| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TopLink Developer's Guide 10g Release 3 (10.1.3.1.0) Part Number B28218-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes the various components that you must configure in order to use a relational project.
For more information, see the following:
Table 20-1 lists the configurable options for relational projects.
This chapter also describes logging in to a database during development when using TopLink Workbench. For more information, see "Logging in to the Database".
In addition to the configurable options described here, you must also configure the base class options described in Table 19-2.
Table 20-1 lists the configurable options for relational projects.
Table 20-1 Configurable Options for Relational Projects
This chapter also describes logging into a database during development when using TopLink Workbench. For more information, see "Logging in to the Database".
For each relational project, you must specify the database platform (such as Oracle Database 10g). This platform configuration is overridden by the session login, if configured.
For more information, see the following:
To specify the database platform of a relational project, use this procedure:
Select the database object in the Navigator. The Database property sheet appears.
Figure 20-1 Database Property Sheet, Database Platform Options
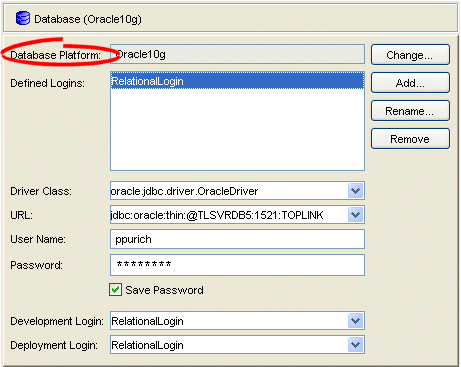
Click Change to select a new database platform for the project. For more information, see "Data Source Platform Types".
Sequencing allows TopLink to automatically assign the primary key or ID of an object when the object is inserted.
You configure TopLink sequencing at the project or session level to tell TopLink how to obtain sequence values: that is, what type of sequences to use.
In a CMP project, you do not configure a session directly: in this case, you must configure sequences at the project level. In a non-CMP project, you can configure a session directly: in this case, you can use a session-level sequence configuration to override project-level sequence configuration, on a session-by-session basis, if required (see "Configuring Sequencing at the Session Level").
Using TopLink Workbench (see "Using TopLink Workbench"), you can configure table sequencing (see "Table Sequencing") and native sequencing ("Native Sequencing With an Oracle Database Platform" and "Native Sequencing With a Non-Oracle Database Platform") and you can configure a preallocation size that applies to all sequences (see "Sequencing and Preallocation Size").
Using Java (see "Using Java"), you can configure any sequence type that TopLink supports ("Sequencing Types"). You can create any number and combination of sequences. You can create a sequence object explicitly or use the default sequence that the platform creates. You can associate the same sequence with more than one descriptor and you can configure a separate preallocation size for each descriptor's sequence.
If you are migrating a BEA WebLogic CMP application to OC4J and TopLink persistence (see "Migrating BEA WebLogic Persistence to OC4J TopLink Persistence" ), the TopLink migration tool does not migrate BEA WebLogic single column sequence tables to TopLink unary sequence tables (see "Unary Table Sequencing"). After migration, you must manually configure your project to use TopLink unary sequence tables if your application originally used single column sequence tables in BEA WebLogic.
After configuring the sequence type at the project (or session) level, to enable sequencing, you must configure a descriptor with a sequence field and a sequence name (see "Configuring Sequencing at the Descriptor Level").
For more information about sequencing, see "Understanding Sequencing in Relational Projects".
|
Note: Changing the project's default sequencing options does not affect descriptors that already exist in the project; only newly added descriptors are affected. |
To specify the sequencing information for the project, use this procedure:
Select the project object in the Navigator.
Select the Sequencing tab in the Editor. The Sequencing tab appears.
