| Oracle® Content Database Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Suite 10g (10.1.3.2) Part Number B32191-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Content Database Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Suite 10g (10.1.3.2) Part Number B32191-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Your initial Oracle Content DB domain configuration is based on default settings. You can change this configuration at any time using the Application Server Control.
When the Oracle Content DB domain is started, it uses the domain properties contained in the repository to determine domain behavior, such as the maximum size of a single file that can be uploaded to Oracle Content DB. Each node (OC4J_Content instance) has a node configuration that determines its run-time behavior. Each service has a service configuration that determines its size and characteristics. The server configuration for each server or agent provides values for properties, such as the default port number or activation period.
This chapter provides information about the following topics:
Domain properties are settings that apply to the entire domain. When the Oracle Content DB domain is started, it uses the domain properties contained in the repository to determine domain behavior, such as the maximum size of a single file that can be uploaded to Oracle Content DB.
You can view all the domain properties using the Application Server Control. Only underlined properties can be changed.
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Domain Properties table row, click the Go to Task icon. The Domain Properties page appears.
Figure 8-1 shows the Domain Properties page.
Click the name of the property you want to change. Only underlined properties can be changed. See Table 8-1 for a list of properties that can be edited.
You may need to move to the next page to find some properties, or you can use the Search field. For example, enter workflow and click Go (or press Enter) to see a list of workflow-related domain properties. You can use the question mark (?) and asterisk (*) wildcards.
Make the changes to the property and click OK.
Return to the Cluster Topology page and restart the Oracle Content DB domain. See "Starting and Stopping the Oracle Content DB Domain" for information about how to do this.
Table 8-1 Oracle Content DB Domain Properties That Can Be Edited
The run-time behavior of a node is specified in its node configuration object. Each node has its own corresponding node configuration. If you want to make permanent changes to a node, such as changing servers or services, modify the node configuration for the node. If you want to make temporary (run-time) changes to a node, modify the node itself. Changes made at run time are lost when the node is restarted.
Nodes and node configurations do not have identical names. Nodes use the name of the corresponding OC4J instance (OC4J_Content). The display name for each node is the same as the OPMN process type.
Nodes and node configurations do not have identical names. Nodes take the name of the corresponding OC4J instance (OC4J_Content), while node configurations have names in the following format:
application_server_instance_name_HTTP_Node
The display name for each node is the same as the OC4J instance name (OC4J_Content), and is also used as the OPMN process type for the node. For example, you can start OC4J_Content using the following OPMN command:
opmnctl startproc process-type=OC4J_Content
For the OC4J_Content node to function properly, it must be set to Active in its node configuration object. See the following section for more information.
This section contains the following topics:
You can make changes to existing node configurations, such as changing which protocol servers and agents run on a node.
|
Important: You must restart the node for your changes to take effect. |
To modify a node configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Node Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Node Configurations page, click the name of the node configuration you want to modify.
Change the node configuration properties, as necessary. The node configuration properties are described in Table 8-2.
