. To do so, run theconfigCCR command from the /ccr/bin/ directory within the Oracle home directory of the provisioned database.If the host where the database is being provisioned does not have a direct or indirect connection to the Internet, then specify the e-mail address and leave the other fields blank.
In this case, after you complete the installation process, manually collect the configuration information and upload it to My Oracle Support. To understand how the configuration information can be manually collected and uploaded, see the steps outlined in Manually Collecting and Uploading Configuration Information to My Oracle Support.
Click Next.
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC, and click Submit. If the details you provided seem to be missing on this page, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".
After the Deployment Procedure ends successfully, instrument the database to collect configuration information. For information about instrumenting the database, see Instrumenting the Database for Configuration Collections.
This section describes how you can provision a gold image of Oracle RAC.
Note:
Ensure that you use a gold image that was created using the Oracle home directory of a RAC database. You cannot use a gold image that was created using the Oracle home directory of a standalone database.This section covers the following:
The following describes the different phases involved in this Deployment Procedure:
Table 5-3 Deployment Phases for Provisioning Gold Image of Oracle RAC
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Select Source Allows you to select the gold image of Oracle Clusterware, Oracle RAC, and ASM (optional). |
 |
Select Hosts Allows you to select the target hosts, which should form the cluster, and the network interfaces (public and private). |
 |
Credentials and Schedule Allows you to specify host credentials required for accessing the hosts where the gold image needs to be provisioned, and schedule the Deployment Procedure to run immediately or later. |
 |
Configure Cluster Allows you to specify configuration values for the cluster, create new starter database, and enable backup and recovery options. |
 |
Storage Allows you to specify a partition name and mount location, and select a mount format and storage device for storing data. |
 |
Configuration Allows you to provide additional parameters for configuring the clusterware. |
 |
Oracle Configuration Manager Allows you to configure Oracle Configuration Manager so that security updates can be sent. |
 |
Review Allows you to review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC. |
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the following prerequisites.
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in the following sections:
Ensure that you create gold images of existing Oracle RAC database and Oracle Clusterware.
To understand how you can create a gold image, see Creating Gold Image.
Ensure that the target hosts have the necessary hardware and software required for Oracle RAC. The hardware requirements include setting up of the following:
Private Network: The network interface cards must be installed on each node and connected to each other.
Shared Storage Between Nodes: The shared storage is required for OCR, Voting disks and the data files.
Ensure that the Virtual IPs are set up in the DNS. If you choose to set up the Virtual IPs locally, then the IP addresses can be specified using the Deployment Procedure, and the procedure will set them up for you.
If you want to use standard response files while provisioning the database, then edit the dbca.rsp file available on the installation medium, and store it in the Software Library.
To understand how response files work, see the Oracle Database Installation Guide for Linux available at one of these URLs:
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db111/homepage
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db102/homepage
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db10g/portal.portal_demo3
To understand how you can upload the response file to the Software Library, see Uploading Database Response File to Oracle Software Library.
If you want to use a custom template to create a structure for the database, then create a template (a .dbt file), and store it in the Software Library.
To understand how a template can be created and used for creating databases, see Appendix D, "Creating Templates for Oracle Database".
To understand how you can upload the template to the Software Library, see Uploading Database Template File to Oracle Software Library.
Ensure that operating system users such as oracle and crsuser are available on all nodes of the cluster. These users must be a part of the relevant operating system groups such as dba and oinstall.
For more information, see Oracle Clusterware Installation Guide available at:
Ensure that the User IDs for operating system users and the Group IDs for operating system groups are identical on all nodes of the cluster.
Ensure that you do NOT use an NIS-based operating system user.
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has the privileges to run the Deployment Procedure and its commands on the target hosts. If you do not have the privileges to do so, that is, if you are using a locked account, then request your administrator (a designer) to either customize the Deployment Procedure to run it as another user or ignore the steps that require special privileges. For information about customization, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has write permission on the staging areas used for placing software binaries of Oracle RAC database.
Deployment Procedures allow you to use staging locations for quick file-transfer of binaries and prevent high traffic over the network. While providing a staging location, ensure that the operating system user you use has write permission on those staging locations. For information about staging area, see Staging Area.
While selecting the source, remember to remove sqlnet.ora from the list of files mentioned in Files to Exclude.
Ensure that the umask value on the target host is 022.
To provision a gold image of an Oracle RAC installation, follow these steps:
In Grid Control, click theDeployments tab.
On the Deployments page, in the Deployment Procedure Manager section, click RAC Provisioning Procedures.
On the Deployment Procedure Manager page, in the Procedure subtab, from the table, select one of the following, and click Schedule Deployment.
To run the Deployment Procedure on UNIX platforms, Select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For UNIX.
To run the Deployment Procedure on Microsoft Windows platforms, select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For Windows.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Select Source page of the Deployment Procedure.
On the Select Source page, do the following:
In the Select Source section, select Select from Software Library.
In the Source for Clusterware section, click the torch icon and select the generic component that has the gold image of Oracle Clusterware. Ensure that you select only components that are in "Ready" status. Once you select the component name, the application automatically displays the component location.
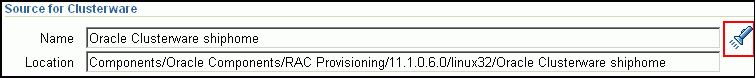
Note:
If you do not see the required component in the Software Library, then follow the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".In the Source for RAC section, click the torch icon and select the generic component that has the gold image of Oracle Database. Ensure that you select only components that are in "Ready" status. Once you select the component name, the application automatically displays the component location.
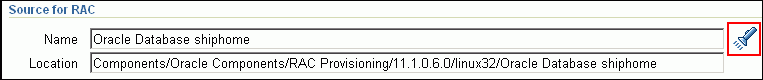
Note:
If you do not see the required component in the Software Library, then follow the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".(Optional) In the Source for ASM section, do one of the following:
If you do not want to deploy ASM, then retain the default selection, that is, Do not Provision ASM.
If you want to deploy ASM in the same Oracle home as the Oracle RAC, then select Use the same source as the RAC home. Alternatively, if you can select Choose a component and upload an ASM component from the Software Library.

