| Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B25209-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) B25209-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter introduces the Oracle Application Server administration tools.
It contains the following topics:
Oracle realizes that the procedures you use to monitor and administer your application server components can vary, depending upon the size of your organization, the number of administrators you employ, and the types of components you manage. As a result, Oracle offers options for managing your Oracle Application Server installations.
These management options can be divided into the following categories:
Managing Oracle Application Server with Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control
Managing Oracle Application Server Using the OPMN Command Line
Managing Oracle Application Server Using the admin_client.jar Utility
Using Other Tools to Monitor the Built-In Performance Metrics
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control is installed with every instance of Oracle Application Server. As a result, you can immediately begin managing your application server and its components from your Web browser.
From the Application Server Control Console, you can monitor and administer a single Oracle Application Server instance or a cluster topology, which consists of multiple application server instances and the applications deployed to the OC4J instances within those application servers.
The Application Server Control Console organizes a wide variety of performance data and administrative functions into distinct, Web-based home pages for specific features of the application server and Oracle Containers for J2EE. The Enterprise Manager home pages make it easy to locate the most important monitoring data and the most commonly used administrative functions—all from your Web browser.
In addition to the Application Server Control, you can also use the opmnctl command-line tool, which provides a command-line interface to Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN). For example, you can use this command line (opmnctl) to:
Start and stop applications and application server instances
Associate two or more application server instances to form a cluster
Display a summary of the instances that are part of a cluster
|
See Also: Section 1.5.1, "Getting Started with Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN)"Oracle Containers for J2EE Configuration and Administration Guide for information about configuring and managing OC4J clusters with Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server Administrator's Guide for complete information about OPMN command-line |
Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) also provides a command-line utility—admin_client.jar—that can be used to perform operations on active OC4J instances.
For many functions, the admin_client.jar utility replaces the admin.jar utility, which is used exclusively for the standalone configuration of the Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) OC4J server.
Unlike the admin.jar utility, you can use the admin_client.jar utility to manage OC4J instances in a managed, Oracle Application Server environment, as well as OC4J instances in a standalone OC4J environment.
You can perform the following tasks with the admin_client.jar utility:
Deploy applications to a specific OC4J instance or to all instances within a cluster
Undeploy an application
Incrementally update a deployed EJB module with modified classes
Create a new shared library
Stop, start or restart a specific application, on a specific OC4J instance or cluster-wide
|
See Also: "Using the admin_client.jar Utility" in the Oracle Containers for J2EE Configuration and Administration Guide |
After you install and start Oracle Application Server, the application server automatically begins gathering a set of built-in performance metrics. These built-in performance metrics are measured continuously using performance instrumentation inserted into the implementations of Oracle Application Server components.
The Application Server Control Console presents a subset of these performance metrics in an organized fashion on the application server component home pages. For example, the OC4J performance metrics are presented as a series of charts on the OC4J Performance page.
Alternatively, you may want to view the complete set of built-in performance metrics, or you may need to monitor a specific set of application server component metrics. Oracle Application Server provides a set of command-line and servlet-based tools to view the Oracle Application Server built-in performance metrics directly, outside of the Application Server Control Console.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control provides Web-based management capabilities designed specifically for Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3).
The following sections provide more information:
Application Server Control New Features for 10g Release 3 (10.1.3)
About the Application Server Control Underlying Technologies
For this release, Application Server Control provides the following benefits and feature improvements over previous versions:
For 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), the Application Server Control has been completely re-designed with a new architecture. The Application Server Control is now deployed as a standard J2EE application (ascontrol) that runs within every OC4J container you create. In small deployments, the OC4J instance that hosts the Application Server Control can also be used to deploy customer applications.
This new architecture eliminates the need for a separate Oracle Management Agent, which was required for the Application Server Control in previous Oracle Application Server releases. As a result, the management software requires less disk space and fewer system resources. You can then manage and monitor your applications with minimal impact on your application server environment.
For 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), the Application Server Control is based on the Java Management Extensions (JMX) technology.
Specifically, Application Server Control implements the following Java technology standards:
The JSR 77 J2EE Management specification
Application Server Control takes advantage of container-defined MBeans provided by the 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) OC4J container, as well as application-defined MBeans, provided by applications that are developed and configured in accordance with the specification. These MBeans provide configuration, monitoring, and state management capabilities.
