| Oracle® Content Database Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Suite 10g (10.1.3.2) Part Number B32191-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Content Database Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Suite 10g (10.1.3.2) Part Number B32191-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
You can use the Application Server Control to manage Oracle Content DB processes, including starting and stopping servers and managing nodes. You can also manage Oracle Content DB domain and node processes from the command line using the opmnctl utility. To manage Oracle Content DB using the Application Server Control or opmnctl, OPMN must be started on all middle tiers.
This chapter provides information about the following topics:
An Oracle Content DB domain is a logical grouping of Oracle Content DB nodes and an Oracle Database instance that contains the Oracle Content DB data.
The Oracle Content DB software runs as a set of middle tier processes, called node. Oracle Content DB node processes manage one or more services, agents, and protocol servers.
Each node runs on a particular middle tier, or in other words, within a particular Oracle home. You can have multiple middle tiers on the same computer.
Each node runs as part of an OC4J process. On each middle tier, the OC4J instance for the Oracle Content DB node is OC4J_Content. You cannot have more than one node on a single middle tier.
You can start and stop the domain using the Application Server Control. Even if your domain is distributed across multiple middle tiers, you can start and stop the domain from a single middle tier.
The steps described in the following sections assume that all Oracle Application Server instances for Oracle Content DB are part of the same cluster. See Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide for information about how to configure OracleAS Clusters.
To start the Oracle Content DB domain from any middle tier:
Access the Application Server Control.
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select all Oracle Content DB processes (OC4J_Content instances) across all middle tiers. If you only have one middle tier, you only need to select one OC4J_Content process.
Figure 7-1 shows the Cluster Topology page.
Click Start. The entire Oracle Content DB domain is started across all middle tiers.
|
Note: Oracle HTTP Server (HTTP_Server) must also be running on each middle tier for Oracle Content DB to function properly. |
To restart the Oracle Content DB domain from any middle tier:
Access the Application Server Control.
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select all Oracle Content DB processes (OC4J_Content instances) across all middle tiers.
Click Restart, then on the Confirmation page, click Yes. Only those processes that are running are affected. Processes that are not running will not be started.
To stop the Oracle Content DB domain from any middle tier:
Access the Application Server Control.
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select all Oracle Content DB processes (OC4J_Content instances) across all middle tiers.
Click Stop, then on the Confirmation page, click Yes. The entire Oracle Content DB domain is stopped across all middle tiers.
|
Note: If you are performing scheduled maintenance and want to stop one middle tier at a time, you can start and stop individual node processes. See "Starting, Stopping, and Restarting OC4J_Content Instances" for more information. |
You can use the Application Server Control to start, stop, and restart nodes (OC4J_Content instances), as well as modify run-time node properties.
You can also use the opmnctl utility to start, stop, and restart nodes, as well as check node status; see "Managing Oracle Content DB from the Command Line" for more information.
This section contains the following topics:
You can start, stop, and restart OC4J_Content instances (in other words, Oracle Content DB node) using the Application Server Control. Even if you have multiple middle tiers, you can start, stop, and restart OC4J_Content instances from a single middle tier, regardless of where the OC4J_Content instances are located.
If an OC4J_Content instance fails to start, stop, or restart, check the logs for more information. Click Logs in the upper right corner of any Application Server Control page to search for and view the application.log file for the OC4J_Content instance.
Starting OC4J_Content Instances
To start an OC4J_Content instance using the Application Server Control:
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select the OC4J_Content instance you want to start.
Click Start. The Status column displays a green arrow pointing up, indicating that the OC4J_Content instance is up.
Stopping OC4J_Content Instances
To stop an OC4J_Content instance using the Application Server Control:
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select the OC4J_Content instance you want to stop.
Click Stop.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes. The Status column displays a red arrow pointing down, indicating that the OC4J_Content instance is down.
Restarting OC4J_Content Instances
You can only restart OC4J_Content instances that are already started.