Click Next.
On the Select Hosts page, do the following:
In the Hosts to Include in Cluster section, click Add and select the target hosts that should form the cluster. To see more details about the selected hosts, click Show Options.

Note:
When you click Add, the Select Target pop-up window appears. On this page, by default, the Show Suitable Hosts option is selected and the table lists only those hosts that are best suited for provisioning. If you do not find the host you want to add, then select Show All Hosts to view a complete list of hosts.By default, Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are automatically prefilled with values. Edit them and specify values that match with your environment. Optionally, you can also specify their IP addresses.

Note:
If the prefilled, default values of Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are incorrect, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".If you already have these details stored in cluster configuration file, then click Import From File to select that cluster configuration file. This file typically contains information about the new hosts to be added. To understand how a cluster configuration file looks, see the sample file shown in Sample Cluster Configuration File.

To configure the private and public network interfaces, click Select Interfaces. By default, the interfaces that have the same name and subnet for the selected target hosts are displayed. However, you can also choose to view all the interfaces for the selected target hosts. You can either select one of the existing interfaces or specify a completely new one if the interface you want to use does not exist.

In the Network Interface Configuration section, review the details of the private and public interfaces.
Click Next.
On the Credentials/Schedule page, do the following:
In the Target Host(s) Credentials section, retain the default selection, that is, Use Preferred Credentials.
Note:
You can optionally override these preferred credentials. The credentials you specify here are used by the Deployment Procedure to run the provisioning operation. If this environment is secure and has locked accounts, then make sure that:The credentials you specify here have the necessary privileges to switch to the locked account for performing the provisioning operation.
The Deployment Procedures has been customized to support locked environments.
For more information, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
From the Host Credentials list, select Different for each Oracle Home if you want to use different operating system credentials for each Oracle home, or Same for all Oracle Homes if you want to use the same set of credentials for all Oracle homes. Depending on the selection you make, specify the credentials. Ensure that the users belong to the same group (dba/oinstall).
Note:
If you are using vendor clusterware, then ensure thatroot and the operating system users, such as oracle and crsuser, owning the clusterware and various Oracle homes are a part of the operating system groups required by the vendor clusterware.
For example, if your system uses High Availability Cluster Multiprocessing (HACMP) clusterware, then create or check for the existence of the group hagsuser. Ensure that the relevant operating system users and root user are members of this group.
For more information, refer to the Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation and Configuration Guide.
In the Schedule section, schedule the Deployment Procedure to run either immediately or later.
Click Next.
On the Configure Cluster page, do the following:
In the Cluster Name and Location section, review the default name and location details provided for Oracle Clusterware and Oracle RAC Database. While Oracle recommends you to retain the default values, you can always edit them to provide custom values.
For security purposes, the clusterware configuration sets the ownership of Oracle Clusterware home and all its parent directories to be owned by root. Hence, Oracle recommends you to install Oracle Clusterware outside the Oracle base of the Oracle RAC home.