In addition, Application Server Control includes a new MBean browser that provides complete support for JSR 77 and Application Defined MBean operations, such as viewing MBean attribute values and statistics, MBean method invocation, subscription to JMX notifications, and state management.
The JSR 88 J2EE Application Deployment specification
Application Server Control provides a JSR 88-based deployment wizard to simplify deployment and redeployment of J2EE applications, task-oriented deployment plan editors to assist you in assigning or mapping the common deployment descriptors at deploy time, and a generic deployment plan editor so you can access all deployment descriptors for advanced configuration.
The Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI)
Application Server Control provides a new JNDI browser, which hierarchically displays the JNDI bindings for each application.
From the Application Server Control, you can configure auditing, logging, security, and reliability parameters for Web Services deployed in your OC4J instances. In addition, you can use Oracle Web Services Manager as your exclusive Web Services management solution, or you can use it in concert with the standard auditing, logging, reliability, and security management features.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server Web Services Developer's Guide for information about developing and managing Web services with Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3)Information about Oracle Web Services Manager on the Oracle Technology Network (OTN): http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/webservices_manager/ |
With Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), you can use Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN) to associate two or more application server instances to form an Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) cluster. When you configure your environment in this manner, you can use a single instance of the Application Server Control to remotely manage all the instances in the cluster.
In a typical production data center, administrative operations (for example, configuration, application deployment, and process control and monitoring) are performed by different sets of administrators, depending upon the data center deployment and security policies.
Typically a super administrator, who is granted full privileges, delegates administrative responsibilities to other administrators who are assigned limited privileges to only carry out specific administrative operations. With 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) Application Server Control, you can assign one of three standard administrative roles to each user.
The Application Server Control Console relies on related technologies to discover, monitor, and administer the Oracle Application Server environment. These technologies automatically perform many of the management tasks as you select options and functions within the Application Server Control Console. For example, they discover the components of each application server instance, gather and process performance data, and provide access to application configuration information.
Table 2-1 provides a summary of the underlying technologies leveraged by the Application Server Control Console.
Table 2-1 Summary of the Application Server Control Underlying Technologies
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Application Server Control Console uses DMS to gather performance data about your Oracle Application Server components. For more information, see Oracle Application Server Performance Guide. |
|
|
OPMN provides process control and monitoring for application server instances and their components. It gathers component status information, and distributes the status information to components that are interested in it. Application Server Control uses OPMN for such tasks as starting and stopping the components of your application server instance. For more information, see Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server Administrator's Guide. |
At any time while using the Application Server Control Console, you can click Help at the top of the page to get more information. In most cases, the Help window displays a help topic about the current page. Click Contents in the Help window to browse the list of help topics, or click Search to search for a particular word or phrase.
Use the following sections to get started with the Application Server Control Console and become familiar with the Enterprise Manager home pages within the Application Server Control Console:
Using Application Server Control to View and Manage an OC4J Instance
Creating Administrative Users and Assigning Administrative Roles
Using Application Server Control to View the Application Server Components
Using Application Server Control to Manage a Cluster Topology
About MBeans and the Application Server Control MBean Browsers
The following sections describe how to display the Application Server Control Console and introduce you to the initial home pages you should see when you display the Application Server Control Console for the first time:
The URL for the Application Server Control Console, including the port number, is included in the text file that displays at the end of the Oracle Application Server installation procedure. This text file is saved in the following location after you install the application server:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/install/readme.txt (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\install\readme.txt
The Application Server Control Console URL typically includes the name of the host computer and the port number assigned to the Application Server Control Console during the installation. For example, on UNIX:
http://mgmthost1.acme.com:7777/em
To view the Application Server Control Console from the Oracle Application Server Welcome Page:
Display the Oracle Application Server Welcome Page by entering the following URL in your Web browser:
http://hostname.domain:port
For example:
http://sys42.acme.com:7777
|
Note: The default port for Oracle HTTP Server (and, as a result, the Welcome page) is provided at the end of the Oracle Application Server installation, as well as in the following text file in theinstall directory of the application server Oracle home:
readme.txt |
Click Log on to the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control Console.
Enterprise Manager displays the administrator logon dialog box.