Use this table to enter data in the following fields to configure the sequencing information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Preallocation Size | Specify the default preallocation size (see "Sequencing and Preallocation Size"). Default is 50. The preallocation size you configure applies to all sequences. |
| Default Sequence Table | Select this option to use table sequencing (see "Table Sequencing") with default sequence table name SEQUENCE, default sequence name field SEQ_NAME, and default sequence counter field SEQ_COUNT. |
| Native Sequencing | Select this option to use a sequencing object (see "Native Sequencing With an Oracle Database Platform" or "Native Sequencing With a Non-Oracle Database Platform") created by the database platform. This option applies only to Oracle, Sybase, Microsoft SQL, and IBM Informix database platforms. |
| Custom Sequence Table | Select this option to use table sequencing (see "Table Sequencing") with a sequence table name, sequence name field, and sequence counter field name that you specify. |
| Name | Specify the name of the sequence table. |
| Name Field | Specify the name of the column used to store the sequence name. |
| Counter Field | Specify the name of the column used to store the sequence count. |
Using Java, you can configure a project to use multiple, different sequences as Example 20-1 shows.
Example 20-1 Configuring Sequencing at the Project Level in Java
// Enable native sequencing for the project as the default. Configured the default preallocation size project.getLogin().useNativeSequencing(); project.getLogin().setSequencePreallocationSize(50); // Configure the EMP_SEQ to not use preallocation DefaultSequence empSequence = new DefaultSequence("EMP_SEQ", 1); project.getLogin().addSequence(empSequence); // Configure the PROJ_SEQ to use a seperate sequence table UnarySequence projSequence = new UnarySequence("PROJ_SEQ_TAB", "COUNTER"); project.getLogin().addSequence(projSequence);
This section describes how to define a login to a relational database. After you define a login, you must designate its role (see "Configuring Development and Deployment Logins").
After you create a login (see "Configuring Login Information") and specify it as a development login (see "Configuring Development and Deployment Logins"), you can log in to a database instance (see "Logging in to the Database").
To create or edit a database login, use this procedure:
Select the database object in the Navigator. The Database property sheet appears.
Figure 20-3 Database Property Sheet, Database Login Fields
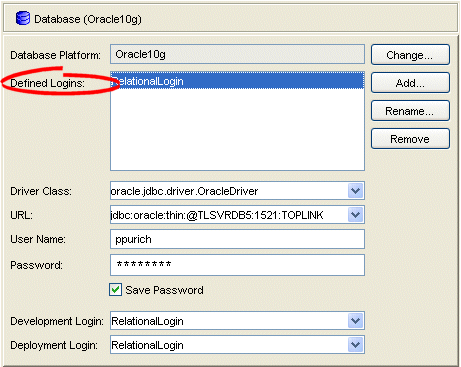
Click Add to create a new Defined Login.
Use this table to enter data in the following fields on the Database property sheet to configure the database login:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Defined Logins | Login used to access the database. Click Add to add a new login, or Remove to delete an existing login. |
| Driver Class | The JDBC driver to use to connect to the database. |
| URL | The URL used to connect to the appropriate database. |
| User Name | The name required to log in to the database. |
| Password | The password required to log in to the database.
Note: When exporting Java source and deployment XML (see "Exporting Project Information"), TopLink Workbench writes the database password (if applicable) using JCE encryption (when using JDK 1.4). Refer to Oracle TopLink Getting Started Guide for information on using password encryption with JDK 1.3 and earlier. For information on how to specify password encryption options, see "Configuring Password Encryption". |
| Save Password | Whether or not to save the Password for this Defined Login. |
This section describes how to designate a defined login's role. For information on how to define a login, see "Configuring Login Information". TopLink recognizes the following login roles:
Development Role
While using TopLink Workbench to develop a project (see "Development Role: Development Login"), you must define a login (see "Configuring Login Information") and designate it as the development login. The development login is stored in the TopLink project file. TopLink Workbench uses the information in the development login whenever you perform a data source operation from within TopLink Workbench. For example, when you read or write schema information from or to a data source during application development, the development login information is never written to a sessions.xml or project.xml file and is overridden by the deployment login (or the session login) at run time.
For more information on how to use a development login to connect to a database, see "Logging in to the Database".
CMP Deployment Role
If you are creating a CMP project (see "CMP Deployment Role: Deployment Login"), you may define a run-time login (see "Configuring Login Information") and designate it as the deployment login. This is the login that the application will use at run time, unless overridden in the sessions.xml file, CMP deployment file, or through Java code.
Non-CMP Session Role
If you are creating a non-CMP project (see "Non-CMP Session Role: Session Login"), Oracle recommends that you use the sessions.xml file to store the sessions your project uses at run time (see "Data Source Login Types").