The default cluster name you see here is based on the host cluster name you provided in the Agent Deploy application in Enterprise Manager Grid Control, while deploying Management Agents on a cluster. The scratch location you see here is a temporary location on the target host where temporary files are placed before provisioning and configuring Oracle RAC.
For Additional Parameters, specify any additional parameters you want to run while installing Oracle Clusterware. For example, -debug.
You can specify any Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) parameter that can be used in this provisioning operation. Using these parameters, you can even change the installation type of the database. For example, INSTALL_TYPE=SE. Ensure that the parameters are separated by white space.
Note:
If this entire section (Cluster Name and Location section) is disabled, then it is clear that each node has a Management Agent, but they were NOT installed using the Cluster Install option available in the Agent Deploy application. To resolve this issue, ensure that you convert the standalone Management Agents to a cluster agent. For more information, see Appendix I, "Converting Standalone Oracle Management Agent to Cluster Agent".In the Database Details section, retain the default selection for creating a starter database.

Note:
If the database creation steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this section.If you want to create a general-purpose database, then leave all the fields in this section blank. Otherwise, provide the required details as described in this step.
If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be available on the target host, in a shared location accessible from the target host, in the Software Library, or in a location where an existing database is running.
Note:
From the Software Library or from the location where an existing database is running, only a.dbt template file can be used. However, from the target host or a shared location, any template file can be used.If you do not have a custom response file, then select Do not use response file, and provide the global database name, the credentials, and the additional parameters you want to run while creating the starter database.
Note:
Ensure that the database name you specify is in the format database_name.database_domain. It must have 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters. For example, orcl.mydomain.com. Also note that the credentials you provide are used for SYS, SYSTEM, SYSMAN, and DBSNMP accounts.If you want to use the structure of an existing database and have a custom template to structure the new database, then in Template File for Database, specify the full path to a location where the template file is available. The file may be available on the target host or on a shared location accessible from the target host.
Note:
If you do not store the response files and templates in a central location, you can always customize the Deployment Procedure to add another step that copies the response file or template to the target host before invoking the configuration tools to create the database.In the Backup and Recovery Details section, retain the default selection, that is, Do not Enable Automated Backups if you do not want to have backups taken.

Alternatively, if you want to enable automated backups, select Enable Automated Backups, specify the full path to a directory location from where the backed-up files can be recovered, and provide the operating system credentials for running the backup job. Note that recovery location is the same location as the backup location because this where the files are backed up and also recovered from.
In the ASM Instance Details section (appears only if you had selected to deploy ASM), retain the default selection, that is, Create ASM Instance, and specify the credentials, additional ASM parameters to be used, and the ASM disk string to be used.

Important:
If you are provisioning Oracle Database 10g and Oracle ASM 10g, then ensure that you specify the same password for database as well as ASM.If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create ASM database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be availableon the target host or on a shared location accessible fromt he target hosts.
If you do not want to use a response file, then select Do not use response file.
Click Next.
On the Storage page, do the following:
In the Shared Storage Configuration section, provide details about the storage devices and click Next. Specify the partition name and the mount location, and select the mount format and a storage device for storing data. While partition name is the path to the location where the device is installed, mount location is the mount point that represents the partition location.