Enter the Oracle Application Server administrator user name and password and click OK.
The user name for the administrator user is oc4jadmin. The password is the one you supplied during the installation of Oracle Application Server.
If you are managing a single Oracle Application Server instance, Enterprise Manager presents you with the OC4J Home page (Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1 Managing an OC4J Instance from the OC4J Home Page
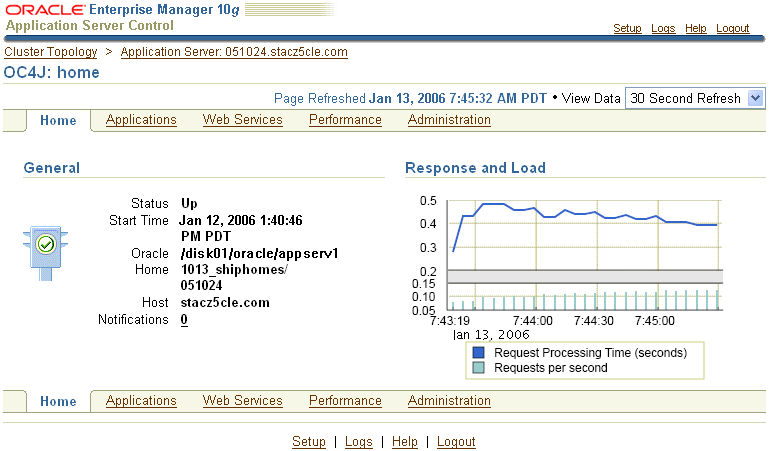
Use the OC4J Home page to obtain general information about the OC4J instance, and to view the response and load chart. Select a refresh interval from the View Data drop-down menu to monitor the response and load metrics over a period of time. To start, stop, or restart the OC4J instance, navigate to the Cluster Topology page, select the instance, and click Start, Stop, or Restart.
The OC4J Home page and its related Applications, Web Services, Performance, and Administration pages are designed to provide you with a central, Web-based view of the OC4J instance and the applications and Web services deployed to the instance.
For more information, click Help at any time while using the OC4J Home page. The online help provides reference information about the fields on each page, as well as links to related tasks and related documentation that can help you get started.
When you install Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), a default super administrator account is created. This account is called oc4jadmin and you set the password for this account during the Oracle Application Server installation.
After you log in to the Application Server Control Console using the oc4jadmin account, you can then create additional administrative roles. For example, you can create an account and default password for the each of the administrators who manage your Oracle Application Server environment:
Click Setup at the top of any Application Server Control Console page.
Click Users to display the Users page.
Click Create to create a new administrator account.
Follow the instructions on the screen to provide a name for the account, a default password, and to assign a role to the user you are about to create.
Refer to Table 2-2 for a description of the administrative roles you can assign to a user.
Click Help if you need further information.
Table 2-2 Administrative Roles That You Can Assign to Application Server Control Administrators
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
|
ascontrol_admin |
Assign this role to administrators who need complete administrative privileges and access to the Application Server Control application and pages. You can consider these administrators the "super users" assigned to manage your Oracle Application Server and OC4J environment. |
|
ascontrol_appadmin |
Assign this role to administrators who need to manage all deployed applications, except the default and Application Server Control (ascontrol) applications. These administrators can manage the applications you deploy, but they cannot create new administrative users or make global configuration changes. |
|
ascontrol_monitor |
Assign this role to administrators who must monitor the Oracle Application Server and OC4J environment, but do not need to make any configuration changes to the applications or the OC4J instance. This role is essentially a read-only role. This role is applied automatically to all administrative users that you create. If you do not apply the ascontrol_admin or ascontrol_appadmin role, then the account can be used for monitoring only. |
After you get familiar with the OC4J Home page, you can then obtain a wider view of your application server environment.
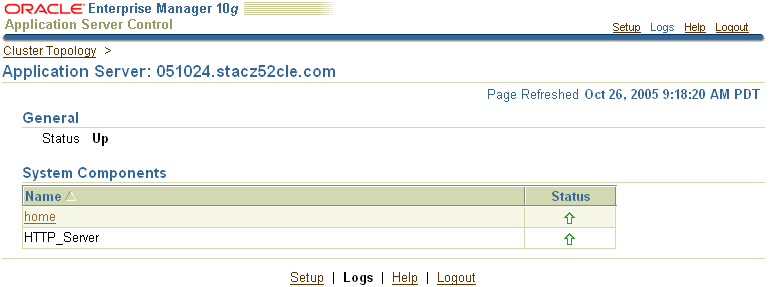
Click the name of the application server instance in the locator links to display the Application Server page. For example, in Figure 2-1, click Application Server: 051024.stacz5cle.com.