To specify different development and deployment database logins, use this procedure:
Select the database object in the Navigator. The Database property sheet appears.
Figure 20-4 Database Property Sheet, Development and Deployment Login Options
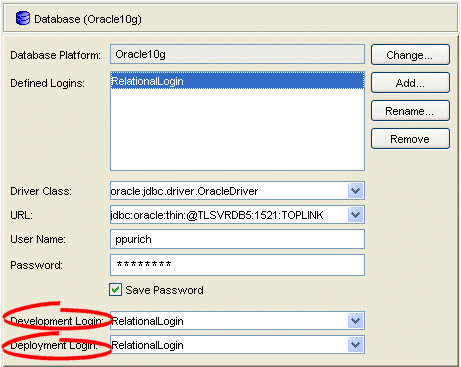
Use this table to enter data in the following fields on the Database property sheet to configure the login:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Development Login | The Defined Login to be used by TopLink Workbench during development to connect with the database, and to read or write table information.
For more information on how to use a development login to connect to a database, see "Logging in to the Database". |
| Deployment Login | The Defined Login to be used by your TopLink-enabled application during deployment. |
Using TopLink Workbench, after you create a login (see "Configuring Login Information") and specify it as a development login (see "Configuring Development and Deployment Logins"), you can log in to a database instance.
You must log in to the database before importing or exporting table information.
To log in to the database, use one of the following procedures:

Select the database object in the Navigator and click Login. TopLink Workbench logs in to the database.
Right-click on the database object in the Navigator and choose Log In to Database from the context menu, or choose Selected > Log In to Database from the menu.
The database icon in the Navigator window changes to indicate you are now logged in to the database.
You can configure TopLink to use parameterized SQL and prepared statement caching for all named queries and finders.
These setting apply only to named queries (see "Named Queries")–not to all queries in general or write operations.
Generally, to use parameterized SQL, you should configure it on the session's login (see "Configuring JDBC Options"). Configuring at the session level ensures that all queries will use parameterized SQL.
|
Note: For applications using a J2EE data source or external connection pool, you must configure statement caching in the J2EE server's data source–not in TopLink. |
Table 20-2 summarizes which projects support query statement caching and binding configuration.
Table 20-2 Project Support for Default Named Query Caching and Binding
| Descriptor | Using TopLink Workbench |
Using Java |
|---|---|---|
|
Relational Projects |
|
|
|
EIS Projects |
 |
 |
|
XML Projects |
 |
 |
This section describes configuring statement caching and binding options at the project level. This configuration applies to all named queries you create on the descriptors in this project.
You can also configure named query statement caching and binding options at the query level to override this project-level configuration on a query-by-query basis (see "Configuring Named Query Options").
Using parameterized SQL, you can create and store queries that are complete except for one or more bound parameters. The TopLink runtime binds the current parameter values when executing the query. This approach avoids the preparation of SQL execution and, thus, improves the performance of frequently executed SQL statements.
By default, Oracle TopLink writes data directly into its generated SQL, and does not use parameterized SQL. This is due to the fact that many JDBC drivers do not fully support parameter binding and impose restrictive size or type limits. For more information, see "Parameterized SQL (Binding) and Prepared Statement Caching".
To specify the named query options, use this procedure:
Select the project object in the Navigator.
Select the Defaults tab in the Editor. The Defaults tab appears.
Figure 20-5 Defaults Tab, Named Queries Options
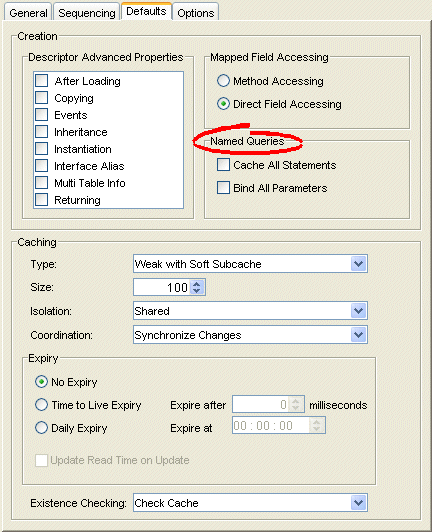
Use this table to enter data in following fields on the Defaults tab to specify the named query options for newly created descriptors.:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Cache All Statements | Caches the query's prepared statement in the TopLink statement cache. |
| Bind All Parameters | Binds all of the query's parameters. |
Using TopLink Workbench, you can configure options that apply when you generate database tables from the descriptors you define in your TopLink Workbench project. The resulting tables and columns will conform to the naming restrictions of the project's target database.