While configuring the storage device, at a minimum, you must have a partition for at least OCR, Voting Disk, and data files. You cannot designate the same storage device to multiple partitions.
Oracle recommends designating the OCR and the OCR Mirror devices to different partitions. Similarly, Oracle recommends designating the Voting Disk, Voting Disk1, and Voting Disk2 to different partitions.
Before clicking Next, do the following:
- If you want to clear the data on selected raw devices before creating and configuring the cluster, then select Clear raw devices.
- If you have configured only for a few storage devices, then select Do not provision storage for others that you do not want to provision.
- Specify the ASM disk string to be used.
In the Options section, select the ASM redundancy mode. The default is None, which requires 7 GB of space. While Normal requires 16 GB of space, High requires 32 GB.
(Optional) On the Configuration page, do the following:
Note:
If the configuration steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this page.In the Bonding Interface (Private Interconnect) section, select Configure Bonding Interface if you want to configure the bonding interface. To bind the interfaces, specify details as described in Table 5-5.
In the Sysctl File Configuration section, select Configure Sysctl file if you want to configure the sysctl.conf file. Specify the mode of editing the system configuration file and the location of the reference system configuration file used for modifying the kernel parameters.
The default mode is append. You can however select edit to modify, and replace to replace the current sysctl.conf file.
Ensure that the reference file you specify is available in a shared location accessible by the Oracle Management Service.
On the Configure Oracle Home page, do the following:
If the host where the database is being provisioned has a direct connection to the Internet, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password.
An e-mail address is required so that security updates and install updates can be sent. You can specify any e-mail address, but Oracle recommends you to specify the My Oracle Support user name. For example, john.mathew@xyz.com.
If the My Oracle Support password is incorrect, you will be allowed two more attempts. However, if your password is incorrect in all three attempts or if it is left blank, then you are registered anonymously, which means, the configuration information will be collected and uploaded to My Oracle Support but the uploaded information will not be associated with your My Oracle Support account. Therefore, if you log in to My Oracle Support with your credentials, you will not see this information displayed against your account. However, if you had specified an e-mail address, then you will continue to receive security updates and other notifications from Oracle to that e-mail address.
If the host where the database is being provisioned has an indirect connection to the Internet through a proxy server, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password, and then in the Connection Details section, specify the proxy server details.
Note:
You can change the proxy server settings any time after the Deployment Procedure ends. To do so, run theconfigCCR command from the /ccr/bin/ directory within the Oracle home directory of the provisioned database.If the host where the database is being provisioned does not have a direct or indirect connection to the Internet, then specify the e-mail address and leave the other fields blank.
In this case, after you complete the installation process, manually collect the configuration information and upload it to My Oracle Support. To understand how the configuration information can be manually collected and uploaded, see the steps outlined in Manually Collecting and Uploading Configuration Information to My Oracle Support.
Click Next.
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC, and click Submit. If the details you provided seem to be missing on this page, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".
After the Deployment Procedure ends successfully, instrument the database to collect configuration information. For information about instrumenting the database, see Instrumenting the Database for Configuration Collections.
This section describes how you can provision Oracle RAC that is identical to the one available on the installation medium.
This section covers the following:
The following describes the different phases involved in this Deployment Procedure:
Table 5-4 Deployment Phases Involved in Provisioning Oracle RAC
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Select Source Allows you to select the generic components for Oracle Clusterware, Oracle RAC, and ASM (optional). |
 |
Select Hosts Allows you to select the target hosts, which should form the cluster, and the network interfaces (public and private). |
 |
Credentials and Schedule Allows you to specify host credentials required for accessing the hosts where Oracle RAC needs to be provisioned, and schedule the Deployment Procedure to run immediately or later. |
 |
Configure Cluster Allows you to specify configuration values for the cluster, create new starter database, and enable backup and recovery options. |