The resulting Application Server page is shown in Figure 2-2. This page lists the components of the application server instance, including the OC4J instances created in this instance and the Oracle HTTP Server. The Oracle HTTP Server instance appears in this example because a Web server was installed as part of this particular application server installation. The actual list of components shown on the Application Server page will vary depending upon the installation type you selected.
Figure 2-2 Viewing the Components of the Application Server Instance
In a typical production environment, two or more application server instances are installed and configured to work as a cluster. The following sections describe how you can use the Application Server Control Console to manage multiple instances in a cluster:
Viewing the Cluster Topology and Locating the Active Application Server Control
Enabling Remote Management by Setting Administrator Credentials
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server Installation Guide for information on configuring a cluster during the Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) installationSection 6.1, "Configuring Cluster Topologies" for information on configuring clusters after installation |
In a clustered environment, the first page you see when you display the Application Server Control Console is the Cluster Topology page (Figure 2-3).
You can also view this page at any time by clicking Cluster Topology in the Application Server Control Console. The resulting Cluster Topology page provides you with a high-level view of the application servers, OC4J instances, Web servers, and applications deployed to the cluster.
Note that each OC4J instance in the cluster automatically includes an ascontrol application, which represents the Application Server Control. However, only one Application Server Control is used to manage all the Oracle Application Server instances in the cluster.

To identify the active Application Server Control, which is being used to manage the cluster, click Expand All to view all components of the cluster, and then locate the active ascontrol application, which is identified by the active Application Server Control icon.
Note that the OC4J instance that is used to deploy the active ascontrol application is called the Administration OC4J instance. You can identify the Administration OC4J instance during the Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3) installation procedure.
The Oracle Application Server instance that contains the active Application Server Control is called the administration instance. By default, any Application Server Control administrator can use the active Application Server Control Console to manage the administration instance.
However, before administrators can manage the other, remote Oracle Application Server instances in a cluster, an Application Server Control user with the ascontrol_admin role (sometimes called super user privileges) must enable remote management for other administrators who do not have those privileges.
If you do not enable remote management for an instance, Enterprise Manager prompts you for valid administrator credentials when you click the name of the instance on the Cluster Topology page.
To enable remote management for other instances in the cluster:
Log in to the Application Server Control Console using an administrative user account with ascontrol_admin (super administrator) privileges.
Click Setup on any page in Application Server Control Console.
Click Administrator Credentials.
If you have the proper privileges, Enterprise Manager displays the Administrator Credentials page, which lists OC4J instances in the cluster.
Select one or more of the OC4J instances and click Set Administrator Credentials.
Enter the user name and password of an Application Server Control account with ascontrol_admin (super administrator) privileges.
Click OK to enable remote management of the instance.
After you perform this task, all Application Server Control administrators can manage the remote Oracle Application Server instance, as well as the administrative instance.
For example, after you enable remote management for an instance, other administrators—even those with only the ascontrol_monitor role—can navigate to the OC4J Home page for the remote Oracle Application Server instance and perform the management tasks that they have the privilege to perform.
Note that the role assigned to a user applies to all instances in the cluster. For example, if you are assigned only the ascontrol_monitor role, you will not be able to perform configuration management tasks on any instance in the cluster.
For the purposes of Oracle Application Server 10g Release 3 (10.1.3), a group is a loosely synchronized set of like-named OC4J instances that belong to the same cluster topology. Specific configuration operations can be executed simultaneously on all OC4J instances in the group.
For more information, refer to the following sections:
There is no utility or command for creating a group. You create a group by creating two OC4J instances that have the same name and reside in the same cluster.
For example, suppose you install two Oracle Application Server instances and configure them as a cluster. If you create an OC4J instance called home in one instance, and then you create an instance called home in the second instance, a new group called home automatically appears in the Groups section of the Cluster Topology page (Figure 2-4).