To specify the default table generation options, use this procedure:
Select the project object in the Navigator.
Select the Options tab in the Editor. The Options tab appears.
Figure 20-6 Options Tab, Table Generation Options
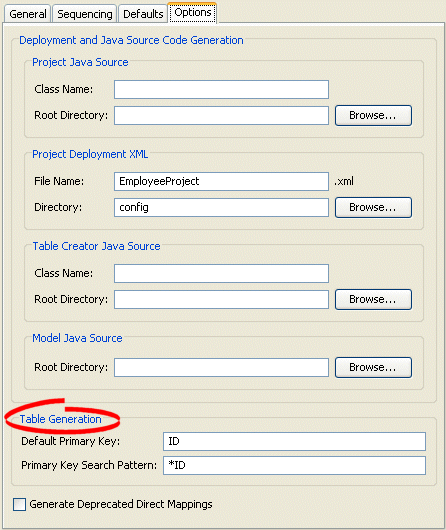
Use this table to enter data in the following fields to specify the default export and generation options.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Primary Key | Enter the default name to use when generating primary keys. |
| Primary Key Search Pattern | Enter the default search pattern to use when generating primary keys. |
Using TopLink Workbench, you can configure options that apply when you export Java source code that you can use to create database tables.
To specify the default Java code generation options, use this procedure:
Select the project object in the Navigator.
Select the Options tab in the Editor. The Options tab appears.
Figure 20-7 Options Tab, Table Creator Java Source Options
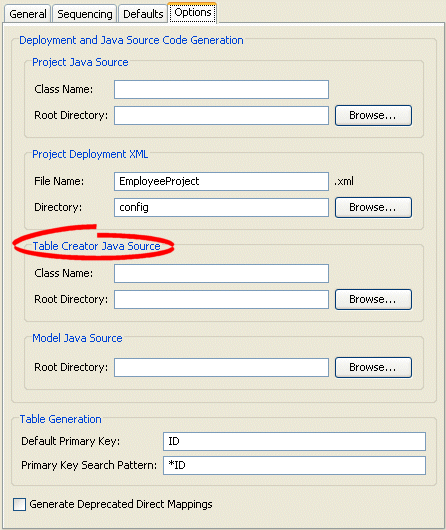
Use this table to enter data in the following fields to specify the default table creator options.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Class Name | Base class name to use when generating table's Java source code from the project. |
| Root Directory | Directory for storing the generated source code. |
Using TopLink Workbench, you can export a project as Java source. You can configure the class name and root directory that TopLink Workbench uses when exporting the project to Java source code.
For more information on exporting a project as Java source, see "Exporting Project Java Source".
To specify the default Java code generation options, use this procedure:
Select the project object in the Navigator.
Select the Options tab in the Editor. The Options tab appears.
Figure 20-8 Options Tab, Project Java Source Options
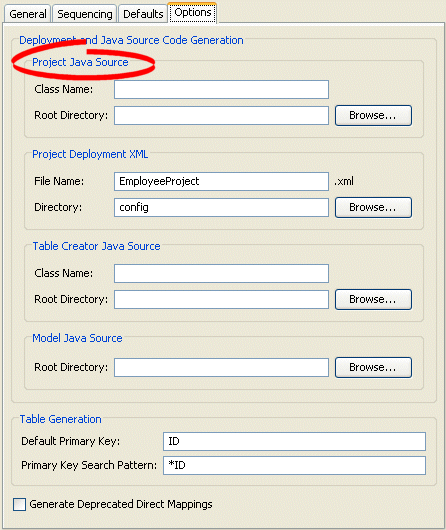
Use this table to enter data in the following fields to specify the default export and generation options:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Class Name | Base class name to use when generating Java source code from the project. |
| Root Directory | Directory for storing the generated source code. |