 |
Storage Allows you to specify a partition name and mount location, and select a mount format and storage device for storing data. |
 |
Configuration Allows you to provide additional parameters for configuring the clusterware. |
 |
Oracle Configuration Manager Allows you to configure Oracle Configuration Manager so that security updates can be sent. |
 |
Review Allows you to review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC. |
Before running the Deployment Procedure, meet the following prerequisites.
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites described in the following sections:
Ensure that you upload the software binaries of Oracle RAC database and Oracle Clusterware to the Software Library.
To understand how you can upload the software binaries to the Software library, see Uploading Software Binaries to Oracle Software Library.
Ensure that the target hosts have the necessary hardware and software required for Oracle RAC. The hardware requirements include setting up of the following:
Private Network: The network interface cards must be installed on each node and connected to each other.
Shared Storage Between Nodes: The shared storage is required for OCR, Voting disks and the data files.
Ensure that the Virtual IPs are set up in the DNS. If you choose to set up the Virtual IPs locally, then the IP addresses can be specified using the Deployment Procedure, and the procedure will set them up for you.
If you want to use standard response files while provisioning the database, then edit the dbca.rsp file available on the installation medium, and store it in a location accessible from the target hosts. The file may be on the target host or on a shared location.
To understand how response files work, see the Oracle Database Installation Guide for Linux available at one of these URLs:
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db111/homepage
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db102/homepage
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db10g/portal.portal_demo3
To understand how you can upload the response file to the Software Library, see Uploading Database Response File to Oracle Software Library.
If you want to use a custom template to create a structure for the database, then create a template (a .dbt file), and store it in a location accessible from the target hosts. The file may be on the target host or on a shared location.
To understand how a template can be created and used for creating databases, see Appendix D, "Creating Templates for Oracle Database".
To understand how you can upload the template to the Software Library, see Uploading Database Template File to Oracle Software Library.
Ensure that operating system users such as oracle and crsuser are available on all nodes of the cluster. These users must be a part of the relevant operating system groups such as dba and oinstall.
For more information, see Oracle Clusterware Installation Guide available at:
Ensure that the User IDs for operating system users and the Group IDs for operating system groups are identical on all nodes of the cluster.
Ensure that you do NOT use an NIS-based operating system user.
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has the privileges to run the Deployment Procedure and its commands on the target hosts. If you do not have the privileges to do so, that is, if you are using a locked account, then request your administrator (a designer) to either customize the Deployment Procedure to run it as another user or ignore the steps that require special privileges. For information about customization, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
Ensure that you use an operating system user that has write permission on the staging areas used for placing software binaries of Oracle RAC database.
Deployment Procedures allow you to use staging locations for quick file-transfer of binaries and prevent high traffic over the network. While providing a staging location, ensure that the operating system user you use has write permission on those staging locations. For information about staging area, see Staging Area.
Ensure that the umask value on the target host is 022.
To provision a fresh Oracle RAC installation, follow these steps:
In Grid Control, click the Deployments tab.
On the Deployments page, in the Deployment Procedure Manager section, click RAC Provisioning Procedures.
On the Deployment Procedure Manager page, in the Procedure subtab, from the table, select one of the following, and click Schedule Deployment.
To run the Deployment Procedure on UNIX platforms, Select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For UNIX.
To run the Deployment Procedure on Microsoft Windows platforms, select Oracle Clusterware / RAC Provisioning For Windows.
Enterprise Manager Grid Control displays the Select Source page of the Deployment Procedure.
On the Select Source page, do the following:
In the Select Source section, select Select from Software Library.
In the Source for Clusterware section, click the torch icon and select the generic component that has the software binaries of Oracle Clusterware. Ensure that you select only components that are in "Ready" status. Once you select the component name, the application automatically displays the component location.