Figure 2-4 Groups Section of the Cluster Topology Page
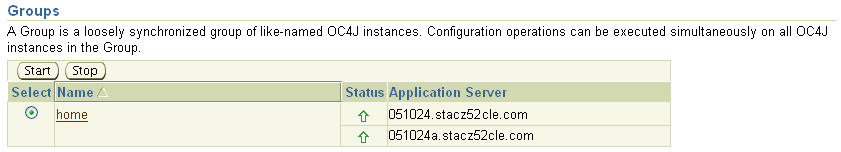
After you create a group, you can perform some common administrative tasks automatically across multiple OC4J instances.
Specifically, from the Group Home page, you can, in one step, perform each of the following tasks across multiple OC4J instances:
Process management operations, such as start, stop, or restart
Deployment operations, such as deploy, undeploy, and redeploy
JDBC management operations, such as creating, modifying, or removing JDBC data sources and connection pools
JMS Provider operations, such as creating and removing JMS destinations, and creating, modifying, or removing JMS connection factories
To display the Home page for a group, simply click the name of the group in the Groups section of the Cluster Topology page.
|
See Also: "About Groups" in the Application Server Control online help |
During the Oracle Application Server installation procedure, Oracle Universal Installer prompts you for two important pieces of information. How you respond to these prompts has a direct affect on how groups are configured for your Oracle Application Server environment.
Note the following when you are installing multiple Oracle Application Server instances that will be part of a cluster or a group:
Each OC4J instance in a group must have the same name.
During the Oracle Application Server installation, Oracle Universal Installer prompts you for the name of the default OC4J instance. If you want the default OC4J instance of each Oracle Application Server installation to be part of a group, be sure to enter the same default OC4J instance name for each Oracle Application Server instance you install.
Note that you cannot change the name of an OC4J instance later. On the other hand, you can later create additional OC4J instances within an application server installation.
Each OC4J instance in a group must have the same oc4jadmin password.
During the Oracle Application Server installation, Oracle Universal Installer prompts you for the initial oc4jadmin password. If you plan to create and use groups, be sure to enter the same oc4jadmin password for each Oracle Application Server instance you install. Otherwise, you will have to reset the password after the installation.
A managed bean (MBean) is a Java object that represents a JMX manageable resource in a distributed environment, such as an application, a service, a component or a device.
MBeans are defined in the J2EE Management Specification (JSR-77), which is part of Java Management Extensions, or JMX, a set of specifications that allow standard interfaces to be created for managing applications in a J2EE environment.
You can create MBeans for deployment with an application into OC4J, enabling the application or its components to be managed and monitored through the Application Server Control Console.
|
See Also: "Using MBeans in OC4J" in the Oracle Containers for J2EE Configuration and Administration Guide |
Application Server Control provides a set of MBean browsers that allow to you browse the MBeans for an OC4J instance, a cluster, or for a selected application. You can also perform specific monitoring and configuration tasks from the MBean browser.
For more information, see the following sections:
To view the System MBean Browser, which contains the MBeans specific to the selected OC4J instance:
Navigate to the OC4J Home page for the OC4J instance.
Click Administration to display the OC4J Administration page.
Click the task icon in the System Bean Browser row of the table.
Enterprise Manager displays the System MBean Browser. Click Help if you need more information about using the System Bean Browser.
Note that the online help also provides a set of topics that provide a tour of the MBean Browser, including online demonstrations of using the MBean browser.
|
See Also: "Step 1: Explore the Structure of the MBean Browser" in the Application Server Control online help |
To view the MBeans for a specific application:
Click Applications on the OC4J Home page to display the list of applications deployed to the OC4J instance.
Click the name of a deployed application.
Click Administration to display the Application Administration page, which contains a table listing the various administration tasks you can perform for the selected application.
Click the appropriate task icon in the table to browse the System MBeans associated with the selected application or to view the MBeans defined for the application.
Enterprise Manager displays the selected MBean Browser page.
To view the MBeans associated with the cluster topology, click Cluster MBean Browser on the Cluster Topology page.
Enterprise Manager displays the Cluster MBean Browser, which highlights the MBeans used to manage the cluster and any groups defined within the cluster.