To restart an OC4J_Content instance using the Application Server Control:
On the Cluster Topology page, in the Members table, select the OC4J_Content instance you want to restart.
Click Restart.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes. The OC4J_Content instance is stopped, then started again.
You can make run-time changes to nodes, such as changing the service used by the node or changing servers. Changes made at run time are lost when the node is restarted. If you want to make permanent changes, modify the node configuration for the node and then restart the node.
To modify a node at run time using the Application Server Control:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
In the Services section, you can create, modify, or delete services for this node. See "Managing Services at Run Time" for more information.
In the Servers section, you can create, modify, or delete servers for this node. See "Managing Servers at Run Time" for more information.
You can use the Application Server Control to create or delete service for a particular node. When you create a service, you specify what service configuration object provides its properties.
You can make temporary (run-time) changes to a service by modifying the service from the Content DB Home page. You can also dynamically configure the Committed Data Cache, Read-only Connection Pool, and the Writeable Connection Pool while the service runs. Changes made to services at run time are lost when the node is restarted.
You can also make permanent changes to a service by modifying its service configuration; see "Managing Service Configurations" for more information.
This section contains the following topics:
You can create services for a particular node by modifying the node at run time, or by modifying the appropriate node configuration. You can also create services when you create node configurations.
To create a service by modifying the node at run time:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Services section, click Create.
On the Create Service page, enter a name for the service. It must be unique within the node. Service names are not case-sensitive.
Choose a Service Configuration on which to base this service.
Click OK on the Create Service page.
These changes will be lost when the node is restarted.
To permanently add a service to a node by modifying its node configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Click the name of the node configuration for which you want to add a service.
In the Services section, click Add.
On the Add Service page, enter a name for the service. It must be unique within the node. Service names are not case-sensitive.
Select a Service Configuration on which to base this service.
Select Active if you want this service to be automatically started by the node.
Click OK on the Add Service page.
Click OK on the Edit Node page.
Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
You can make run-time changes to services, such as limiting concurrent sessions or choosing whether or not to accept new sessions. Changes you make at run time are lost when the node is restarted. To make permanent changes to a service, edit the service configuration directly. See "Modifying Service Configurations" for more information.
To modify run-time service parameters:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Services section, click the name of the service you want to modify.
Click the Administration tab.
In the Service Properties table row, click the Go to Task icon.
You can change the following properties:
Concurrent Sessions: You can have an unlimited number of concurrent sessions, or you can limit concurrent sessions to a specified number. If you have an unlimited number of concurrent sessions, you may run out of memory. See "Oracle Content DB Sizing Guidelines" for more information.
Accepting New Sessions: Select this option if you want the service to accept additional sessions.
Disposed on Last Disconnected Session: Select this option if you want the service to shut down automatically when the last session is disconnected.
Click Apply to save your changes.
Use the locator links to return to the Content DB Home page.
These changes will be lost when the node is restarted.
You can change the service configuration for a particular service from the Edit Node Configuration page:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Node Configurations page, click the name of the node configuration that uses the service you want to modify.
In the Services section, click the name of the service you want to change.
Select a new service configuration from the Configuration list and click OK.
On the Edit Node page, click OK.
Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
The Committed Data Cache provides caching of the attribute values of frequently used objects without a database request, improving performance and scalability. Least recently used data is periodically purged from the cache. Each service has its own Committed Data Cache.
You can make run-time changes to the Committed Data Cache properties for a service using the Application Server Control. You can also view Committed Data Cache statistics for a service. See "Monitoring Service Performance" for information about viewing or resetting the statistics.
See "Oracle Content DB Sizing Guidelines" for more information about cache settings.
To make run-time changes to Committed Data Cache properties:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the name of the service you want to modify.
Click the Administration tab.
In the Data Cache table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Figure 7-2 shows the Committed Data Cache Administration page.