Note:
If you do not see the required component in the Software Library, then follow the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".In the Source for RAC section, click the torch icon and select the generic component that has the software binaries of Oracle Database. Ensure that you select only components that are in "Ready" status. Once you select the component name, the application automatically displays the component location.

Note:
If you do not see the required component in the Software Library, then follow the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".(Optional) In the Source for ASM section, do one of the following:
If you do not want to deploy ASM, then retain the default selection, that is, Do not Provision ASM.
If you want to deploy ASM in the same Oracle home as the Oracle RAC, then select Use the same source as the RAC home. Alternatively, if you can select Choose a component and upload an ASM component from the Software Library.

Click Next.
On the Select Hosts page, do the following:
In the Hosts to Include in Cluster section, click Add and select the target hosts that should form the cluster. To see more details about the selected hosts, click Show Options.

Note:
When you click Add, the Select Target pop-up window appears. On this page, by default, the Show Suitable Hosts option is selected and the table lists only those hosts that are best suited for provisioning. If you do not find the host you want to add, then select Show All Hosts to view a complete list of hosts.By default, Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are automatically prefilled with values. Edit them and specify values that match with your environment. Optionally, you can also specify their IP addresses.

Note:
If the prefilled, default values of Private Host Name and Virtual Host Name are incorrect, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".If you already have these details stored in a cluster configuration file, then click Import From File to select that cluster configuration file. This file typically contains information about the new hosts to be added. To understand how a cluster configuration file looks, see the sample file shown in Sample Cluster Configuration File.

To configure the private and public network interfaces, click Select Interfaces. By default, the interfaces that have the same name and subnet for the selected target hosts are displayed. However, you can also choose to view all the interfaces for the selected target hosts. You can either select one of the existing interfaces or specify a completely new one if the interface you want to use does not exist.

In the Network Interface Configuration section, review the details of the private and public interfaces.
Click Next.
On the Credentials/Schedule page, do the following:
In the Target Host(s) Credentials section, retain the default selection, that is, Use Preferred Credentials.
Note:
You can optionally override these preferred credentials. The credentials you specify here are used by the Deployment Procedure to run the provisioning operation. If this environment is secure and has locked accounts, then make sure that:The credentials you specify here have the necessary privileges to switch to the locked account for performing the provisioning operation.
The Deployment Procedures has been customized to support locked environments.
For more information, see Chapter 23, "Customizing Steps to Run as Another User".
From the Host Credentials list, select Different for each Oracle Home if you want to use different operating system credentials for each Oracle home, or Same for all Oracle Homes if you want to use the same set of credentials for all Oracle homes. Depending on the selection you make, specify the credentials. Ensure that the users belong to the same group (dba/oinstall).
Note:
If you are using vendor clusterware, then ensure thatroot and the operating system users, such as oracle and crsuser, owning the clusterware and various Oracle homes are a part of the operating system groups required by the vendor clusterware.
For example, if your system uses High Availability Cluster Multiprocessing (HACMP) clusterware, then create or check for the existence of the group hagsuser. Ensure that the relevant operating system users and root user are members of this group.
For more information, refer to the Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation and Configuration Guide.
In the Schedule section, schedule the Deployment Procedure to run either immediately or later.
Click Next.
On the Configure Cluster page, do the following:
In the Cluster Name and Location section, review the default name and location details provided for Oracle Clusterware and Oracle RAC Database. While Oracle recommends you to retain the default values, you can always edit them to provide custom values.
For security purposes, the clusterware configuration sets the ownership of Oracle Clusterware home and all its parent directories to be owned by root. Hence, Oracle recommends you to install Oracle Clusterware outside the Oracle base of the Oracle RAC home.

The default cluster name you see here is based on the host cluster name you provided in the Agent Deploy application in Enterprise Manager Grid Control, while deploying Management Agents on a cluster. The scratch location you see here is a temporary location on the target host where temporary files are placed before provisioning and configuring Oracle RAC.
For Additional Parameters, specify any additional parameters you want to run while installing Oracle Clusterware. For example, -debug.
You can specify any Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) parameter that can be used in this provisioning operation. Using these parameters, you can even change the installation type of the database. For example, INSTALL_TYPE=SE. Ensure that the parameters are separated by white space.
Note:
If this entire section (Cluster Name and Location section) is disabled, then it is clear that each node has a Management Agent, but they were NOT installed using the Cluster Install option available in the Agent Deploy application. To resolve this issue, ensure that you convert the standalone Management Agents to a cluster agent. For more information, see Appendix I, "Converting Standalone Oracle Management Agent to Cluster Agent".In the Database Details section, retain the default selection for creating a starter database.