Table 8-2 Node Configuration Properties
| Property Name | Description and Usage Notes |
|---|---|
|
Description |
Description of the node configuration. |
|
Access Control |
The access level associated with the node configuration. Keep the default value. |
|
Active |
Whether the node configuration is enabled in the Oracle Content DB repository. |
|
Maximum Sessions Per User |
The maximum number of user sessions allowed for a given user. The default value is 50. If this limit is reached, no new sessions for that user will be allowed on that node until a session ends, either through a logout or a session time out. To allow an unlimited number of sessions for each user, set the value to 0. Because this value is set for each node, different users may experience different session limits. For example, if you have multiple middle tiers, user sessions may be distributed in different ways, depending on load balancing. |
|
Maximum Concurrent Requests Per User |
The maximum number of outstanding requests allowed for a given user. An outstanding request is a request that the server is still processing, such as a search. The default value is 3. To allow an unlimited number of outstanding requests for each user, set the value to 0. Outstanding requests are also limited across all users, through the property |
|
Transaction Timeout (seconds) |
The inactivity timeout period for a transaction that spans multiple requests. This setting usually applies to Web services clients, because they are the only clients that can have transactions that span multiple requests. If there is an outstanding transaction and there is no request on the corresponding session for the transaction timeout period, the transaction will time out. The default value is 120. Do not set this property to a value lower than 15. |
|
Transaction Timeout Check Interval (seconds) |
The interval between successive checks for transactions that need to be timed out. The default value is 30. Follow these guidelines for setting this value:
|
|
Guest Session Pool Target Size |
The number of sessions kept in the guest session pool. If the number of sessions in the guest pool is equal to the Guest Session Pool Target Size up on the return of a session, the session will be disconnected, rather than returned to the pool. The default value is 10. If you are not allowing guest access, you can set this value to 0. |
|
Guest Session Pool Maximum Size |
The maximum number of guest sessions that can be in use at a given time. The default value is 100. If you are not allowing guest access, you can set this value to 0. This value must be greater than the Guest Session Pool Target Size (if the Guest Session Pool Target Size is greater than 0). |
|
System Session Pool Target Size |
The number of sessions kept in the system session pool. If the number of sessions in the system pool is equal to the System Session Pool Target Size up on the return of a session, the session will be disconnected, rather than returned to the pool. The default value is 5. Do not set this property to a value lower than 5. |
|
System Session Pool Maximum Size |
The maximum number of system sessions that can be in use at a given time. The default value is 50. This value must be greater than the System Session Pool Target Size. |
In the Services section, you can add, edit, or remove services for this node.
To add a service, click Add, specify information for the service, and click OK.
To change service properties, click the name of the service you want to modify. On the Edit Service page, change the appropriate information and click OK.
To remove a service, select it and click Remove. Each node must have at least one active service.
In the Servers section, you can add, edit, and remove protocol servers and agents for this node. You can also activate or deactivate servers for the node.
To add a server, click Add, specify information for the server, and click OK. To actively run a protocol server or agent on this node, make sure to select Active and Initially Started.
To change server properties, click the name of the server you want to modify. On the Edit Server page, change the appropriate information and click OK.
If you want a server to automatically start when the node is started, on the Edit Server page, select Active and Initially Started.
To remove a server, select it and click Remove.
To activate or deactivate multiple servers, click Activate/Deactivate. On the Activate/Deactivate Servers page, you can move servers between the Active Servers list and the Inactive Servers list. Then, click OK.
On the Edit Node page, click OK to save the changes. You must restart the node for your changes to take effect.
You can specify command-line arguments for the Java VM for this node. See "Calculating Xmx Settings" for more information about how to determine the correct Xmx setting.
To adjust the Java parameters and arguments for a node:
Connect to the Application Server Control.
From the Cluster Topology page, click the OC4J_Content instance for which you want to change Java parameters.
Click the Administration tab.
In the Server Properties table row, under the Properties heading, click Go to Task.
In the Command Line Options section, under the Start-parameters: Java Options heading, you can add additional options to the Options table. You can also select Verbose:gc to log all garbage collection activity, or enter the amount of memory for the Java heap in the Initial heap size field.
Click Apply.
Return to the Cluster Topology page, select OC4J_Content, and click Restart.
A service configuration holds the default values used when a service is started for an Oracle Content DB node. This section explains how to manage service configurations using the Application Server Control.
This section contains the following topics:
Each service configuration specifies values for service properties such as session parameters, the sizes of the data cache and database connection pools, and the default search timeout period. See Appendix D, "Service Configuration Properties" for a complete list of service configuration properties. Service configurations are uniquely named in a domain.
Whenever a new Oracle Content DB schema is created, three service configuration objects are generated:
SmallServiceConfiguration
MediumServiceConfiguration
LargeServiceConfiguration
These objects are named to reflect the sizes of their data caches.