Figure 7-2 Committed Data Cache Administration Page
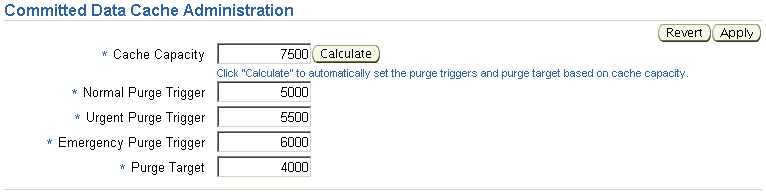
You can change the following cache settings:
Cache Capacity: The absolute maximum size of the data cache of the service, in LibraryObjects. (The LibraryObject class is the base class for all persistent Oracle Content DB objects.) The service data cache holds the attribute values of recently used LibraryObjects.
After you specify Cache Capacity, you can click Calculate to automatically fill in the values for the other parameters based on the capacity you specified.
Normal Purge Trigger: The cache size, in LibraryObjects, at which the service data cache schedules a low-priority purge of data that has not been recently used.
Urgent Purge Trigger: The cache size, in LibraryObjects, at which the service data cache schedules a high-priority purge of data that has not been recently used. The value must be greater than the Normal Purge Trigger value.
Emergency Purge Trigger: The cache size, in LibraryObjects, at which the service data cache performs an immediate purge of data that has not been recently used. The value must be greater than the Urgent Purge Trigger value, but less than the Cache Capacity value.
Purge Target: The target cache size, in LibraryObjects, upon completion of a purge cycle. The value must be less than the Normal Purge Trigger value.
Click Apply after you are finished specifying cache settings.
Changes you make at run time are lost when the node is restarted. To make permanent changes to Committed Data Cache properties, edit the service configuration directly. See "Modifying Service Configurations" for more information.
Table 7-1 maps the properties on the Committed Data Cache Administration page with their service configuration parameter equivalents.
Table 7-1 Committed Data Cache Service Configuration Properties
| Property | Service Configuration Parameter Equivalent |
|---|---|
|
Cache Capacity |
|
|
Normal Purge Trigger |
|
|
Urgent Purge Trigger |
|
|
Emergency Purge Trigger |
|
|
Purge Target |
|
There are two connection pools used by each service: the Read-Only Connection Pool and the Writable Connection Pool. The Read-Only Connection Pool is a set of database connections shared by the sessions to perform database read operations. The Writeable Connection Pool is a set of database connections shared by the sessions to perform database read and write operations within a database transaction.
A minimum number of connections are created in each pool when the service is started. Depending on the number of concurrent operations performed by the sessions, and the type of operations, additional connections may be added to each pool up to a specified maximum.
You can make run-time changes to the Connection Pool properties for a particular service using the Application Server Control. You can also view Read-Only and Writeable Connection Pool statistics for a particular service. See "Monitoring Service Performance" for information about viewing or resetting the statistics.
See "Oracle Content DB Sizing Guidelines" for more information about connection pool settings.
To improve performance, Oracle Content DB reuses Oracle prepared statements (objects used to query and update the database) when possible. Because Oracle Content DB stores statements in the statement cache, similar queries can reuse existing statements. Least recently used statements are purged when the number of statements in the cache equals the Statement Cache Purge Trigger value.
You can manage statement cache settings from the Connection Pool Administration page. You can also view statement cache statistics (number of attempted purges and purge count) on the Connection Pool Statistics page. See "Monitoring Service Performance" for more information.
To make run-time changes to Connection Pool properties:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the name of the service you want to modify.
Click the Administration tab.
In the Read-Only Connection Pool or Writable Connection Pool table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Figure 7-3 shows the Read-Only Connection Pool Administration page.