Note:
If the database creation steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this section.If you want to create a general-purpose database, then leave all the fields in this section blank. Otherwise, provide the required details as described in this step.
If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be available on the target host, in a shared location accessible from the target host, in the Software Library, or in a location where an existing database is running.
Note:
From the Software Library or from the location where an existing database is running, only a.dbt template file can be used. However, from the target host or a shared location, any template file can be used.If you do not have a custom response file, then select Do not use response file, and provide the global database name, the credentials, and the additional parameters you want to run while creating the starter database.
Note:
Ensure that the database name you specify is in the format database_name.database_domain. It must have 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters. For example, orcl.mydomain.com. Also note that the credentials you provide are used for SYS, SYSTEM, SYSMAN, and DBSNMP accounts.If you want to use the structure of an existing database and have a custom template to structure the new database, then in Template File for Database, specify the full path to a location where the template file is available. The file may be available on the target host or on a shared location accessible from the target host.
Note:
If you do not store the response files and templates in a central location, you can always customize the Deployment Procedure to add another step that copies the response file or template to the target host before invoking the configuration tools to create the database.In the Backup and Recovery Details section, retain the default selection, that is, Do not Enable Automated Backups if you do not want to have backups taken.

Alternatively, if you want to enable automated backups, select Enable Automated Backups, specify the full path to a directory location from where the backed-up files can be recovered, and provide the operating system credentials for running the backup job. Note that recovery location is the same location as the backup location because this where the files are backed up and also recovered from.
In the ASM Instance Details section (appears only if you had selected to deploy ASM), retain the default selection, that is, Create ASM Instance, and specify the credentials, additional ASM parameters to be used, and the ASM disk string to be used.

Important:
If you are provisioning Oracle Database 10g and Oracle ASM 10g, then ensure that you specify the same password for database as well as ASM.If you have a custom response file that already has the options enabled, then select Use response file to create ASM database, and specify the full path to a location where the file is available. The file may be available on the target host or on a shared location accessible from the target hosts.
If you do not want to use a response file, then select Do not use response file.
Click Next.
On the Storage page, do the following:
In the Shared Storage Configuration section, provide details about the storage devices and click Next. Specify the partition name and the mount location, and select the mount format and a storage device for storing data. While partition name is the path to the location where the device is installed, mount location is the mount point that represents the partition location.