Use the Application Server Control to create or edit service configuration objects. The services read their service configuration properties only when they start. You must stop and restart the affected nodes for changes to take effect. The changes you make this way are applied each time you start a service and overwrite any changes you make on a service while it is running.
Figure 8-2 shows the Service Configurations page.
Use the Application Server Control to create service configurations.
To create a new service configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Service Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Service Configurations page, decide whether or not to create a new service configuration based on the properties of an existing service configuration.
Select a service configuration and click Create Like to base the new service configuration on an existing service configuration (highly recommended).
Click Create to create the service configuration without basing it on an existing configuration.
In both cases, the New Service Configuration page appears. If you clicked Create Like, the service configuration properties have been filled with those of the existing service.
Figure 8-3 shows the New Service Configuration page.
Figure 8-3 New Service Configuration Page
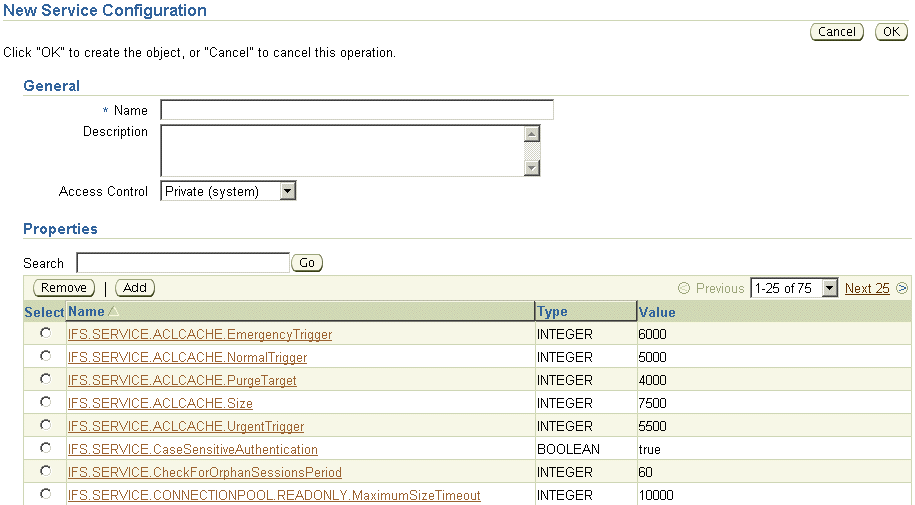
In the General section, enter a name for the new service configuration.
Enter a description of the service.
Keep the default value for Access Control.
Add, remove, or update the properties of the new service.
Click OK.
You can use the Application Server Control to make changes to service configurations, such as changing the capacity of the Committed Data Cache or changing the number of maximum concurrent sessions. Changes take effect when the node is restarted.
To modify a service configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Service Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Service Configurations page, click the name of the service configuration you want to modify.
On the Edit page, update the information in the General section, as necessary:
Description: Enter a description of the service configuration.
Access Control: Keep the default value.
To add new properties for this service configuration, follow these steps:
In the Properties section, click Add.
Provide a name for the new property.
Select a Type (such as string, integer, or Boolean). The page refreshes to display the appropriate Value field. For example, if you select BOOLEAN, a true or false list is displayed.
Enter or select a value for the property.
Click OK.
To edit a service configuration property, click the name of the property, update the value, and click OK.
To remove a property from this service configuration, select the property, click Remove, then click Yes.
Click OK.
Services only read their service configuration properties as they start. You must stop and restart the node on which the service is running before your changes will take effect. When the node restarts, the changes you made to the service configuration overwrite any run-time changes made on the service.
You cannot delete a service configuration that is being used by a service. If the service configuration you want to delete is being used by a service, perform one of the following tasks:
Change the service configuration being used by the service by modifying the node configuration
Delete the service from the node configuration
You cannot delete the service if it is the only service defined in the node configuration. Each node must have at least one active service.
To delete a service configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Service Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Service Configurations page, select the service configuration you want to delete.
Click Delete.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes.