Figure 7-3 Read-Only Connection Pool Administration Page
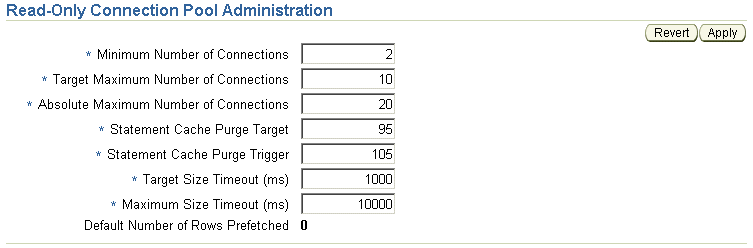
Figure 7-4 shows the Writable Connection Pool Administration page.
Figure 7-4 Writable Connection Pool Administration Page

On the Read-Only Connection Pool Administration page or Writable Connection Pool Administration page, you can change the following settings:
Minimum Number of Connections: The initial number of database connections in the connection pool.
If you change this property, ensure the value you specify is greater than the current size for this connection pool. You can view the current connection pool size from the Performance tab for the service. See "Monitoring Service Performance" for more information.
Target Maximum Number of Connections: The target maximum number of database connections in the connection pool. The value must be greater than or equal to the Minimum Number of Connections value.
Absolute Maximum Number of Connections: The absolute maximum number of database connections in the connection pool. The value must be greater than or equal to the Target Maximum Number of Connections value.
Statement Cache Purge Target: The target cache size, in number of statements, for the statement cache upon completion of a purge cycle. The value must be less than the Statement Cache Purge Trigger value.
Statement Cache Purge Trigger: The cache size, in number of statements, at which the statement cache schedules a purge.
Target Size Timeout: The maximum period, in milliseconds, that the service will postpone a connection allocation request when there are no unallocated connections, when the current size of the connection pool is greater than or equal to its target size but less than the maximum size. If a database connection does not become available within this period, a new connection will be created.
Maximum Size Timeout: The maximum period, in milliseconds, that a service will postpone a connection allocation request when there are no unallocated connections, when the current size of the connection pool is equal to its maximum size. If a database connection does not become available within this period, the allocation request will fail, and an exception will occur.
Click Apply after you are finished specifying connection pool settings.
Changes you make at run time are lost when the node is restarted. To make permanent changes to Connection Pool properties, edit the service configuration directly. See "Modifying Service Configurations" for more information.
Table 7-2 maps the properties on the Read-Only Connection Pool Administration page and Writable Connection Pool Administration page with their service configuration parameter equivalents.
Table 7-2 Connection Pool Service Configuration Properties
| Property | Service Configuration Parameter Equivalent |
|---|---|
|
Minimum Number of Connections |
|
|
Target Maximum Number of Connections |
|
|
Absolute Maximum Number of Connections |
|
|
Statement Cache Purge Target |
|
|
Statement Cache Purge Trigger |
|
|
Target Size Timeout |
|
|
Maximum Size Timeout |
|
You can delete services for a node by modifying the node at run time, or by modifying the appropriate node configuration.
If you delete a service with active sessions, and if there are data transfers in progress over those sessions, data may be lost when you delete the service. In addition, any servers using this service will stop accepting new requests.
To delete a service by modifying the node at run time:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Services section, select the service you want to delete and click Delete. Each node must have one active service.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes.
If you delete a service at run time that is defined in the node configuration, the service will reappear on the node when the node is restarted. To permanently delete the service, you must remove it from the node configuration, as described in the following section.
To permanently remove a service from a node by modifying its node configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Node Configurations page, click the name of the node configuration that uses the service you want to remove.
In the Services section, select the service you want to remove and click Remove.
You cannot remove a service if it is the only service defined in the node configuration. Each node must have at least one active service.
Click OK.
Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
You can use the Application Server Control to create or delete server for a particular node. When you create a server, you specify what server configuration object provides its properties.
You can make temporary (run-time) changes to a server by modifying the server from the Content DB Home page. Changes made to servers at run time are lost when the node is restarted.
You can also make permanent changes to a server by modifying its server configuration. See "Managing Server Configurations" for more information.