While configuring the storage device, at a minimum, you must have a partition for at least OCR, Voting Disk, and data files. You cannot designate the same storage device to multiple partitions.
Oracle recommends designating the OCR and the OCR Mirror devices to different partitions. Similarly, Oracle recommends designating the Voting Disk, Voting Disk1, and Voting Disk2 to different partitions.
Before clicking Next, do the following:
- If you want to clear the data on selected raw devices before creating and configuring the cluster, then select Clear raw devices.
- If you have configured only for a few storage devices, then select Do not provision storage for others that you do not want to provision.
- Specify the ASM disk string to be used.
In the Options section, select the ASM redundancy mode. The default is None, which requires 7 GB of space. While Normal requires 16 GB of space, High requires 32 GB.
(Optional) On the Configuration page, do the following:
Note:
If the configuration steps are disabled in the Deployment Procedure, then you will not see this page.In the Bonding Interface (Private Interconnect) section, select Configure Bonding Interface if you want to configure the bonding interface. To bind the interfaces, specify details as described in Table 5-5.
In the Sysctl File Configuration section, select Configure Sysctl file if you want to configure the sysctl.conf file. Specify the mode of editing the system configuration file and the location of the reference system configuration file used for modifying the kernel parameters.
The default mode is append. You can however select edit to modify, and replace to replace the current sysctl.conf file.
Ensure that the reference file you specify is available in a shared location accessible by the Oracle Management Service.
On the Configure Oracle Home page, do the following:
If the host where the database is being provisioned has a direct connection to the Internet, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password.
An e-mail address is required so that security updates and install updates can be sent. You can specify any e-mail address, but Oracle recommends you to specify the My Oracle Support user name. For example, john.mathew@xyz.com.
If the My Oracle Support password is incorrect, you will be allowed two more attempts. However, if your password is incorrect in all three attempts or if it is left blank, then you are registered anonymously, which means, the configuration information will be collected and uploaded to My Oracle Support but the uploaded information will not be associated with your My Oracle Support account. Therefore, if you log in to My Oracle Support with your credentials, you will not see this information displayed against your account. However, if you had specified an e-mail address, then you will continue to receive security updates and other notifications from Oracle to that e-mail address.
If the host where the database is being provisioned has an indirect connection to the Internet through a proxy server, then specify an e-mail address and My Oracle Support password, and then in the Connection Details section, specify the proxy server details.
Note:
You can change the proxy server settings any time after the Deployment Procedure ends. To do so, run theconfigCCR command from the /ccr/bin/ directory within the Oracle home directory of the provisioned database.If the host where the database is being provisioned does not have a direct or indirect connection to the Internet, then specify the e-mail address and leave the other fields blank.
In this case, after you complete the installation process, manually collect the configuration information and upload it to My Oracle Support. To understand how the configuration information can be manually collected and uploaded, see the steps outlined in Manually Collecting and Uploading Configuration Information to My Oracle Support.
Click Next.
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for provisioning Oracle RAC, and click Submit. If the details you provided seem to be missing on this page, then see the workaround described in Appendix A, "Troubleshooting Issues".
After the Deployment Procedure ends successfully, instrument the database to collect configuration information. For information about instrumenting the database, see Instrumenting the Database for Configuration Collections.
Table 5-5 Configuration Page - Element Description
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Bonding Device Name |
Specify the name of the bond to be created. For example, bond0 |
|
Subnet Mask |
Specify the subnet mask for the IP address. For example, 255.255.255.0 |
|
Default Gateway |
Specify the default gateway for the bonding device. For example, 10.1.2.3 |
|
DNS Servers |
Specify the Domain Name Server (DNS) list for the bonding device. For multiple DNS servers, the values should be comma- separated. Default values are picked up from the /etc/resolv.conf file. Entries provided here will be appended. |
|
Slave Devices List |
Specify the list of slave devices for the bonding device. For multiple slave devices, the values should be comma-separated. For example, eth1,eth2,eth3. |
|
Bonding Mode |
Specifies one of four policies allowed for the bonding module. Acceptable values for this parameter are:
|
|
Domain Name |
Specify the domain name for the assigned host name. For example, foo.com |
|
Primary Slave Device |
Specify the interface name, such as eth0, of the primary device. The primary device is the first of the bonding interfaces to be used and is not abandoned unless it fails. This setting is particularly useful when one NIC in the bonding interface is faster and, therefore, able to handle a bigger load. This setting is only valid when the bonding interface is in active-backup mode. |
|
ARP Interval |
Specify (in milliseconds) how often ARP monitoring occurs. If using this setting while in mode 0 or 2 (the two load-balancing modes) the network switch must be configured to distribute packets evenly across the NICs. The value is set to 0 by default, which disables it. |
|
MII Interval |
Specify (in milliseconds) how often MII link monitoring occurs. This is useful if high availability is required because MII is used to verify that the NIC is active to verify that the driver for a particular NIC supports the MII tool. If using a bonded interface for high availability, the module for each NIC must support MII. Setting the value to 0 (the default), turns this feature off. When configuring this setting, a good starting point for this parameter is 100. |
|
MII Interval Down Delay |
Specify (in milliseconds) how long to wait after link failure before disabling the link. The value must be a multiple of the value specified in the miimon parameter. The value is set to 0 by default, which disables it. |
|
MII Interval Up Delay |
Specify (in milliseconds) how long to wait before enabling a link. The value must be a multiple of the value specified in the miimon parameter. The value is set to 0 by default, which disables it. |
|
NTP Server |
Specify the NTP server for the assigned host name. For example, 1.2.3.4. |
The following shows the contents of a typical cluster configuration file:
# Cluster Configuration file # Node information
# Public Node Name
|
Private Node Name
|
Private IP (Optional)
|
Virtual Host Name
|
Virtual IP (Optional)
|
node1.domain.com |
node1-priv.domain.com |
- |
node1-vip.domain.com |
- |
node2.domain.com |
node2-priv.domain.com |
10.2.109.103 |
node2-vip.domain.com |
134.2.109.103 |