A server configuration holds the default values used when a server is started for an Oracle Content DB node. This section explains how to manage service configurations using the Application Server Control.
This section contains the following topics:
Server configurations specify their server types as Java classnames. In addition to the server type, each server configuration specifies values for parameters relevant to that type. See Appendix E, "Server Configuration Properties" for more information.
Most of the server configuration information is used by the server itself. Only the server Java class entry is used by the node to instantiate a new server.
When Oracle Content DB is installed, server configurations are automatically created for each protocol server and agent. You can edit these configurations, or create additional server configurations using the Application Server Control. Any changes you make will appear the next time the node is restarted, or when the server is unloaded and then loaded again.
Server configuration objects are of two types:
Abstract: Used to set base values for the properties, which can then be inherited by some other configuration. You cannot start a server from an abstract server configuration.
Non-abstract: Can be used to start servers.
When you create a new server configuration, you can let it inherit the properties from one or more server configurations. You can use the same values as inherited, or use different values.
Inheritance operations are accessed from the New Server Configuration page, shown in Figure 8-4. See "Creating Server Configurations" for more information on creating new server configurations.
Figure 8-4 Inheritance Operations on the New Server Configuration Page
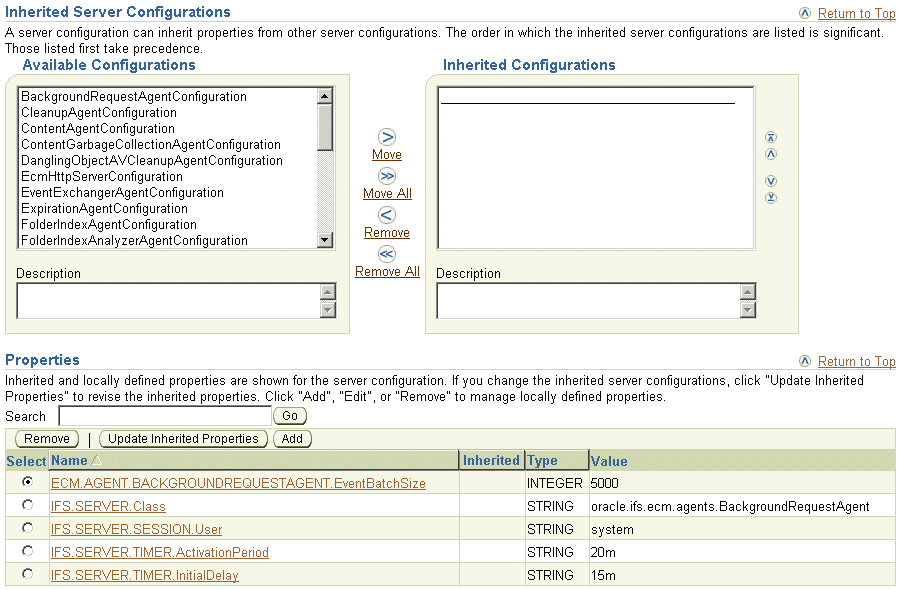
To change the value of an inherited property, create a new property in the inherited server configuration that is identical in name to the one in the parent server configuration, but has values that override those in the parent server configuration.
View the inherited properties to determine whether the property in the current server configuration object is local to this object or taken from a parent server configuration object. You can also differentiate between inherited server configuration objects and those that are local to the server configuration.
Use the Application Server Control to create new server configurations.
To create a new server configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Server Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Server Configurations page, decide whether or not to create a new server configuration based on the properties of an existing server.
Select a server configuration and click Create Like to base the new server configuration on an existing configuration.
Click Create to create the server configuration without basing it on an existing configuration.
In both cases, the New Server Configuration page appears. If you clicked Create Like, the server configuration properties have been filled with those of the existing server.
On the New Server Configuration page, in the General section, enter a name for the new server configuration.
Enter a description of the server.
Keep the default value for Access Control.
Select Abstract to prevent this server from being instantiated. An abstract server configuration is used to set base values for properties, which can then be inherited by another server configuration. You cannot start a server from an abstract server configuration.