This section contains the following topics:
You can create servers for a particular node by modifying the node at run time, or by modifying the appropriate node configuration. You can also create servers when you create node configurations.
To create a server by modifying the node at run time:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Servers section, click Create.
On the Create Server page, enter a name for the server. It must be unique within the node.
Select a Service Name to support this server.
Select a Server Configuration on which to base this server.
If you want this server to be started after it has been created, ensure that Start the server after it has been created is selected. Otherwise, deselect this option.
Click OK.
These changes will be lost when the node is restarted.
To permanently add a server to a node by modifying its node configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Click the name of the node configuration for which you want to add a server.
In the Servers section, click Add.
On the Add Server page, enter a name for the server. It must be unique within the node.
Select a Server Configuration on which to base this service.
Select a Service to support this server.
For Initial Priority, select the Java thread priority of the server.
Select Active to deploy this server on the node at run time. If you do not select this option, this server will not appear in the Servers list on the Node page.
Select Initially Started if you want this server to be automatically started by the node. You should only select this option for active nodes.
Click OK.
On the Edit Node page, click OK.
Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
Which servers and agents start up with the node are defined in the node configuration. Any servers and agents marked "Active" and "Initially Started" in the node configuration are started automatically when you start the domain.
You can also manually start, stop, restart, suspend, and resume servers from the Content DB Home page for a particular node. The Create, Delete, and Reload buttons are discussed in separate sections.
To manage servers from the Content DB Home page for a particular node:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
Figure 7-5 shows the Servers section of the Content DB Home page.
Figure 7-5 Servers Section of Content DB Home Page
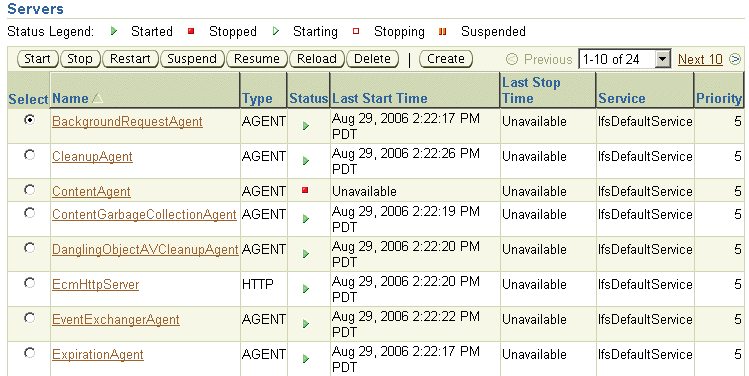
On the Content DB Home page, in the Servers section, there is a list of all servers for this OC4J_Content instance. Check the Status column to see whether a particular server is started, stopped, starting, stopping, or suspended. Use the following buttons to manage servers:
Start: Use this option to start a server that is not running.
Stop: Use this option to stop a server that is running or suspended.
Restart: Use this option to stop and then start a server that is running. This option does not refresh the server configuration information.
Suspend: Use this option to suspend a server that is running.
Resume: Use this option to resume a server that is suspended.
The Suspend and Resume functions are not available for all protocol servers.
If a server fails to start, check for errors in the application.log file for the OC4J_Content instance.
Which servers and agents start with the node are defined in the node configuration. Servers and agents marked Active and Initially Started in the node configuration are started automatically when you start the domain.
To ensure that a particular server starts when the node restarts, you must modify the node configuration for the node where the server is running:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Click the name of the node configuration you want to modify.
In the Servers section, select the server you want to change and click Edit.
Select Initially Started.
Click OK.
On the Edit Node page, click OK.
You can make run-time changes to servers, such as changing the Java thread priority of the server or changing run-time server properties. Changes you make at run time are lost when the node is restarted or when the server is reloaded. To make permanent changes to a server, edit the server configuration directly. See "Modifying Server Configurations" for more information.
To modify run-time server parameters:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Servers section, click the name of the server you want to modify.
In the General section, click Change Priority to change the Java thread priority of the server. On the Change Priority page, select a new priority and click OK. Most servers and agents let you change the Java thread priority at run time, but a few servers do not provide this option.
The run-time properties for the server are displayed in the Runtime Properties section. Properties that can be modified at run time are displayed as links. Click the name of a property to update it. Some run-time properties can only be modified when the server is stopped.
Use the locator links to return to the Content DB Home page.
These changes will be lost when the server is reloaded or when the node is restarted.
To change the configuration used by a server, delete the existing server and then create a new server from the Content DB Home page. Alternatively, you can change the configuration for a server from the Edit Node Configuration page:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Click the name of the node configuration that contains the server you want to modify.
In the Servers section, select the server you want to change and click Edit.
Select a new server configuration from the Configuration drop-down list.
Click OK.
On the Edit Node page, click OK.
Changes take effect when the server is reloaded or when the node is restarted.
If you modify a server configuration, you need to reload the server before the changes take effect. Restarting a server and reloading a server are different functions:
Restart stops and then starts the server. You can only restart servers that are started. Restarting the server will not pick up changes to server configuration properties.
Reload does the following:
Stops the server, if it is not stopped already.
Deletes the server.
Creates a new instance of the server, picking up any changes to the server configuration properties.
Returns the server to the state it was in when you clicked Reload (stopped, running, or suspended).
Both restarting and reloading a server will disconnect any users connected to that server.
To reload a server:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Servers section, select the server you want to reload (for example, EcmHttpServer).
Click Reload, then click Yes on the Confirmation page. The server picks up the new server properties.
You can delete servers from a node by modifying the node at run time, or by modifying the appropriate node configuration.
To delete a server by modifying the node at run time:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, in the Servers section, select the server you want to delete and click Stop, if it is not stopped already. You cannot delete a server that is running or suspended.
Select the server again and click Delete.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes. The server still appears in the server list, but the following message is displayed: "This server is configured but not loaded now."
If you delete a server at run time that is defined in the node configuration, the server will reappear on the node when the node is restarted. To permanently delete the server, you must remove it from the node configuration, as described in the following section.
To permanently remove a server from a node by modifying its node configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
Click the name of the node configuration that contains the server you want to remove.
In the Servers section, select the server you want to remove and click Remove.
Click OK.
Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
Use opmnctl, the command-line tool for OPMN, to manage the Oracle Content DB domain and nodes. The OPMN command-line tool can be found in:
ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin
Use the following command to check the status of Oracle Content DB nodes (OC4J_Content instances) on the local middle tier:
./opmnctl status
Include the @cluster option to check nodes on all middle tiers, as follows:
./opmnctl @cluster status
Starting, Stopping, or Restarting the Oracle Content DB Domain
Use the following commands to start, stop, or restart Oracle Content DB domain processes (OC4J_Content instances) across all Oracle Content DB middle tiers:
./opmnctl @cluster startproc process-type=OC4J_Content ./opmnctl @cluster stopproc process-type=OC4J_Content ./opmnctl @cluster restartproc process-type=OC4J_Content
Starting, Stopping, or Restarting Node Processes
Use the following commands to start, stop, or restart Oracle Content DB node processes (OC4J_Content instances) on the local middle tier:
./opmnctl startproc process-type=OC4J_Content ./opmnctl stopproc process-type=OC4J_Content ./opmnctl restartproc process-type=OC4J_Content
To start, stop, or restart a particular Oracle Content DB node process on a remote middle tier, include the Oracle Application Server instance name for the remote middle tier. For example:
./opmnctl @instance:remote_instance_name startproc process-type=OC4J_Content
If you are unsure of which Oracle Application Server instance name to use, use the opmnctl @cluster status command to list Oracle Application Server instance names.
|
Note: Before you log in to Oracle Content DB after starting a node process (OC4J_Content instance), make sure that both the OC4J_Content instance and Oracle HTTP Server are running. To do this, use the following command:opmnctl status |