In the Inherited Server Configurations section, select the existing configurations from which the new configuration will inherit properties. Select configurations from the Available Configurations list and move them to the Selected Configurations list.
If you change the list of inherited server configurations, click Update Inherited Properties in the Properties section to display the properties of the inherited server configurations.
The order of the items in the Inherited Configurations list determines which configuration takes precedence.
To edit server configuration properties, follow these steps:
In the Properties section, click the name of the property you want to change.
Update the value of the property.
Click OK.
Inherited server configuration properties cannot be edited. Inherited properties display an icon in the Inherited column, and their names are not rendered as links. To change the value of these properties, add a new property that is identical in name to the inherited property, but with a value that overrides the value of the inherited property.
To add new server configuration properties, follow these steps:
Click Add in the Properties section.
Enter a name for the new property. If you are adding a property to override an inherited property, make sure the name matches the inherited property.
Select a Type (such as string, integer, or Boolean). The page refreshes to display the appropriate Value field. For example, if you select BOOLEAN, a true or false list is displayed.
Enter or select a value for the property.
Click OK. If you added a property to override an inherited property, the property name changes to a link, and the Inherited icon no longer appears.
To remove server configuration properties, select a property and click Remove.
After you complete the server configuration, click OK.
You can use the Application Server Control to make important changes to server configurations, such as changing which configurations to inherit and editing, adding, or removing server configuration properties. Changes take effect when the server is reloaded or when the node is restarted.
See Appendix E, "Server Configuration Properties" for more information about specific server configuration parameters.
To modify an existing server configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Server Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Server Configurations page, click the name of the server configuration you want to modify.
On the Edit page, update the information in the General section as necessary:
Description: Enter a description of the server configuration.
Access Control: Keep the default value.
Abstract: Choose whether to make the server configuration abstract. An abstract server configuration is used to set base values for properties, which can then be inherited by some other server configuration. You cannot start a server from an abstract server configuration.
In the Inherited Server Configurations section, use the arrow buttons to add or remove server configurations from which this server configuration will inherit properties.
If you change the list of inherited server configurations, click Update Inherited Properties in the Properties section to display the properties of the inherited server configurations.
The order of the items in the Inherited Configurations list determines which configuration takes precedence.
To edit server configuration properties, follow these steps:
In the Properties section, click the name of the property you want to change.
Update the value of the property.
Click OK.
Inherited server configuration properties cannot be edited. Inherited properties display an icon in the Inherited column, and their names are not rendered as links. To change the value of these properties, add a new property that is identical in name to the inherited property, but with a value that overrides the value of the inherited property.
To add new server configuration properties, follow these steps:
Click Add in the Properties section.
Enter a name for the new property. If you are adding a property to override an inherited property, make sure the name matches the inherited property.
Select a Type (such as string, integer, or Boolean). The page refreshes to display the appropriate Value field. For example, if you select BOOLEAN, a true or false list is displayed.
Enter or select a value for the property.
Click OK. If you added a property to override an inherited property, the property name changes to a link, and the Inherited icon no longer appears.
To remove server configuration properties, select a property and click Remove.
After you complete the server configuration, click OK.
Servers only read their server configuration properties when they are reloaded, or when the node is restarted. You must reload the server before your changes will take effect. See "Reloading Servers" for more information. These server configuration changes overwrite changes you make on a server while it is running.
You cannot delete a server configuration that is being used by a server. If the server configuration you want to delete is being used by a server, first edit the node configuration to remove the server, then delete the server configuration. Alternatively, you can change the server configuration being used by the server.
To delete a server configuration:
Connect to the Application Server Control and go to the Content DB Home page. See "Accessing the Oracle Content DB Home Page" for information about how to do this.
On the Content DB Home page, click the Administration tab.
In the Server Configurations table row, click the Go to Task icon.
On the Server Configurations page, select the server configuration you want to delete.
Click Delete.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes.